How is it transmitted?
The most common and typical route of transmission of the causative agent of syphilis is sexual. Infection can occur through vaginal, oral or anal sex. As already mentioned, infection is most likely with skin manifestations of syphilis; the most contagious are hard chancre - painless ulcers that form during primary syphilis. Erosive papules that appear with secondary syphilis also pose a great danger, but with nonspecific rashes it is possible to become infected. The sexual route of transmission of syphilis is the most common, since during intimate intimacy microtraumas are formed on the mucous membranes and skin, through which the pathogen actually penetrates.
Another route of transmission of infection is transplacental (from mother to fetus). It is known that in the first three years after the mother is infected, the likelihood of developing congenital syphilis increases. The pathogen penetrates the placenta at 4–5 months of pregnancy, but there are cases of infection as early as 10 weeks of gestation.
Blood transfusion is another way of contracting syphilis. The transfusion route is possible at any stage of infection, including the incubation period. Currently, all donor blood is thoroughly checked, so this route of transmission of infection is practically excluded.
It is almost impossible to become infected through household contact, but in medical practice this has still happened. The infection is not transmitted through shared utensils and household items, but in close contact with a patient this is still considered possible.
There is another way of infection - professional. We are talking about laboratory employees, as well as sex workers. There are known cases of syphilis infection among surgeons, dentists and obstetricians-gynecologists.
At risk for the disease:
- prostitutes;
- homosexuals;
- persons who are promiscuous;
- persons practicing group sex;
- asocial elements of society;
- drug addicts;
- patients with gonorrhea;
- patients with hemophilia.
Classification of the disease
Syphilis is divided into forms and types, due to different timing, routes of spread and varied symptoms.
According to the degree of damage, syphilis is divided into:
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary.
In addition, it can be:
- hidden,
- congenital,
- late,
- chronic.
Primary syphilis - stage 1 of infection, a distinctive feature is the appearance of chancre. Chancres often appear on the genitals, since the sexual tract is the most common route of transmission of infection. Chancres can also appear on the face, mouth, mammary glands, and legs. Primary syphilis has no other manifestations.
Secondary syphilis - stage 2 of infection. It is characterized by the appearance of a papular rash. At this time, the patient experiences inflammation of the lymph nodes, damage to the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Tertiary syphilis develops in people who have not received treatment or have not completed treatment for the disease. Syphilitic granulomas appear on the mucous membrane, skin, bones, and internal organs, which destroy these structures. Currently, this stage is rare, since at stages 1 and 2 the disease can be successfully treated.
Latent syphilis is considered the most dangerous because the patient has no symptoms, but it poses a danger to others. Syphilis is classified as late if more than 2 years have passed since infection and symptoms have just appeared. Syphilis, which has developed over decades, is called chronic; it slowly destroys the body, and is not always accompanied by symptoms.
Interpretation of positive serological reactions to syphilis in patients without clinical manifestations of syphilis
Sevashevich A.V., Smirnova T.S.
State Health Institution City Dermatovenerologic Dispensary, St. Petersburg
Purpose: to evaluate positive serological reactions to syphilis in patients without clinical manifestations of syphilis.
Materials and methods: in connection with the implementation of the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 87 of March 28, 2001 “On the improvement of serological
diagnostics of syphilis", the abolition of the Wasserman reaction and the transition to other types of serological diagnosis of syphilis
Ca, practicing doctors have many questions in the interpretation of positive serological reactions in different categories
sick. A positive microreaction persists for a long time, and ELISA and RPGA can persist for life, i.e.
so-called serological fixation occurs. To the Consultative, Treatment and Preventive Department (KLPO) of the City Clinical Internal Affairs Department
Patients of the city's dermatovenerological institutions were referred with positive results of serological reactions to syphilis without clinical manifestations of the disease.
According to the observations of specialists from the KLPO GorKVD, diagnostic difficulties arise when resolving the following issues:
— criteria for cure of patients with syphilis;
— exclusion of false positive reactions;
— diagnosis of latent syphilis;
— examination of pregnant women with positive KSK reactions.
