Unfortunately, breastfeeding does not always go without problems. Often, a young mother is faced with the fact that her nipples hurt during breastfeeding. In this situation, it can be extremely difficult and sometimes unsafe to feed the baby. It is important to identify the cause of such an unpleasant symptom in the early stages and begin to eliminate it.
Nipple sensitivity during lactation can cause discomfort to a nursing woman.
Causes
During pregnancy and especially after childbirth, increased synthesis of prolactin occurs. It is needed to produce breast milk. In this case, the mammary glands increase in size, the ducts become overfilled with breast milk.
These changes are the cause of physiological chest pain during breastfeeding. They are due to adaptation to the lactation process, but prolonged pain cannot be ignored. Only a doctor can distinguish physiological changes from pathology.
You need to see a doctor if:
- intense pain is present for a long time;
- the woman’s general condition has worsened;
- a mass formation has appeared in the chest;
- there is a rash, peeling, irritation on the skin of the breast or bleeding cracks on the nipples.
If you have the listed symptoms, you need to undergo an examination by a mammologist to determine the cause of the pain and take adequate measures.
Incorrect grip
Early breastfeeding is important, that is, a newborn baby should be fed within an hour after birth. If the baby cries or is worried, he needs to be fed. You can’t take his breasts away; after he’s eaten, he’ll let go of it himself. These simple rules will ensure sufficient milk production, satiety of the baby, and the desired duration of lactation.
To avoid pain during breastfeeding, a young mother should teach her baby to latch onto the breast correctly. To do this, a woman, preparing for feeding, runs her nipple along the baby's lower lip; reflexively, he opens his mouth wide. The mother pulls the baby's head to the breast so that he captures not only the nipple, but also the nipple area. In this case, the nipple is at the level of the root of the tongue, so it is not injured by the gums.

Otherwise, you need to stop feeding and re-attach the baby to the breast, helping him to latch onto the breast correctly. Complications of improper latch include cracks, abrasions of the nipples, insufficient milk consumption for saturation, increased gas production in the baby.
First aid. How to eliminate unpleasant sensations
Let's talk about what a woman can do on her own to ease the discomfort:
- Put the baby to the breast as often as possible (1-2 times every 2 hours). Then the baby's sucking reflex will be weaker, and the discomfort will decrease accordingly.
- Before putting your baby to your breast, massage the nipples yourself with your fingers or roll a piece of ice over them.
- Avoid dampness, ventilate the breast, especially before feeding.
- After feeding, apply ice or treat the mammary gland with lanolin cream.
- Use special medical breast pads.
These methods are only valid for discomfort. If cracks in the nipples have already appeared, then it is necessary to begin treatment.
Tides
Hot flashes are a physiological phenomenon that does not require treatment. This name is associated with the sensations of a woman: the breast is filled from the inside, the nipple hardens and swells. The temperature may rise slightly. Read more about other reasons for fever after childbirth →
Often, a nursing woman notices painful sensations of a bursting nature in the chest area. They indicate the intense secretion of milk by glandular tissue, its accumulation in the ducts and are a signal for feeding the baby. Especially often, lactation is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, tingling, burning in primiparous women at the very beginning of the feeding procedure.
Milk letdowns can be triggered by drinking a hot drink, eating a large meal, pumping, or feeding the baby for more than 15-20 minutes. To avoid breast overfilling with milk, you need to feed the baby more often.
Lactostasis
This phenomenon is associated with stagnation of produced milk, a violation of its secretion from the milk ducts. With this pathology, the milk ducts are blocked by condensed milk.
The causes of lactostasis can be:
- incorrect position of the child or mother during feeding;
- mechanical damage and compression of a woman’s breast (injuries, tight underwear);
- violations of pumping technique and improper nipple capture;
- long breaks between breastfeeding;
- short feeding time;
- holding the breast while sucking;
- hypothermia of the mammary glands;
- hyperlactation;
- insufficient fluid intake.
A clearly defined, painful, compacted area appears in the mammary gland. The skin in this area becomes hot to the touch, tense, and hyperemic. Your temperature may rise.

