What tests need to be taken?
The balance of hormones is responsible for the functioning of the body. When it is violated, the development of various diseases is observed.
Blood tests for sex hormones
It is considered justified to conduct hormone tests for women:
- luteinizing;
- follicle-stimulating;
- atymüllerian;
- progesterone;
- prolactin;
- estradiol;
- testosterone.
Blood tests for thyroid hormones
Thyroid panel hormones are:
- thyroid-stimulating;
- triiodothyronine;
- thyroxine.
Tests for menopause
The age period greets the ladies with its surprises. Menopause or menopause is a special stage in the life of every woman. And it is not surprising that the production of hormones may fail. This period is usually expressed in mood swings, headaches, and increased sweating. The gynecologist prescribes the following tests:
- FSH is follicle stimulating hormone.
- Estradiol is a sex hormone that controls menstruation.
- “Progesterone” – during menopause, its absence is normal.
- “Luteinizing hormone” - menopause shows increased levels of the hormone.
Follicle-stimulating hormone allows you to determine the level of another important hormone - estradiol. If its concentration in the body is less than thirty-five units, then this indicates that menopause has entered the female body
An excessively reduced estradiol level can lead to osteoporosis and early atherosclerosis.
How to get tested correctly
When submitting biological material, it is necessary to indicate the day of the cycle, the duration of pregnancy or the moment of menopause. If a woman is undergoing a course of antibacterial or hormonal therapy, this nuance must be reported to the laboratory assistant.
Before taking the tests, it is recommended:
- avoid sexual intercourse the day before the examination;
- do not take a hot bath;
- do not visit the sauna and steam bath;
- no smoking;
- do not overload yourself physically.
Estradiol
It has a versatile effect on all female genital organs. Its role is especially important in the development of the uterine mucosa and preparing it for pregnancy. This hormone is secreted by the maturing follicle, corpus luteum of the ovary, adrenal glands and even adipose tissue under the influence of FSH, LH and prolactin. In women, estradiol ensures the formation and regulation of menstrual function and the development of the egg. A woman ovulates 24-36 hours after a significant peak in estradiol. After ovulation, the hormone level decreases, and a second, smaller amplitude, rise occurs. Then there is a decline in the concentration of the hormone, which continues until the end of the luteal phase.
Why do you need a blood test for hormones?
Hormonal imbalance is considered a normal variant during pregnancy, the postpartum period or menopause. However, even in such situations it is necessary to monitor his condition. Hormone analysis is most often prescribed for:
- gaining excess weight;
- inability to conceive a child;
- often recurrent acne;
- diagnosing breast tumors;
- decreased libido;
- problems with pregnancy;
- susceptibility to genetic diseases;
- disruption of the functioning of the digestive tract;
- ovarian neoplasms;
- pregnancy diagnosis;
- hirsutism.
When and why are they appointed?
Hormonal levels and the functioning of the entire body have a direct relationship. Hormonal imbalance can provoke serious pathological conditions. Women are most often referred for hormone testing by gynecologists and endocrinologists. Such an examination is appropriate for the following pathologies and conditions:
- Hormone tests when planning pregnancy. They will show the general condition of the female body, as well as the possibility of conception and normal bearing of the unborn child. Tests when planning pregnancy necessarily include testing for: estradiol, progesterone, FSH, LH, testosterone, prolactin, thyroid hormones, DHAES and AMH.
- During menopause. After 45 years, if there are complaints, the gynecologist can send the woman to take hormone tests. To understand whether menopause is occurring, it is enough to determine: FSH, LH and estradiol. With age, women experience changes in the concentration of these biologically active substances. Tests for female hormones during menopause make it possible to select adequate replacement therapy and assess the overall need for taking hormonal medications.
- With dysfunction of the reproductive system. If there are pathologies of this kind, the patient is prescribed a whole group of tests that determine the female hormonal profile: FSH, LH, prolactin, estradiol, TSH, DGAES, cortisol, progesterone. The listed biologically active substances optimally show the state of the reproductive mechanisms, therefore they are considered the most important in diagnosing female infertility.
- For depression and sudden mood swings. The amount of sex hormones, thyroid hormones and endorphins directly affects a person’s emotional state. Taking this into account, if the patient has a depressive mood, a competent specialist will definitely prescribe her an analysis for TSH, free T3 and T4, and cortisol.
