Hemoglobin norms for people of different genders and ages
| Age category | Hemoglobin norm, g/l | |
| Women | Men | |
| Up to 2 weeks | 135-200 | 135-200 |
| 2 weeks – 1 month | 115-180 | 115-180 |
| 1-2 months | 90-130 | 90-130 |
| 2-6 months | 95-140 | 95-140 |
| 6-12 months | 105-1400 | 105-140 |
| 1 year – 5 years | 100-140 | 100-140 |
| 5-12 years | 115-145 | 115-145 |
| 12-15 years | 112-152 | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 115-153 | 117-160 |
| 18-65 years old | 120-155 | 130-160 |
| Over 65 years old | 120-157 | 125-165 |
Determining the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is part of a routine blood test. At the same time, specialists analyze the number of red blood cells and their qualitative characteristics.
The hemoglobin level itself does not allow the patient to make an accurate diagnosis, but it is an important signal about a deviation in health.
There are also special indicators that reflect the hemoglobin content in the body in the amount required for normal life. So, among them there is a color indicator - this is the degree of saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobins. The degree of saturation of an individual red blood cell with the substance in question is also determined.
Hemoglobin in children
Hemoglobin standards for adults and children, as can be seen from the table above, are different. The structure of the substance itself also differs. Thus, in adults, only the “adult” form of hemoglobin circulates in the circulatory system. Newborns have their own, special form of hemoglobin - fetal. It transforms and is replaced by a normal one in the first months of life.
Disturbances in the structure of hemoglobin
As a result of the individual characteristics of the body, hemoglobin can acquire various irregular forms, which affects the ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen. Thus, the following violations are distinguished:
- abnormal hemoglobins;
- carbohemoglobin - it is formed during carbon monoxide poisoning. The substance is a persistent compound that is unable to absorb and transport oxygen;
- methemoglobin - formed during poisoning;
- Glycated hemoglobin, a common companion to diabetes mellitus, can also be formed in healthy people with excess glucose in the blood.
Increased hemoglobin: what is dangerous and what to do
An increased concentration of hemoglobin in the blood may be evidence of oxygen starvation. Because of it, the bone marrow is activated and begins to produce more red blood cells, and blood viscosity increases. Thus, a high hemoglobin content in the blood indicates increased blood clotting, which can lead to the formation of blood clots. As viscosity increases, the flow of oxygen to tissues and organs slows down.
Increased hemoglobin in women
In women, an increased concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is observed quite rarely.
However, in cases where a patient is diagnosed with a similar condition, it is worth approaching the issue of health with all responsibility. An increased concentration of hemoglobin in the blood may indicate the presence of heart disease, the appearance of malignant neoplasms and cardiopulmonary failure.
You need to worry about your hemoglobin level if it exceeds the normal level by 20 units. Deviations less than this indicator are not particularly dangerous.
Increased hemoglobin in men
An increase in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood in men, as a rule, is a consequence of some bad habits, in particular smoking.
When the level of hemoglobin in the blood increases, there is a high risk of developing diseases of the kidneys, liver, lungs and heart.
Causes of high hemoglobin concentration in the blood
An increase in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood indicates that the functioning of certain organs and their systems has been disrupted. But there are cases when an increased hemoglobin concentration is normal: for example, when the patient lives in a mountainous area.
The main reasons for increasing the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood are:
- smoking;
- severe dehydration;
- acquired heart defects, which are accompanied by increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation;
- congenital heart disease with a change in skin color from pinkish to gray and blue;
- increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood;
- increasing the amount of hemoglobin in the blood plasma;
- impaired intestinal patency;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- excess of vitamins B6 and B12 in the body;
- malignant neoplasms.
Physiological causes of increased hemoglobin concentration in the blood
As mentioned above, one of the reasons for the increase in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is living at high altitudes: there the level of oxygen is lower, because of this the body is forced to produce more hemoglobin.
Frequent and long-term exposure to fresh air also increases hemoglobin concentration.
Pregnancy can affect the amount of hemoglobin in the blood of women.
The health status is also affected by the characteristics of professional activity.
