What is CT of teeth, differences from MRI
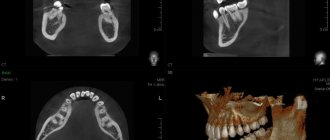
Three-dimensional x-ray examination of teeth is a method of x-ray examination that allows you to obtain a high-quality image of the soft tissues of the face and teeth in high resolution. This technique, compared to two-dimensional ones, improves the quality of diagnosis, often allowing one to avoid many errors in the treatment process.
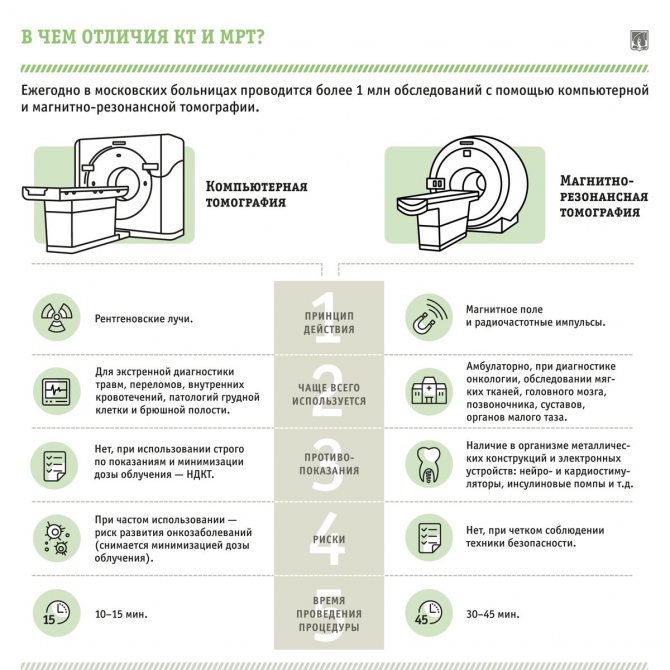
While conducting the examination, the dentist has the opportunity to observe the condition of the patient’s jaws on the screen, examining the image in different projections. Moreover, the accuracy of such diagnostics largely depends on the equipment used. CT (kate) is more suitable for assessing the condition of hard tissues, which distinguishes it from MRI, which allows viewing soft tissues.
Advantages of the method
- The ability to rotate, enlarge, and examine images in any projection and section, which is impossible with conventional 2-dimensional scanning.
- The examination lasts only a few seconds (8-20 seconds).
- Complete diagnostic information.
- Maximum security.
- Digital information format.
- Detection of any pathological processes at an early stage.
- No prior preparation required.
- 3D reconstruction without distortion or artifacts.
- A wide range of purposes - from endodontic dental treatment and implantation to maxillofacial operations.
Indications and contraindications
CT involves x-ray radiation, but dentistry uses safe devices, which makes this procedure harmless when performed once. However, its implementation has its own indications and contraindications.
In what cases is 3D tomography of teeth prescribed in dentistry:
- search for defects in the root part of the tooth - perforations and cracks;
- identification of instruments in the root canal that were accidentally left in it during endodontic treatment;
- diagnosis of pathologies of the temporomandibular joint;
- identification of benign and malignant neoplasms in the jaw area;
- preparation for endodontic treatment;
- diagnosis of disease of the maxillary sinuses;
- comprehensive orthodontic diagnostics.
A CT scan of the upper jaw, as well as the lower jaw, must be performed during preparation for prosthetics and implantation. The study is also important if it is necessary to augment bone tissue and perform surgery in the facial area.
Contraindications to computed tomography in dentistry are standard. There are no absolute restrictions for CT, but it is prohibited to perform it at any stage of pregnancy. The presence of metal structures in the patient’s body will also be a contraindication.
Indications for this type of examination
A 3D image for dental examination is used in the diagnosis of complex injuries and diseases of the jaw. Indications for prescribing computed tomography include:
- incorrect position of the tooth in the gum;
- neoplasms in the maxillary sinuses or jaw;
- extensive inflammatory process;
- malocclusion;
- disorders of motor functions of the mandibular joint;
- difficulties with implantation and prosthetics;
- fractures of the lower jaw;
- diagnosis of caries complications;
- planning orthopedic treatment and evaluating its results;
- planning cephalometric changes;
- diagnosis of periodontitis.
