Causes
30% of women in labor experience bleeding. The character can be different - weak, smearing, strong, abundant. This could be due to several reasons:
- Attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine walls - implantation, at the beginning of pregnancy. The process can damage blood vessels and cause bleeding. Similar to menstruation, but lasts for 1-2 days, then usually stops. This is natural and is not considered a deviation;
- Due to hard work, physical activity, or deep penetration during sexual intercourse, the cervix of the uterus can be damaged. The result is bleeding, which usually goes away within a couple of hours;
- low levels of hormones in the body. Sometimes the ovaries do not produce enough progesterone and because of this, the body begins to start the process of menstruation, as a result, the lining of the uterus is detached and discharge appears. This may affect the implantation of the fertilized egg;
- Breakthrough bleeding occurs due to hormonal imbalance. May appear in the first trimester and in the second;
- the most common reason is a threatened miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Accompanied by pain with increasing intensity. This can happen due to a variety of circumstances: infections, developmental defects, dehydration, mechanical injuries to the abdomen, use of medications and much more. Doctors still cannot identify all the causes of miscarriage; each case is considered individually;
- Another common phenomenon is an ectopic pregnancy, that is, the fertilized egg is not fixed in the uterus, but remains in the fallopian tube and begins to develop there. This condition is dangerous for a woman and urgent hospitalization is necessary;
- bleeding can occur due to a stop in the intrauterine development of the child, that is, during a frozen pregnancy. The discharge is spotting, accompanied by pain in the abdominal area;
- premature placental abruption - can occur at any time, most often in the second and third trimester. It can lead to the death of the baby, so at the first symptoms you need to consult a doctor;
- an infection in the body can cause bleeding, it is necessary to be treated, if ignored, then serious complications are possible, including the death of the child;
- cervical erosion - occurs in half of women; during pregnancy, the disease is not dangerous, but requires regular medical supervision.
For any bleeding or suspicious discharge, you should contact a gynecologist.
What is implantation bleeding?
About 30-40% of women experience slight blood loss after the embryo implants in the uterus. This phenomenon is known as implantation bleeding. Since this happens early in your cycle, it may even be the first sign you realize you're pregnant. Bleeding usually occurs in the first weeks of pregnancy, since the uterus is an organ rich in blood vessels that can easily become damaged. When the embryo sticks to the inner wall of the uterus, the small veins and arteries that normally connect to the endometrium rupture and this can cause bleeding. If this occurs, usually 6-10 days after fertilization, it usually coincides with the theoretical date of menstruation and can therefore be confused with the onset of menstruation. There is no set pattern, and implantation bleeding may occur in one or all of a given person's pregnancies.
Diagnosis and treatment
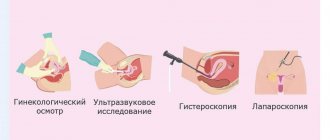
The doctor will conduct an examination, take a smear from the vagina, and prescribe an ultrasound of the pelvis. The woman also needs to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis and group determination. Based on the results, the gynecologist will prescribe further treatment.
In case of a miscarriage, you will need to clean the uterus; if an ectopic pregnancy is detected, then a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. If the cause of bleeding is the threat of miscarriage, then the woman will be prescribed medications to maintain pregnancy and bed rest, and hospitalization is possible.
How to recognize implantation bleeding?
The first question for many people is how to recognize that it is implantation bleeding and not just the beginning of a cycle, in other words, how are these types of bleeding different? The most common reason for confusion here is that bleeding occurs 10 to 14 days after conception, around the time that menstruation would have occurred if conception had not occurred. However, vaginal bleeding can occur any time during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. Blood loss may last 1-3 days, and the amount of discharge is usually less than during menstruation, although the color may be darker. It may appear as a light spot or light persistent bleeding, and there may or may not be blood mixed with mucus. The color may vary depending on how long it took to leave the body. Fresh bleeding appears red, it may appear pink or orange if mixed with other vaginal discharge, and old blood may appear brown due to oxidation.
Prevention
Prevention measures are simple and consist of stabilizing and maintaining a calm state:
- good nutrition;
- moderate exercise, if there are no contraindications;
- walk more in the fresh air;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- eliminate stress;
- avoid heavy physical work and stress;
- Visit your doctor in a timely manner and follow the recommendations.
It is useful to do gymnastics and special exercises for pregnant women. But sometimes heuristics can be prohibited by high activity; more often this applies to women with a threat of miscarriage, they are prescribed bed rest.