- For hair loss. If there is an excess of “male” hormones of the androgen group in a woman’s body, then the structure of her hair may well deteriorate. They will also become brittle and will fall out more rapidly. In addition, a woman may begin to notice a decrease in libido, hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face and body according to the male pattern), and changes in the voice. In this case, the woman needs to evaluate androgenic function.
- For growth disorders. Disruption of the somatotropic function of the pituitary gland can cause retardation in physical development, growth retardation, muscle weakness or osteoporosis. If a girl or young woman is noticeably stunted, a laboratory assessment of growth hormone (GH) will be recommended.
- For acne. Problems with the skin are typical for adolescents during puberty and women in PMS (this is a normal variant). But if acne appears permanently, does not go away by the age of 25–30, and its appearance is not associated with the menstrual cycle, then the patient needs to be examined. In such cases, a TSH test and a reproductive panel are appropriate.
- For diabetes. This disease is directly related to hormonal imbalances. First of all, diabetes develops against the background of a deficiency of insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. Patients with suspected diabetes mellitus are sent for laboratory evaluation of thyroid function, and a test for glycosylated hemoglobin is also performed.
- In case of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The activity of the digestive tract is also regulated by a variety of hormones. If there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, the gastroenterologist may send the patient to study the main hormone in this area - gastrin. Its main function is to stimulate the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells of the fundus of the stomach.
- For obesity or lack of appetite. Rapid weight gain or loss can also be caused by hormonal imbalances. Body weight and energy metabolism are regulated by leptin. It is always included in a complex of studies on the problems of weight gain or loss. In some cases, a study of cortisol and adrenaline may be necessary.
People who care about their health are aware of how much hormonal levels affect their overall well-being and mood. However, trying to independently regulate your hormonal state is quite dangerous. The best solution would be to contact a specialized specialist. He will be able to objectively assess the condition, prescribe the necessary tests, and based on their results, select adequate treatment.
A large list of hormonal tests is immediately prescribed in rare cases. As a rule, 1-3 indicators that are responsible for the functioning of a particular organ are sufficient. If desired, the patient can undergo tests without the recommendation of a specialist.
Testing for hormones
Hormones, entering the bloodstream, are responsible for metabolic and biochemical processes. Thanks to the analysis, it is possible to diagnose hormonal imbalance, determine its cause and carry out therapy.
When to take it
It is recommended to be examined for:
- estradiol - on days 2-4 of the cycle, if necessary, to establish the time of ovulation - in the middle of the cycle;
- progesterone - on the 22nd day of the cycle, with scanty discharge - in the middle of the cycle;
- follicle-stimulating and luteinizing - on days 2-4 of the cycle or from 8 to 18 as recommended by a doctor;
- prolactin - regardless of the day of the cycle.
How to donate blood for hormones
The material being studied is venous blood. The analysis is carried out on the recommendation of a doctor, regardless of age. When undergoing a course of treatment, you need to stop taking medications, and if this is not possible, tell your doctor.
For each specific case, the optimal period for conducting the examination is determined. In addition, it is recommended:
- at least two days before the analysis, avoid physical and psychological stress;
- on the eve of the examination, avoid drinking alcohol, fatty and spicy foods;
- do not have sexual intercourse for at least three days before the examination;
- Do not smoke several hours before the procedure.
It is better to take a hormone test on an empty stomach in the morning.
What is the price
The study can be free if the patient has a referral and applies to a public medical institution.
In a private clinic the price will be about 600 rubles, it all depends on the type of analysis. Additionally, you will need to pay 200 rubles for collecting the test material.
When is it necessary to take prolactin?
Prolactin takes an active part in various processes of the human body. It helps regulate the water and salt entering the body, and affects reproductive function.
Both men and women can be prescribed this hormone, although the reasons for prescribing this test will be somewhat different in both cases. So, a doctor may prescribe prolactin for a woman in the following cases:
- Unreasonable secretion of milk from their mammary glands;
- Insufficient production of milk required during feeding;
- Failures or absence of menstruation for a long time;
- Post-term pregnancy;
- Suspicions of infertility;
- Suspicion of the development of a tumor in the pituitary gland;
- Gynecological bleeding with an unclear cause;
- Problems with conception;
- Decreased sexual activity;
- Weight gain.
