During critical days, it is recommended to refrain from planned surgical interventions, as well as from undergoing routine tests.
A blood test involves a general analysis, a biochemical test, a hemostasiogram (or a coagulogram that determines blood clotting parameters). During menstruation, some deviations are possible, which in certain cases can be interpreted as diseases or a tendency to them.
The influence of changes in the body during menstruation:
- Normally, during menstruation, the body spends from 80 to 150 ml of blood. However, these values can vary significantly. Due to heavy discharge during menstruation, the level of hemoglobin can decrease significantly, the ESR and the level of leukocytes in the blood increase. This is due to blood loss. Even in healthy women, values can vary, which confuses the doctor.
- The volume of fluid in the body decreases. Therefore, during menstruation, a woman may experience slight dehydration if the drinking regime is not followed. This will lead to changes in the general blood test parameters, and to a lesser extent, coagulograms and biochemistry.
- Coagulability decreases. For normal rejection of the functional layer of the endometrium of the uterine cavity, the blood becomes less viscous, which is noticeable when examining in detail tests for fibrinogen, clotting time, and D-dimers.

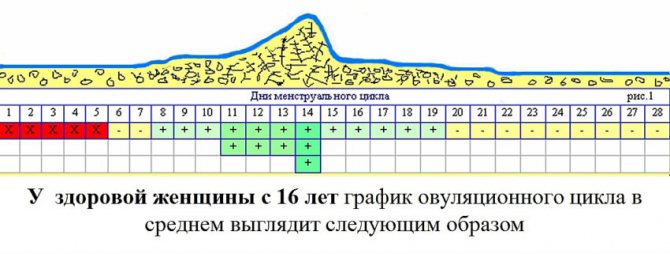
The most optimal time to take a blood test is the middle of the cycle and the second phase - from days 10-12 to 28. This applies to all standard types of research.
On any day, blood is taken for subsequent detection:
- HIV, hepatitis, syphilis;
- for the study of sexually transmitted infections for ELISA;
- blood for the TORCH complex when planning pregnancy;
- for thyroid hormones, prolactin, testosterone, DHEA, cortisol and others.
Tests for sex hormones are taken on the following days:
- on days 5-7 - estrogens, FSH, LH;
- on days 21-23 - progesterone.
If tests need to be taken as planned, then it is better to choose the most suitable days. Otherwise, they will have to be retaken.
The following changes in tests are possible if taken during critical days:
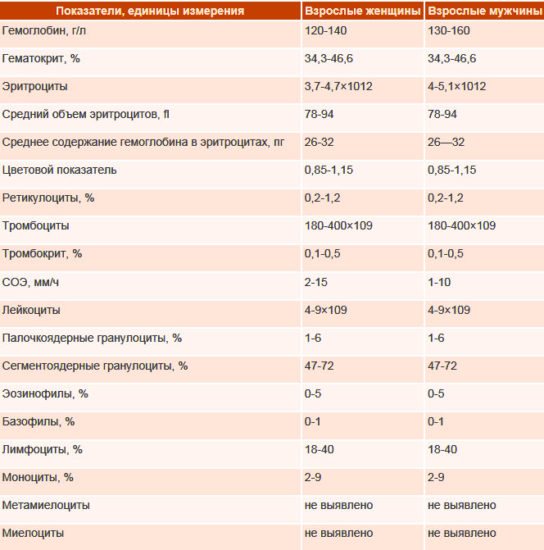
- general blood test: decreased hemoglobin level, increased ESR, leukocytes, decreased platelet level;
- coagulogram: decreased coagulation ability;
- biochemical study: decreased level of total protein.
However, in some cases the changes will not be noticeable, the indicators will fit into the norms.
A theoretical urine test can be carried out without paying attention to the day of the cycle. However, if the test is taken during menstruation, the woman must ensure that the vaginal discharge does not fall into the collection jar. For this purpose, it is necessary to carefully close the entrance to the vagina with a cotton pad, or better yet, insert a tampon, and then carry out hygienic measures.