Main contraindications
3D computed tomography of teeth is based on x-rays, so this procedure cannot be called completely safe. The radiation exposure during this examination ranges from 0.045 to 0.06 mSv. This is not a very high figure, given that the annual exposure limit is 5 mSv (according to the Russian Ministry of Health).
As for contraindications, they are standard for all types of x-ray examinations. The main limitation is the period of pregnancy (especially in the first trimester). In this case, the situation is considered individually, based on the ratio of harm to the child and benefit to the mother.
If a contrast agent is used (it is not used so often in CT scans of the teeth and jaw), then the following can be added to the contraindications:
- Patients suffering from thyroid diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Allergy to drugs containing iodine.
The lactation period is not a contraindication, but after the procedure at least 48 hours must pass before the next breastfeeding.
Can this be done for children?
Many parents think that the use of 3D computed tomography is impossible in childhood due to the negative impact on the child’s body. This is not entirely true, because special attention to this study is given specifically in pediatrics.
If you follow all safety rules and do not exceed the frequency of procedures (for children – once a year), then the examination will not lead to any pathological changes in the child’s body.
3D CT in pediatric dentistry allows you to assess the condition of the sinuses, gums and see the rudiments of baby teeth. This method also allows you to identify malocclusion pathologies in a child.
How to prepare for research
No special preparation is required for the study. Before the procedure, the dentist asks you to remove jewelry and remove various objects that may interfere with the scan. If there are orthopedic structures with metal elements in the mouth, they will have to be removed.
Expert opinion
Ravcheeva Yulia Anatolyevna
General dentist
Before the procedure, it is important to notify the doctor about previous orthopedic treatment and tell whether there are metal crowns or other structures in the mouth. This is necessary so that the specialist can change the device settings to obtain an accurate result.
Before the procedure itself, the radiologist puts a special apron on the patient that covers the chest and abdomen. An important aspect of the research will be who conducts it. It is possible that in clinics a regular nurse works instead of a radiologist, so it would be a good idea to ask the specialist for a certificate of advanced training in the field of radiography.
Features of the use of CTCL in dentistry
In dental practice, cone beam tomography of the jaw is used to solve complex problems:
- removal of roots or “figure eights”;
- removal of a foreign body, fragment;
- canal inspection;
- exclusion of jaw neoplasms;
- detection of bone tissue destruction;
- assessment of periapical dentin tissues of teeth;
- detection of anomalies and birth defects;
- preparation for implant installation.
The examination remains the only diagnostics in dentistry that allows one to correctly assess the position of the canals, the condition of the pulp, and the presence of nerve endings. This is an important part of the examination before complex operations on the periosteum and implantation of an osteoprosthesis.
Due to its high effectiveness, the risk of metal pin rejection and other complications is reduced several times. Advantages of CBCT of the jaw over other techniques:
- Comfort for the patient, absence of unpleasant sensations, which is important for people who are afraid to go to the dentist.
- Minimum time spent on a quality examination, which reduces the number of visits to the dental office.
- To examine dental canals, the use of CBCT is the only way to measure the length. It is easier for the doctor to choose the ideal shape of a filling or pin.
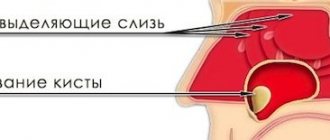
In addition to studying the condition of teeth and bones, CBCT allows you to examine soft tissues. This helps to timely detect a cyst in the root of a molar, a fistula or an oncological tumor in the oral cavity, and select therapeutic agents. The data obtained is subsequently used in preparing the operation. Dentists can create a visual model and show the patient what the face will look like after all the procedures, and make sure that the crowns are in the optimal shape.
Study radiation dose
Many people naturally ask what is the radiation dose of cone beam computed tomography. This research method has a much lower x-ray load than when examining with spiral tomography. This is due to the high rotation speed of the tube. However, you should not prescribe this diagnosis yourself, since only a doctor can assess the actual need for it.
In addition, the following factors should be taken into account:
- Conducting conventional fluorography gives an exposure of 0.18 mSv;
- from the natural background of the Earth, each person receives radiation of about 1000 μSv;
- The maximum permissible dose at which no significant changes occur in the human body is 5000 μSv.
