Chemical composition, description and characteristics of potatoes
Potato tubers are 76.3% water. The share of dry matter accounts for 23.7%, including :
- starch;
- organic acids;
- proteins;
- mineral salts;
- pectin fibers;
- saturated fatty acids;
- Sahara;
- vitamin complex.
70–80% of all dry matter is starch . Its concentration in fruits depends on the early ripening of the varieties. Also, the level of starch decreases during storage, in particular at low temperatures.
Carbohydrates in potatoes are represented by glucose, fructose, sucrose and maltose (the latter is formed during the germination of root crops). Mature potatoes contain little sugar (within 1.5%). At a temperature of +10°C they accumulate in tubers, at higher temperatures they are consumed.
Dietary, taste and beneficial properties make potatoes an almost ideal product . It is also used for the treatment and prevention of a wide range of diseases:
- it has a beneficial effect on the functions of the hematopoietic organs, cardiovascular, nervous and urinary systems, and digestive tract;
- prevents diabetes, obesity;
- alleviates the condition of people suffering from osteochondrosis, arthritis, arthrosis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- protects against atherosclerosis, influenza, upper respiratory tract infections, stabilizes blood pressure.
Ideally, you should eat potatoes from your own harvest or grown in safe conditions . To increase yields and reduce fruit ripening time, agronomists use chemicals and growth stimulants, and products to protect plants from bacteria and insects.

The soil and air can be contaminated. Potatoes accumulate nitrates and harmful compounds in the peel and fruit , which can cause food poisoning, cause vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain in a nursing mother and child.
Advice. If you buy potatoes in stores or at the market, be sure to pay attention to the appearance of the product and storage conditions. Ask the seller for a certificate from the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision or other documents confirming the quality of the vegetable.
Vitamins and microelements
The biological value of potatoes is determined by its vitamin and mineral composition . High doses of ascorbic (22.2%) and nicotinic (9%) acids, and pyridoxine (15%) were found in root vegetables. Contains vitamins in smaller amounts:
- A (beta-carotene);
- E (alpha tocopherol);
- N (biotin);
- K (phylloquinone);
- group B (thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, choline, pantothenic acid, folate).
Macronutrients presented:
- potassium;
- calcium;
- sodium;
- magnesium;
- silicon;
- gray;
- phosphorus;
- chlorine

Microelements found in tubers:
- cobalt (50%);
- chromium (20%);
- copper (14%);
- iron;
- manganese;
- fluorine;
- iodine;
- molybdenum;
- zinc, etc.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of potatoes depends on the cooking method and ranges from low to high. The highest GI is for baked potatoes - 95 units, mashed potatoes - 90 units, it is slightly lower for chips and fried potatoes - 80 units.
Boiled jacket potatoes have a glycemic index of 65–70 units . Raw potatoes have the lowest GI, but such potatoes are not recommended for a nursing mother.
Interesting on the topic:
Can I eat asparagus while breastfeeding?
Is it possible to eat melon while breastfeeding?
Beneficial properties of potatoes during breastfeeding
Potatoes contain many useful substances that are important for the growth of infants and the recovery of women after childbirth:
- Vitamin A (retinol) is an antioxidant, normalizes metabolism, is important for healthy teeth and bones, and strengthens the immune system.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - fights infections in the body, takes part in hematopoiesis processes, improves the condition of blood vessels and small capillaries, increases their strength and elasticity.
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) - necessary for normal growth and development, supports the health of the digestive and cardiovascular systems.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) has a beneficial effect on the nervous system, reduces excitability, fights depression, and eliminates stress. It also normalizes blood circulation, lowers blood pressure, and, together with vitamin B9, creates new blood cells.
- Vitamin B4 (choline) - enhances intestinal and stomach motility, stimulates the transmission of nerve impulses, improves memory and brain performance.
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) - takes part in metabolic processes, activates the formation of steroid hormones. During breastfeeding, the body's need for pantothenic acid increases from 11 to 20 mg.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - affects the metabolism of amino acids and fats, protects against atherosclerosis, supports the activity of the nervous system.
- Vitamin B7 (biotin) is important for the health of tendons, prevents hair and nails from becoming brittle, ensures healthy skin, and normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid) - neurological damage, cancer, and anemia are associated with folate deficiency in a woman’s body. Their insufficiency before pregnancy and during the entire period of gestation can cause serious developmental defects in the baby, termination of pregnancy, and stillbirth.
