Many patients in dental clinics are already well acquainted with orthopantomography - a diagnostic radiographic examination that allows one to assess the condition of the dental system. A panoramic digital dental photograph is taken by rotating two x-ray-emitting and x-ray-receiving plates in opposite directions around a person's head. In this case, a flat panoramic image of both jaws is obtained on film or on a computer monitor.
What is OPTG?
What is a dental panoramic photograph (OPTG)? The abbreviation stands for orthopantomogram of the jaws. This type of diagnostic measure simultaneously scans the upper and lower jaw, producing a detailed image.
Orthopantomogram radiodiagnosis visualizes the condition of hard and soft tissues, the maxillary sinus, the temporal region, as well as the mandibular region. Thanks to this, the dentist and otolaryngologist see the full picture of the patient’s health condition, they determine the diagnosis and draw up an adequate treatment regimen.
An orthopantomogram is performed using digital equipment; the results are printed on photographic film, saved on a medium or sent by e-mail to the patient.
Digital radiography of the dentition is a comprehensive study that identifies pathologies at the initial stage of development.
An orthopantomogram visualizes:
- hidden carious cavities;
- carious lesions of the root part of the tooth;
- focal growths, tumors, cysts;
- condition of the tissues surrounding the tooth (periodontal);
- root canals, quality of their filling;
- pathologies of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses;
- damage of various etiologies and atrophic processes;
- development and condition of molars in children;
- signs of pericoronitis during the eruption of the third molar (wisdom tooth);
- pathologies of congenital and acquired nature.
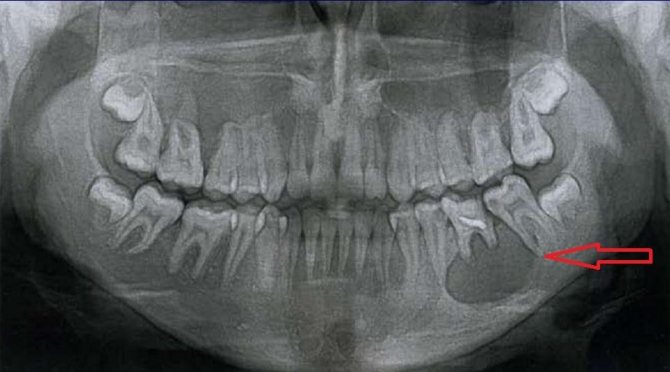
Extensive radicular cyst
Dental X-ray: types of images, harm, contraindications
One of the traditional and very popular diagnostic methods in the dental industry is x-ray examination. What can be seen on a dental x-ray? A dental photograph allows you to determine the degree of damage to hard tissues, identify hidden caries, assess the quality of previously performed dental treatment, and also timely diagnose foci of inflammation in the periodontium.
X-ray images allow you to clearly demonstrate not only the condition of bone tissue, but also identify many negative changes. This is extremely important for making an accurate diagnosis and determining the appropriate treatment regimen.
If earlier outdated X-ray machines were used, now they have been replaced by more modern radiovisiographs, which have a number of advantages:
- Minimal exposure.
- Fast examination.
- Receiving results on the day of the examination, which is very important for timely diagnosis.
Content
- Are x-rays harmful?
- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications
- Are dental x-rays harmful during pregnancy?
- What can be seen on a tooth image during an X-ray examination?
- Main types of dental x-rays
- What does a panoramic dental photograph provide?
- Using Contrast
- Preparation for the procedure
- How is a dental x-ray done?
- Decoding the received data
- Why do dental x-rays take place?
- How often can children’s teeth be x-rayed without harming their health?
- Orthopantomogram or CT?
- Where can I do it?
Are x-rays harmful?