During the examination (about 300 patients per year), serological tests were used: microprecipitation reaction (MR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); passive hemagglutination reaction (RPHA), immunofluorescence reaction modified by RIFabs., complement fixation reaction (CFR) with cardiolipin and treponemal antigens. In order to identify specific and nonspecific changes, patients were examined by an otorhinolaryngologist (bone-air dissociation), an ophthalmologist (uveitis, chorioretinitis, optic disc atrophy, etc.); a therapist (emphasis of the second tone on the aorta, systemic murmur in the cardiac region), a neurologist (autoreflexia and other microfocal symptoms), as well as an infectious disease specialist and a psychotherapist, and if indicated, a psychiatrist. When clinical symptoms were identified, lumbar puncture, cyto-biochemical-serological study of cerebrospinal fluid, MRI and MRA of the brain, ultrasound of cerebral vessels, and ultrasound of the heart were performed to clarify the diagnosis. In the absence of signs of visceral syphilis, neurosyphilis and other forms of syphilis, but with positive ELISA, RPGA, RIF reactions, the conclusion “serological fixation” is valid. When deciding on the presence of syphilis in pregnant women, the following were taken into account:
1) careful collection of anamnesis;
2) examination of partners with staging of all serological reactions (MR, ELISA (IgM, IgG), RPGA, RIF, RIT);
3) consultations with all specialists.
When determining false-positive reactions, it is necessary to have data on the patient’s concomitant diseases and the results of a complete serological study.
Results: three groups of patients were identified:
Group I - 64.0% of those consulted received full anti-syphilitic treatment for various forms of syphilis suffered from 1 to 10 or more years ago, but negative serological reactions (complete or partial) did not occur in them, and in 17% of people in this group neurosyphilis was detected.
Group II - patients with a history of syphilis in early pregnancy: of them - 6.0% were sent for preventive treatment due to serological relapse; 1.2% were diagnosed with latent syphilis - these were pregnant women with newly detected positive reactions.
Group III - patients with false-positive serological reactions (28.8%) were left without specific treatment during clinical serological control (CSC).
Conclusions: due to the difficulties of diagnosis, these issues require additional, in-depth, scientific study to develop a unified tactics for the management of patients in this category.
‹Enzyme immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test for preventive examination for syphilisUpPatient satisfaction with the procedure as the basis for the work of an aesthetic medicine clinic ›
Symptoms of syphilis
Since the disease goes through 3 stages, replacing each other, the symptoms at different stages will vary:
- The appearance of chancre. This is a round ulcer with smooth edges and a dark red bottom. When rubbed, a liquid may be released from the formation, which contains live and active pale spirochetes. A couple of weeks after the appearance of chancre, inflammation begins in the lymph nodes. At this time, the pathogen has already spread throughout the body and multiplies in the internal organs. At the end of the first stage, a general intoxication syndrome occurs.
- The appearance of a rash on the body. The rash most often appears after the ulcer has healed. Red-brown spots appear on the neck, chest and upper back. They are called the necklace of Venus, they do not hurt, do not itch and, apart from aesthetic discomfort, do not cause any inconvenience. At this stage, fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, headache and muscle pain, patchy hair loss, fatigue, and weight loss appear. In every 10 patient, pathologies of the joints, bones, and nervous system are detected in stage 2.
- Pallor of the rash. There are more of them in places of friction. Serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, respiratory tract, and brain occur. Since the pathology affects internal organs, it can be fatal.
Important! Without treatment, syphilis affects the eyes (ocular syphilis) and the brain and nervous system (neurosyphilis).
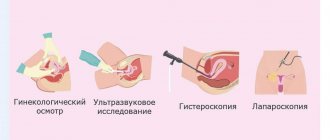
Diagnosis of syphilis
It is very important to identify syphilis at its first stage, at which time it is easier to treat and does not leave complications. Diagnostic measures begin with a visual examination of the skin and mucous membranes. During the examination, the doctor discovers dense purulent foci. You can differentiate chancre from other formations using palpation - it is painless.
For accurate diagnosis, a number of laboratory tests are required:
- RSKk;
- RMP;
- RPR;
- RSKt;
- RPGA;
- ELISA.
For research take:
- discharge from erosions, ulcers and papules;
- lymph;
- blood serum;
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- umbilical cord and placenta tissue.
