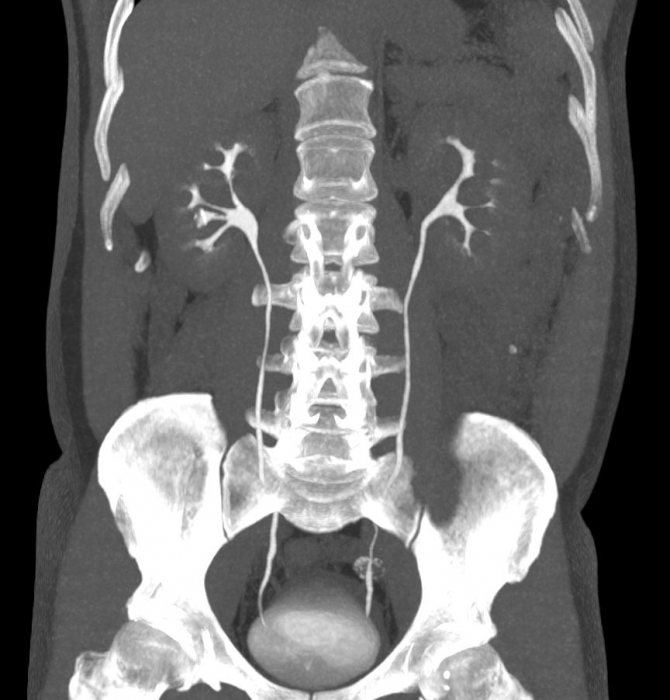
CT image acquisition
A CT scanner has a tube rotating around the object being examined and rows of sensors that receive radiation.
- The tube rotates around the object, irradiating it with precisely specified parameters.
- Radiation is perceived by detectors as it passes through the object and is attenuated to varying degrees.
- The radiation attenuation coefficient is measured at a number of points.
- The data is processed mathematically and displayed on the screen in the form of black and white images.
To analyze images from computed tomography, the Hounsfield scale has been developed - a quantitative assessment of the density at each point. The higher the value, the denser the object. So gas has the minimum density, and metals have the highest.
To assess structures that are similar in density, a system of “windows” was developed: “pulmonary”, “soft tissue”, “bone”. In the first, lung tissue is clearly visible, in the second - soft tissue structures (internal organs), in the third - bones.
CT scan
Recording pictures on film
In the past, MRI images were always recorded on film. The advantage of film is that you can view pictures without a computer. However, only a limited number of images can be placed on one sheet of film (if you try to transfer all frames to film media, the cost of an MRI examination increases significantly due to the high cost of film). In addition, computers are now available in almost all doctors' offices, so more and more doctors are asking for images on CD media.
Recording media
Files can be written to any media - DVD, CD, compact drive and others. Disk for CT, MRI, radiography, etc. is no different from discs for recording music and films. It can be purchased at any digital store.
- Small studies, such as CT scans of the brain and paranasal sinuses, take 50-300 MB and can be recorded on a CD.
- Studies with contrast enhancement in several phases (abdomen, lungs) are larger - up to a gigabyte, they are recorded on DVD.
- Choose a larger disk, because... the price difference is insignificant.
Many clinics have a service for sending data by email or cloud storage.
Check to see if you need to buy a disc. In many clinics it is already included in the price.
File Format
Data is recorded in DICOM format.
- DICOM files contain information about the patient, study, series of examinations, and individual images (scans).
- The file can be opened with any DICOM viewer such as eFilm.
- MRI, CT, CBCT, and X-ray are recorded in DICOM format.
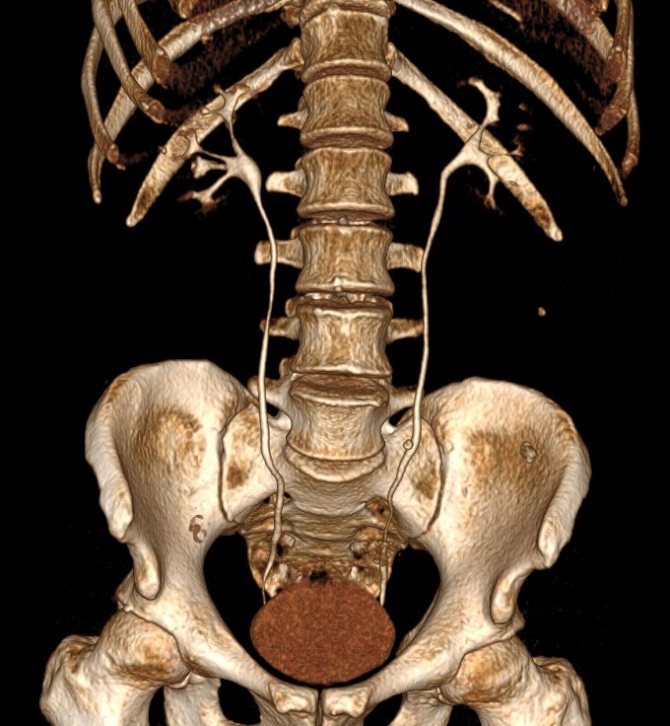
This format allows you to carry out angular and linear measurements, change brightness and contrast. The initial data obtained from tomography are used:
- for reformatting images in various planes;
- three-dimensional reconstructions.
