- patient's age;
- diagnostic purposes;
- primary diagnosis;
- patient's health condition.
All about diagnostics
How does ultrasound differ from MRI?
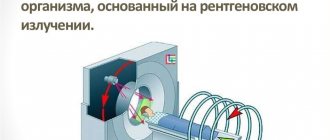
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the interaction of a magnetic field with radiofrequency pulses. The powerful magnetic field generated by the tomograph communicates with hydrogen atoms located in the tissues and organs of the human body. Protons move perpendicular to the tomograph and produce signals. They are analyzed by a computer program and converted into a three-dimensional image, from which the doctor makes a diagnosis. Cartilaginous and soft tissues are especially amenable to this research method.
For in-depth diagnosis of diseases and lesions of a specific human organ, MRI uses a contrast agent. Contrast is achieved through intravenous administration of drugs based on gadolinium salts. As it settles in the structures, the contrast agent visualizes internal organs, soft tissues, cartilage and blood vessels even more clearly, which makes it possible to establish the most accurate diagnosis. The specific chemical formula of the drug enhances and accelerates the effect of the magnetic field.
Ultrasound has a different operating principle. It is based on the penetration of ultrasonic waves into soft tissue, generated by a small sensor that comes into contact with the skin. The waves reflect echoes sent back by internal organs. The image is displayed on a special monitor, which is monitored by the doctor directly during the examination. The specialist gets the opportunity to study various processes in the body in real time.
Both ultrasound and MRI are used to examine any internal organs and soft tissues.
With their help they examine:
- Brain;
- Organs of the chest, abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- ENT organs;
- Vessels;
- Structures of the musculoskeletal system.
To examine bone tissue, doctors prefer to use radiography and computed tomography, which is also based on the effects of x-ray radiation.
However, in terms of depth and reliability of diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging wins. It is often prescribed in addition to an ultrasound examination if the result is unclear.
Preparation for the procedure
Since diagnosing the abdominal organs is a rather labor-intensive process due to the possibility of confusing food particles with pathologies, therefore the procedure is advised to be carried out in the first half of the day; you should not eat food 12 hours before the examination. Two days before the procedure, you need to exclude gas-forming foods, for example, cabbage, peas. Also added to the list of prohibited foods are carbonated and alcoholic drinks, baked goods, milk, kefir, cottage cheese, sour cream and vegetables with coarse fiber. Before the examination itself, the doctor may prescribe a laxative or an enema. When performing a CT scan, children are sedated or put to sleep to ensure immobility during the examination.
The scanning procedure takes very little time (15-20 minutes with ready results). Upon entering the office, the patient takes off all jewelry and metal objects and changes into a disposable set of clothes. In this way, doctors eliminate distortions from various objects. Next, the patient is placed on a moving table and lies motionless. The radiologist may ask you to hold your breath for a couple of seconds. Communication takes place via speakerphone; a speaker and microphone are installed in the gantry of the device. The doctor may also order an abdominal CT scan with contrast to better visualize the tissues of your body. Contrast is a drug that contains particles of iodine or barium. Thanks to them, X-rays send a signal to the device’s sensor, after which the image enters the computer.
How else does MRI differ from computed tomography and ultrasound?
The three research methods differ in contraindications and limitations.
The greatest number of contraindications are noted for CT:
- Childhood;
- Pregnancy;
- Diabetes;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Multiple myeloma;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Individual iodine intolerance;
- General serious condition of the patient.
MRI without contrast has the only contraindication – the presence of electronic and metal implants. If a contrast agent is used during magnetic resonance imaging, it should be performed with caution in people with allergies, asthmatics, and people with chronic renal failure.
Ultrasound has no contraindications. Some restrictions apply only to transrectal and transvaginal studies.
What to choose, ultrasound or CT?
This or that method is chosen by the attending physician, based on the specific clinical case.
When to choose tomography?
Preference is given to tomography in cases where there is an unclear clinical picture or in an emergency situation, for example, bleeding or stroke. In most cases, CT is used as an additional diagnostic method, allowing an extremely detailed examination of organs and systems. The tomograph will cope where ultrasound is not informative: the brain, blood vessels, dense formations, nerve fibers.
When should you choose ultrasound?
Preference is given to ultrasound examination in the case of primary diagnosis. Ultrasound is also indispensable in pregnancy management. This technique is used in situations where other methods are not available due to existing contraindications. Ultrasound examination is considered a low-cost method that is suitable for most patients.
Benefits of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging has objective advantages over ultrasound:
- Possibility of studying organs inaccessible to ultrasound (inner ear, pituitary gland, thymus, spinal cord, etc.); · Obtaining a clearer three-dimensional image;
- Availability of simultaneous examination of cartilage, soft tissue and bone tissue;
- Obtaining a detailed image and the ability to detect small pathological foci (from 1 mm, including metastases);
- The effectiveness of the study is over 98%.
The use of a contrast agent in MRI allows cancer to be diagnosed at an early stage without a biopsy. Detection of malignant neoplasms by ultrasound is possible only if they are large in size.
The choice of a specific diagnostic method is best left to a specialist. The attending physician may order several studies to obtain objective data.
MSCT and CT: what is the difference?
Many patients who are scheduled for examination are interested in what kind of computed tomography is available and which one is better to choose. As for the second point, it makes sense to rely on the opinion of the attending physician. Let's try to figure out the first question here.
Depending on the type of equipment, there are several types of CT:
- Linear computed tomography is an outdated method that is practically not used in modern clinics due to the high radiation exposure and long duration of the procedure. Only one slice is captured in one step.
- Spiral and multilayer computed tomography are improved types of x-ray diagnostics. The main difference between CT and SCT is that the emitter moves in a spiral around the area under study, scanning it in different planes. This allows you to significantly reduce the procedure time and the amount of radiation exposure. Today, patients are most often prescribed MSCT. What kind of examination is this? Multislice tomographs differ from spiral tomographs in that they have several rows of detectors, due to which scanning and data collection are carried out continuously. The examination takes a minimum of time, while it is possible to study the smallest structures. MSCT allows you to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of the studied area and examine the desired area from different angles.
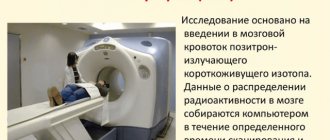
- Computed positron tomography is the most modern diagnostic method based on the use of radioisotopes. Unlike standard CT, PET studies not the physical features of organs and tissues, but the chemical processes occurring in them. This makes it possible to identify cancer before a tumor forms, while other methods detect the problem after the tumor has appeared and reached a certain size. The examination is also effective in searching for distant metastases.
Advantages of ultrasound diagnostics
Spinal diseases are complex and require long-term therapy, and sometimes serious surgical intervention. Considering this fact, the key to successful treatment is timely diagnosis of ailments localized in the vertebral areas. Since the spinal column is hidden under the skin, tendons, muscle tissue, and has a complex multi-layered and multi-stage structure, it is very difficult to “get” to it. And here the most modern and effective, and also not too expensive, method is ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the spine is a non-invasive diagnostic examination method based on the principle of echolocation
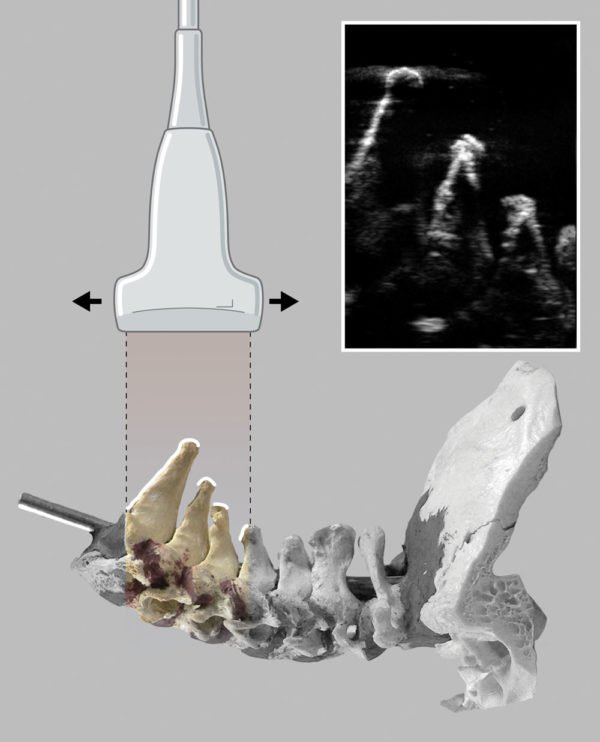
The illustration shows how the ultrasound beam is reflected from the bony surfaces of the lower cervical vertebrae
There are many diagnostic methods used for diseases of the vertebral structures. Ultrasound is prescribed in cases where the following symptoms and conditions are present:
- impaired sensitivity of the limbs;
- loss of coordination skills;
- difficulty walking;
- dizziness;
- constantly present headaches, the genesis of which is not clear;
- painful or simply unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations in the back (compression, tension, tension);
- there is deformation of posture;
- constant or recurrent joint pain;
- inhibition of movements and difficulty bending and bending in the spine;
- numbness in the arms or legs;
- presence of arterial hypertension;
- visual disturbances;
- respiratory disorders;
- hearing aid dysfunction.
Table. Advantages of ultrasound.
Advantage Description Harmlessness When performing the procedure, the doctor does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, which certainly happens with any x-ray method, as well as with CT and MRI. Repeatability It follows from harmlessness, it is for this reason that the procedure can be repeated as many times as necessary, in any time interval. Ease of implementation No special training required, no contraindications. Non-invasiveness This is very important, since the patient often already experiences back pain in order to be subjected to it during the diagnosis. The procedure is comfortable for the patient and painless. Affordability This is a relatively inexpensive study that almost everyone can afford.. Modern ultrasound machine
Ultrasound machine
Modern ultrasound machine
Ultrasound machine
What can you see?
Bone structures on the monitor are visible in the form of layers that give a strong acoustic signal. Such a drawing is not informative, so dense formations are not the goal of the method. Ultrasound examinations of the spine are used only to determine the condition of soft tissue organs and their parts. These include the following:
- ligaments between vertebrae;
- intervertebral discs;
- back muscles;
- spinal cord;
- spinal membrane;
- vascular cords.
The main pathologies detected by ultrasound of the spine are:
- hernial protrusions;
- tumors;
- softening and hardening of intervertebral discs;
- developmental anomalies;
- traumatic injuries;
- spinal cord rupture;
- swelling of the ligamentous apparatus;
- spinal deformities.
The study may reveal additional data on the condition of neighboring organs: kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder, uterus. The information is used in the differential diagnosis of diseases.
Methodology
For ultrasound of the spine, a conventional convex sensor with a wave frequency of 2.0-3.5 MHz is used. Almost all medical institutions have such equipment. If you plan to study the vascular pattern, the sensor must have a Doppler channel with a frequency of 2.0 MHz. This type of ultrasound device belongs to the expert class.
If the material supply of an institution allows the purchase of more expensive equipment, preference is given to ultrasound scanners with 3D functions. This allows the doctor to build a three-dimensional image. Each part of the spine has its own specific techniques.