A venereologist diagnoses and treats syphilis.
Crosses, dashes and pluses in decoding analysis: how to understand
The results of some serological tests may be presented in the form of a table with crosses or dashes in the columns. How is this result deciphered? For example, the MR or microprecipitation reaction is calculated in digital equivalent, showing the quantitative titer of infection.
RW (Wasserman reaction) involves obtaining test indicators in the form:
- dash (negative test);
- one or two crosses (weakly positive);
- three crosses (positive);
- four crosses (strongly positive test).
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The presence of even one cross in the results is the basis for prescribing the following clarifying tests. A dash in the table does not guarantee the absolutely certain absence of the disease.
The results of the RIF are also indicated in the form of pluses or crosses - from one to four. If a person shows a dash (minus), it means there is no syphilis. Results in the form of one, two, 3 crosses or 4 pluses indicate the presence of the disease.
RPGA does not give any quantitative associations as a result - it shows either the complete absence of the disease, or its presence in the past or present.
ELISA results are more difficult to decipher. They are presented in the form of a table of antibody classes IgA, IgM and IgG. Next to each value there is a dash or cross. By comparing the presence or absence of a specific type of antibody, the attending physician can draw a conclusion about the stage of the disease and the duration of infection.
After conducting a comprehensive examination for syphilis, the doctor summarizes all the results obtained into a single extended table, using the method of pros and cons. By placing crosses and dashes depending on whether the result of a particular test was positive or negative, the attending physician can form a picture of the disease.
Treatment of syphilis
Treatment of syphilis is based on the impact on the cause of the disease, that is, on the pathogen. This treatment is called etiotropic therapy.
Drug treatment consists of taking antibiotics:
- penicillins;
- tetracyclines;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
Local treatment consists of using ointments, creams or gels, the action of which is aimed at mitigating the skin manifestations of the disease.
To generally strengthen the body and combat neurological symptoms, physiotherapy is prescribed, but it, of course, cannot be the main thing in the fight against infection.
Adjuvant treatment may also be used. The patient is prescribed:
- vitamin complexes;
- dietary supplements;
- immunomodulators.
Treatment tactics for pregnant women will depend on the duration of pregnancy and the severity of the disease. In some cases, when the disease threatens the child with dangerous pathologies, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. But most often, pregnant women are prescribed antibiotics.
There are no traditional methods for treating syphilis. Self-medication will not lead to a positive effect; therapy should only be selected by a doctor.
Rules for obtaining a test for syphilis
To get a referral to the laboratory, you need to visit your local physician. If you want to get tested faster, this can be done in a private laboratory without a referral (for example, Invitro laboratories do a test for syphilis quickly and anonymously).
How to get tested for syphilis? Blood is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. You can only drink clean water.
Preparation: two days before the test, you need to exclude fatty foods and especially alcohol from your diet.
How is the analysis taken? in the usual way from a finger or ulnar vein.
How long does it take to test for syphilis? The test result is usually ready the next day. The transcript can be taken from a doctor or laboratory.
How long is the analysis valid? For up to three months.
If a positive result is obtained, it is recommended to contact a dermatovenerologist for further examination. Interpretation of tests is the job of a doctor; you shouldn’t rack your brains on your own to find the right answer.
Consequences and prognosis
Regardless of whether syphilis manifests itself or not, in any case it has a negative effect on internal organs. The list of complications of syphilis includes the following:
- damage to the cardiovascular system;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- neurological deficits;
- impairment of intellectual abilities and memory;
- blindness;
- hearing loss;
- meningitis.
Development is possible:
- IHD;
- gastritis;
- hepatitis, up to coma and death;
- osteoarthritis;
- syphilitic pneumonia.
In the primary form of syphilis in men, the following may appear:
- phimosis;
- balanoposthitis;
- gangrene of the genital organ;
- balanitis
As for the prognosis of the disease, it depends on the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With primary and secondary syphilis, the treatment prognosis is favorable; the third stage can lead to disability of the patient.
With congenital syphilis, the prognosis for treatment is positive, but only if adequate treatment is started immediately.
Algorithm for diagnosing syphilitic infection at different stages
In the primary seronegative period (up to 2 months after infection), a search for treponema is carried out in a dark field or using fluorescent antibodies.