- Vitamin E (tocopherol acetate) - helps a woman lose excess weight, supports metabolism in the heart and skeletal muscles, nervous system, liver, and improves blood circulation.
- Vitamin K - creates favorable conditions for normal kidney function, participates in the absorption of calcium and vitamin D, regulates blood clotting processes, and takes part in the metabolism of bone tissue.
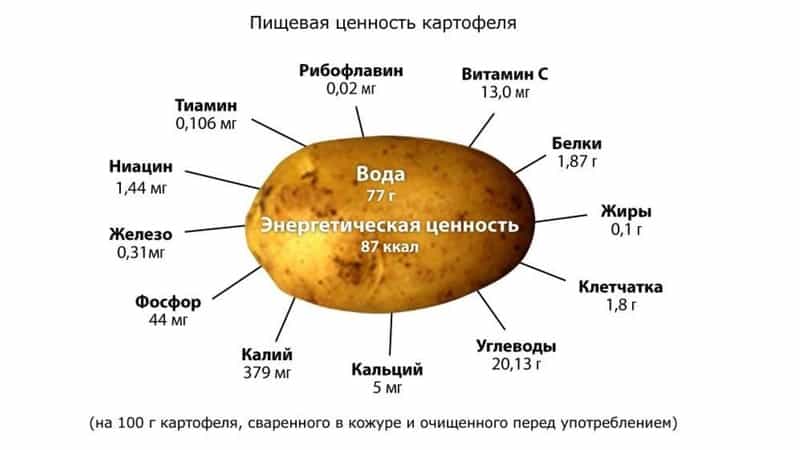
When breastfeeding, potatoes are valued for their content:
- calcium - participates in the construction of bone tissue, mineralization of teeth;
- magnesium - maintains a constant body temperature, has a vasodilating effect, relieves muscle spasms;
- iron - enriches brain tissue with oxygen, stimulates thinking and the development of cognitive functions;
- iodine - necessary for normal functioning of the thyroid gland and the growth of the child;
- copper and manganese - protect brain cell membranes from free radicals.
Can a nursing mother eat boiled potatoes and what are their benefits?
Those women who adhered to any strict diets before pregnancy are sure to know that when losing weight, potatoes are necessarily excluded from the diet almost completely. This applies not only to fried potatoes or french fries, but also to simply boiled vegetables.
During lactation, pediatricians also recommend following a diet, but does it have anything in common with weight loss programs? Not really. The main feature of a diet for a nursing mother is that, first of all, it should be as balanced as possible and should not exclude any types of foods, and therefore potatoes simply must be present in it.
In addition, boiled potatoes are considered the most useful and suitable for women who are breastfeeding. This product retains all the advantages of a fresh vegetable and has the most pleasant taste.
Useful properties of boiled potatoes
Let's take a closer look at the beneficial properties of boiled potatoes.
- Boiled potatoes are rich in quickly digestible carbohydrates and consist almost entirely of them. This makes it useful for those nursing mothers who, due to stress, have lost a lot of weight and are exhausted. In addition, such nutritious food allows you to quickly get enough and gives a significant boost of energy.
- Potatoes contain a large amount of fiber, which is known to help the digestive system function properly. Boiled potatoes can help relieve constipation and normalize intestinal function. This will also improve the quality of absorption and assimilation of nutrients.
- Potatoes, although not in very large quantities, contain vitamin C. This compound is known for its antioxidant properties. Vitamin C also helps strengthen the immune system, which allows the body of the mother and baby to better resist diseases and avoid infection.

- A number of substances contained in boiled potatoes have an anti-inflammatory effect. These compounds act throughout the body, but they are especially active in the digestive system, eliminating any foci of inflammation and protecting tissues from them.
- Potatoes contain a significant amount of potassium. This microelement is necessary for our body to remove excess fluid from it. Since many nursing women suffer from edema, this feature of potatoes turns out to be extremely useful. Also, high potassium levels help lower blood pressure, which reduces the load on the cardiovascular system and allows it to function better.
In addition to lowering blood pressure, potatoes have an additional effect on the blood system due to the presence of B vitamins in it. These substances reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, eliminating the risk of thrombosis, and also strengthen the walls of blood vessels, making them stronger and at the same time elastic.