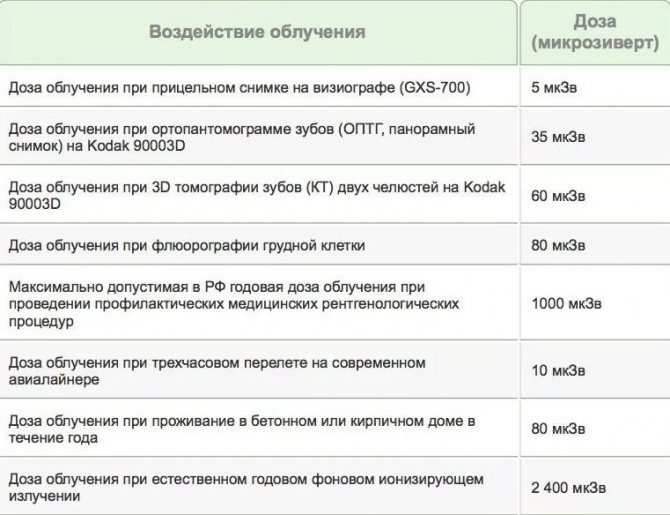
Many patients in dental clinics ask the question: is it harmful to their health to take dental x-rays? According to SanPiN standards, the permissible level of gamma ray radiation is 1000 microsieverts (µSv) per year. A feature of modern X-ray examinations is the fact that the exposure time of the device is reduced to a minimum, so the radiation dose is insignificant.
As for specific numbers, one procedure using a digital radiovisiograph is equivalent to 2 microsieverts. As for research using film, the dose is 10 microsieverts.
When answering the question of how harmful dental x-rays are, it should be noted that the frequency of examination is determined by the attending physician. On average, you can take about 100 photos over the course of a calendar year. It is obvious that even in a complex clinical case, such a number of x-ray examinations will not be needed.
Indications for the procedure
X-ray examination of teeth is an extremely important procedure, which allows specialists to determine the exact diagnosis of the patient, as well as determine the sequence of further actions. In the treatment of many diseases, this is the first step towards recovery.
This examination is based on gamma radiation. X-rays pass through organic tissue, resulting in an image. The image is obtained based on the ability of certain body structures to absorb this radiation.
Why are dental x-rays taken? With their help, you can diagnose the following pathologies:
- Periodontitis.
- Abscess.
- Periodontitis.
- Hidden caries.
- Developmental anomalies of the TMJ.
- Cysts and other neoplasms.
Identification of pathologies is not the only indication for this study. X-rays are also required in the following cases:
- Treatment of dental canals.
- Before installing implants.
- After tooth resection.
- Prosthetics.
Contraindications
The radiation dose during an X-ray examination is minimal. But this does not mean that this procedure can be carried out without any restrictions.
The main contraindications include:
- Pregnancy
- Problems with low immunity
- Mental disorders
- Bleeding
Are dental x-rays harmful during pregnancy?
The issue of performing x-rays in pregnant women is quite acute. According to the same SanPiN standards, this procedure is possible even if the woman is “in pregnancy.” The difficulty is that it is impossible to determine the exact effect of radiation on the structure of the fetus, so there are certain limitations.
X-rays are prohibited in the early stages of pregnancy (first trimester), i.e. at a time when the fetus is just beginning to form, so it is susceptible to the negative effects of gamma rays. If we talk about the 2nd and 3rd trimester, then pregnant women can take an X-ray of the tooth, but this procedure should be carried out only in extreme necessity, when other research methods are impossible.
What can be seen on a tooth image during an X-ray examination?
This procedure is considered a fairly informative diagnostic method, allowing to identify up to 90% of all pathological processes. So what does a dental x-ray show? The following changes can be seen in the picture:
- Inflammatory process.
- Atrophy.
- New developments in this area.
- Initial signs indicating the development of caries.
An X-ray also allows you to get a detailed picture and evaluate the quality of the dental canal filling procedure.
Main types of dental x-rays
X-ray is a fairly broad concept that includes a number of diagnostic procedures using various types of equipment. Widely used in dentistry:
- Extraoral radiography.
- Intraoral.
- Electroradiography.
- CT.
- Teleroentgenogram (TRG).
- Orthopantomogram (OPTG).
- X-ray procedure using a contrast agent.
Extraoral radiography
This type of study is carried out if intraoral radiography is impossible for some reason. This may be lockjaw or the patient's gag reflex. The disadvantage of this method is the insufficient accuracy of imaging oral tissues.
Intraoral (bite) examination
This type of examination is carried out using a special film (5x6 or 6x8 cm), which the patient must press between the teeth.
During the procedure you cannot move, and you also need to hold your breath. Otherwise, the image may not be clear. However, this recommendation applies to all types of photographs.