What to do? Regular light breast massage should be performed during and before feeding. Take a position that is comfortable for feeding, changing the position of the baby each time. It is important to practice frequent application specifically to the sore breast to completely empty the milk ducts. Apply compresses made of cloth moistened with cool water to the area of compaction.
If, after following these simple rules, the symptoms do not go away within two days, you should seek medical help. After the doctor's permission, you can carefully rub absorbable ointments into the skin over the lump or take other therapeutic measures. Possible complication if left untreated: non-infectious mastitis.
Insufficient milk supply
Let's first determine by what criteria we can say that the baby really does not have enough milk. Here are reliable signs of milk deficiency:
- infrequent urination of the child: less than 6-8 times per day;
- poor weight gain (less than 450-500 grams per month).
That's all! Neither frequent and prolonged feedings, nor the child's frequent crying, nor the child's refusal to suckle at the breast, nor the volume of milk “eaten” by the child at one time (control weighing), nor soft breasts are true signs of a lack of milk. If you find out for yourself that there is really little milk, then you need to find the real reason for the deficiency. And remember, there are many ways to improve lactation. Check yourself whether you are doing everything according to the rules of natural feeding. Because, most often, hypogalactia is caused precisely by factors associated with violation of these rules:
- Rare feedings.
- Incorrect attachment of the baby to the breast.
- No night feedings.
- Using pacifiers or pacifiers.
- Supplementation with water or additional feeding.
- Short feedings.
- Poor breast emptying with lactostasis.
- Incorrect introduction of complementary foods.
In these cases, there is only one piece of advice - correct all the mistakes, and the milk will not take long to arrive. It is possible that you will need professional help. In particular, if the amount of supplementary feeding is already quite large. But in any case, be patient and you will succeed! Some people advise the mother to eat and drink more, get more rest, or take medication to increase milk production. Understand that you can sleep around the clock and drink liters of lactation teas. But if you do not put your baby to your breast as expected, milk will not increase.
Remember, the main stimulator of lactation is the child.
Carry your baby in your arms more often, provide skin-to-skin contact, latch on to the breast more often and let the baby suckle as much as he wants, feed at night, take every opportunity for sleep and rest, drink so as not to feel thirsty and eat enough. Let someone else go to the store for groceries, and you can rest. After all, only you can give your baby the most valuable nutrition for him - breast milk. Sometimes, at the stage of the maternity hospital, delayed lactation is observed, due to severe stress, traumatic birth, fatigue and the mother’s lack of self-confidence. In such cases, the support of loved ones and medical personnel is very necessary. Taking certain medications (such as diuretics) can lead to milk deficiency. Consult your doctor and find an adequate replacement for this drug. Cases when a child really needs supplemental feeding are very rare. The volume and type of supplementary feeding must be selected individually, under the supervision of a doctor. But in any case, try to put your baby to your breast as often as possible, give milk replacer from a cup or spoon, and continue breastfeeding for as long as possible. After 6 months, with the gradual introduction of complementary foods, you will eliminate the milk replacer. The baby will eat purees, cereals and continue to breastfeed.
Mastitis
Pain during breastfeeding can be caused by an inflammatory process. It is a consequence of lactostasis or infection due to non-healing cracked nipples, breast injuries, exacerbations of chronic infections. Severe pain during breastfeeding always indicates pathology.
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Poor general condition (high temperature, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite).
- The pain is intense, often pulsating.
- Swelling, redness, hardening of the breast.
- Local increase in temperature (hot chest skin).
If such manifestations occur, the mother needs to take all measures to combat lactostasis. Particularly important is frequent breastfeeding or expressing milk using a breast pump.
It is necessary to monitor the nature of the discharge from the nipple. If, instead of milk, a discharge resembling pus appears, feeding should be stopped and immediately consult a specialist. The appearance of pus indicates the formation of an abscess, which can threaten the life of the mother.