What disk is MRI recorded on?
The results of scanning performed using a magnetic field are provided in the form of images of the area of interest. Previously, photos after MRI were taken on special film. Modern equipment records information with detectors that transmit it to a complex computer program that displays slides on a monitor. This principle is embedded in both CT and MR diagnostics.
Many people are interested in the question: “What kind of disk is needed to record an MRI?” The accuracy and completeness of disclosure of the information received depends on the correctly chosen method of storing information.
Discs for tomography can be of four types: CD(DVD)-R, CD(DVD)-RW. A distinctive feature of electronic media is capacity. DVD has a larger image capacity compared to CD. Information about the organ of interest and its surrounding structures can be recorded on a CD. By recording data on an electronic medium, the attending physician can take a comprehensive approach to analyzing the results and assess the extent of the spread of pathological processes. Recording images in oncology is important, since in order to choose treatment tactics it is necessary to obtain accurate information about the course of the disease and the involvement of surrounding tissues.
A DVD disc for MRI should be chosen if you need images after a contrast examination of the abdominal cavity, mammary glands or pelvis (when scanning these areas, from 1500 to 2500 photos are obtained) or when simultaneously examining several areas.
Data analysis and decoding
Data analysis is carried out by the radiologist who conducted the study. In case of complex pathology, the analysis is carried out jointly by several doctors.
Since the received data is digital, it is possible to involve remote specialists located anywhere in the world to decipher it.
There are services for re-analysis of radiographs (second opinion of a radiologist).
- To get an accurate second opinion, you need to provide your doctor with as much relevant information as possible.
- It is necessary to send data in DICOM format, the previous conclusion, the results of other studies - instrumental, laboratory, clinical.
- A second opinion from a radiologist is a paid service. The cost depends on the type of study (when analyzing radiography and PET/CT, it differs tenfold).
Decoding data by a doctor
- Decoding and issuance of the report is carried out by a radiologist or radiologist. A doctor must have a certificate to carry out his activities.
- The conclusions of other specialists (pulmonologists, traumatologists) based on X-rays, CT, and MRI have no legal force.
- Doctors of other specialties take into account the data of x-ray methods, but the conclusion is issued only by a radiologist.
Attention: only a certified radiologist .
How to view a study at home
Most often, a viewing program is recorded on the disk with the results of the study, which is automatically installed when it is opened. If it is missing, you can use third-party programs, for example, eFilm (paid) or RadiAnt DICOM Viewer.
- You need to insert the storage medium into the drive, select “install from disk” and wait for completion. Further actions depend on the program interface.
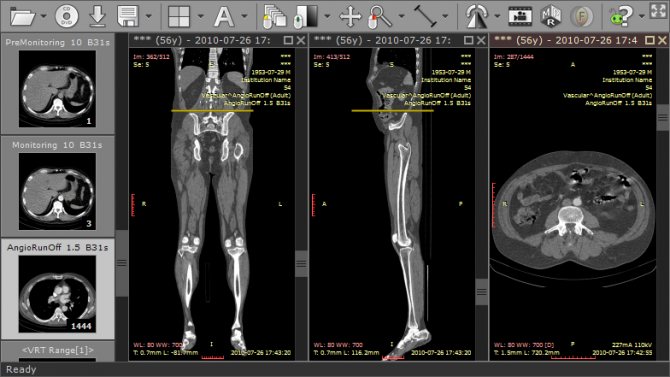
- Select a series of images if there are several of them on the disk, for example, the head and stomach. A window will open with axial images that can be “scrolled” up (to the head) and down (to the legs).
Often multiple windows open with axial, coronal, and sagittal images linked together.