Men have to donate blood to determine the concentration of prolactin in the case of:
- The appearance of problems with libido, decreased potency;
- Enlarged mammary glands;
- Testicular dysfunction;
- Decrease or complete absence of sperm;
- The appearance of discharge from the nipples;
- Suspicions of infertility;
- Sudden deterioration of vision.
The doctor may also prescribe blood testing for this hormone for men and women if they often suffer from headaches or chronic inflammation of the genitals. Regardless of the reason for prescribing this analysis, venous blood is used as the test material, with a volume of at least 2 ml. Unfortunately, there is always a risk of getting an erroneous result. But you can reduce the likelihood of receiving a false answer if you donate blood for prolactin correctly.
What tests should be taken for female hormones?
Testosterone
Testosterone is a steroidal androgenic hormone, its level is determined by:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- ovarian neoplasms;
- bleeding;
- problems with the course of pregnancy;
- inflammation of the uterus.
Estrogens
Hormones are produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands. This group includes estradiol, estriol and estrone. They are responsible for fertilization and pregnancy.
Progesterone
Responsible for implantation of the egg and bearing a child; its production occurs in the corpus luteum of the ovaries. Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- absence of menstruation;
- problems with fertilization;
- cycle disruption.
Prolactin
Responsible for the growth of breast tissue and the production of breast milk. Information about prolactin levels is necessary to determine ovulatory dysfunction.
Estradiol
Produced in the ovaries, adrenal cortex and placenta. Responsible for ovulation, conception and pregnancy.
Follicle stimulating (FSH)
The analysis is considered justified in case of problems with fertilization, bearing a child and cycle disruption.
Luteinizing (LH)
The main function of this hormone is the production of estrogens, progesterone and the formation of the corpus luteum. Indications for analysis are:
- cycle disruption;
- endometriosis;
- problems with conception;
- uterine bleeding;
- impossibility of pregnancy.

Growth hormone level
A normal level of somatotropic hormone is necessary for the full growth and development of all organs and systems. For children, hormone levels are extremely important during growth (normal bone development) and puberty.
Indications for conducting research on this hormone are carried out if the patient has delayed growth and sexual development, early sexual development, accelerated growth, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia, a tendency to hypoglycemic conditions, constant sweating, porphyria.
Increased production of pituitary growth hormone can be observed if the patient has:
- pituitary gigantism;
- acromegaly;
- dwarfism;
- chronic renal failure;
- hypoglycemia;
- decompensated forms of diabetes;
- alcoholism;
- post-traumatic conditions.
Also, hormone levels can increase when treated with insulin, corticotropin, glucagon, estrogens, norepinephrine, dopamine, propranolol, dopamine agonists, arginine, oral contraceptives, etc.
A decrease in the level of somatotropic hormone is observed with gopophyseal dwarfism, hypopituitarism, hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex, chronic sleep deficiency, postoperative interventions, hyperglycemia, treatment with progesterone, glucocorticosteroids, alpha-blockers, beta-adrenergic agonists, bromocriptine, corticosteroids, etc.
Normal sex hormones in women
Normal indicators vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Ratio of FSH and LH
Before puberty, the normal ratio between FSH and LH is 1:1. With age, this proportion changes and becomes 1:1.5. The indicated value is considered the norm before the onset of menopause.
Hormone progesterone
Normal indicator:
- 0.3-2.2 nmol/l - in the follicular phase;
- 0.5-9.4 nmol/l - during ovulation;
- 7.0-56.6 nmol/l - at the luteal stage;
- less than 0.6 nmol/l - during menopause.
During pregnancy, this indicator will depend on the trimester.
| Trimester | Norm |
| 1 | 8,9-468,4 |
| 2 | 71,5-303,1 |
| 3 | 88,7-771, 5 |
Estradiol
| Cycle phase | Norm, pg/ml |
| follicular | 57-227 |
| ovulatory | 127-476 |
| luteal | 77-227 |
At the onset of menopause, the normal value is 19.7-82 pg/ml, and during pregnancy it ranges from 210 to 26960 pg/ml.
Testosterone levels in women
Testosterone is divided into two types:
- Free - determines only free testosterone, depends on age (up to 20 years - 0.13-3.09 pg / ml, from 20 to 39 - 0.14-2.6 pg / ml, over 60 - 0.14-1 .8 pg/ml).
- Total - indicates the total amount of the hormone, regardless of whether it is associated with protein transport. The norm is 0.26-1.3 ng/ml.