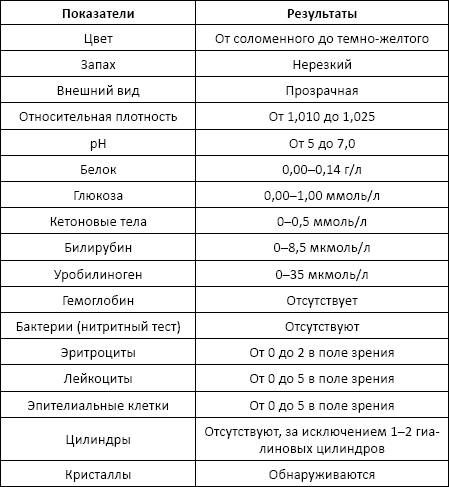
If you do not take care of this, then the elements of the discharge along with the blood will end up in the urine, which can cause false results:
- the appearance of fresh red blood cells in the urine from menstrual flow, usually a sign of injury to the urinary tract;
- there is a change in the color of urine when blood gets in, this also happens with diseases of the liver, kidneys, and some infections;
- leukocytes from vaginal discharge, normally this indicates inflammation in the urinary system.
A urine test taken during menstruation without following the basic rules will lead to the need for a repeat test, at a minimum, and in some cases, to an incorrect diagnosis.
Whether or not an ultrasound examination can be performed depends on which organ will be examined. During critical days, if this does not cause discomfort to the woman, you can undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, lymph nodes throughout the body, and blood vessels anywhere. For ultrasound examination there are only some restrictions on the days of the cycle if the genital organs are examined.
In case of a preventive examination, ultrasound of the uterus and appendages should be performed on the 7-10th day of the cycle. It is assumed that at this time there is still a small spotting discharge from the genital tract. However, these days are the most informative for searching for pathology of the uterine cavity and cysts on the ovaries. For endometriosis, it is better to do an ultrasound on the eve of menstruation, on the 25-26th day.
In emergency cases, an ultrasound of the genital organs is performed on any day of the cycle to help establish a diagnosis and, if necessary, perform monitoring.
There is no point in visiting a gynecologist during menstruation , unless, of course, the reason is bleeding or suspicion of some serious pathology. An inspection can be carried out, but its information content is somewhat reduced.

Taking any smears from the vagina or cervix, even in the presence of only spotting and very slight discharge, is not informative . In any case, they will show signs of inflammation, and if the material was collected for oncocytology, malignant cells can be missed due to the abundance of leukocytes and red blood cells in the specimen.
PCR tests for sexually transmitted infections can be carried out only after the complete cessation of discharge from the genital tract, otherwise the results may be incorrect.
Read more in our article about tests during menstruation.
Changes in blood composition during menstruation
During menstruation (menarche), the upper layer of the endometrium of the uterus is shed. This leads to bleeding from the woman's genital tract. The following changes occur in the peripheral blood:
- an increase in ESR, which is a marker of inflammation; this is considered normal during menstruation;
- reducing the number of platelets and clotting factors, this is necessary to reduce the viscosity of biological fluid and prevent the formation of clots;
- decrease in the number of leukocytes;
- decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells due to blood loss;
- changes in hormone ratios;
- decreased plasma levels.
Important! All changes occur within normal limits; in a healthy woman they do not affect or slightly change the state of health. Losses are quickly replenished after menstruation ends.
Blood readings are normal during menstruation
The following changes in tests are possible if taken during critical days:
- general blood test: decreased hemoglobin level, increased ESR, leukocytes, decreased platelet level;
- coagulogram: decreased coagulation ability;
- biochemical study: decreased level of total protein.
However, in some cases the changes will not be noticeable and the indicators will fit into the required standards.
Recommendations for donating blood
To undergo laboratory tests, you must follow the recommendations of your doctors. They will help to obtain reliable data in one study.
- You should not eat food 12 hours before testing. During the day - drink alcohol. 2-3 hours before - smoking.
- Laboratory tests are carried out only in the morning, with the exception of hormonal studies.
- Stop taking medications 5 days before donating biological fluid. If this causes a sharp deterioration in health, the drug is not discontinued, but the doctor is warned about it.
- It is not recommended for women to take tests on menstruation days, as the data will not be reliable.
For donation, recommendations are supplemented. Biological fluid cannot be given to persons under the age of majority, pregnant women, lactating women, infectious patients, people with addiction (alcohol, drugs).