Opening the disk with the original data is easy. This does not require special knowledge or skills. It is much more difficult to understand what is actually written there.
Electronic media for recording MRI studies: marketing ploy or benefit to patients?
Recording examination results on electronic media is becoming increasingly accessible. However, the attitude of patients towards this service is still ambiguous. Some are happy to switch to a new data storage format, while others consider it an extravagance that they can easily do without. Who is right?
We talked about electronic media in medical practice with diagnostic X-ray technicians.
Why is it important for a doctor to know the results of previous examinations?
Olga Niyazova:
So that the radiologist can assess the dynamics of the patient’s condition. There are a lot of practical examples on this topic.
So, our doctors evaluate many factors: for example, the size of tumors and hernias. Comparison with previous results allows you to answer the questions of the referring clinician, understand whether it has become better, worse, or the condition has remained unchanged, whether the prescribed treatment helps or does not help, and whether it needs to be adjusted.
Alexandra Krupnova:
The doctor needs to have information from previous studies so that he can accurately and clearly assess the dynamic condition of the patient. Comparison of data is only possible if there is an electronic medium with the full amount of information. Making an accurate diagnosis and prescribing the correct treatment are within the competence of the attending physician, and only with a dynamic examination can one trace changes over a certain period of time and, if necessary, adjust treatment. Often, radiologists indicate in the description the time period after which it is best to undergo a control examination to see how the picture has changed during this time.
Comparison of data is only possible if there is an electronic medium with the full amount of information
Svetlana Derun:
This helps the doctor make the MRI examination as effective as possible. Previous results are needed to focus the doctor’s attention on a specific anatomical area or organ: where the patient previously had a problem; to be able to study the area of interest specifically, using special programs and techniques, to quickly understand where in the body the source of trouble is located, and most importantly, to write a conclusion more accurately, since the manifestations of painful symptoms can be similar and may suggest completely different diseases.
Determining the dynamics is a reliable way to determine the onset of the current disease. Dynamic observation helps to trace changes in the tissues of the examined organ, where various cysts can be observed (they grow or not), benign tumors, etc., the correctly prescribed treatment will depend on this.
When visiting a doctor, patients usually take with them the results of past tests, x-rays (at least printed ones), or, as a rule, people do not understand how important this information is and do not keep it?
Olga Niyazova:
Unfortunately, people do not always understand the importance of previous examinations. When recording, we talk about the need to take this data with you. But not everyone fulfills the request. This is usually done by people with chronic diseases; those who are under constant surveillance.
Alexandra Krupnova:
As a rule, patients do not provide the results of previous examinations. They do not know how important the information is for the radiologist, who, by analyzing, creates a more accurate picture.
Svetlana Derun:
Not all patients take data from previous examinations with them. They usually have to be reminded of this. Often people do not understand the importance of having these documents. Some cannot find the results of previous examinations, do not store them or have lost them.
How is information on electronic media better than traditional statements and photographs?
Olga Niyazova:
Firstly, we can display a limited number of images on film, but the entire volume of the study is recorded 100% on electronic media. Secondly, there is no way to load the film back into the computer, so it is difficult to compare the data. Thirdly, the quality of visualization on electronic media is higher. You can open each picture: enlarge, rotate and examine in more detail. But on film the picture is shown more finely and from only one angle.
In addition, electronic media takes up much less space than a pile of papers and large films.
Having the patient's complete study protocol on electronic media makes it possible to consult in absentia with leading specialists in specialized areas both in Russia and abroad.
Alexandra Krupnova:
One of the most important advantages of electronic media is the availability of complete information.
Svetlana Derun:
First of all, it is convenient and reliable. This type of media does not take up much space. You can save the data to your computer and view the three-dimensional image.
This is necessary primarily for the patients themselves. After all, we copy important examination results for ourselves before pasting them into the medical record. It is better to store MRI examination data on a disk or flash drive.
We store data in our database for a limited amount of time, and the recording on the media is always available to the patient.
The disk contains 5 times more images than are displayed on the image
The disk contains 5 times more images than are displayed on the image.
Attending physicians can view the entire examination data on a computer, zoom in on areas of interest, and assess the condition of the organ over time.
Electronic storage of information allows you to receive consultations from doctors living in another city or abroad without leaving your home, simply by sending images via the Internet.
Is the number of patients wishing to purchase electronic media growing? Have people already appreciated the convenience of the new format?
Olga Niyazova:
We try to explain to patients the need to record studies and the advantages of the electronic format. Many, wanting to track the dynamics of their condition after treatment, come with our carriers and use them as their outpatient card.
