Previous Next MRI of the pituitary gland is a separate, separate scan protocol and should not be confused with MRI of the brain. These are two different examinations. The focus of tomography of the pituitary gland is the pituitary gland itself and the area of the sella turcica. The technique for studying the pituitary gland using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is based on the relaxing properties of hydrogen atoms. Most people are made up of water, the molecules of which include hydrogen protons. Depending on the saturation of water, soft and bone tissues have different relaxing properties, and therefore appear differently on tomograms.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
MRI of the pituitary gland with and without contrast - what is the difference?
When a patient comes to the MRI center for examination of the pituitary gland, depending on the diagnostic purposes, he is offered an MRI with or without contrast enhancement. It should be said right away that tomography of the pituitary gland in the vast majority of cases must be carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent. It is contrast that makes it possible to detect all, even very small pituitary tumors. For example, using non-contrast, native MRI, it is impossible to find a pituitary microadenoma due to its small size. It is the introduction of contrast that allows doctors to:
- assess the distribution, boundaries and relationship of pathological processes;
- identify all neoplasms, their size, location and degree of fusion with surrounding tissues;
- identify and evaluate inflammatory processes and the level of tissue necrosis;
- assess the degree of vascularization, that is, the rate of accumulation and release of the contrast agent, for differential diagnosis. This characteristic allows specialists to judge the benignity or malignancy of the neoplasm.
Indications
There are a lot of hormones produced by the pituitary gland, and with the help of MRI of the pituitary gland, doctors have a chance to understand where the cause of many pathological processes in the body lies. The symptoms of diseases of this organ depend on the production of which hormone is disrupted by the tumor. So:
- Many pathological processes in the brain in the pituitary gland zone change the synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
- Tumors in the sella turcica area can cause overproduction of cortisol, the excess production of which leads to Cushing's disease.
- Growth hormone (somatotropic hormone) is responsible for the growth of the entire body. Overproduction of this substance due to adenoma causes the process of acromegaly.
- A lack of luteinizing hormone and oxytocin, which are responsible for ovulation, causes infertility in women and a lack of testosterone in the stronger sex.
- A pituitary adenoma can affect the production of prolactin, which directly regulates the functioning of the mammary glands.
- Failures in the synthesis of follicle-stimulating hormone lead to a lack of follicle growth in the ovaries in the fair sex and the formation of low-active sperm in men.
- A disruption in the production of antidiuretic hormonal substances leads to problems with urination and can cause the development of diabetes insipidus.
- There is also a hormone of the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland, the so-called lipotropin and proopimelanocortin, which control the pigmentation of our skin and enhance the metabolism of fats.
What will a tomography of the pituitary gland with contrast show?
Most often, as a result of magnetic resonance diagnostics, the following diseases of the pituitary gland are detected:
- Rathke's pouch cyst. It is also called a pseudocyst because it is often a residual structure of Rathke's pouch.
- Pituitary ectopia is an abnormal development of the pituitary gland or its abnormal position.
- Empty sella turcica.
- Macro- and microadenomas of the pituitary gland.
- Congenital adrenogenital syndrome.
- Lymphocytic hypophysitis is an autoimmune pathology characterized by inflammatory changes.
- Tumor of benign and malignant nature.
- Hamartoma is a tumor of the hypothalamus.
- Craniopharyngioma is a benign tumor in the area of the sella turcica.
- Cancer metastases in the pituitary gland area.

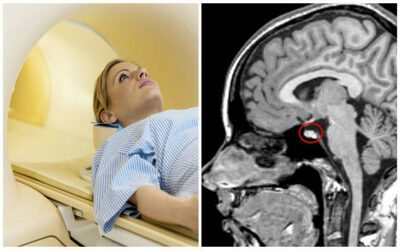
MRI of the pituitary gland: what the study will show
The vast majority of MRI studies of the pituitary gland are prescribed when the following diseases and conditions are suspected:
Pituitary adenoma
This tumor is formed from glandular cells. As an adenoma develops, the pituitary tissue grows and can put pressure on the optic nerves, leading to visual impairment. The tumor can produce certain hormones, depending on the location in a certain lobe of the pituitary gland, which causes the target glands to work harder, releasing more substances into the blood than the body needs to maintain certain functions.
Pituitary adenomas are divided into:
- Hormone-secreting. Can provoke the development of endocrine diseases and conditions, for example: hyperprolactinemia, acromegaly, etc.
- Hormonally inactive.
Pituitary adenomas are also classified by size:
- microadenomas (less than 10 mm);
- macroadenomas (more than 10 mm);
- giant adenomas (more than 40 mm).
An MRI examination of the pituitary gland can produce sections about 1 mm thick, which can even detect microadenomas up to 2 mm in size.