High hemoglobin is less dangerous than low hemoglobin. However, this does not mean that excess hemoglobin levels can be ignored.
Symptoms of increased hemoglobin and its consequences
With elevated hemoglobin, a person may not experience any changes in health at all, but may also suffer from the following health problems:
- increased fatigue;
- weak appetite;
- drowsiness;
- pain in the joints;
- high blood pressure;
- migraine;
- itching;
- discomfort in the stomach;
- rapid formation of bruises.
What to do if your hemoglobin level is high
If the increased concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is not associated with the presence of serious diseases, then its content can be reduced through nutrition and medication. Thus, among the medications, experts distinguish: Curantil, Cardiomagnyl, Trental and Aspirin. You can start using the above and other drugs only after consulting a specialist - you should not self-medicate.
In order to lower hemoglobin levels, you should:
- increase the amount of fluid consumed;
- reduce the amount of fat, sweets and eggs you consume. It is not recommended to take multivitamins and medications containing copper and iron;
- It is recommended to increase the amount of seafood, white meat, legumes, nuts and vegetables consumed.
What is hemoglobin?
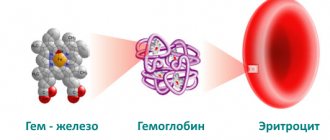
Hemoglobin is a component of blood, or more precisely, a special iron-containing protein with a complex structure that plays the role of a “courier” in the body: it carries oxygen from the organs of the respiratory system to tissues and cells, and then makes the return journey, delivering carbon dioxide to the organs of the respiratory system gas. For the body to function properly, it is important that the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is always within normal limits (fluctuations due to age-related changes and pathological conditions are allowed).
An increase in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, as well as a decrease in it, leads to metabolic disorders and the emergence of a long list of diseases and pathologies.
ology. In addition, a decrease in hemoglobin concentration can cause deterioration in the condition of hair and skin, causing muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches and dizziness. An acute form of anemia (lack of hemoglobin) leads to fainting, hallucinations and even brain hypoxia.
Hemoglobin is found inside erythrocytes (red blood cells), contained in the blood in strictly defined volumes. As the number of red blood cells in the blood decreases, the hemoglobin concentration also decreases. The brain, spleen and liver are responsible for the number of red blood cells in the blood. In the latter, red blood cells are destroyed, and the hemoglobin contained in them is utilized. One red blood cell contains approximately 400 million hemoglobin molecules.
Hemoglobin formula and its properties
The hemoglobin formula is as follows:
С2954Н4516N780O806S12Fe4
The molecular weight of the substance is 66,800 g/mol.
The formula of hemoglobin and the features of its structure have not only theoretical, but also practical value. Thus, the structure of hemoglobin is quite complex, despite the fact that it contains only 2 components:
- heme;
- globin
Heme
Heme is a natural pigment that contains porphyrin and iron compounds. The total proportion of heme in the structure of the substance is small - it is 4%. At the center of the heme molecule is iron, whose main function is to capture oxygen in the upper respiratory tract.
Heme formula:
C34H32O4N4
In the presence of strong oxidizing agents in the blood, divalent iron contained in the heme molecule is oxidized to trivalent, and the heme itself is converted into hematin; hemoglobin turns into methemoglobin.
Globin
Globin is an albumin protein, which accounts for 96% of the mass of the substance in question. It consists of two circuits: 2a and 2b.
Each a-chain, in turn, consists of 141 amino acids, and each b-chain consists of 146 amino acids.
Human globin differs from animal globin in that it does not contain the amino acids leucine and cystine.
Globin chains form 4 hydrophobic pockets, each of which contains 1 heme. The pockets allow the iron to capture oxygen without being subject to oxidative processes.
Properties of hemoglobin
The main property of the substance in question is its ability to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. One hemoglobin molecule is capable of binding 4 oxygen molecules. Oxyhemoglobin is a fragile compound of oxygen and hemoglobin that forms in the capillaries of the lungs and disintegrates in cells.
The ability of hemoglobin to be converted into oxyhemoglobin by binding to oxygen is of great importance in maintaining blood pH.