“An absolute indication for a contrast study is any space-occupying formation in the body, detected during diagnosis or previously identified.” Quote from the material: “Why do we need contrast in MRI?”
Alexandra Krupnova:
Recently, there has been an increase in patients wishing to purchase electronic media. People appreciated the convenient data storage format, thanks to which the doctor receives complete information necessary to monitor their health.
Svetlana Derun:
The number of patients willing to purchase electronic media on their own initiative is not yet growing.
In your opinion, why do some people refuse to record information on electronic media? What prevents modern people from switching to a new data storage format, what psychological barriers remain? How can you overcome them?
Olga Niyazova:
When registering, patients are told the cost of the examination. And it’s difficult for people to pay more than they expected. Many initially do not take with them more than the cost of the examination. Therefore, we strive to inform patients already during a telephone conversation about the need to save results and the advantages of electronic media.
Many people do not use computers and do not understand how to display information from a disk or flash drive onto it.
There is a category of patients who do not want to repeat an MRI because they hope that no more health problems will arise.
For many, the referring physician does not use media in their practice. We explain that the data is necessary primarily for radiologists, who will next describe the study, and is also important for assessing the dynamics of the condition.
This can be overcome by providing greater information to both patients and colleagues.
Alexandra Krupnova:
I believe that in times of market relations, people developed a fear of imposed services. Indeed, if you look around, you can see that everywhere we are offered additional services that must be paid for.
In the case of recording on an electronic medium, the patient makes an investment in the future and saves information about his health
But in the case of recording on an electronic medium, the patient makes an investment in the future and saves information about his health. It is possible to overcome this barrier only by explaining to the patient why the data needs to be stored in this form.
Svetlana Derun:
The main reasons: lack of information and financial difficulties. I have encountered the following situations:
— some doctors do not look at data electronically, many simply do not have a computer;
- the patient does not understand why this is needed;
— the patient is experiencing financial difficulties and is not ready to purchase a carrier at the moment. Sometimes people do not have more than the cost of the examination with them;
- the patient simply does not need it.
Of course, there are regular patients who have already purchased the carrier from us, appreciate its importance and use it for diagnosis in our center and other cities. For those who come for the first time, we explain what it is for, and together we overcome all barriers.
Do you think it is possible in the near future to make a complete transition to storing medical data in electronic form? Are doctors ready for this?
Olga Niyazova:
A complete transition is, of course, possible. But there are many obstacles that need to be cleared. First of all, it is necessary to provide all doctors with computers at their workplaces and train them to work with data on electronic media.
Alexandra Krupnova:
I believe that the transition to electronic storage of medical data is inevitable. It will be very convenient for doctors, as it will allow them to receive complete information about the patient’s health.
Svetlana Derun:
If this develops in some other way, for us – doctors and patients – this will open up additional opportunities and give quick access to the results of the examinations completed.
Interviewed by: Daria Ushkova
Where can I read a CT scan?
After receiving the scan results, you need to consult a doctor for a transcript. This is usually done by a radiologist who directly specializes in screening examinations - MRI or CT. It is advisable to make sure that the doctor has the appropriate certificate - only in this case can you be sure of the reliability of the results. It is necessary to provide not only scans on disk, but also a card with preliminary diagnostics - only in this case is it possible to evaluate all the information and compare it with existing results of other examinations. It will not be possible to quickly get a description - for a doctor to examine the images and all CT projections, it will take 1-3 hours.
The interpretation of the result is not always included in the cost of the procedure; in some centers it is priced separately. But in most specialized clinics, the patient receives not only scans recorded on a medium, but also a transcript of the results, certified by a doctor.
How to load tomograms onto the screen
When the MRI image is opened, it will become clear what the picture is. But often an absolutely inexplicable mixture of dark colors is shown.
There are several ways to view tomograms:
- Sagittal. Scans are the easiest to understand. The method looks like a longitudinal section of the area under study, inspection is carried out in profile;
- Transverse. The most difficult option for people who are not professionally involved in deciphering MRI results. The method forms many horizontal parallel planes. The MRI image is always black and white. To recognize organs, detected pathologies are based on shades of color (contrast).
The programs make it possible not to depend on the level of computer RAM, but if you want to expand the functionality of the software, technical characteristics are of no small importance.
The application allows you to perform the following operations:
- You can change the spatial orientation and view the image from any angle;
- Changing brightness and contrast parameters;
- Scaling an object;
- Carry out the necessary measurements of length, height, width, volumetric indicators.
