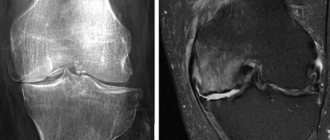
MRI shows cancer?
The MRI method visualizes the structural degeneration of tissues, determines transformations in the shape, size and boundaries of internal organs, and shows pathological changes in the blood supply to the studied area. Thanks to such a detailed picture, layer-by-layer photos obtained during the examination will show cancer tumors in the initial stage, before atypical cells metastasize into regional lymph nodes and neighboring tissues.
Magnetic resonance imaging reveals neoplasms of the parenchyma of internal organs, soft tissues, nervous structures, including the spinal cord and brain, and vascular tumors. The use of contrast during the procedure increases the information content of the method and helps to determine changes at the initial stage of tumor development. Malignancy of benign formations is also clearly visible on MRI images.
Despite the information content and reliability of the method, the radiologist does not make a final diagnosis. Its task is to identify indirect signs of pathology and recommend additional examination. If an oncological process is suspected, the attending physician will order laboratory tests and take a tissue sample for a biopsy. Only after a comprehensive examination will the diagnosis be established.
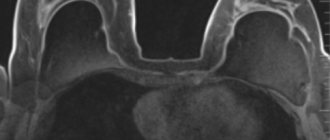
Anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain on MRI
The objectives of the method depend on the scanning area:
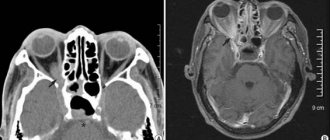
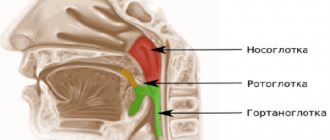
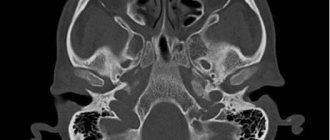
- examination of the head and neck visualizes pathological processes in the nasopharynx, thyroid gland, paranasal sinuses, and also shows neoplasms in the trachea and esophagus;
- a brain scan reveals tumors that have affected the central nervous system and cause compression of brain tissue;
- examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvis visualizes neoplasms and metastases of internal organs and blood vessels supplying this area;
- MRI of the spinal cord shows the size of the lesion, the presence of metastases, the effects of tumor pressure on the cerebrospinal membranes and nerve roots;
- examination of the chest cavity reveals damage to the mediastinal organs and blood vessels in this area, with its help breast cancer is determined;
- examination of the spine and musculoskeletal system is carried out if the localization of the process in soft tissues is suspected or if it is necessary to reduce the radiation dose to the patient.
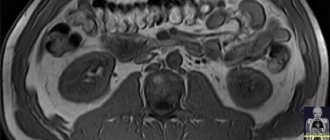
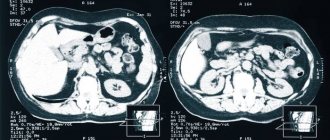
What does MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space show?
The abdominal cavity contains the organs of the digestive system and the endocrine glands. MRI helps to examine the structure of parenchymal organs: the liver with ducts, pancreas, spleen, retroperitoneal kidneys and adrenal glands, as well as lymph nodes and visceral fat. Hollow organs (esophagus, stomach, intestinal loops) are not assessed by MRI.
MRI is prescribed in the following situations:
- stones in the biliary system - MRI will show the presence of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder, common bile duct or bile ducts. A special mode - MR cholangiography is used in diagnosing the causes of obstructive jaundice;
- detection of primary hepatocellular cancer, as well as determination of the spread of metastases from oncological processes of another localization;
- inflammatory liver diseases of various nature (viral, toxic, autoimmune hepatitis), the presence of fibrotic or cirrhotic restructuring;
- diagnosis of pancreatic diseases of inflammatory or tumor origin with identification of cystic degeneration, areas of destruction and assessment of the patency of the common pancreatic duct;
- study of the structure of the spleen, the presence of cysts, various tumors and traumatic injuries;
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, kidney carbuncle);
- violation of the outflow of urine from the kidneys - MRI shows the location of the kidney block and helps determine its nature (calculus, tumor).
To increase the diagnostic information, an MRI of the abdominal cavity is performed on an empty stomach or 4 hours after eating or drinking.
What does cancer look like on an MRI?
MRI is based on the effect of a magnetic field on water molecules in the cells of the human body. When scanning, pulses penetrate to a given depth and provide a response from the tissues being studied. The intensity of the response depends on the saturation of the structures with liquid.
During the study, the tomograph converts the received data into a series of layer-by-layer photographs that reflect the state of the scanned area. To increase the information content and determine the malignancy of the process, a contrast agent is used - a preparation of gadolinium salts. This is a metal-containing solution, which, when administered intravenously, stains the network of blood vessels and visualizes in detail the nature of the blood supply to the area. The drug is safe for humans, practically does not cause allergic reactions and is completely eliminated from the body after a few days.
An MRI scan for cancer reveals benign and malignant neoplasms, but the process can be differentiated with 100% accuracy only based on the results of a biopsy. A radiologist can assume malignancy of the process based on some signs:
- features of the lesion contour;
- degree of homogeneity of the site;
- vascularization and contrast agent uptake;
- perifocal edema.
On MRI, on T1-weighted images, tumors appear as dark spots with a clear or blurred outline. A malignant tumor is characterized by the absence of a pronounced border with healthy tissues. This is explained by the growth characteristics of atypical cells and their infiltration into intact structures. Benign formations push healthy tissues apart, forming a contour that is clearly visible in an MRI photo.