Is it possible to donate blood during menstruation?
During menarche, changes in peripheral blood and hormonal balance occur. Some women experience severe abdominal pain, during which they use painkillers, the presence of which is contraindicated during donation, but is allowed for research of biological fluid.
When taking tests that are not recommended during menstruation, false positive results may occur:
- the presence of inflammation (increased ESR);
- hypoglycemia (low blood sugar);
- insufficiency of the immune system (decreased leukocytes);
- anemia (decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin);
- decreased level of clotting, which occurs with infections, blood diseases (hemophilia).
A doctor may miss the following diseases due to false negative data:
- increased coagulability, which indicates a tendency to form clots and the risk of thrombosis and heart attacks;
- oncological diseases;
- allergies to foods, medications, herbs;
- liver pathologies (decreased bilirubin).
Why you shouldn't donate blood during your period
There are laboratory tests that will show erroneous results if done during your period. They are presented in the table.
| Analysis | Erroneous data |
| General clinical blood test (CBC) | Increase in ESR; decrease in platelets, leukocytes, red blood cells and hemoglobin |
| Biochemistry | Minor changes in the amount of bilirubin, enzymes, protein |
| Tumor markers | False positive or negative result due to hormone surge |
| Clotting factors | The total number of factors decreases sharply. The amount of D-dimer (an indicator of the risk of thrombosis) is greatly overestimated |
| Glucose | Reducing sugar levels |
| Allergy tests | False negative results due to decreased sensitivity of the body to irritants |
| Immunogram | Decrease in the number of lymphocytes, leukocytes, immunoglobulins |
Important! Menstruation is a contraindication for blood donation. The procedure leads to a deterioration in health.
After the procedure, a woman will experience:
- dizziness due to decreased blood pressure and blood sugar;
- nausea, which can turn into vomiting, which will further reduce the amount of fluid in the body;
- sudden loss of strength;
- dehydration due to lack of plasma;
- decreased body temperature, chills.
During menarche, a small amount of intravascular fluid is lost. If blood loss increases, it affects the body. An additional contraindication for donation during menstruation is the use of medications by a woman (painkillers, hormonal drugs in case of cycle failure). There are exceptions in the form of emergency donation, which will help save a person’s life.
Permitted blood tests
There are laboratory tests where you can donate blood during your period. The presence of hormones is used to judge a woman’s ability to conceive, the health of her reproductive system, and the presence of ovulation.
- Luteinizing hormone stimulates the formation of estrogen, which causes ovulation. The study is carried out in the middle of the cycle.
- Prolactin is responsible for the occurrence of lactation. The analysis is carried out at different times of the cycle at the same time of day.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone - is found in different concentrations depending on the phase of the cycle. The maximum peak occurs during ovulation. Examine several times during the month.
- Estradiol - determines the reproductive function of a woman. If it is disturbed, additional uterine bleeding appears. The analysis is carried out several times per cycle.
In addition to studying hormones, other tests are allowed that will not give false results:
- blood type, Rh factor (these data are constant throughout life);
- PCR - determines the exact number of pathogenic microorganisms, their variety (their number does not depend on the formed elements and plasma);
- serology - testing that determines the presence of viruses in biological fluid;
- analysis for HIV, AIDS, syphilis, tuberculosis.
Conducting an ultrasound during menstruation: when it is possible and not
Whether or not an ultrasound examination can be performed depends on which organ will be examined. During critical days, if this does not cause discomfort to the woman, you can undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, lymph nodes throughout the body, and blood vessels anywhere. For ultrasound examination there are only some restrictions on the days of the cycle if the genital organs are examined.
In case of a preventive examination, ultrasound of the uterus and appendages should be performed on the 7-10th day of the cycle. It is assumed that at this time there is still a small spotting discharge from the genital tract. However, these days are the most informative for searching for pathology of the uterine cavity and cysts on the ovaries.
If the doctor is trying to establish or refute the diagnosis of endometriosis, then it is better to do an ultrasound on the eve of menstruation, on the 25-26th day. At this time, the lesions are largest in size and have clearer outlines.