Electroradiography
This study differs from a traditional x-ray in the following features:
- The image is clearer and more informative, so even the slightest nuances are noticeable.
- It is possible to determine the density, condition and volume of periodontal tissues.
- Using these images, you can more accurately diagnose areas of hemorrhage, cysts and other formations.
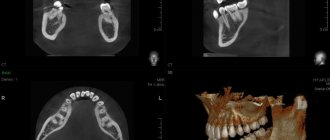
CT scan
This study is carried out using a special device - a tomograph. This method is based on taking a three-dimensional image (3D visualization effect) in digital format.
The main advantage of this method is its high information content, because in the image it is possible to reproduce the projection of the jaw in a three-dimensional version. A specialist can easily examine the condition of bone tissue and assess the extent of diseases and pathological processes. The exposure to radiation is negligible due to the short duration of the procedure.
During operation of the tomograph, the image is immediately transmitted to the monitor screen. The result of the study can be easily recorded on digital media for further provision to dental clinics.
Teleroentgenogram (TRG)
This type of diagnosis allows you to examine not only the jaw structure, but also obtain a photograph of the entire skull in front and profile. It is one of the most informative diagnostic procedures in dentistry.
TRG is mandatory before installing braces, and is also widely used before upcoming operations as a preparatory measure.
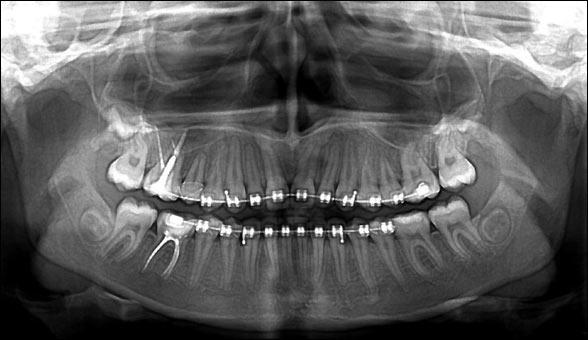
Orthopantomogram (OPTG)
This is one type of research that is in sufficient demand. Using this technique, it is possible to obtain images of absolutely all jaws and teeth.
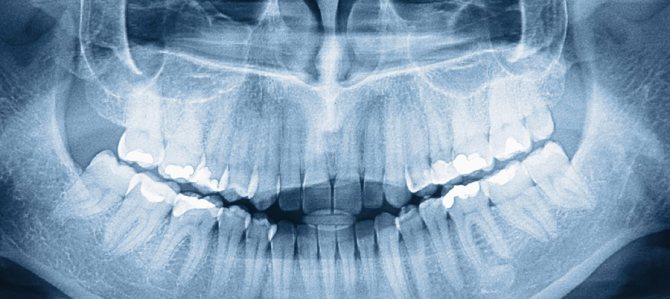
What does a panoramic dental photograph provide?
The resulting image gives the specialist the following information:
- The presence of fibroids and other neoplasms.
- Hidden caries.
- Identify unerupted teeth and their exact position.
- Identify bone diseases.
Other indications for OPTG include an upcoming implantation procedure, planned surgery, and other complex procedures.
Using Contrast
The use of X-rays with a contrast agent (sialography) is indicated if it is necessary to assess the condition of the ducts of the salivary glands. Before the procedure, they are filled with iodine-containing compounds. This type of diagnosis allows you to identify a number of pathologies: salivary stone disease, inflammatory foci and the presence of stones.
Preparation for the procedure
No special preparation is required for the upcoming procedure. If your doctor prescribed this examination, it means that you have no contraindications or restrictions. Therefore, preparation only boils down to the fact that you will need to remove all metal objects from yourself, and also put on a special protective vest.
How is a dental x-ray done?
Answering the question of how dental x-rays are taken in dentistry, it should be noted that the procedure depends on its specificity and type. In general, the examination takes no more than 5 minutes, and the radiation itself lasts only a few seconds.
In our diagnostic X-ray center you can take the following types of images:
- 3D (CT) Digital
- 2D (OTPG) Panoramic
- 2D (TRG) Teleradiogram
- 2D (TMJ) Sonogram
Bite shot
This type of research is considered traditional, without losing its relevance to this day. With its help, you can examine several elements of the dentition at once.