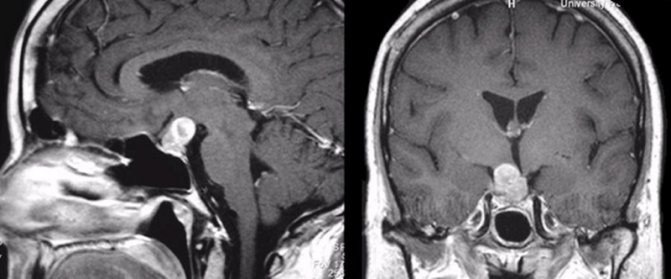
Pituitary adenoma detected during MRI with contrast
Malignant pituitary adenomas are extremely rare. If the course of the disease is malignant, MRI images will show how the tumor grows into other brain tissues.
Metastases to the pituitary gland from other organs are an even more rare occurrence, which is accompanied by severe symptoms in the form of visual impairment, even loss of vision, and severe headaches.
Problems with conception caused by increased levels of the hormone prolactin
MRI of the pituitary gland may be prescribed to women who have problems conceiving or who are about to enter into an IVF protocol.
An excess of the hormone prolactin, produced by the anterior pituitary gland, can lead to amenorrhea, infertility, and impaired libido.
Examination of the pituitary gland is necessary for differential diagnosis, since an increased amount of prolactin in the blood does not always indicate a malfunction of the gland.
Empty sella syndrome
This is the name for a pathology in which the meninges fill the cavity of the skull called the sella turcica, which leads to compression of the pituitary gland.
An empty sella turcica can be either a congenital structural feature or an acquired pathology and is most often asymptomatic. In some cases, the disease may be accompanied by severe symptoms.
The patient may experience:
- intense persistent headaches;
- autonomic disorders;
- mood swings;
- visual disturbances.
If the presence of the syndrome is suspected, an MRI of the area of the sella turcica and pituitary gland is prescribed in order to exclude or confirm the suspected diagnosis.
Other, less common endocrine diseases
Using magnetic resonance imaging of the pituitary gland, the following can be detected:
- Cushing's syndrome;
- acromegaly;
- diabetes insipidus;
- gigantism.
These diseases and conditions occur because the pituitary gland produces either too much or too little hormones, which in turn causes other endocrine glands to release too much or too little hormone into the blood.
Referral for MRI and preparation
Most medical centers in St. Petersburg accept patients for tomography of the pituitary gland, both with and without a referral from a doctor. If a person has concerns or doubts about his health, he can independently come to the diagnostic center and voice the problem. Radiologists will help you decide on the area of study, and based on the results of the tomography, advise on further steps. If the patient has any medical history or results of previous examinations, it is better to bring them with you for diagnosis. The tomographic procedure of the head does not require any special preparation from the patient. You can do it any day without having to diet.
Preparation and performance of MRI
A little preparation will be required before administering the MRI contrast agent and undergoing the procedure to ensure the results of the examination are as detailed as possible and the patient does not encounter problems
Therefore, it is important not only to familiarize yourself with the features of the study, but also to prepare for it in advance.
Preparation
You should start preparing for an MRI a few days before the procedure.
This is very important to obtain the most accurate results. The first element of preparation is a conversation with the doctor, during which all important information about the patient is clarified, which could become a contraindication for MRI.
Therefore, it is very important to remember whether you have previously had surgery with the installation of implants or other metal elements. This is especially true for dental procedures.
After this, it will be very easy to prepare for the procedure, because... there are no special requirements. You only need to follow these rules:
Prepare psychologically
It is important to set yourself up for the absence of fear, the rapid completion of the procedure, and a positive result. This should be done a few days before the MRI. Stop using makeup
From the editor: Causes and types of numbness on the left side of the body
It is recommended not to use cosmetics before undergoing brain imaging, because this may harm the accuracy of the result. Remove all metal items and electronic devices. It is best not to take anything metal or electronic with you, so as not to accidentally forget about these things. If you have them with you, be sure to remove them before performing the diagnostics.
It is strictly forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages before the tomography. It is also not recommended to smoke, be nervous, or influence your brain or blood vessels in any way.
These rules apply to any type of MRI with contrast.
However, when examining the abdominal cavity, it is important to adhere to a strict diet, avoiding junk food, and also not to eat a day before the procedure, while refusing to drink liquids 5 hours before the MRI
Procedure for tomography of the pituitary gland with contrast
To do an MRI with contrast, before the scan begins, a special drug is injected into the patient through a vein, which almost never causes an allergic reaction. The magnetic resonance examination procedure is painless for a person and takes 40 minutes. To obtain high-quality MRI images, the patient must lie still without moving his head. Native MRI of the pituitary gland can be performed in situations where a person has contraindications to the administration of a contrast agent - renal failure, bronchial asthma, pregnancy. The price for an MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is not the cheapest, since the cost of the contrast agent will need to be added to the price of the basic scan, which is calculated based on the patient's weight. But the information content, accuracy and diagnostic value of contrast magnetic resonance imaging are worth the expense.