- Kidney stones are most often formed due to an increased amount of protein in the body. Boiled potatoes contain practically no such substances, since they consist mainly of carbohydrates, which makes them a wonderful product for nursing mothers suffering from urolithiasis. In addition, this vegetable contains magnesium, which is known to break down calcium deposits and alleviate the condition.
- B vitamins, in addition to having a positive effect on the cardiovascular system, can also have a beneficial effect on the brain. They contribute to its better supply of oxygen and strengthen the nervous system as a whole, thanks to which the development of the baby occurs more actively and faster.
Possible harm and contraindications
Despite all the positive properties of potatoes, infants may experience allergic reactions in the form of itching, peeling, redness of the skin, and rashes.
Excessive consumption of nitrate fruits causes food poisoning, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain.
Uncontrolled consumption of potatoes leads to constipation and intestinal colic in a newborn, which is associated with the starch content in the tubers.
Contraindications to eating potatoes include allergies. It is recommended to limit portions or exclude it from the diet for people with type 2 and type 3 diabetes.
For reference. There is an opinion that potatoes cause excess weight due to their high starch content and high calorie content. But this is true if you overuse fried potatoes, mashed potatoes with added milk and butter, seasoning everything with sauces and mayonnaise.
What could be the danger?
A nursing mother should not eat green potato tubers . They contain solanine, a toxic substance that first causes excitement and then depression of the nervous system, destroys red blood cells, disrupts kidney function, worsens skin condition, and provokes cancer.
Solanine can cause poisoning. Symptoms include vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, headache, intestinal spasm, and fever. But this is possible after eating several kilograms of green, unpeeled and thermally untreated potatoes.
Rules for eating potatoes during breastfeeding
It is better to eat homegrown varieties that do not contain chemicals and other harmful substances. In the first month, the mother should carefully try all the foods on the list of permitted ones, including potatoes.

To find out how a newborn will react, you need to eat a little boiled or baked vegetable without fat and observe the reaction. If a woman did not suffer from allergies during pregnancy, then such negative manifestations will not occur when feeding the baby with breast milk.
You need to give up fried potatoes or mashed potatoes with added butter, milk, eggs. Firstly, all these products are highly allergenic, and secondly, they load the child’s immature digestive tract and cause flatulence, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and bloating. The list of restricted products includes raw vegetable tubers, juice, high-calorie dishes based on it: chips, snacks, french fries.
When planning meals in the first month, it is better to give preference to purees prepared in water with the addition of a few drops of olive oil. This dish will help improve the process of bowel movement after childbirth and activate gastrointestinal motility. Later, you can eat baked and boiled potatoes, add them to salads, soups, use them as a filling for dumplings, and prepare potato pancakes.
For reference. Breastfeeding experts recommend keeping a food diary. It will help you create a list of foods that a nursing mother can and cannot eat.
Young potatoes are best consumed during the ripening season .
Early varieties are most likely saturated with nitrates, which will cause intoxication. It is better to eat potatoes separately or together with other vegetables and fresh herbs. You cannot combine it with meat products, as they are heavy on the stomach and require a lot of energy to digest them.
How to cook potatoes correctly?
During breastfeeding, potatoes need to be prepared so that the dish is healthy, tasty, and appetizing just by looking at it. There won’t be any particular difficulties here - there are hundreds of recipes that are easy to use in the kitchen. You don’t need any special cooking skills – even an inexperienced housewife can handle these delicious culinary masterpieces.
In the first weeks after childbirth, you should limit yourself to boiled potatoes with a drop of salt. It should be seasoned with olive oil. If the baby does not have any digestive problems, after a week you can supplement the dish with herbs (a sprig of dill, a few “curls” of parsley).
Immediately after the birth of the baby, it is recommended to introduce liquid soup with a few pieces of potatoes into the diet. It is advisable to use low-fat broth - this will help prevent constipation, which often worries nursing mothers.
Potatoes baked in the oven will be no less useful. The main condition is not to bake too old tubers that have accumulated solanine over the winter. Before cooking, you should thoroughly wash each vegetable and ensure that there are no spoilage spots.
Vegetable stew is another hearty and healthy dish for a nursing mother. Do not use fatty sauces - it is better to complement your culinary masterpiece with vegetables (onions, carrots). After the baby is one and a half months old, season the stew with low-fat sour cream.