The patient heals a special film between the teeth, after which the procedure itself is carried out. Using a bitewing X-ray, you can determine the feasibility of correcting your bite and identify tartar and caries.
Panoramic
If you have been prescribed an x-ray of all teeth at the same time, many may have a question - what is this procedure called? This refers to a panoramic image that is taken using an orthopantomogram.
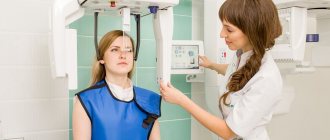
Before the examination, the patient's head must be securely fixed, because any movement can make the image unclear. After this preparation, the procedure begins: a special apparatus rotates around the head (there is a film on one side of the device, and a tube on the other).
If we talk about how often an orthopantomogram of teeth can be taken, then up to 10 panoramic images per year are permissible, and when using modern equipment, many times more.
Digital (3D)
The resulting digital image is highly detailed. The patient's head is also fixed, after which the tomograph rotates around it. Scanning occurs in three planes, and the image is immediately displayed on the monitor screen.
Decoding the received data
The most important stage of the entire process is the interpretation of the image that was obtained during the study. Healthy tissues of the gums and teeth in the picture are colored gray, fillings and implants will be a characteristic white color. But what does a dental cyst and other neoplasms look like on an X-ray? It is quite easy to see it, because it will appear as a dark area with clear contours (round or oblong shape).
Why do dental x-rays take place?
This question does not sound entirely correct, because this type of research is the main diagnostic tool in many medical fields, including dentistry.
X-ray examination reveals the following complications:
- Cysts and other neoplasms.
- Inflammation characteristic of periodontium.
- Tooth cracks.
- Overhanging fillings.
- Hidden caries.
- Allows you to identify the location of wisdom teeth.
It is also advisable to take an x-ray if dental treatment has already been carried out, but the dentist needs to make sure there are no complications. Bite correction is also necessarily accompanied by x-rays at all stages of this process.
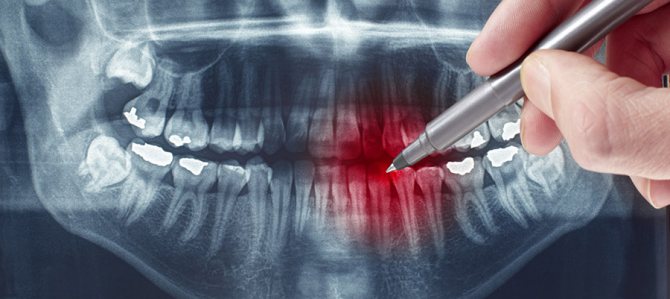
How often can children’s teeth be x-rayed without harming their health?
Exposure to X-rays, one way or another, negatively affects the cells of the human body. The point is only in the dosage of this radiation and the frequency of procedures.
If in the fetus in the womb and a newborn baby the most susceptible organ is the brain, then in children from 3 to 12 years old it is the skeletal system. If the radiation dose is exceeded, there is a risk of slowing bone growth.
Under normal circumstances, any X-ray examination should not be performed on children under 7 years of age. But there are cases when the danger of the disease is much higher than the potential harm from exposure to gamma rays. In this case, an x-ray is a mandatory procedure.
As for frequency, the standard option is only 2 examinations per year. In this case, the radiation dose will be minimal.
Orthopantomogram or CT?
First you need to answer the question - what is the difference between a panoramic dental image and a CT scan? Using OPTG, you can only make 2D images, which are quite accurate, but miss a number of information due to the plane of the resulting image.
Therefore, from the point of view of greater information content, a 3D image using CT will be most preferable. Using a three-dimensional image, you can examine the structure of tissues from different sides, in any section and at any angle. Another advantage is the ability to construct a panoramic orthopantomogram image.
Where can I do it?
If you need to undergo an X-ray examination, then you can use diagnostic services. We have all the necessary equipment to take high quality and detailed images with safety for your health and the health of your children.
To make an appointment, you need to leave an online application on our website, or call our contact phone number.