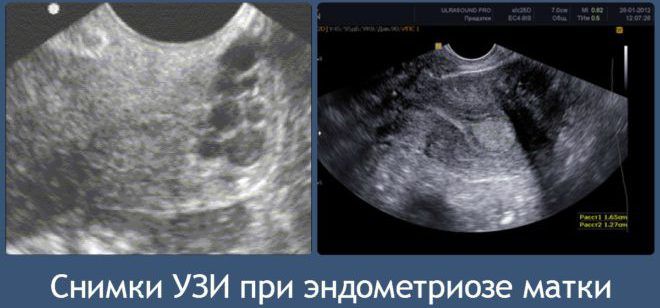
In emergency cases, an ultrasound of the genital organs is performed on any day of the cycle to help establish a diagnosis, if necessary, to carry out monitoring according to generally accepted recommendations.
How long after menstruation can you donate blood?
For each laboratory test, there are restrictions for women to donate blood. In order for the studies to show reliable results and not have to repeat the testing, you need to know about the recommended time of the cycle phase for taking the tests presented in the table.
| Analysis | Cycle phase |
| UAC | Middle (12-16 days) |
| Biochemistry | From 10 to 20 days |
| Clotting factors | Middle (12-16 days) |
| Glucose | 3 days before menstruation and 7 days after it |
| Tumor markers | 5 days before menstruation and 7 days after it |
| Allergy tests | 5 days before menstruation and 7 days after it |
| Immunogram | 5 days before menstruation and 7 days after it |
Donation is carried out 5 days before menarche and 7 days after their end. These days, the body is not preparing for the endometrium, the amount of hormones is stable and does not affect the body. After the end of menstruation (about 7 days from its start), the intravascular fluid is restored, the number of formed elements stabilizes. The time period before menarche (5 days) is indicated so that the body can prepare for endometrial rejection without unnecessary stress on the body.
Donation before and after the menstrual cycle

Using a menstrual calendar makes things easier
If possible, it is worth moving the expected date of blood donation to a safer period. According to doctors, 4-5 days after the end of the critical days, the body completely replenishes lost water, salts and red blood cells. However, this indicator is individual for each girl. To make sure that the body is ready for the procedure, doctors prescribe a number of special tests.
Attention! Keeping a women's calendar will make it easy to calculate the most favorable days for donation!
Doctors advise donating at least 5-6 days before your period. Donating blood is a stressful situation for the body; to compensate for losses, it is necessary to mobilize all the regenerative mechanisms of the body. You should not be exposed to it during the period when the body is busy preparing for critical days.
Consequences of donating during menstruation
In addition to the disruption to a woman's physical condition when donating during menarche, there are additional health risks. The following negative processes may occur:
- menstrual irregularities (failure, delay, premature onset);
- changes in hormone levels due to stress on the body;
- scarcity of biological fluid secretions during menstruation due to a decrease in the amount of plasma;
- reducing the body's resistance to pathogenic microorganisms.
Consequences of donation during menstruation

Donating blood during menstruation can lead to consequences
What can a woman who decides to donate blood during her period expect? Here are some of the most common consequences:
- Failure of the menstrual cycle. For many girls, the procedure can be a great emotional shock. Any stress adversely affects the regularity of the female cycle;
- The amount of menstrual flow decreases significantly. In this way, the body tries to replenish blood loss after the procedure;
- Over the next few days, the woman experiences weakness and pain, often leading to fainting;
If possible, you should avoid donating blood during menstruation. Otherwise, the girl risks spending the next few days in bed, restoring her physical condition.
Is it possible to donate plasma during menstruation?
To donate plasma, whole blood is taken from the patient. It is filtered in a medical device, and the formed elements (platelets and red blood cells + saline) are returned back inside the vessels located on the other arm. Up to 12 procedures per year are allowed. Plasma is restored faster than formed elements. Its amount depends on the fluid consumed.
Regardless of the fact that the amount of plasma quickly returns to normal, doctors do not advise donating it during menarche due to the following risks:
- a sharp decrease in the amount of plasma, leading to blockage of blood vessels with a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- deterioration of the patient's well-being.
The timing for donating plasma is 3 days before menarche and 10 days after, when the amount of fluid returns to normal. It is recommended to drink plenty of water to help this process go faster.