Due to the short examination time, the radiation dose of cone-beam computed tomography is in the range of 40–120 mSv. If we examine the skull with spiral computed tomography, the radiation exposure will increase from 400 to 600 mSv. In addition, testing on a cone-beam tomograph allows one to exclude further examination using other diagnostic techniques, which results in a low total radiation exposure to the body of the person being examined.
Where is the research applied?
The operating principle of cone beam computed tomography is based on visualization of the examined area. This device is not only distinguished by the ability to obtain a three-dimensional model of the problem area, but also by its compactness and safety. Research on it began for the first time in the USA, then came to Europe.
Modern devices are equipped with a robotic arm that allows you to select the desired trajectory for the task of sensor movements. Basically, they allow examination to be carried out on a small area, but, if necessary, the gluing function is used to expand the volume.
This type of tomography is widely used to identify problems in the following areas of dental research:
- Therapeutic dentistry allows us to identify acute inflammatory processes not only of the teeth, but also of the soft tissues surrounding them. Used to study canals, recognize the area of tooth root destruction, and control therapy.
- Surgical dentistry allows you to determine the location of the inflammation, its size, and the location of bone collection for the implant. It is used to detect pathologies formed as a result of low-quality therapy, surgical intervention, and allows you to detect parts of the tooth remaining after extraction.
- In orthopedics, it allows you to accurately draw up a treatment plan, assess the condition of the supporting tooth, and promptly identify complications that have developed due to the installation of the structure.
- In orthodontics, it is used for planning, allowing you to make the right decision about the need to remove teeth that interfere with the installation of the prosthesis.
The use of cone beam computed tomography is widely known not only in dentistry, but also for solving problems:
- in implantology, it allows you to prepare the patient for implantation, assess the condition of the bones, and obtain accurate information about the place where the manipulation is supposed to be carried out;
- Maxillofacial surgery is used to assess bone injury, detect tumors, and treat inflammation;
- Otorhinolaryngology allows you to assess the condition of the nasal cavity and its sinuses, make the right decision on the advisability of operations, monitor and adjust treatment.
This is interesting: The recovery period after tooth extraction: common problems, tips and recommendations
These directions have a small scanning area, usually assessing the conditions of the jaw bones, nasal septum, soft and bone tissues of the skull. Most often, this method is used to diagnose congenital pathologies of the palate, select implants, study diseases of the nasal sinuses, and abnormal positions of teeth, when other methods do not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Limitations of the study
Although the cone beam computed tomography method is considered an innovation that allows you to accurately determine the condition of the area under study, it must be borne in mind that it belongs to the category of radiation techniques and therefore requires some caution. First of all, it is prescribed in a limited manner:
- for children under 5 years of age. For this category of the population, this research method can be prescribed only if there are vital indications;
- persons suffering from renal failure;
- people who cannot remain still for 2–3 minutes;
- patients who have pronounced pain syndrome;
- pregnant women.
During pregnancy, any tomography or radiography is contraindicated. The only exception is a vital need to obtain urgent medical care, provided that the benefit from the examination for the mother is lower than the expected risk to the fetus. You should also talk to your doctor about preparing yourself to reduce the risk of harmful effects from x-rays.
Carrying out the procedure in the third or second trimester reduces the likelihood of developing pathologies in the fetus. Cone beam tomography requires the appointment of a doctor who can adequately assess all the risks to the body from this study.
Children's Study
There are cases where it is necessary to conduct this study for young children. Of course, a child’s body is more sensitive to radiation, but if there are serious indications, diagnosis should not be abandoned. If the child does not have an absolute contraindication to the study, then this method can be used even for babies in their first year of life.
Such restrictions include:
- birth injury;
- congenital anomalies;
- allergic reactions to drugs used to give anesthesia;
- heart disease.
Older children tolerate this examination quite easily
Before children are examined, they should not be fed for 2.5 hours before the intended procedure, otherwise aspiration pneumonia may form. When at the time of the study the child is already 4 years old, you should talk to him. At the same time, try to explain the procedure, be sure to emphasize that mom and dad will be nearby at all times.
For younger children, the examination is performed under anesthesia. Moreover, during the diagnosis, parents can be with the baby and wear lead aprons for protection.