Myxoid liposarcoma of the soft tissues of the thigh on MRI
Cancer tumors on MRI have a heterogeneous structure. This is explained by foci of necrosis, the presence of calcifications and cysts, which are characteristic of oncological formations. Areas of benign changes in the images do not have inclusions; they look homogeneous, clearly defined areas.
Malignancy of the lesion can be assumed when contrast is administered, when layer-by-layer photographs show that the tumor has its own developed network of blood vessels and another variant of indicator accumulation. Benign formations are characterized by a linear arrangement of arterioles, which are quickly encrusted with a gadolinium solution. The circulatory system of the malignant area has its own branched structure, the vessels intertwine and anastomose with each other, delaying the contrast. If an MRI shows a heterogeneous tumor without a clear contour and, upon administration of contrast, a tangled network of capillaries is revealed, the presence of a malignant process can be assumed.
Due to the infiltration of cancer cells into healthy tissue, a picture of perifocal edema appears on the tomogram. This is due to an increase in the volume of fluid in the cells. In the photographs, a blurred halo of irregular shape is visible around the dark area. Such a symptom may also indicate malignancy of the process.
Signs of cancer in the picture
After the procedure, the doctor analyzes the images and carefully examines the contour and structure of the seal.
Based on some signs, the nature of the tumor is revealed and conclusions are drawn on the prognosis for the patient. We list the criteria by which cancer is determined on MRI:
- Borders - cancer is characterized by the absence of an even contour; such seals have irregular bends and protrusions. The shape of the malignant formation is elongated, bifurcated, and disproportionate.
- The structure of the compaction - in the image, cancer is determined by uneven contrast, dense and loose areas are noted. If a homogeneous substance is observed, the tumor is most likely benign.
- Vascular anatomy - in the case of cancer, there is an abundant blood supply, the lines are incorrectly directed and connected to each other. Benign seals have a relatively parallel arrangement of blood vessels.
The cancer grows rapidly, so the pictures show irregular borders and heterogeneous tissue structure.
Cancer
Intensive development requires more nutrition, which leads to the proliferation of blood vessels and exhaustion of the body.
Does MRI show metastases?
MRI is used to diagnose primary cancer and to detect metastases in regional lymph nodes and distant areas. The method allows you to determine the localization of the lesion, study the type and structure of the tumor, and the degree of its growth into surrounding tissues. MRI images visualize the nature of the blood supply to the formation, the level of damage to the organ or space where it was detected.
Contrast magnetic resonance imaging allows one to differentiate metastases from the primary lesion. In case of cancer, MRI shows secondary damage to soft tissues, internal organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, parts of the brain and spinal cord. Metastases localized to the bone substance are usually visible without the use of contrast.
Metastases to the sacrum in breast cancer
Determination of regional and distant secondary lesions allows us to determine the extent of cancer and prescribe effective treatment. It will be aimed at removing and suppressing the growth of cancer cells from the primary site and metastases. Using MRI, the doctor monitors the effectiveness of treatment measures, observing the development of the tumor over time.
Is it possible to miss a tumor in the pictures?
The option of erroneous diagnosis is possible only in one case - if a low-field tomograph is used that generates a low-frequency field.
In these situations, nuclear magnetic resonance does not allow us to examine the contours of the tumor, and it is not possible to distinguish the nature of the pattern from the surrounding tissues.
When examined with such devices, oncology is confused with the following seals:
- suppuration;
- accumulation of blood and fluid;
- cysts.
Therefore, if you suspect cancer, it is recommended to be examined using mid-field and high-field devices of 1.5-3 T (Tesla).
In rare cases, misdiagnosis occurs when procedures are violated, causing interference on the monitor.
Is it possible to do MRI for oncology?
Electromagnetic pulses do not have a negative effect on the body. The use of MRI for the differential diagnosis of tumors is safe for humans and does not have a stimulating effect on the growth and development of cancer cells. This is the advantage of the method over computed tomography and the use of ionizing radiation.
Using a magnetic field, you can scan the human body an unlimited number of times, which allows you to monitor the development of the process during the therapeutic treatment of cancer.
MRI is used to identify the primary tumor and for preventive purposes in patients who are at risk for cancer. In this case, a full scan is used, which reflects the condition of all organs and structures, soft tissues and bone substance of the musculoskeletal system, including joints.
Determining the focus at the initial stage, before the penetration of atypical cells into the lymph nodes and surrounding structures, increases the effectiveness of antitumor therapy. The possibility of using conservative treatment is of great importance in the case of cancer affecting vital organs, when surgical intervention is impossible without causing harm to the patient’s health.
Monitoring the tumor and monitoring the effectiveness of the measures taken using MRI scanning allows you to promptly respond to the slightest changes and adjust therapy, achieving stable remission.
Diagnosis of cancer in St. Petersburg
A timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. That’s why it’s so important to choose a clinic where experienced doctors will diagnose you using modern equipment. Otherwise, you risk wasting time and money and contributing to the development of pathology.
MRI at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center means only qualified doctors with many years of experience, modern equipment and confidence in the result!
Sign up for an MRI at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center near the Baumanskaya metro station (see map) by phone or leave a request on the website.
Baumanskaya metro station (see map) 8
leave a request on the website
Equipment
The oncology department in Moscow is equipped with the highest quality magnetic resonance imaging scanner Siemens Magnetom Skyra (64 slices). The fundamental difference of this device is the double magnetic field strength (3 Tesla), which allows diagnostics to be carried out with high accuracy. The equipment has an acoustic noise suppression system. Thanks to it, the comfort of MRI for the patient increases. Convenience is also ensured by a wide 7 cm open tunnel. The lightweight design of the coils and MoodLight create a pleasant, calming atmosphere during diagnostics.