The leading activity of our clinic is the treatment and diagnosis of diseases of the immune system. We will be happy to help you restore the proper functioning of the immune system, conduct and decipher an immunogram. You can take an immune status test (immunogram) in our clinic 7 days a week. At your request, we will offer you the help of an immunologist.
- What is an immunogram
- Why do you need an immunogram?
- Main indications for immune examination
- Screening for infections
The main function of the human immune system is to identify, neutralize and remove genetically foreign substances from the body. These can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, various toxins, etc. If one of the links of the immune system weakens or, on the contrary, becomes overly activated, a disease is possible. This could be an infection (for example, herpes virus, thrush, etc.), an allergy, a malignant tumor (a healthy immune system destroys emerging tumor cells every day), an autoimmune disease (an attack of the immune system against healthy tissues of the body). Different immune cells and molecules do different jobs. There are no medications “for the entire immune system,” so before starting treatment, you need to determine the cause of the immune system disorder (do an immunogram). An immunogram is a series of tests that help determine where exactly, in which of the immune processes the breakdown occurred. The immunogram indicators usually show that some processes in the immune system are proceeding normally, while others are suppressed or, conversely, over-activated. Immunological treatment must hit the target, work exactly where there are disorders. The main task of any immune treatment is to help weakened immune processes recover, not to interfere with properly functioning processes, and to “cool” overly activated ones. Simply donating blood for an immunogram is not enough: you need to correlate the immunogram indicators with the general condition of the body, current diseases, quality of sleep and mental well-being.
What is an immunogram?
An immunogram is a comprehensive study of the main indicators of the human immune system. Typically, the main material for studying the immune status is venous blood, but saliva, cerebrospinal fluid and scrapings from the nasopharynx can be used for research.
What does an immunogram show? Main parameters:
- State of cellular immunity. Markers of immunocompetent cells, the number of different types of immune cells and their percentage are determined. Types of immune cells are like branches of the military: each type of cell has its own job.
- State of humoral immunity. The level of immunoglobulins IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE is examined. Immunoglobulins are antibodies that can bind foreign agents. Circulating immune complexes (CIC) are studied.
- Interferon status. Interferons or interferon status are examined. Interferons are signaling molecules that transmit excitatory or inhibitory signals from cell to cell. Interferons also have a direct destructive effect on viruses and tumor cells. Interferon status will help assess the content of alpha and gamma interferons in the blood, the ability of immune system cells to produce interferons.
- Complement system – complement components C3 and C4. Complement is an element of innate immunity, i.e. a complex of proteins designed to protect the body from foreign agents. The complement system works regardless of the presence/absence of immunological memory for specific microbes: it recognizes microbes by their common characteristics.
- Function of phagocytosis. This is the ability of immune cells to capture foreign organisms. The phagocytic function of neutrophils is usually tested using the NBT test (nitroblue tetrazolium test).
- In some cases, autoimmune markers are determined. These are circulating immune complexes, antinuclear factor and various autoantibodies directed against the tissues of one’s own body.
- Immunoglobulin E ( IgE ) can be detected. IgE is involved in allergic reactions.
- Eosinophil cationic protein ( ECP ). A protein released during the allergic process. A high level of eosinophilic cationic protein can determine the current allergic process and infestation by large parasites.
- Condition and function of the thymus gland. This is the gland in which T-lymphocytes mature and undergo “training”. To do this, you can look at the corresponding markers in a blood test for immune status and evaluate the structure and size of the thymus gland using computed tomography (CT scan of the chest).
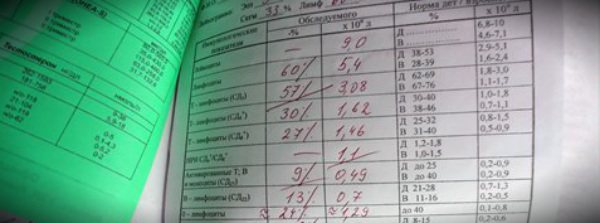
Some important immunogram indicators:
| Cells: | Markers: |
| B lymphocytes | CD19, CD20, CD22 |
| Natural killer cells (NK cells) | CD3-CD16+CD56+ |
| All T-lymphocytes, including T-helpers, T-cytotoxic, T-killers | CD3 |
| Killer T cells | CD3+CD16+CD56+ |
| T helper cells | CD3+CD4+ |
| Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (formerly called suppressor T cells) | CD3+CD8+ |
| Cells to which interleukin-2 can bind. These include regulatory T cells, which may be involved in inhibiting inflammatory responses. | CD3+CD25+ |
Other specific parameters (extended immunogram) are less commonly used, depending on the goals and objectives of the search.