Sign up for a study by phone
(812) 332-52-54
Indications for prescribing a panoramic image
Panoramic scanning has extensive readings. Diagnosis provides detailed information regarding oral diseases, which helps in treatment.
An orthopantomogram is part of the diagnosis of the dentition before prosthetics. This allows the specialist to assess the condition of the bone tissue, the position of the teeth, and the presence of pathological changes. Using the image, the option of the prosthesis and the pin are selected.
OPTG has the following indications:
- deep damage to periodontal tissue (reveals a group of pathologies);
- the presence of neoplasms of unknown etiology, for the purpose of clarification;
- odontogenic periostitis on the gums (flux);
- during injury to the jaw area.
The photo is taken before root removal to avoid the development of complications, as well as before installing a brace system. A scan is recommended before tooth extraction to evaluate the root system, especially for the figure eight.
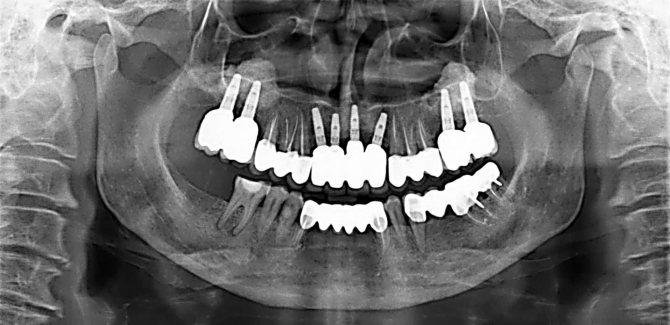
When is a panoramic x-ray needed?
Dentists ask patients to do an orthopantomogram in the following cases:
- An orthopantomogram should be performed if the patient intends to correct the bite and install braces.
- A panoramic photograph is necessary if the patient requires treatment with aligners.
- During the period of preparing teeth for implantation and prosthetics, OPTG helps to see whether there is enough bone tissue for the procedure, whether a sinus lift is required, how many implants and what sizes will need to be used, and whether the healing process will be difficult.
- After analyzing the OPTG, the doctor can decide whether to remove the wisdom tooth or carry out treatment. The picture shows the position of the eights and their condition.
- Before any surgical intervention in the oral cavity, it is necessary to take an x-ray.
- An orthopantomogram is prescribed for children to monitor the growth of permanent teeth. It helps to identify pathology, malocclusion, and inflammation of soft tissues in a timely manner.
Stages of diagnostics
A panoramic photograph is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure, completely painless, and does not take much time. The average duration of the manipulation is 30-40 seconds, and after 5-10 minutes the finished image is obtained.
Scanning is carried out in stages:
- Metal jewelry and items should be removed.
- The patient is taken inside the orthopantomograph and helped to put on a protective apron.
- A special plate is clamped between the teeth, while the lips are closed.
- You need to stand quietly in the position chosen by the doctor.
- The device makes a circular motion around the head for 40 seconds. You can receive a finished photo with a description of the result after 10 minutes.
Digital or film orthopantomogram: what to choose?
Digital equipment today has practically replaced film analogues from practice. Although they cost clinics more, they do not require the costs of consumables and darkroom equipment.
In addition, film devices are characterized by a higher degree of radiation.
A panoramic image taken digitally is instantly transferred to the doctor’s computer and entered into the patient’s electronic record. If desired, the latter can receive the image on disk or in printed form.
Finally, the image quality with digital equipment is much higher than with film equipment. This means that the specialist receives better information for further work.
Advantages and disadvantages of panoramic scanning
Many experts say that survey radiography of the jaws has more advantages than disadvantages. The diagnostic results are accurate and help to fully assess the condition of the dental system.
Positive sides:
- Research safety. The radiation exposure received during panoramic radiography is 0.02-0.03 mSV, which is significantly less than during standard fluorography. This helps to carry out the diagnosis several times, including for the elderly and children.
- Speed of implementation. The scanning duration is less than a minute. After 5-10 minutes, the results are delivered to your hand, sent by email or saved to a digital medium.
- High quality image. Panoramic images have high resolution, help to see the pathological process in the early stages of development and prevent further progression.
- Technical sophistication. The device has various control modes, which helps to study adult patients and children with disabilities.