For primary seropositive, secondary and latent syphilis, RMP and ELISA are used, and RPGA is used as a confirmatory test.
In patients with relapses of secondary syphilis, elements of the rash are examined, trying to isolate treponemes from them for microscopic examination.
In the tertiary period, bladder cancer is negative in a third of patients. ELISA and RPGA are positive, but they may not indicate tertiary syphilis, but a previous disease. A weakly positive test indicates recovery rather than tertiary syphilis.
When making a diagnosis of “congenital syphilis,” the presence of the disease in the mother, the difference in the rates of breast cancer in the mother and child, positive ELISA and RPGA in the newborn, and immunoblotting are taken into account.
Pregnant women must be examined for syphilis, especially those who have already had a stillbirth, an undeveloped pregnancy, or early miscarriages. They carry out RMP, ELISA, RPGA. They are examined for the presence of the disease before terminating pregnancy.
Prevention
It is enough to see at least once what syphilis looks like to forever decide to give up promiscuous sexual intercourse. This is the most effective way to prevent this disease.
If a person has to live with a sick person, strict hygiene rules must be observed. Despite the fact that the risk of household transmission of infection is minimal, it still exists. Also, a person living with an infected person must periodically visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics to make sure that infection has not occurred.
If you have sexual contact with an infected person, it is recommended to immediately urinate, wash your genitals with laundry soap, and wipe your private parts with a disinfectant solution. This treatment is effective only in the first 48 hours after possible infection, since during this period of time the pathogen is still on the skin and mucous membrane. After more than 3 hours, such treatment is useless.
Syphilis is a dangerous disease that in the vast majority of cases is transmitted sexually. The disease is insidious in that even in the absence of symptoms, it can affect any organ of the human body and provoke various ailments. It is important to understand that cure for syphilis does not guarantee protection against re-infection. Immunity to Treponema pallidum is not developed. Therefore, you should always adhere to preventive measures, and at the first suspicion of a disease, immediately consult a doctor. With timely treatment, syphilis can be successfully treated. But untreated syphilis will destroy the body for years and can be fatal.
Decoding the results: false, erroneous, false positive, false negative
Why should you immediately consult a doctor when the first signs and symptoms of syphilis appear? The fact is that even if you take tests yourself in the nearest laboratory, only a qualified venereologist can correctly decipher their indicators.
Any types of serological tests are usually prescribed as express diagnostics, or during medical examinations. Their results can be negative, weakly positive if the antibody concentration does not reach a certain level, or positive. In addition, each type of test may result in false positives or false negatives. Positive reactions from non-treponemal tests are usually verified by results from specific treponemal tests.
Treponemal serologic tests may also be negative, equivocal, weakly positive, or positive. For example, immunoblotting is prescribed to confirm or refute the results of the initial examination. The detection of IgG and IgM antibodies in the blood is indicated by stripes.
If both the nonspecific primary screening and the specific serological reaction show a negative result, it means that the person is healthy, or the infection occurred less than 10 days ago.
A positive reaction in pregnant women can also be present with non-treponemal screening, however, if an immunoblotting test was further carried out and it gave a negative result, this means the absence of the disease.
Can an error creep into the test results? There is always some possibility that the analysis showed erroneous results. Therefore, in the diagnostic process, the doctor must pay attention to external factors that do not depend on the patient.
False-positive tests may appear if a person has:
- diabetes;
- alcohol or drug intoxication;
- measles, mononucleosis, hepatitis;
- heart diseases;
- tumor of any type;
- pregnancy;
- autoimmune disease.
Most types of tests can detect the presence of the disease, but only if it has reached a certain stage of development. For example, RW will show the presence of infection with 100% probability, but only a month after the pathogen enters the body. Tertiary syphilis appears in RW results with a probability of up to 75%.
It is more appropriate to diagnose early stages through ELISA tests. If a person has no other diseases, its reliability tends to 96%.
A negative reading may indicate the absence of disease. A questionable result is a reason to prescribe a repeat examination. If a patient has antibodies to syphilis, this is not a reason to panic - qualified and timely treatment can cope with the disease, if present, without any dangerous consequences.