Deciphering an immunogram is a process that is performed by a doctor based on the results of an immunogram and other studies, including x-rays, ultrasound and examination of the patient. Without the presence of the patient, the immunogram is quite difficult to interpret and it is not always possible to do it correctly. For example, if immunity was initially reduced, and the patient fell ill with some kind of inflammatory disease (for example, the herpes virus was activated), then during an active inflammatory process the immune system will work more aggressively and the immunogram may become falsely normal. The picture of overly activated immunity can be observed if the patient initially had normal immunity, but he has recently been ill or suffered a vaccination or injury. Deciphering the immunogram can be carried out simultaneously with the examination of the patient in the office of an immunologist. What is important here is a full physical examination of the patient by an immunologist, with an assessment of the condition of the lymph nodes, mucous membranes, respiratory organs, joints, skin, etc. This helps to correctly decipher and interpret the immunogram, taking into account personal characteristics and the current state of health.
Preparation for the study of immune status. An immunogram is done in conjunction with a general blood test. You need to donate blood for an immunogram in the morning, on an empty stomach. In order to avoid distortion of the results in the analysis, we recommend refraining from drinking alcohol and smoking 1-2 days before examining your immune status. Donating blood for an immunogram is not recommended during menstruation and against the background of acute infectious diseases occurring with high fever.
An immunogram can be taken at our clinic. Based on the results of the study, we will offer you a consultation with an immunologist, who will give a transcript of the immunogram, recommend appropriate treatment or refer additional examination, if required.
The cost of an immunity test (immunogram) depends on the number of indicators that need to be taken into account when prescribing treatment.
Preparation for the procedure
To conduct the study, blood is taken from a vein and from a finger. In order for the doctor to receive undistorted data, the following rules must be followed:
- Avoid serious physical activity and drinking alcohol at least 24 hours before the test;
- Do not eat before the test (the last meal is a light dinner no later than 8-10 hours before the test);
- Smokers need to refrain from smoking at least 3-5 hours before blood sampling, preferably a day before.
For many patients, having blood drawn is a cause of stress and anxiety. It is important to remain as calm as possible, as these conditions may affect the test results. If you fail to follow the above recommendations, you must definitely notify the laboratory assistant and your attending physician.
This will allow you to make adjustments when studying the results of the study or postpone the analysis to a more appropriate time.
Why do you need an immunogram?
The immune system is a complex system. When planning treatment, we must clearly understand what exactly violations in the immune system have occurred and why. Then treatment can be confidently directed exactly where it is needed. There is no cure for the entire immune system. Modern medicines make it possible to selectively, “point” help a particular immune process, and an immunogram helps to determine effective and safe points of application of treatment. This treatment is more reliable, requires less medications and meets safety criteria.
We can offer you a full laboratory examination of immunity and assistance from an allergist-immunologist in “deciphering” immunity tests. There is a profitable special offer
| Type of immunogram | Immunogram result |
| Standard immunogram |
|