A little secret that should be used in preparation - for purees and casseroles, it is recommended to use yellow tubers. Such potatoes boil better, when kneading they turn into a homogeneous mass, there are no lumps. The soup should be prepared from varieties that have red skin - the slices retain their shape well, do not boil into porridge, and leave the broth clear and with an appetizing appearance.
It is strictly forbidden for nursing mothers to consume raw tubers or juice squeezed from potatoes (without heat treatment, the vegetable is often used in the treatment of certain diseases). After such experiments, the risk of the baby developing skin irritation, allergies, colic, and even indigestion increases sharply.
What is better to combine potatoes with?
An excellent combination with potatoes are meat products. You should use only low-fat varieties (chicken, rabbit, veal), but it is better not to rush - add tasty ingredients 2-3 months after birth. If you are preparing a dish using store-bought meat, it is recommended to soak the product for 2-4 hours (fill with cold water), bring to a boil, and drain the first broth. Only after this proceed to the main cooking processes.
Another great addition to potato dishes is boiled fish (you can also steam it). It is recommended to combine it with vegetables, do not experiment with spices, just salt and a few grains of pepper.
Can I have fried potatoes while breastfeeding?
Fried potatoes are one of the most favorite dishes of many families, but women during lactation are better off excluding this delicacy from their menu for several months. The baby's digestive tract is not fully developed, so heavy foods can cause colic and loose stools.

4-5 months after giving birth, you can gradually eat fried potatoes; the daily norm should not exceed only 70-80 g. It is recommended to enjoy your favorite dish no more than twice a week.
Recipes with potatoes for nursing mothers
Thanks to the variety of potato-based dishes, you can make a nursing mother’s diet tasty, healthy and with minimal preparation time .
Potatoes and meat stewed in a slow cooker
Ingredients for 6 servings:
- potatoes - 1 kg;
- dietary meat (beef, veal) - 500 g;
- onions - 1 pc.;
- carrots - 1 pc.;
- tomatoes - 2 pcs. or 1 tsp. tomato paste;
- water - 1 l;
- vegetable oil - 2 tbsp. l.;
- Bay leaf;
- salt and herbs to taste.
Recipe:
- Rinse the meat, remove excess moisture with a paper towel, cut into small pieces.
- Heat vegetable oil in a preheated multicooker bowl, add meat, cook with the lid open on the “Fry” mode until a slightly golden crust forms.
- Cut the onion into small cubes, grate the carrots. Add to meat. Cook with the lid closed for 15 minutes until the vegetables become soft.
- Peel the potatoes, cut into medium-sized pieces, add to the meat and vegetables. Pour boiling water over everything. The amount of water can be changed depending on the desired consistency.
- Add tomato paste or finely chopped peeled tomatoes, bay leaf, salt, and mix everything.
- Cook for 40–50 minutes on the “Stew” mode. Before serving, decorate with herbs.
Baked potatoes with cheese
Ingredients:
- potatoes - 1 kg;
- low-calorie cheese (for example, Mozzarella, Suluguni) - 150 g;
- vegetable oil - 1 tsp;
- salt - to taste;
- greenery.
Recipe:
- Peel the potatoes, cut into small circles.
- Grease a baking dish with oil and distribute the potatoes evenly.
- Salt and add spices (it is better to use dried herbs). Sprinkle grated cheese on top.
- Cover with foil. Bake in a preheated oven for 30–40 minutes at +180°C.
- Remove the foil and leave in the oven for another 10-15 minutes until golden brown.
Casserole
Products:
- potatoes - 0.5–0.7 kg;
- Mozzarella cheese - 150 g;
- low-fat milk - 100 ml;
- sour cream - 100 g;
- butter - 50 g;
- egg - 1 pc.
Preparing potato casserole:
- Peel the tubers, cut into 4–6 parts (depending on the size of the fruit), cook until tender.
- Drain the water from the potatoes, add all the ingredients except cheese, add salt, and grind well until smooth.
- Place the potato mixture in a baking dish, smooth it out, spread sour cream on top, and sprinkle with grated cheese.
- Preheat the oven. Bake at +180–200°C for about 30–40 minutes.
Potatoes with cottage cheese
Products per serving:
- potatoes - 2 pcs.;
- low-fat cottage cheese - 50 g;
- sour cream 15% fat - 50 g;
- garlic - 1 clove;
- salt and herbs to taste.