The MRI viewer allows you to save MR scans in DICOM format as WMV video files or JPEG drawings. Copying to the clipboard is available for subsequent use in presentations, drawing up conclusions, for the most detailed presentation of the results of a magnetic resonance examination.
Computed tomography of the bronchi and lungs, the essence of diagnosis, indications and harm
Switch to English registration. Phone or email. Another's computer. Radiation diagnostics today.
View full version : What should MRI results be recorded on disk? I don’t know if I’m asking the question in the right section, I apologize if it’s in the wrong section, but I’m going to go to the consumer protection society and I want to know for sure whether I’m right. The situation is as follows: I come to do an MRI of the spine at a paid clinic, without a referral, because the attending physician herself called them and said that she needed one. I only tell them what they were told to do with the contrast. I have some claustrophobia.
Lung diseases are among the most common and dangerous today. The reason for such terrifying statistics is the polluted ecological environment. The main factor in the treatment of diseases is timely diagnosis of pathological processes. One of the most accurate studies is computed tomography of the lungs.
News
Many patients, having X-ray photographs (films) in their hands, do not know how to send them by email to the doctor. Our tips will help the patient to correctly photograph an x-ray or scan the results of an x-ray, and then send the MRI or CT images to the doctor.
The solutions are as follows:
If your MRI or CT images are on X-ray film.
Large sheets of magnetic resonance or computed tomography results can be photographed with a digital camera, then the resulting file can be sent to the doctor. It is better to take pictures on a white monitor screen (by opening a blank page in Paint or Word) or on a light window.
You can also try scanning them on a regular scanner with the lid open (be careful with your eyes!).
Note: Do not photograph the entire CT or MRI film, but each part of it (small square). Remember, the better the research images, the more adequate the consultation.
If your x-rays are on disk.
In case the X-ray, MRI or CT results files are located on the disk in a special format.
Open the disk with the study through Explorer with the right mouse button, find the folder called DICOM.
Create an archive using the winRAR program or simply upload the files to a file hosting service.
Upload the archive to a file hosting service. Easier than mail or Yandex, here user access to files is simplified. Yandex disk requires registration, the initial storage volume for files is 3 GB, which is more than enough, to be able to download your file, make it public. On mail without registration, the download volume is limited to 100 MB, with registration - up to 1 GB.
https://disk.yandex.ru/ , https://files.mail.ru/
Send the doctor a link to the file.
If there is no DICOM folder on the CD, then you can archive all its contents, upload the archive to a file hosting service and send a link to it to the doctor.
Remember that in this case, the doctor will need additional effort to review your images.
REFERENCE. FOR PATIENTS. How to place research data from CDs and DVDs.
Dear patients! For the most objective consultation, it is necessary to record your examination (CT, MRI) on disk. In some medical centers this is a paid service. To record the study on disk, contact the institution where you underwent CT/MRI. The data from the disk needs to be archived (rar or zip format), upload the archive to a file hosting service, and provide a link to the archive on your forum topic.
1. Archiving the folder with the study: open the disk with the study through Explorer with the right mouse button, find the folder called dicom. Further on the drawings
*
*
*
*
*
2. Upload the archive to a file hosting service. Mail or Yandex is better, here user access to files is simplified. Yandex disk requires registration, the initial storage volume for files is 3 GB, which is more than enough, to be able to download your file, make it public. On mail without registration, the download volume is limited to 100 MB, with registration - up to 1 GB.
https://disk.yandex.ru/ , https://files.mail.ru/
3. Get a link to your file from a file hosting service and copy this link here to your forum topic.
Print CT images
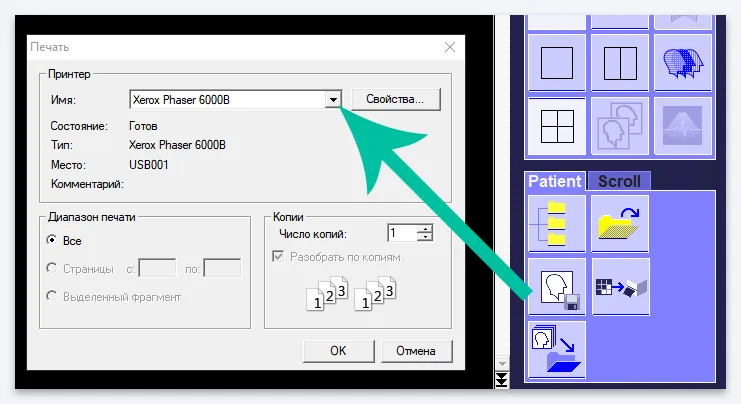
To print an image directly from Syngo fastView
, select this item, select the “Patient” tab in the Main Menu, and in it select the “Print” item. Or select the printer icon in the Tab Menu:
In the window that opens, select your printer (make sure it is connected to your computer and configured first), then click OK. The image that is currently open in the Image Display Window will be printed, that is, if multiplanar reconstruction is selected, three CT images, a 3D model and all axes in the position they are placed will be printed.