| Extended immunogram |
|
| Interferon status |
|
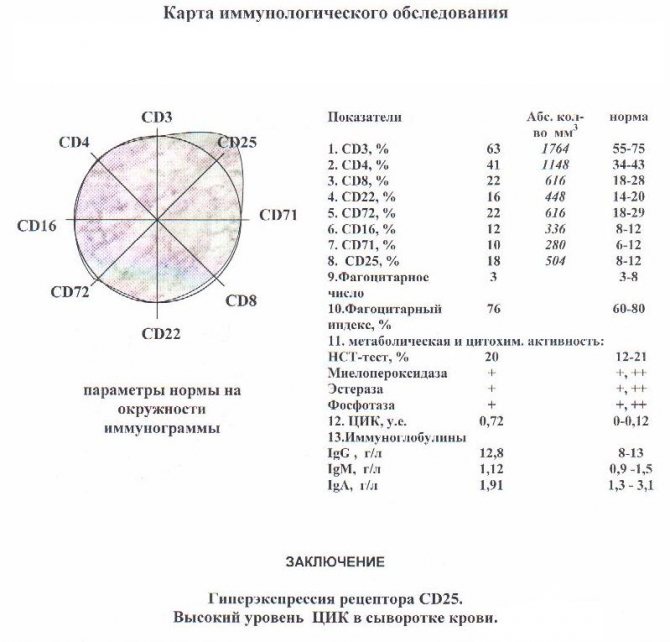
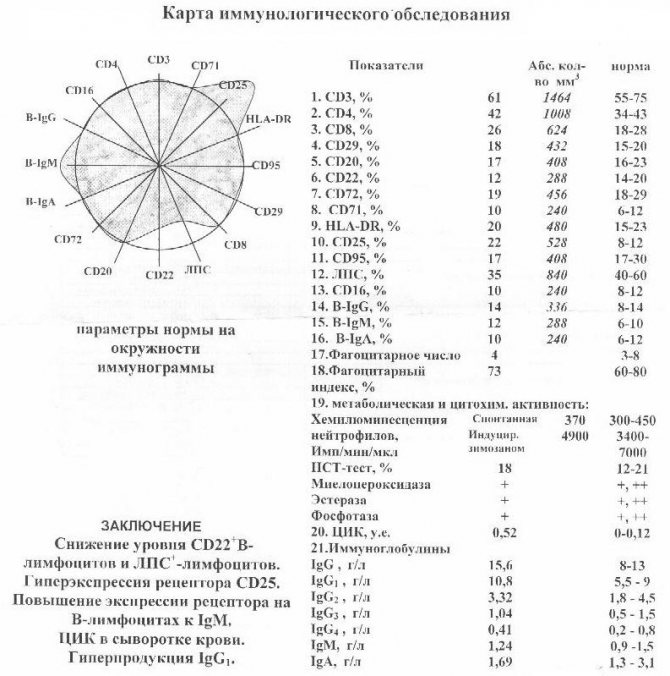
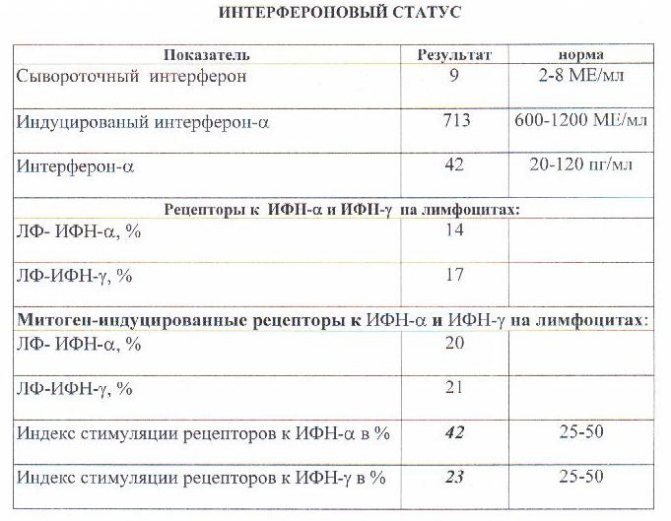
Samples of research results with transcripts
"Myths" about immunity
Fresh fruits and vegetables will improve weakened immunity
Undoubtedly, these products are useful for many diseases. In particular, they are a source of plant fiber, which stimulates normal digestion. With atrophy of the gastric mucosa, they improve the secretion of digestive juices and help in processing food. However, the amount of vitamins obtained from fruits and vegetables is extremely small and cannot help treat immune disorders;
Identified immunodeficiency in a child does not need to be treated; it will go away on its own after puberty.
This opinion is very common not only among the population, but also among a certain group of doctors. Such a judgment is very dangerous - the question of the need for treatment in each individual case is decided by an immunologist. And if the risk of frequent and severe infections exceeds the risk of side effects from medications (which are quite rare), therapy is necessary for the child;
Immunomodulators are absolutely useless in the treatment of immunodeficiencies
Several years ago, a large study was conducted that confirmed that the use of immunomodulators reduces the duration of treatment for ARVI by only 1 day or less. That is, they have a completely insignificant effect. This argument is often used by some doctors and patients, justifying their refusal to use them for primary immunodeficiencies. Does anything in this argument bother you?
- First, the aim of the study was to evaluate the effect on duration of treatment, but not on the prevention of infectious diseases.
- Secondly, it was carried out on healthy people who did not suffer from immunodeficiencies. If you study foreign literature and the results of suitable research works, you can find the following information. Immunomodulators have relatively little effectiveness, but they prevent the development of severe and frequent infections in people with primary immunodeficiencies, and also reduce the likelihood of death.
At the moment, there are other, more effective medicines abroad to maintain the body’s defense systems. Their price alone is many times higher, and availability in Russia is extremely limited. Therefore, immunomodulators, lysates of microorganisms, interferon preparations are one of the options for treating these diseases in the Russian Federation.
Main indications for immune examination
We examine the immune system if the disease occurs with its participation. Mainly:
- The presence of chronic inflammation anywhere when the immune system is unable to cope with the infection (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, gastritis, dysbacteriosis, prostatitis, ureaplasma, thrush, herpes, etc.);
- The presence of an autoimmune, rheumatic disease , when the immune system can show aggression towards healthy tissues of the body, mistaking them for foreign;
- Frequent (more than 6 times a year) and long-term “colds” : infectious diseases of the skin, mucous membranes, respiratory tract with a long course and low effectiveness when treated with antibiotics
- Allergy;
- Neuroinfections , including arachnoiditis;
- Risk of cancer (decreased antitumor immunity, unfavorable heredity, radiation exposure, etc.), condition after surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
- Increased temperature for 2 weeks for no reason
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Loss of body weight for no apparent reason
- Feeling tired, muscle pain, loss of performance
- Frequent relapses of herpes, thrush, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, dermatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, bronchitis and other chronic inflammatory diseases
How is the research conducted?