Throughout pregnancy, it is necessary to carefully monitor your well-being and discharge, and if bleeding begins, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What are other symptoms of implantation in early pregnancy?
Since implantation bleeding only occurs in about a third of pregnancies, you'll likely be among the majority who don't experience it. However, your vigilance for the signs and symptoms of successful implantation is probably still massively high! So what are the other early signs that you might be pregnant? These may include:
Morning sickness
This can begin as early as 4 weeks after conception (10-14 days after embryo transfer), although it more often occurs around 6 weeks. Fortunately, for those who go through it, morning sickness is usually temporary and usually improves by 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Sensitivity to smells and tastes
Sudden sensitivity to smell and taste can be a sign of early pregnancy and undoubtedly contributes to ongoing stories about pregnant women's "cravings" for certain foods. Both increased sensitivity and morning sickness are the result of hormonal changes occurring in your body.
Frequent urination
It may seem strange when your baby is still very young, but the need to urinate more frequently in early pregnancy is one of the most common symptoms. It is also the result of hormonal changes that cause faster blood flow through the liver and kidneys to remove waste as efficiently as possible. In addition, the uterus quickly increases in size even at this early stage of pregnancy and therefore puts more pressure on the bladder, especially at night.
Breast tenderness
The well-known symptom of breast tenderness is another sign of early pregnancy. This is the result of an increase in blood flow and fluid retention in the mammary glands against the background of a sharp increase in the level of female sex hormones in the blood serum.
Stomach cramps
Cramping may occur on its own or be accompanied by slight bleeding, which may be a signal of implantation. You might think that all these possible early signs and symptoms of pregnancy would make it easy to be sure that it is happening. But the fact is that some symptoms are also present in some people as a precursor to their normal monthly cycle with premenstrual syndrome. So, despite all the possible clues, the only way to be sure of pregnancy is to take a pregnancy test and confirm the pregnancy with your doctor.
Measures to help a pregnant woman with bleeding
After finding out all the possible reasons, a fair question arises: what to do if bleeding begins in the first trimester of pregnancy? How to stop bleeding, and can a woman do this on her own before doctors arrive or if it is impossible to call them. Whatever the reason for bleeding during pregnancy, if possible, you should call an ambulance as soon as possible or start stopping the bleeding on your own, and only then get to the nearest medical center.
In the meantime, while the doctors are on the way, you must immediately take a lying position and wait for their arrival. Under no circumstances should you even move. It is also undesirable to drink, especially drinks with even a small amount of caffeine or other central nervous system stimulants are strictly prohibited, otherwise the bleeding may increase significantly.
If relatives are present with the woman, and the ambulance is delayed, then it is permissible to give the pregnant woman a safe drug that stops blood loss. One of the available herbs is suitable as such a medicine.
Plants that have a hemostatic effect:
- Nettle.
- Field horsetail.
- Shepherd's purse.
- Water pepper.
- Leaves and especially cherry twigs.
It is better to prepare a decoction of hemostatic herbs more concentrated than provided in the recipe (usually one tablespoon per glass of boiling water). This is done so that a woman experiencing uterine bleeding does not drink large amounts of liquid. But you need to take this remedy in small sips, monitoring the condition of the pregnant woman.
There are also a lot of pharmaceutical drugs to stop bleeding, but their use must be agreed with your doctor. Therefore, during periods of pregnancy, it is better not to prescribe medications on your own; the arriving ambulance team will, from a professional point of view, take all necessary measures. The actions of doctors in cases where a pregnant woman may experience severe bleeding are primarily aimed at stopping it. And after this, the woman is taken to the hospital to take blood for analysis and carry out other diagnostic procedures in order to find out the cause of blood loss.
Pregnancy is a wonderful time, and many women believe that it brings only positive emotions. Ideally, this is how it should be: no periods or pads, no protection during sex, dreams of a beautiful and healthy baby. Therefore, expectant mothers who encounter some difficulties and ailments for the first time begin to panic and set themselves up for a bad pregnancy outcome. So why not prepare for possible complications in advance?
Unfortunately, the conditions of modern life, especially in a metropolis, are not entirely suitable for bearing a child. The health of pregnant women is affected by poor ecology, unnatural food, chemicals, and stress. Of course, during pregnancy you can reduce the influence of these factors, but you will not be able to completely get rid of it.