Description of the diagnostic procedure
To understand how computed tomography is done, it is worth considering a step-by-step description of the process:
- immediately before the procedure, the specialist will ask you to remove all metal jewelry to avoid equipment malfunctions,
- then the patient puts on a special protective vest to reduce the degree of radiation exposure to the body as a whole,
- the patient stands or sits with his back to the device, and his chin is fixed using a special stand - this is necessary to eliminate unnecessary movements and get the most accurate image possible,
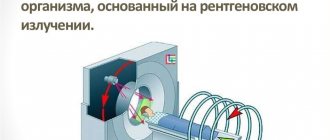
- after turning on the device, a scanner with an emitting tube begins to rotate around the patient’s head - it is this that transmits the three-dimensional image to the computer.
The photo shows a tomography being performed
The procedure lasts less than a minute. The diagnosis is completely painless and does not require any serious preparation from the patient.
Carrying out tomography
During a dental scan, the patient can stand or lie down, depending on the equipment used. The mouth can be either open or closed. While the machine is operating, the X-ray detector will rotate around the area being examined, and you must remain stationary during this time. It takes no more than 50 seconds when scanning the entire jaw and about 10 seconds when obtaining images of several teeth.
In a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan of the mandible (and maxilla), the machine rotates around the head. One revolution produces up to 200 2D images, which are then combined into a 3D image.
How does the procedure and decoding work?
To take a 3D photograph of teeth, a standing or sitting patient needs to bite a special plate and fix his position in the device using a fixing stand. During the entire scanning time, you must remain absolutely still.
The tomograph sensor makes a series of revolutions around the patient’s head for 8-20 seconds, producing about 200 images in different projections. Processing digital data takes 5-15 minutes, after which the information is written to a disk or flash drive. No preparation is required, you just need to remove all metal jewelry from your neck, ears, and hair before the procedure.
What does the photo look like?
The data obtained during the survey takes the form of multiple projections. To create a three-dimensional model, a computer program assembles them into a separate whole. If further diagnostics take place in an office equipped with computer equipment, the doctor opens the image in electronic form from a digital media. The latter is given to the patient after the tomography. To get a more complete picture of the problem, the dentist can rotate the model, finding the area of interest, and also display the corresponding projection of the teeth on the screen. You can enlarge small elements, create slices, take the necessary measurements and other operations online.
The doctor may request a printed photograph of a three-dimensional model of the jaw. In this case, the patient is given an image in the format 8x5 or 5x5 cm. Up to a dozen main projections and sections are imprinted on them. This option is considered less convenient for diagnostics and is used mainly in offices that are not equipped with computer equipment.
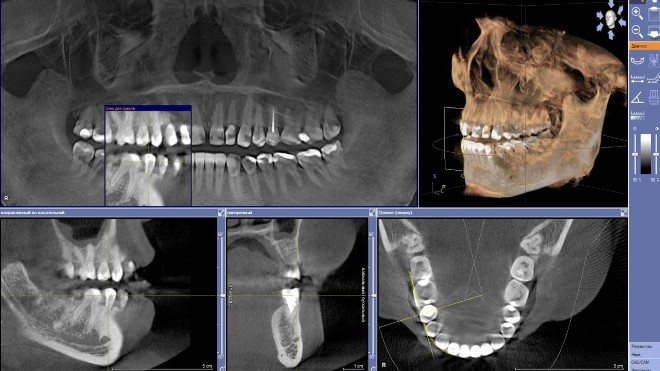
What You Can Find
3D dental X-ray provides the opportunity to obtain the following information:
- visualization of the condition of teeth and gums in a three-dimensional model;
- the presence and size of foci of pathologies;
- the effectiveness of treatment or surgery;
- location, nature and size of neoplasms, cysts and other tumors;
- determination of the main parameters of the jaw and its geometry;
- graphic recording of the location of nerves;
- counting the amount of bone tissue.
This is interesting: Favorable days for dental treatment and prosthetics in [year] year according to the lunar calendar
Cost of the procedure
The price of the study is largely determined by the area being examined and the type of apparatus. The additional cost depends on the need to print the image or burn it to disk for further study by a radiologist.