After taking blood from the patient, it is placed in two tubes. In one, it is mixed with an anticoagulant, which prevents it from clotting. In another, the blood clots for natural reasons.
A tube of clotted blood is used to assess the composition of the plasma. To do this, red blood cell clots are removed and the plasma is analyzed using various methods. This provides valuable information about the state of humoral immunity - the amount of immunoglobulins and other indicators of the functioning of the immune system.
Blood with an anticoagulant is studied by direct microscopy and other methods that allow the number of leukocytes, lymphocytes and other cells responsible for protecting the body to be counted.
an immunogram
for adults and children 2-3 times with a break of a couple of weeks.
This will provide information about changes in immunity over time and will allow a more accurate assessment of the state of the body.
Screening for infections
Simultaneously with the study of the immune system, we usually clarify the presence of infections in the body and the nature of their interaction with the immune system. Humans constantly interact with microbes. Normally, microbes are under the control of the immune system and do not penetrate into the internal environment of the body. But if the immune system is impaired, infection occurs easily. It is better to treat such infections in combination with restoring the immune system. Therefore, the correct examination before treatment is “Immunogram + Infections”. There is a profitable special offer.
What tests for infections are possible:
- Antibodies and PCR blood tests to detect infections.
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis and intestinal infections.
- Examination by a gynecologist (for women) or a urologist (for men) with scraping collection for subsequent laboratory PCR testing and bacteriological culture.
- Collection of bacteriological cultures and PCR smears from the nasal cavity and pharynx, eyes, bacterial culture and PCR examination of urine, sputum, joint fluid, pus, etc.
Analysis transcript
The result of the study is quite complex. a specialist can accurately judge the state of the body using
an immunogram .
It is important to understand that the analysis itself is quite informative, but its results must be compared with other studies, symptoms and life history. Only then will the diagnosis give an accurate result, allow you to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
When decoding, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age. Normal immunogram values in the elderly may differ markedly. This is due to the natural weakening of the body’s defenses and is not a manifestation of pathology
. Noticeable changes relative to normal values for an adult may be observed in the analyzes of children and pregnant women. This is also due to the normal physiological processes occurring in their body.
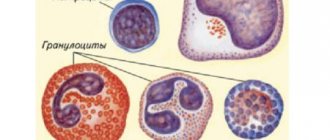
The main cellular indicators of the immunogram include:
- Leukocytes.
This is the main element of cellular immunity. There are several varieties (lymphocytes, granulocytes, basophils, neutrophils). In addition to their quantity, an important indicator is the percentage relative to each other. It can be used to judge the shift in the leukocyte formula “to the left” or “to the right”. The shift reflects the development of pathological processes or infections in the body; - Monocytes.
They are large in size and are the largest cells in the bloodstream. Responsible for antiparasitic immunity, destruction of cancer cells and infectious agents. Able to influence the state of the coagulation system; - Macrophages.
There are relatively few of them in the blood; most of them work in tissues and organs. They are responsible for tissue immunity and can stimulate the work of other components of the body’s defenses; - Eosinophils.
These cells produce various antibodies, their number increases sharply with the development of allergic reactions; - Neutrophils.
This is a type of white blood cell that phagocytizes (absorbs) infectious agents and other foreign particles that enter the body; - Basophils.
They participate in phagocytosis and produce a certain amount of antibodies. Mainly perform a regulatory function.

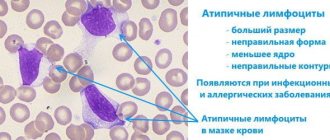
Changes in the immunogram can also be observed in the humoral components of immunity. These include:
- CD antigens.
They are located on the membranes of almost all cells. Based on them, the “friend or foe” system works, which allows the body to identify foreign or degenerated cells; - IgG .
This is a set of specific proteins that are produced in response to the penetration of infectious agents, allergens or toxins. When specific immunoglobulins encounter a target, they attach to the membrane or signal protein and serve as a marker for other components of the immune system; - IgM .
Produced to neutralize viral infections, it is a component of the inflammatory process; - IgA .
Forms the primary immune response, found in large quantities in the mucous membranes; - IgE .
One of the most active components of inflammatory and allergic reactions. Interacts with histamine cell receptors. In response, they release large amounts of histamine and other components into the tissues that cause general and local manifestations of allergies (swelling, redness, contraction of smooth muscles).
These are the main indicators that doctors pay most attention to when diagnosing a patient’s condition.
You can see their normal values for an adult in the table: