Brief description of the procedure
- Total procedure time: 30 min.
- Use of contrast agent: yes, intravenous
- Preparation and preliminary examinations: no
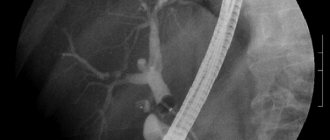
CT angiography of the abdominal arteries with bolus contrast and 3D reconstruction is a technique for highly accurate diagnosis of the condition of the vascular system.
Modern equipment (multispiral tomograph) provides a detailed image with a lower radiation dose compared to classical radiography. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to assess the condition of the walls of blood vessels in real time (at the moment the contrast passes through them), forming the most complete picture of the presence of mechanical, tumor, infectious and other vascular lesions. And processing the results with a special program allows you to obtain a three-dimensional model of the vascular system with the possibility of detailed examination of the area under study in different planes. The combination of these advantages ensures an accurate diagnosis and facilitates the planning of surgical interventions.
Advantages of the method
CT gives a small radiation dose, so the procedure can be repeated several times. Compared to other high-precision diagnostic methods, computed tomography has very few limitations. Since the CT machine does not create a magnetic field, this procedure can be performed even on patients with metal structures in the body, as well as those who have a pacemaker and other electronic implants.
Moscow has a large number of medical centers equipped with modern CT machines.
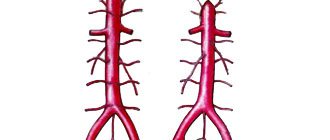
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels
CT angiography of cerebral vessels allows one to study the state of arterial and venous circulation in the brain. This diagnostic method is used by introducing a certain contrast agent into the bloodstream, which makes it possible to visualize the vessels in the area under study. There is also a technique for creating a three-dimensional model of the vascular bed, which facilitates diagnosis and analysis of the data obtained. Thanks to CT of the brain vessels, it is possible to analyze and assess the condition of arteries and veins, as well as identify pathological conditions of the blood supply.
When is a CT scan of the brain vessels prescribed?
This diagnostic method is widely used by specialists when they suspect the presence of abnormalities in the structure of the brain or the vascular bed of the cranial cavity. It is also used for diagnosing brain tumors of various origins, in cases of tissue ischemia, and in the presence of suspected stroke or thrombosis. CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck is prescribed in the presence of neurological symptoms, which indicate abnormalities and pathological phenomena in the bloodstream of the brain. Also performed before vascular operations.
Indications for CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches
- the presence of an aneurysm, i.e. saccular protrusion of the vessel wall, and other vascular anomalies;
- vascular thrombosis;
- atherosclerotic lesions of the abdominal aorta and its branches;
- abdominal pain of unknown origin;
- planning tactics for surgical interventions on blood vessels;
- control study after vascular surgery;
- tumor growth into blood vessels;
- traumatic injury;
- aortic dissection.
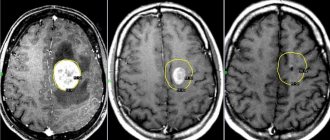
What does a brain CT scan show?
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels is a fairly indicative method for diagnosing vascular pathologies and is widely used in medical clinics. This type of study clearly visualizes the structure of the vascular bed and the condition of the walls of veins and arteries, therefore it is used to diagnose aneurysms (pathological protrusion of the wall of a blood vessel that occurs as a result of changes or damage).
CT angiography of cerebral vessels reflects the movement of blood in the bloodstream. Thanks to this, it is possible to diagnose blood flow disorders, determine the localization of thrombosis, atherosclerotic plaques or emboli that impede normal blood flow. Also, the described angiography method makes it possible to diagnose various vascular malformations, kinks, pathological looping and narrowing of the lumen.
This method allows you to determine the presence and location of brain tumors and the degree of their vascularization.
Contraindications to CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches
- pregnancy, which is associated with x-ray radiation from the device, which can cause fetal malformations;
- period of breastfeeding - the contrast agent penetrates into breast milk, therefore, if this study is unavoidable, it is not recommended to put the baby to the breast within 2 days after the CT scan;
- the patient’s body weight is large – the computed tomograph cannot withstand a load of more than 200 kg;
- individual intolerance to contrast;
- severe renal failure - if the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired, the removal of the contrast agent can be significantly difficult;
- severe condition of the patient - in such patients, a diagnostic procedure with the introduction of contrast can be potentially dangerous in terms of further deterioration of health.
Carrying out the procedure
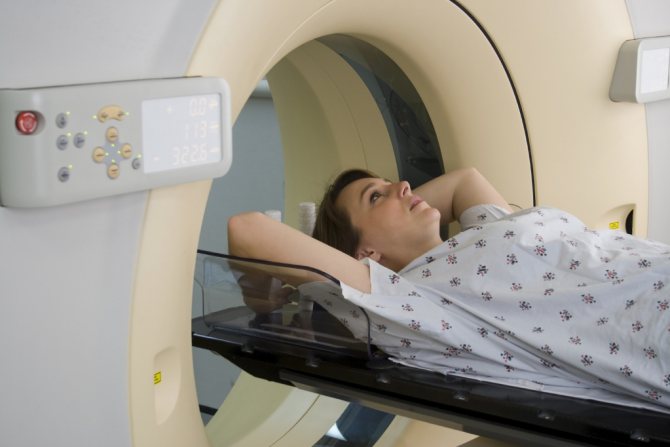
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels with contrast is a diagnostic method that is based on the use of X-rays generated in a special tube of the device. X-ray radiation affects a specific area under study, and tomograph sensors receive and analyze the data, building them into a single picture. Thanks to this, the specialist, reviewing the results obtained, draws a conclusion about the state of the department being studied. In the future, this allows you to make a correct and accurate diagnosis, select individual treatment and improve the patient’s quality of life.
How is the procedure done? In the absence of contraindications, and after a series of clinical tests and preparatory measures, the patient is placed on a special tomograph table. In this case, a contrast agent is injected into the bloodstream. Next, the tomograph is put into operation. The tomograph table automatically moves to the required position. During the diagnosis, the patient should lie still so that the resulting picture is not blurry. The duration of the procedure is 15-25 minutes.
Using Contrast
The use of contrast is a prerequisite when performing computed tomography of cerebral vessels. This substance allows you to accurately visualize the vascular bed of the area under study, identify pathological abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels and determine the presence of neoplasms in the cranial cavity. The contrast agent is a safe compound, does not cause harm and is quickly eliminated from the body.
Alternative Methods
In addition to CT angiography, Doppler ultrasound (USD) can also be performed. The principle of ultrasound scanning is based on the reflection of ultrasonic signals by constantly moving formed elements - blood cells. Using this method, it is possible to visualize the characteristics of blood flow and the presence of obstacles in the lumen of blood vessels. Duplex scanning of blood vessels is considered a more effective method. Thanks to duplex examination, it is possible not only to visualize the features of the vascular wall, the presence of blood clots and other changes, but also, thanks to color mapping, to find out the speed of blood flow and other characteristics of blood flow.
If CT angiography is contraindicated, MRI is used as an alternative.
Indications for the study
CT angiography of the abdominal arteries with bolus contrast and 3D reconstruction is prescribed if:
- the patient is suspected of having an abdominal aortic aneurysm or other changes in the vascular endothelium;
- Marfan syndrome is suspected, causing a dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- atherosclerosis progresses;
- there are traumatic injuries to the spinal cord and arteries;
- the patient has congenital or acquired vascular pathologies;
- there are manifestations of aortitis (infectious lesions of the vascular endothelium).
When performing CT angiography, the condition of the celiac trunk, its branches, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, and renal arteries is assessed.
Preparatory stage and technology
No one will demand significant preparation from the subject. The doctor will only warn that during the scan the device will emit loud beeps, and you should not be afraid of them. Also, before contrast, you will need to refrain from eating and drinking approximately four hours before the start of the diagnostic procedure.
After the patient removes all metal objects and lies down on the medical couch, the x-ray technician will start the scanner.
When a contrast agent is administered, people sometimes feel a sensation of heat or cold that spreads throughout the body as the blood flows. This is considered within the norm.
The manipulation itself lasts from ten minutes to half an hour, which depends on the type of device and the characteristics of the contrast. All this time the patient must be in a horizontal position, remaining completely motionless. Since even adults cannot always maintain one position for a long time, for the convenience of those being examined, auxiliary straps were provided on the couch. And they put a cushion under their heads.
But if something went wrong during the study, the patient will be able to contact the medical staff through feedback. Every modern device has a microphone on the patient side.
All incoming information is instantly transferred to the computer’s memory, which is necessary for building a visual reconstruction in three dimensions.
As soon as the study comes to an end, the doctor will advise you to start drinking more fluids to speed up the elimination of harmful components of the contrast agent.
Many patients are pleased with the fact that the examination is absolutely painless. But you should prepare for the fact that some people examined may experience nausea and headaches due to the contrast. These are quite common phenomena, as is slight redness near the injection site.
Conducting research
The data obtained during CT angiography is processed by special programs with the ability to obtain three-dimensional images and multiplanar reconstructions. The method allows you to build a three-dimensional model, see changes in the vascular system, evaluate their distribution, study different angles, and make sections with a minimum step.
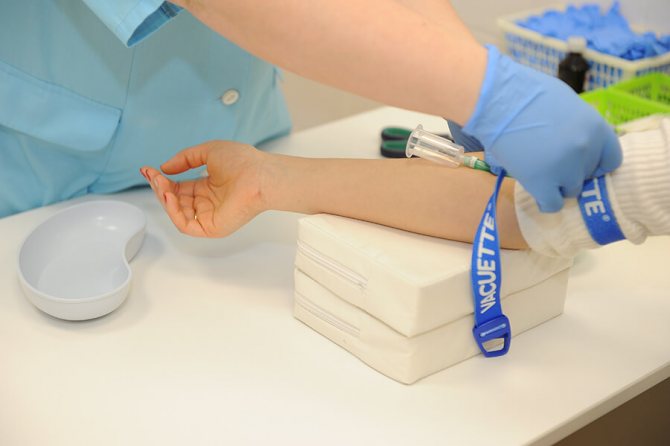
Before scanning begins, a catheter is inserted into the patient's vein. A syringe injector with a contrast agent is connected through it. Contrast injection rate and volume are calculated for each patient based on physiological parameters and age.
The patient lies down on a movable table, which smoothly moves through the aperture of the tomograph. The supply of contrast agent begins, a few seconds after which the emitter and sensors are turned on. All reactions and anxiety during the study should be reported to the doctor. Two-way communication is provided for negotiations. The doctor continuously monitors the patient through a window in the laboratory block. You must lie still while the device is operating. This will allow you to get clear pictures. During the scan, the patient will be asked to hold their breath for 8-10 seconds. The scanning duration is about 5 minutes.
Contraindications and possible complications
Like all diagnostic methods, CT scan of cerebral vessels has its contraindications. Situations that do not allow the use of CT angiography include:
- allergic reactions that develop as a result of exposure to a contrast agent;
- severe liver and kidney disease (inability to properly remove the contrast agent from the body);
- severe degrees of phlebitis - a contrast agent can provoke a worsening of the pathological process in this disease;
- pregnancy, because there is a risk of intrauterine development disorders of the fetus.
Frequent and regular use of X-rays for diagnostic purposes (with CT) increases the likelihood of developing malignant tumors. However, with a single or rare use of cerebral CT with contrast, there are almost no risks.
Advantages
- Angiography of cerebral vessels allows you to choose the right treatment tactics
- Cerebral angiography makes it possible to obtain detailed information about the condition of the cerebral vessels
- The information content of angiography significantly exceeds the capabilities of other methods of non-invasive visualization of blood vessels.
- The use of a catheter makes it possible to combine diagnostic and therapeutic tasks
- After an X-ray examination, no radiation remains in the patient's body.
- Radiation exposure is not dangerous
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
CT angiography is prescribed for:
- cerebrovascular accident;
- swelling, pain, injuries in the neck with suspected blood flow impairment;
- suspected aneurysm, vascular dysplasia;
- preparation for operations and for postoperative monitoring.
The study is contraindicated if:
- allergic reactions to drugs containing iodine;
- renal or heart failure;
- pregnancy;
- thyrotoxicosis.
Order of conduct
The actual scanning takes up to two minutes. A catheter is first installed into the patient’s vein to administer a contrast agent. The total volume of the substance and the rate of delivery depend on the age, weight, and body type of the patient. As the contrast passes through the veins, you may feel hot and slightly dizzy. If the symptoms are severe and you feel unwell, tell your doctor.
To obtain images of the area under study, the patient lies on the manipulation table on his back. During the scanning process, the table will move horizontally to pass through the aperture of the tomograph. The doctor is monitoring the patient from the next office, you can communicate with him via speakerphone, it is constantly working.
It is advisable not to move while the tomograph is operating. Rolling over is prohibited. At a certain point you will need to hold your breath for 8-10 seconds, the doctor will warn you. After the scan is completed, the catheter is removed and the patient leaves the office. The results will be presented after processing the received data.