Prolactin
The normal indicator is the level of the hormone, which ranges from 4 to 33 ng/ml. During pregnancy, the value may increase to 386 ng/ml, however, this process occurs gradually.
Hormone DHEA
Produced by the adrenal glands and in minimal quantities by the ovaries. Up to 35 years of age, the hormone level is considered normal from 2660 to 11200 nmol/l. During pregnancy, the value of the indicator increases, everything will depend on the trimester: in 1 - 3.12-12.48 nmol / l; in 2 - 1.7-7.0 nmol/l; in 3 - 0.86-3.6 nmol / l.
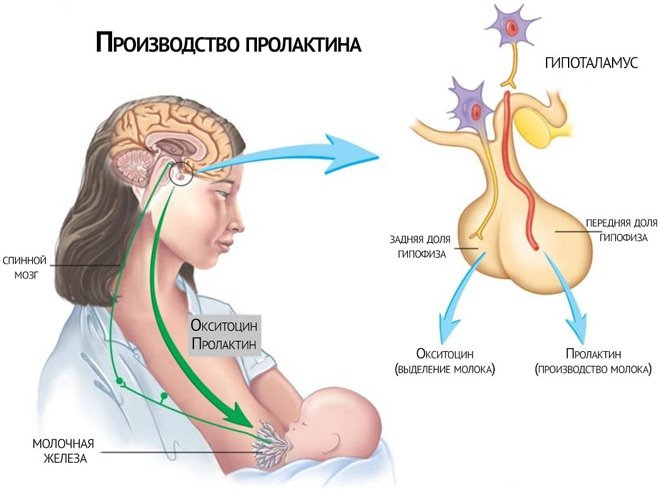
Prolactin
Prolactin is a pituitary hormone necessary for the maturation of the mammary gland. Suppresses the secretion of sex hormones. Normally, it increases during sleep, physical activity, and sexual intercourse.
Serum prolactin is higher in women than in men. During the menstrual cycle, prolactin levels are higher in the luteal phase than in the follicular phase. During pregnancy, starting from the 8th week, prolactin levels begin to increase, which reaches maximum numbers by the end of the third trimester. After childbirth, it decreases and then increases during lactation. Prolactin is subject to daily fluctuations, in the morning the deviation is 100%. Maximum levels of prolactin in men are observed at 5 a.m., in women - between 1 a.m. and 5 a.m. During sleep, the peak is between 5 and 7 a.m., decreasing after waking up and getting up.
An increase in prolactin is possible for the following reasons:
- pregnancy
- galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome
- pituitary tumor
- pathology of the hypothalamus
- hypothyroidism
- renal failure
A decrease in prolactin is usually caused by:
pituitary insufficiency
Decoding indicators
The results of the tests are quite important, because after assessing them, the doctor, together with other examinations, will be able to establish the cause, type of pathology and determine tactics to combat it.
Promotion
An increase in the amount of hormones indicates certain dysfunctions of the body. Estradiol can increase when:
- neoplasms of the genital organs;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- consuming excessive amounts of estrogen-based drugs.
An increase in progesterone may indicate:
- ovarian cyst;
- dysfunction of hormone excretion;
- overdose of progestin drugs.
The increase in FSH is inherent to:
- menopause;
- neoplasms of the ovary, pituitary gland;
- autoimmune diseases;
- infectious diseases.
Luteinizing hormone can increase when:
- hereditary pathologies;
- tumors;
- inflammation of the meninges;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- performing operations on the pelvic organs;
- injuries.
Estradiol
Estradiol is a female sex hormone. It is formed in the ovaries, its level increases in parallel with the maturation of the follicle (under the influence of FSH) and reaches a maximum before ovulation (the release of the egg). Both female and male sex hormones are produced in people of both sexes. Sex differences lie in the ratio of hormones. In men, estradiol is produced in the testicles and is maintained at a constant low level. In women - in the ovaries cyclically.
Sex hormones produced by the gonads are responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics, puberty, sexual and reproductive function. In addition, sex hormones are formed in small quantities in the adrenal cortex: both male and female, and this part is responsible for maintaining gender characteristics during those periods of life when the sex glands are still or no longer working: in childhood and old age.
Targets for the action of sex hormones are available in all systems of the body: nervous, excretory, bone, muscle, cardiovascular, adipose tissue, skin, etc. Thus. sex hormones are involved in the regulation of any activity of the human body. Estradiol, like all estrogens (female sex hormones), stimulates memory processes, improves mood, sleep, strengthens bone tissue, protects against atherosclerosis, improves the functioning of the sebaceous glands and the condition of the skin and hair.
In women of childbearing age, the level of estradiol in blood serum and plasma depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. The highest levels of estradiol are observed in the late follicular phase, especially in the middle of the cycle, and in the luteal phase. During pregnancy, the concentration of estradiol in serum and plasma increases at the time of birth, and after birth it returns to normal on the 4th day. With age, women experience a decrease in estradiol concentration. In postmenopause, a decrease in estradiol concentrations to the level observed in men was noted. Daily fluctuations in the concentration of estradiol in the serum correspond to the daily concentrations of LH: the maximum occurs in the period from 15 to 18 hours when immunoreactive LH decreases at this time, and the minimum occurs between 24 and 2 hours.
A screening study of estradiol levels is carried out on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle.
Reasons for increased estradiol levels:
- estrogen-producing tumors
- hyperthyroidism
- cirrhosis of the liver
- taking hormonal medications (oral contraceptives)
- pregnancy
Reasons for low estradiol levels:
insufficiency of gonadal function
TSH hormone value
The formation of thyroid-stimulating hormone is carried out by the pituitary gland. This is a gland that is located in the brain. TSH affects the thyroid gland and causes it to produce the hormones T4 and T3.
With the help of these hormones, the full functionality of systems such as:
- Sexual
- Cardiovascular
- Gastrointestinal tract
With the normal functioning of these hormones, a complete metabolism in the human body is ensured. Also, these hormones are involved in various mental processes.
If the production of these hormones decreases, this leads to an increase in the concentration of thyrotropin. According to this scheme, the hormones T3 and T4 and TSH interconnectedly regulate each other.
Thanks to the results obtained, endocrinologists and therapists have the opportunity to learn about the patient’s hormonal background and identify certain diseases.
Appointment for analysis
The analysis can be prescribed to patients in various cases. Most often, a doctor’s prescription is made for the development of diseases such as:
- Depression
- Decreased libido
- Impotence
- Alopecia, which is characterized by hair loss for no apparent reason
- Myopathies, etc.
Very often, a TSH test is prescribed for a variety of diseases, since it can be used to assess the condition of the thyroid gland.
Indications for the procedure are cardiac arrhythmia, female infertility, enlarged thyroid gland, etc.
In some cases, patients' body temperature drops below 35 degrees and lasts for several days. To establish the causes of the pathology, the patient is prescribed a TSH test.
The analysis can be prescribed not only to adult patients, but also to young children. It is prescribed to newborn children if thyroid dysfunction is diagnosed.
There is often a need for it if children are diagnosed with delayed sexual and mental development. There are many diseases for which patients are prescribed a thyroid-stimulating hormone test.
In most cases, they are associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Preparation and procedure
Proper preparation means reliable research results
To ensure the reliability of the results, the patient must correctly go through the preparatory stage:
- First of all, he must stop smoking.
- A person is strictly prohibited from drinking alcohol before the procedure.
- Even if you are an athlete, you need to avoid excessive physical activity.
- In order to ensure correct results of the thyroid-stimulating hormone test, you need to stop eating fatty and spicy foods a few days before.
- The patient should try not to be exposed to nervous shocks and stressful situations. This is explained by the fact that a person’s psycho-emotional state also affects the results.
- If patients are taking hormonal medications or medications that suppress hormones, they must be discontinued 14 days before the test. Stopping medications should only be done if advised by the attending physician. Otherwise, medication should be continued.
- Before taking the test, the patient must take vitamin complexes and medications that contain iodine as carefully as possible. This is explained by the influence of iodine on the performance of the thyroid gland, which leads to distortion of the analysis results.
- Before the test itself, the patient is strictly prohibited from eating breakfast. It is best to drink still water and go for analysis. In some cases, you can have breakfast with light foods.
- After eating, the test should be taken no earlier than 3 hours later.
Today you can take a blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormone both in a budget clinic and in a paid hospital. The maximum concentration of TSH is observed in the morning, so it is necessary to take a blood test during this period.
Proper preparation for a TSH test will not only ensure the reliability of the results, but will also help the doctor make the correct diagnosis, which is very important for absolutely all patients