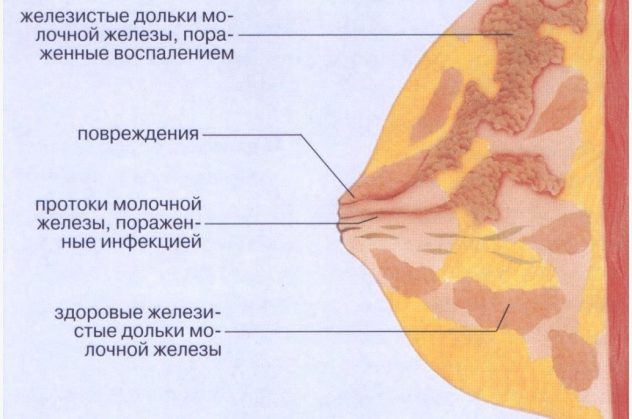
In the early stages of mastitis, the same treatment tactics are used as for lactostasis. In advanced cases, antibiotics are prescribed; in case of complications, surgery is performed.
Problems with breastfeeding
It often happens that a woman has a desire to breastfeed her baby, and she conscientiously listened to lectures at prenatal training courses on feeding a child, and her relatives are all in with both hands, and life makes its own adjustments. In this article we will focus on the most common problems that arise during breastfeeding, which can occur in any woman. But we will not touch upon complex cases that require professional pediatric care. So, the following problems may arise in the maternity hospital.
Cracked nipples
Mild redness, swelling and pain in the nipples are acceptable when breastfeeding immediately after childbirth. Gradually these unpleasant phenomena disappear. Reasons: improper capture and expression of milk, thinning, microtrauma of the skin of the breast and nipples due to frequent washing. Read more about proper breast care and hygiene for a nursing mother →
To reduce pain in the first days after childbirth, you can express about 20 ml of milk before starting feeding. The nipple will then become softer. You should not suddenly remove the nipple from the baby’s mouth, as this can cause injury. When the baby is full, he will release the breast on his own.
Cracked nipples are a pathology that is dangerous due to its complications. If they are detected, you should consult a doctor.
Prevention:
- After feeding, it is advisable not to put on a bra immediately;
- avoid the use of rough underwear;
- teach the baby to suck properly (with capture of the areola);
- Treat the slightest abrasions in the nipple area immediately after feeding with sea buckthorn oil.
Possible complications of cracked nipples are mastitis, the development of septic processes (penetration of Staphylococcus aureus, fungal infection).
How to adapt nipples to feeding
The only reason that nipples hurt when feeding is that they have not yet adapted to such increased attention from the baby. Unpleasant sensations most often occur in the first 10-15 seconds, after which all the negativity goes away and mommy can calmly enjoy feeding.
The next day after childbirth, pain may also occur, which continues for about another month. If after this time the baby is accustomed to latching onto the breast correctly, the pain will stop.
The most common reason for adaptation is that the baby licks the thin top layer of epithelium during feeding, as a result of which the nerve endings are exposed and the woman experiences pain.
Over time, the mother's breasts adapt to their new role, and the nipples can withstand long feedings due to the fact that the skin becomes rougher.
Thrush
Pain in the mammary gland during breastfeeding can be a symptom of candidiasis (thrush). The following signs are characteristic: nipple cracks do not heal for a long time, the skin around it is dry, reddened, painful, sometimes covered with a whitish coating.
The disease is associated with fungal infection of the milk ducts. Causes of fungal infection: decreased immunity, hormonal imbalances, violation of hygiene standards.
This phenomenon is dangerous for the child, he can become infected from a sick mother, so a nursing woman should urgently consult a doctor. He will prescribe antifungal ointments to treat the affected skin areas.
For preventive purposes, the baby is prescribed an antiseptic solution to treat the mouth after contact with the breast. This is especially necessary when white plaque appears on the mucous membranes of the baby’s mouth. At the same time, the general condition suffers - the child is worried and refuses to breastfeed. The disease cannot be started, otherwise the prescription of fungicidal drugs for oral administration will be required.
Vasospasm
Severe vasospasm of the mammary glands is observed in women suffering from Raynaud's syndrome and other autoimmune diseases. Clinical signs: burning pain after feeding, white color and coldness of the nipple after finishing feeding.
Sometimes the disease may first appear after childbirth due to a decrease in immune defense. A woman should consult a doctor for advice. With his approval, you can perform a light breast massage.
It is necessary to exclude cooling of the breast and sudden changes in temperature (after feeding, wrap the breast with a warm cloth to prevent overheating). Do not drink strong tea, coffee, or alcohol. Read more about proper nutrition for a nursing mother →
Adaptation of the mammary glands
This important process takes about three months from the moment the baby is born.