It happens that even minor nervous tension (minor conflict at work, in the market, in public transport) provokes bleeding, as during menstruation. If a blood clot comes with such discharge, it can be quite dangerous and even threaten the life of the fetus. Therefore, you must immediately consult a doctor and follow all his instructions. However, let's try to figure out why the blood clot came out.
Is implantation bleeding the same when you undergo IVF treatment?
People undergoing IVF or any other assisted fertility treatment often wonder whether pregnancy symptoms will be the same if embryo transfer and implantation are successful. In a word, yes. Although some stages of IVF are stimulated by medication, and although the actual joining of the egg and sperm occurs in a laboratory, the end result is identical.
Let's look at a summary of the steps that led to embryo implantation. The first step is ovarian stimulation, which causes the ovaries to produce a number of oocytes. Then, when the oocytes have reached a suitable stage of maturity, they are retrieved during ovarian puncture in order to then be fertilized with prepared sperm in an embryology laboratory. This is the point at which fertilization occurs and embryos are formed. They are cultivated - “grow” in special incubators and undergo the necessary tests (if genetic research of embryos is performed). The healthiest and most viable embryo is then transferred to the woman's uterus. This is, in a nutshell, the final stage of the process. Implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterus after it has been transferred is not part of the assisted reproduction process; this is something that happens naturally in the same way as during normal conception. This final stage is not guaranteed as a result of IVF treatment, just as unprotected sex during ovulation is not guaranteed to result in pregnancy. This explains the absolute sameness of symptoms you can expect between assisted reproduction and natural pregnancy, including any implantation bleeding.
When should you contact a gynecologist?
The task of a pregnant woman is to closely monitor her health and, if strange manifestations are noticed, immediately consult a doctor. First of all, this applies to cases when the color of the leucorrhoea changes or other symptoms appear. It is important to rush to see a gynecologist if you feel a burning or itching in the perineum, vaginal discharge becomes bloody, brownish or greenish, or pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen. Needless to say, self-medication is unacceptable, since it is detrimental to both the expectant mother and the child.
Factors not related to pregnancy
In these conditions, the general well-being of the expectant mother is impaired, the bleeding is quite severe, and the pain increases over time. These factors include:
- fibroids and polyps;
- cervical and endometrial cancer;
- infection;
- blood coagulation disorder.
Fibroids and polyps
These pathologies rarely interfere with the gestational process. Myoma, if it does not grow, does not complicate pregnancy. But there are situations when an actively growing tumor blocks blood access to the embryo, causing its death and rejection. In this case, the discharge will be bloody, with clots, the stomach will be cramped and painful.
If there are polypous formations in the uterine cavity, a woman may be bothered by beige-brown discharge. Pregnancy usually proceeds without any special features. But a large polyp in the cervical canal can contribute to the development of an infectious process in the uterus.
Infections
STDs can be accompanied by postcoital (after intercourse) bleeding, regardless of pregnancy. But this symptom is usually hardly noticeable against the background of the main signs of STIs (itching, burning, atypical discharge).
Blood clotting disorder
This is not the cause of bleeding, but a factor that enhances it. The cause can be any, even the weakest, damaging factor. For example, for women with hemophilia, a small detachment of the chorion is dangerous. It can cause massive blood loss, anemia and fetal death.
Malignant oncology
These diseases are often accompanied by bleeding. Such bleeding is rarely profuse. Such pathologies can be diagnosed during an unplanned pregnancy.
Complications and consequences of uterine bleeding
The most severe complications can occur during ectopic pregnancy:
- rupture of the pipe - entails severe bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which can be fatal;
- Tubal abortion, when the fetus enters the sterile abdominal cavity, can threaten the development of purulent inflammation of the peritoneum - peritonitis.
The most severe consequence of an ectopic pregnancy is the loss of reproductive organs during surgery and subsequent infertility.
If you delay seeking medical help, a miscarriage can result in:
- large blood loss;
- inflammatory processes - salpingoophoritis, endometritis;
- adhesions;
- difficulties with conceiving and bearing a healthy baby;
- infertility.
The loss of a child is a huge stress for a woman and can provoke depression and serious psychological disorders.
Bubble drift is fraught with the following consequences:
- amenorrhea - absence of menstruation;
- high risk of complications during childbirth - labor anomalies, bleeding;
- sepsis;
- metastases in malignant course;
- infertility.
A frozen pregnancy is dangerous due to endometritis; the decomposition of a dead fetus can cause peritonitis and sepsis.