To print an image without service information on it, before printing, click on the “Show/Hide Image Text” icon, see the item “Hide service information on the image”
Make the most of the Tab Menu
View CT images the way you want
In the “View” tab you can select different viewing modes. For computed tomography images, the capabilities of the first two modes, “Stake” (1) and “Stripe” (2), are the same.
The “Stripe” mode is needed if some images in a series themselves constitute a series (this is possible in other types of diagnostics, for example, ultrasound). The only difference between these modes when viewing CT results is the presence of a scroll slider in the “Stripe” mode (2). You can drag it by hovering over it and holding down the left mouse button.
Also, while in Stripe mode, you can open series images in two or four windows at once. To do this, make sure that you are in “Stripe” mode (the icon with the image of three frames should be highlighted), then on the same “View” tab, select the icon with two rectangles or four squares.
In the example, the icon with four squares is selected. The image display window will look like this:
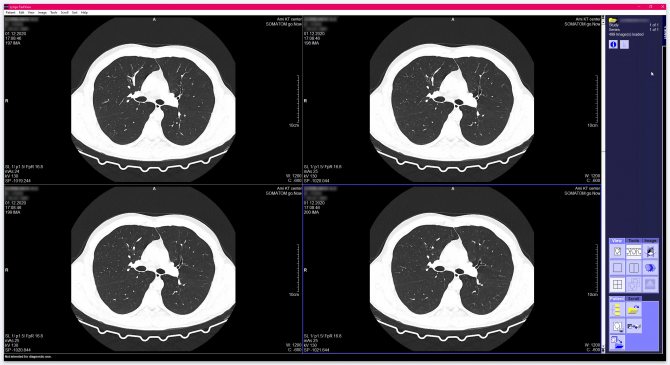
Please note that four consecutive images of the series will be open in four small windows, for example, the 58th frame will be open in the upper left window, the 59th in the upper right, the 60th in the lower left, and the 61st in the lower right .
To open any of these images in full screen, double-click on it with the left mouse button. Double-clicking the left mouse button on the enlarged image will return you to a window with four images (or two if you selected the two-image display mode).
You can also configure the display in 9 or 16 cells. To do this, go to the “View” item in the main menu and select the desired display option:
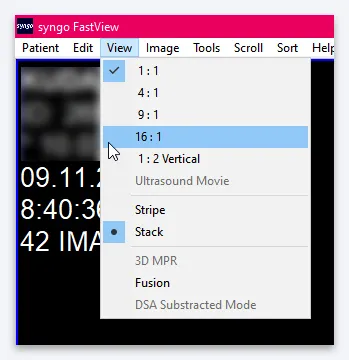
View CT images in multiple views at once
To switch to the mode of viewing images of the selected series in three projections at once, make sure that one of the modes is enabled, when one series of images is expanded to the entire window: “Blow up”, “Stake” or “Stripe”. Click on the “3D MPR” icon in the “View” tab, or open the Main Menu and select “View” → “3D MPR”.
“MPR” - multiplanar reconstruction - is a display on one screen of three orthogonal (perpendicular to each other) projections (sections): axial, frontal (or coronal) and sagittal.
“MPR” - multiplanar reconstruction - is a display on one screen of three orthogonal (perpendicular to each other) projections (sections): axial, frontal (or coronal) and sagittal.
In the window that opens there will be three cells with different projections and a cell with a human model. This model is surrounded by three frames of different colors. If you look closely, you can see that each of the CT image cells also has a colored frame that matches the frame on the model. This way you will understand which projection is located in each cell.
Place the cursor on one of the axes or on the crosshairs of two axes in one of the three cells with CT images and hold down the left mouse button. Now drag the selected axis or axis crosshair inside a cell and watch how the images in the other two cells change. If the image in one or two cells disappears, then the cursor is outside the image in the selected cell.