During this period, a woman may be bothered by:
- constant leakage of milk not associated with feedings;
- spontaneous leakage of milk from the nipple of the other breast when feeding the baby;
- increased discomfort in the chest and nipples when the interval between feedings is more than 4 hours;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen with infrequent breastfeeding.
After three months of breastfeeding, the young mother notices that many unpleasant moments associated with feeding have disappeared. There is no pain in the nipples, a sufficient amount of milk is produced, and feeding the baby does not cause discomfort.
Unpleasant consequences
All these reasons can lead to breast damage and problems such as:
- abraded skin, scratches or blisters. The affected area first turns red, and if the problem is not corrected, an abrasion soon appears. Such symptoms often occur as a result of improper latching on the breast, if the child rubs the skin of the breast with his mouth, especially its lower part. Bubbles can occur if the mother deliberately removes the baby from the mammary gland because she feels pain and discomfort. The baby, in turn, not receiving enough milk, holds the nipple more tightly, damaging it. Therefore, if a nursing mother cannot tolerate chest pain during feeding, you can carefully insert your little finger into the corner of the baby’s mouth, and use the resulting vacuum to remove the breast painlessly.
- Cracks. This is a secondary phenomenon that is observed when abrasions become more advanced. Cracks are dangerous because liquid or blood can be released from the wound, which can easily cause infection.
- Vascular spasms. This manifests itself in a change in the color of the nipple (it turns white) and in the feeling of sharp pain in the mother. The spasm does not last long, after which the situation returns to normal, and the pain gradually goes away.
Painful sensations in the nipples should not always be blamed on the child. The reason may be hidden from the outside - this is poor nutrition, poor-quality linen, as well as mechanical damage. To improve the mother's condition and relieve pain, after feeding, you can make a warm compress from a towel, heating pad or sock with salt. At the same time, it is important to monitor your diet: remove all fatty foods, smoked foods, caffeine, etc.
How to relieve pain?
How to get rid of pain during breastfeeding? This question worries many women who are faced with this problem.
Simple manipulations will help:
- frequent breastfeeding;
- teaching the baby how to properly latch on to the nipple;
- expressing a small amount of milk before feeding if there is severe swelling of the breast and nipple;
- expressing milk between feedings using a breast pump.
To get rid of pain due to stagnation of milk, you need to improve its outflow by increasing physical activity. Bend over and shake your chest - this simple manipulation sometimes works well.
The following steps must not be taken:
- take medications to reduce breast milk production;
- refuse breastfeeding due to pain;
- Express milk frequently and completely;
- limit fluid intake;
- use thermal procedures, including alcohol compresses, on the mammary gland area;
- wear tight clothing;
- take incorrect positions during sleep and during feeding.
The question of how to relieve pain during breastfeeding should be decided with the participation of a doctor. The woman’s task is not to endure discomfort, but to contact a mammologist in a timely manner to prescribe the necessary examinations and select methods to overcome the pain syndrome. This will prevent dangerous complications and preserve the health of mother and baby.
Author: Olga Shchepina, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Therapy for the inflammatory process in the nipples
- Pay attention to the correct application, and in no case allow injury to the nipples.
- If possible, put the baby on the sore breast as often as possible so that he completely empties it.
- Express the remaining milk after feeding, and although this process is very painful, it will help eliminate congestion.
- Apply cool lotions to the area of inflammation, but only when the baby does not need to be fed.
- Warming compresses and other warming procedures are prohibited, because heat is a provoking factor for the increased proliferation of pathogens.
- If the inflammation is excessively strong and long-lasting, then the doctor will prescribe modern antibiotics.
- Inflammation of the nipples can be successfully treated with lotions with vegetable oil, as well as Bepanten , Purelan and Solcoseryl , which are used strictly according to the instructions after each feeding.
If an abscess has formed as a result of inflammation of the nipples, it is removed surgically. Milk from the affected breast must be expressed, but it cannot be given to the baby; feeding can be resumed only when the discharge of pus has completely stopped (See “How to properly express breast milk”).