- Information content. The scan affects the deep layers of tissue, the doctor receives a complete and three-dimensional picture of the condition of the oral cavity.
Among the disadvantages of the diagnostic method, the following are noted:
- In small towns or urban villages the service is not always offered. In megacities, it is not difficult to undergo the examination; in Moscow, more than 15 medical centers offer panoramic scanning.
- The procedure is not recommended during pregnancy. During lactation, you should be examined only as prescribed by a doctor.
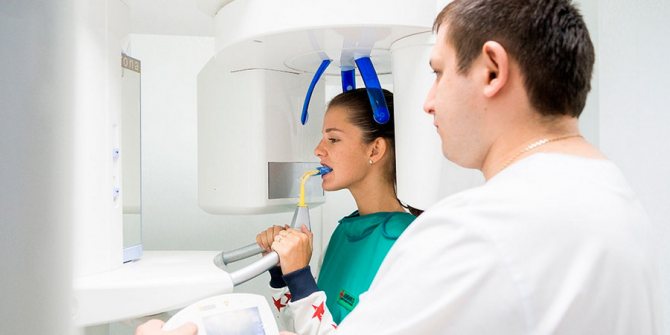
How the research is carried out
The description of the procedure itself is very simple. All manipulations, from completing the examination to obtaining informative images, will not take you more than 15 minutes. The procedure is performed using an orthopantomograph. This device assumes that the patient is in a standing position, and to take pictures, a special plastic stick is first placed in his mouth, which must be pressed tightly with his lips.
Beforehand, you will definitely be asked to put on a lead protective apron and remove all jewelry (earrings, rings), and you will be warned not to move or tilt your head during the examination. After the specialist checks that you are in the correct position, he will turn on the computer program and start the device. Next, a digital sensor will begin to rotate around your head, producing X-rays. Within one minute after this you can be free, but the doctor will need about 10 more minutes to process the data and save it or transfer it to one of the types of media: photo paper, disk, flash card.
When diagnostics are not recommended
Diagnostics are carried out using the latest devices, providing high information content and low radiation exposure. Orthopantomography of teeth has few contraindications:
- Pregnancy period, first trimester. The need for diagnostics is agreed with the gynecologist.
- Breast-feeding. Lactation is not a contraindication, but requires prior consultation with a doctor.
- Children under 3 years old. The study is carried out only after consultation with a pediatrician.
Information content of the image and reading (deciphering) technique
If you undergo an examination at a specialized diagnostic institution, the finished image is usually accompanied by an explanation from a specialist with a list of detected problems. Many people are interested in how to decipher an image on their own, how to read it correctly, and whether it can be understood at all. It should be noted here that in order to correctly explain the results of OPTG, you need to have a good understanding of the anatomy of the maxillofacial apparatus, and without the appropriate education, little can be understood. It is better to entrust this task to an experienced, qualified doctor.
Carrying out panoramic scanning for children
OPTG is rarely prescribed to children, although it is an informative method for studying the dental system.
Diagnostics studies in detail the formation of molars, evaluates the correctness of the bite, the structure of the jaw, and identifies the first problems. Taking a panoramic photo is a mandatory procedure before installing a brace system.
The equipment for OPTG contains a small dose of radiation, but before performing it you will need to consult a pediatrician.
What are the disadvantages of OPTG?
The advantages of this research method are known to everyone: panoramic images make it possible to improve the quality of the doctor’s work and eliminate the risk of errors at any stage of treatment, and to detect a hidden problem in time. But few people talk about the shortcomings, although it’s worth saying a few words about it:
- two-dimensional images: progress does not stand still; research methods have been invented that make it possible to obtain three-dimensional images that are more informative. And the OPTG, for all its advantages, is flat and does not always accurately transmit data,
- the picture does not accurately convey the dimensions: the distortion, depending on the brands of devices used, can range from 15 to 30%,
- the study is not entirely suitable for determining the condition of three-rooted teeth: these include sixes, sevens and eights. The thing is that orthopantomographs reproduce the image in only one section, and the roots of such teeth are in different planes.
On a note! Some doctors call OPTG an approximate research method, because... it shows only a general picture of the dental system, but gives very little information about small processes (for example, it will not be possible to see a perforation or a crack in the root; it will also be difficult to adequately treat curved root canals).