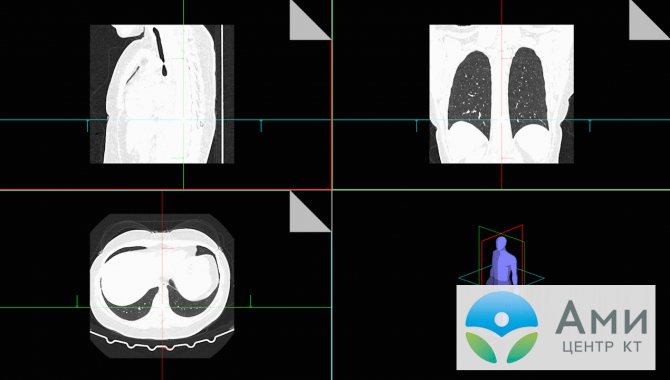
You can also activate the “Blow Up” zoom mode by double-clicking on the image in any of the three cells that you want to view in detail.
Inside the zoom mode, as in normal viewing, you can scroll through images with the mouse wheel. In this case, the axes will remain on the image. They can be brought to the desired location in the enlarged image.
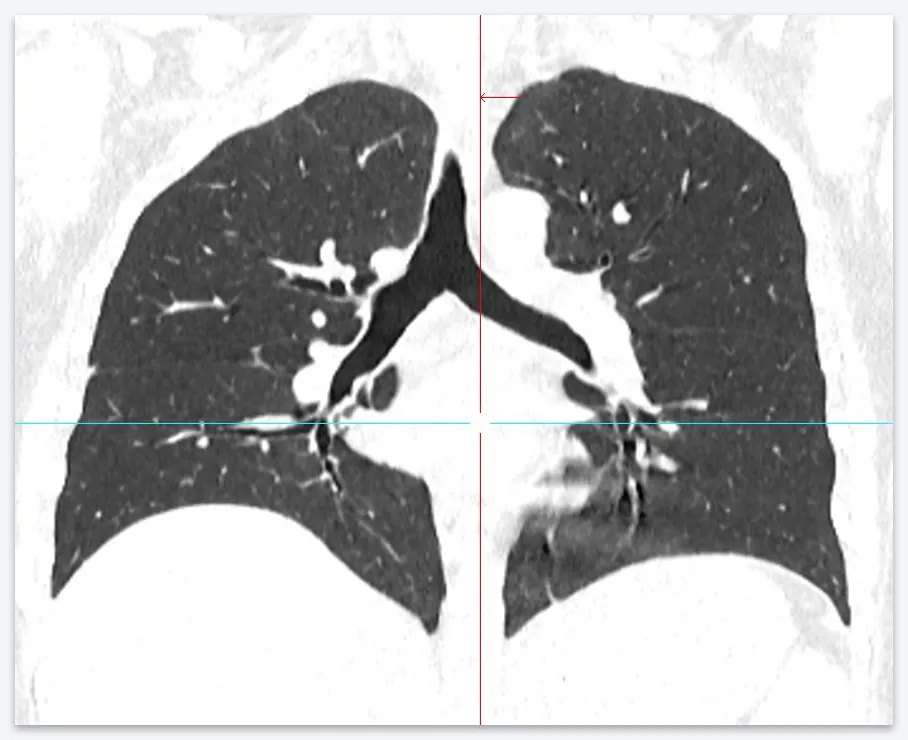
Once you have finished viewing and, if necessary, moved the axes to the position of interest, double-click on the enlarged image. This will take you back to the three-view viewing mode.
Now the images in the two remaining cells will be opened in accordance with the positions of the axes that were set in the “Blow Up” mode.