Contraindications
They are usually divided into absolute (if they are present, MRI is categorically contraindicated) and relative (MRI in such conditions is associated with the development of difficulties and complications; the doctor, using an individual approach, determines whether such a patient should undergo the study or not).
From the editor: What does a change in pressure indicate during a headache?
Absolute contraindications 2:
- the patient has a pacemaker (artificial pacemaker) - the magnetic field during the study can cause malfunctions of this device, which is life-threatening;
- metal implants, fragments and any other metal objects in the patient’s body (cochlear implants, certain types of clips and stents on blood vessels, artificial heart valves, joint replacements, surgical staples, plates, screws or pins, and so on).
Metal teeth are not always a contraindication for examination.
Relative contraindications are as follows:
- the first 2 trimesters of pregnancy (there is no data indicating a negative effect of MRI on the fetus - this study has been used for more than 30 years, including in pregnant women, no side effects have been detected during this time; however, it is not reliably known how the magnetic field may affect the fetus, therefore, in this category of patients, MRI is performed only for strict indications, when the absence of a mother’s diagnosis may be more dangerous than the negative impact of the magnetic field on the growing fetus);
- claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces); patients suffering from this pathology are recommended to take sedatives before the study or, if possible, undergo diagnostics using an open-type device;
- epilepsy;
- extremely serious condition of the patient;
- the patient’s inability to remain still during the examination (in order to achieve immobility, he may be given anesthesia);
- allergy to contrast agent (if MRI with contrast is necessary);
- severe renal failure - again, this applies to MRI with contrast.
Decoding
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the following anatomical features:
- The shape of the sella turcica, the edges of its bottom and walls;
- Pituitary gland, dimensions, its contours;
- Gland structure;
- Chiasm and the distance from the upper surface of the pituitary gland to the chiasm and between the mediobasal parts of the temporal;
- Cavernous sinuses;
- Optic chiasm, carotid siphons;
- Adjacent parts of the brain;
- Sinus of the sphenoid bone.
Example of an MRI report
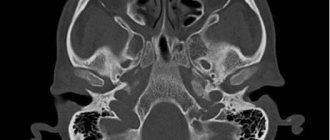
A series of MR tomograms obtained images of the pituitary gland in coronal, axial and sagittal projections.
The pituitary gland in the sella turcica is not enlarged, somewhat asymmetrical in the craniocaudal direction: on the right - 0.8 cm, on the left - 0.7 cm, coronal size - 1.8 cm, sagittal - 1.0 cm. The structure of the pituitary gland is somewhat heterogeneous due to the presence in the central sections of a poorly defined hypointense focus, measuring 0.2x0.2 cm.
The funnel is located in the middle.
The chiasma and suprasellar cistern are without deformations.
After administration of the contrast agent Magnevist 20.0 ml during dynamic observation, the contrast enhancement is expressed unevenly, and there is a lag in the accumulation of paramagnetic by the identified focus.
Conclusion:
— MRI signs of pituitary microadenoma. Recommended: Dynamic MR monitoring in the context of the clinical picture and clinical and laboratory data.
“Second independent opinion” service Medicine is an area where we want to be 100% sure . Therefore, at your request, we will be happy to offer you the service of a second independent opinion from the leading consultant of our clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences , a doctor of the highest category with 18 years of experience in the field of tomography and radiology N.V. Marchenko.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
What determines the price of an MRI?



Doctor's qualifications
It is the medical examination of the radiologist that guarantees the success and quality of interpretation of MRI images.

The price of MRI of the pituitary gland in medical centers in St. Petersburg includes: direct diagnosis, preparation and interpretation of the results, free consultation with a doctor and recording of the results on an electronic medium.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) / MR angiography of cerebral vessels | 3300 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 5180 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 6500 rub. | not implemented | from 6900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland and brain | 7800 rub. | 5180 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9290 rub. | 10790 rub. |
| Comprehensive head diagnostics (MRI of the brain, MRI of cerebral vessels, ultrasound of neck vessels, consultation with a neurologist) | 10900 rub. | 7500 rub. | |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 4000 to 6000 rub. | from 4000 to 6000 rub. |
Preparing for MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast
The scanning does not require lengthy preparations, but there are several recommendations that should be followed:
- refrain from eating five to six hours before the start of the session; you must come for the study on an empty stomach;
- limit fluid and medication intake;
- Listen carefully to the instructions of your doctor, he will tell you how to prepare for an MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast.
For the examination, you must take care in advance of comfortable clothing that does not contain metal inclusions. Check your pockets for loose change, keys, bank cards, etc. Preparation for an MRI study of the pituitary gland with contrast includes collecting the necessary documentation: a referral from a doctor, a medical card or medical history, the results of other studies, if any.