Diagnostic cost
In modern dental clinics, panoramic scanning is performed both before and after surgery. In the first case, you should carefully study the structure of the jaw and identify pathologies, which will allow you to choose the appropriate treatment option. In the second, the need is related to postoperative monitoring - how effective the therapy turned out to be.
The pricing policy for diagnostics is low, but it is necessary to take into account the quality of the equipment, the status of the medical center, and the qualifications of the doctor. A panoramic photo will cost 900-1200 rubles.
Today, panoramic photography is an indispensable method for studying the condition of teeth and periodontal tissues. An orthopantomogram helps to detect the first signs of pathology. Thanks to the image, a further in-depth study is built and treatment tactics are determined.
Bottom line
To properly treat teeth, you need to have an idea of the condition of the jaw and skeletal system. This information can be provided by an x-ray, which is taken with a special orthopantomograph or computed tomograph. The picture is taken in every private clinic and government institutions. The cost depends on the equipment and tariffs of private clinics. In a government institution, you can get an X-ray done free of charge upon referral or for a small fee of 300 rubles.
Orthopantomography is a panoramic image of both jaws in a section in a two-dimensional plane. The absence of a three-dimensional image is a common reason for an incorrect diagnosis. Also, a two-dimensional image does not allow one to see microcracks on the roots of teeth, and in three-rooted teeth only 2 roots are visible. The listed disadvantages speak in favor of computed tomography, although it costs several times more.
Panoramic diagnostics are recommended not only during dental treatment and implantation: it must be performed annually for preventive purposes. This will allow timely detection of hidden caries, internal foci of inflammation, cysts, tumors, and neoplasms.
Sources used:
- Abolmasov N. G., Abolmasov N. N. Orthodontics. – 2008.
- American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID)
- Distel V. A. Dental anomalies and deformations. Omsk — 2004.
- “Orthopedic dentistry. Textbook" (Trezubov V.N.)
Procedure for conducting OPTG
OPTG is performed in a specially equipped X-ray room. The procedure consists of a number of stages.
- The patient removes all jewelry (pendants, chains, piercings, earrings, etc.) and removable dentures. The doctor helps him put on a special apron that protects his internal organs from X-ray radiation.
- The patient stands in front of the orthopantomograph and places his chin in a special niche, lowers his shoulders, and straightens his neck. The doctor fixes his head in the correct position using parietal and frontal clamps.
- The doctor turns on the orthopantomograph and an X-ray tube begins to rotate around the head of the person undergoing examination, taking pictures in various projections. A device mounted opposite this tube accumulates x-ray data and transmits it to a computer screen.
- The doctor interprets the orthopantomogram, prints the image or saves it in digital form on a medium.
The total duration of the procedure does not exceed a minute.
Advantages of an orthopantomogram
An orthopantomogram (abbreviated as OPTG) is a diagnosis of two jaws with their surrounding soft tissues and bone structure. A correctly taken photograph will give the dentist reliable information about the structure of the dentofacial apparatus.
The doctor can examine only about 50-55% of the patient’s oral tissues visually, the remaining 45-50% remain without examination. Even a professional in his field cannot do without orthopantomographic x-rays.
Content:
- Advantages of an orthopantomogram
- Indications for orthopantomography
- Pros and cons of dental x-ray examination
- Stages of the study
The finished image can be printed on paper, special X-ray film, transferred to electronic media, or analyzed from a computer monitor. All images are saved in the computer’s memory, so the doctor can open the image at any time and look at the results.
An orthopantomogram of teeth helps to determine: caries on the surfaces and roots of teeth, the condition of the maxillary sinuses, the presence of impacted teeth (completely not erupted from the gums or partially erupted), neoplasms and pathologies of the jaw bones, at what stage of teething are children’s teeth, the general condition of periodontal tissues and interdental septa, the presence of granulomas, perihilar abnormal changes and cysts.
One of the modern and effective types of orthopantomography is 3D tomography (obtaining three-dimensional images of teeth and nearby tissues). Using tomography, you can examine a person’s jaw in real time, since the images taken are displayed on a computer monitor in different projections (the specific area under study is studied layer by layer).