Approximate prices for a 3D image of the jaw:
- up to 3 teeth - 1000−1300 rubles;
- one jaw on one side - up to 2500 rubles;
- both jaws - up to 4,000 rubles;
- paranasal sinuses - up to 3500 rubles;
- TMJ, both jaws, paranasal sinuses - about 5,000 rubles.
Additionally, you will have to pay for marking the image and printing it. The cost of this will depend on the number of teeth. The image with markings can now be sent to your doctor or any dental clinic to decide on further actions.
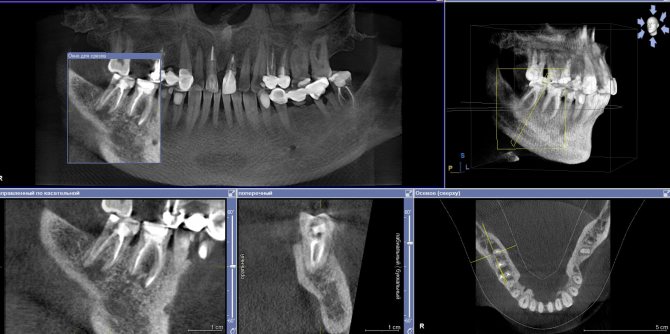
Final 3D image
What equipment is used
A computed tomography scan of teeth can be done using several types of devices. Some of them produce high radiation exposure, while others may produce low-quality images. Some can be used for frequent scanning, while others are dangerous for this. Before the study, you can check with each clinic what kind of equipment is used.
Type of CT in dentistry:
- Step-by-step CT. One of the first types of tomography. The device provides low image quality, and the radiation exposure per procedure is 1.5 times higher than the permissible annual dose.
- Multi-slice CT (MSCT). On such a tomograph, the load is much less and is about 350 μ3 V, and this value still remains dangerous. The clarity of bone structures will be lower than modern devices. Helical tomographs are better suited for scanning soft tissues, including lymph nodes, muscles and salivary glands.
- Cone beam CT (CBCT). A modern version of the study of the dental arch and soft tissues. Such a device provides high image quality while having a low radiation dose.
In modern tomographs, the radiation dose will depend on the body weight of the subject. Thus, for an adult, during a comprehensive examination, the radiation exposure will be about 55 μ3 V, and for children - no more than 15 μ3 V.
To view the resulting volumetric images, you need special programs installed on your PC. They contain various image processing tools. The quality of diagnostics, even on the most modern devices, will partly depend on the software used.
How long does it last?
The duration depends on the type of tomograph. The main recommendation in this matter is to inquire about the type of device before the study and choose a clinic with the most modern high-power device. Its advantages are not only a minimal radiation dose and high detail, but also a much shorter research time. By comparison, the duration of a scan can vary from a few seconds to 15 minutes.

Which is better - panoramic or 3D photography?
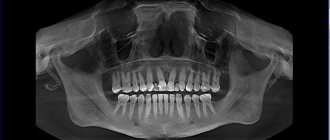
The difference between a CT scan and a standard orthopantomogram is the production of a three-dimensional image. This diagnostic option is more effective, but in some cases it is not necessary. An orthopantomogram can be analogue or digital. The latter is of higher quality, and pictures can be saved to various media. This procedure is also fast, as the entire scanning process takes a few seconds.
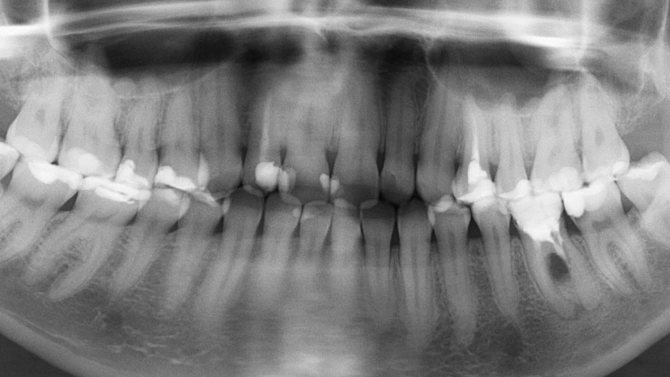
Standard orthopantomogram
Panoramic photography can be taken by everyone, including small children, but not often. Moreover, it is of paramount importance for the child, because it helps to visualize the dentition to prevent problems with bite and early diagnosis of diseases.