Recipe:
- Wash the potatoes in their skins well, remove the adventitious buds (eyes).
- Bake whole tubers in the oven until done.
- Prepare the filling from cottage cheese, finely chopped herbs and garlic, mix and add salt to taste.
- Make a cross-shaped cut in the warm potatoes and fill with filling.
The dish goes well with fresh vegetables.
Potato soup
This soup coats the mucous membranes of the stomach, warms and perfectly saturates the body.
You will need:
- water - 450 ml;
- potatoes - 250 g;
- milk - 200 ml;
- wheat flour - 1 tbsp. l.;
- butter - 20 g;
- chicken egg - 1 pc.;
- salt;
- greenery.
Cooking process:
- Cut the peeled potatoes into cubes and cook over medium heat for 20 minutes.
- Add flour, mix. Remove from heat.
- Mix the cooled mixture in a blender. Bring to a boil again.
- Mix milk with egg and add to soup.
- Beat it in a blender again and boil.
- Before serving, season with butter and fresh herbs.
Potato cutlets
Potato cutlets are an excellent alternative to meat cutlets due to their high protein content. But due to the presence of fish in the recipe, it is not advisable to include such a dish in the diet of a nursing mother in the first month.
Will be needed:
- potatoes - 2-3 pcs.;
- canned pink salmon - 150 g;
- chicken egg - 1 pc.;
- bread crumbs - 100 g;
- garlic - 1 clove;
- lemon juice - 1 tbsp. l.;
- pickled cucumber - 1 pc.;
- salt to taste.
Preparation:
- Boil the potatoes in their skins, peel and mash with a fork.
- Grate the pickled cucumber, squeeze out the juice lightly, and add to the potatoes.
- Put 50 g of crackers, chopped garlic, lemon juice, salt, pink salmon, egg there, mash everything well, mix until smooth.
- Form minced meat into cutlets and roll in breadcrumbs.
- Cover a baking sheet with parchment, grease with vegetable oil, and place the cutlets.
- Bake in a preheated oven for 15-20 minutes until golden brown. Turn over to the other side and leave for another 5-7 minutes.
Potato banana cookies
This is a delicious dietary dessert that is prepared without flour.
Ingredients:
- potatoes - 0.5 kg;
- ripe bananas - 2 pcs.;
- chicken egg - 1 pc.
The recipe is simple:
- Boil or bake potato tubers in their skins. Cool, clean.
- Blend together with the banana in a blender until smooth.
- Add egg, mix well.
- Roll out the dough into a thin layer, use special molds or a regular glass to cut out cookies.
- Line a baking sheet with parchment, place cookies, bake in a preheated oven for 25–30 minutes at +180°C.
Doctors' advice and Komarovsky's opinion
Komarovsky E.O.
Doctors advise trying different foods while breastfeeding . The body itself will tell you what you need to eat in order to provide your baby with nutrients without harming his health.
Potatoes have a low degree of allergenicity , and usually the baby’s body reacts well to the vegetable. You only need to exclude fried potatoes, chips, french fries.
When asked whether nursing women can eat potatoes, Dr. Komarovsky replies: “Medical science categorically rejects any diets for nursing mothers. Everything that a woman ate before pregnancy and during its course can be eaten after the birth of the baby . The only thing is that you shouldn’t experiment with food.”
Reference. Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky is a pediatrician, TV presenter, and author of books on children’s health.
Keep in mind that a newborn's potato allergy may go away over time , especially after three months.
How to properly introduce boiled potatoes into a nursing diet, and in what quantity can you eat them?
Boiled potatoes are one of the main products for a nursing mother, and therefore they are introduced into a woman’s menu quite early - already a week or two after giving birth.
To begin, the nursing mother needs to eat a small piece of boiled vegetable, about a tablespoon. It is advisable to do this in the morning so that you can monitor the baby. If within two days the baby’s behavior has not changed and there are no symptoms of a negative reaction, then the amount of potatoes is increased.
Pediatricians recommend consuming no more than 100-200 grams of this vegetable per day, and it is better to eat potatoes in the morning.
Thus, it will saturate the body with nutrients for the whole day and will not let you get hungry for a long time. If you notice that your child has reacted poorly to a new product, then delay its introduction for at least a couple of weeks or even a month.