To exit the three-view viewing mode, click again on the “3D MPR” icon in the “View” tab:
View research in video mode
To avoid having to rotate the mouse wheel to scroll through images, turn on video viewing mode. To do this, select the “Scroll” tab in the Tab Menu (1), then click on the icon with a picture of a camera with the caption “auto” (2):
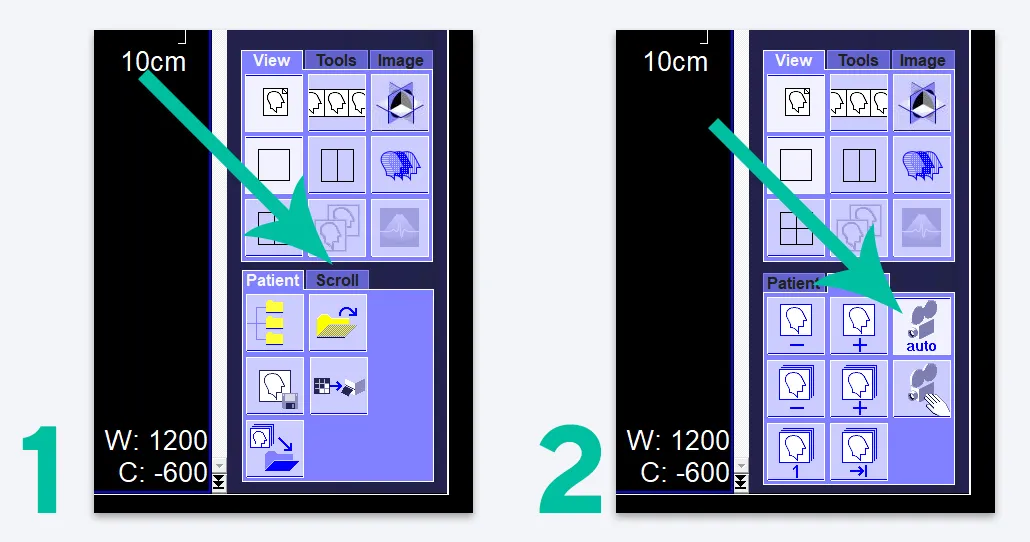
In this mode, the Movie control window will open, where you can adjust the display speed by selecting a frame rate from 1 to 60 per second (1). You can also scroll through images frame by frame (7), pause viewing (2), loop it (after the last frame the first one will be shown again) (5) or run it in the opposite direction (after the last frame the penultimate one will be shown, then the penultimate one, and so on further to the first frame) (6).
You can stop viewing (3) without leaving this mode (the viewing control window remains open, but it will be possible to scroll through images by rotating the mouse wheel or using the arrows (7)). You can also close the View Control Window by clicking the “Close” button (4) and exit the video viewing mode.
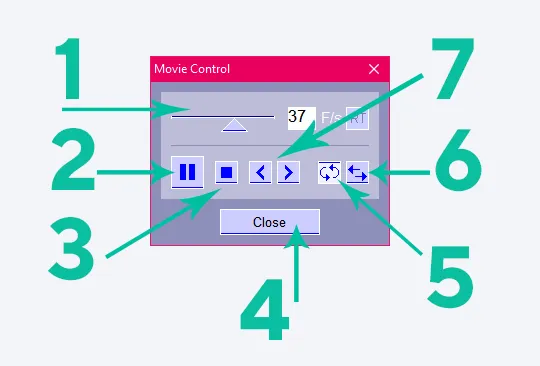
If you are in this mode, you move the cursor over the CT image and click the left mouse button, the viewing will stop. To resume it, click on the “Play” button (►):
If in the “Scroll” tab you select an icon with a picture of a camera and an image of a palm, the interactive mode will be activated. In it, you can scroll through images by holding down the left mouse button and moving the cursor up and down in the Image Display Window. Please note that in interactive mode, the cursor will look different (with a camera icon next to the arrow), and the Status Bar will indicate that this is Interactive Movie mode:
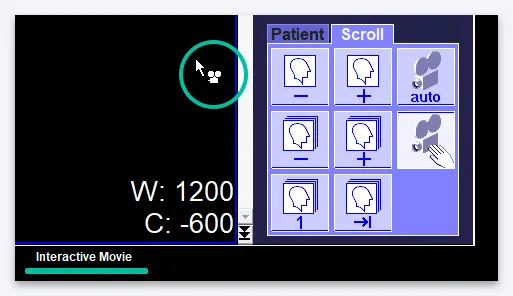
There are other icons in the “Scroll” tab that make it more convenient to scroll through the images in the series.
So, by pressing buttons 1 and 2 you can scroll through images back or forward one by one, buttons 3 and 4 allow you to scroll through series if several series are loaded at once. Button 5 will help you go to the first image of the first loaded series, button 6 will go to the last image of the last downloaded series.
How to open and copy a disk with MRI results?
Copying information from an MRI disk to a computer is not difficult; this can be done using the special “Explorer” function; transfer the files on the disk to a special folder on the computer, which must first be created. If you need to send pictures by email in the future, you will need to archive them, so these files will take up much less space, which will allow you to send them by email without losing image quality. But as for the issue of opening information from an MRI disk, for this you will need to install an additional program. The information recorded on these discs has a special, so-called medical format - dicom or DICOM. You install a special program that reads these images, and there are several of them, both paid and free, and open the MRI image.