What is the difference between CT and MRI of the lungs? When is the procedure prescribed and how safe is it for diagnosing COVID-19?
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are diagnostic procedures that are often prescribed in the study of the bronchopulmonary system. They are used to clarify the diagnosis, as well as during treatment (CT of the lungs for pneumonia) to monitor changes in dynamics. Against the background of the COVID-19 epidemic, the importance of CT scans of the lungs has increased significantly - timely diagnosis helps to identify signs of pneumonia and clarify the extent of damage to the lung tissue. At the same time, it is important to understand what is better for examining the lungs: MRI or CT, in what cases they must be performed, and when there are contraindications.
| CT | MRI | |
| What are you examining? | Skeletal system, thyroid gland, stomach | Brain, oncology, muscles |
| Who is it contraindicated for? | Pregnant | If you have pins, staples, metal prostheses, or a pacemaker |
| How long will it take? | 5 minutes | 30 minutes |
| Are you afraid of confined spaces? | Don't be afraid, CT scans use an open machine | You will have to lie down in a closed “pipe” |
| Do you have a doctor's referral? | A must | It’s possible without it |
What is MRI of the lungs
Magnetic resonance imaging is a type of research in which the condition of internal organs is studied by exposure to a constant magnetic field and radio frequency radiation. This type of diagnostics allows you to study in detail the structure of tissues, including at the chemical level. In most cases, there is no need to administer a radiocontrast agent, which is important for patients who have an allergic reaction to it.
What does an MRI of the lungs show? Diagnostics makes it possible to distinguish soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves, but bone tissue is only indirectly visible in the images.
In this regard, MRI is prescribed in the following cases:
| Disease | The need to use contrast |
| Pneumonia | No |
| Cystic fibrosis | No |
| Tuberculosis | No |
| Pulmonary embolism | Yes |
| Focal formations larger than 3 mm | No |
| Pathologies of venous outflow | Yes |
| Pulmonary artery aneurysm | Yes |
| Vasculitis | Yes |
| Pleurisy with unspecified effusion | Yes |
For diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, CT and MRI of the lungs and bronchi are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis, which shows the result in this case:
- Thickening of the walls of the bronchi.
- Accumulation of fluid and mucus.
- The presence of tumors and metastases in the lungs.
- The presence of inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, empyema).
MRI may also be performed in pediatric patients, especially in those with equivocal CT findings, tumors, and cystic fibrosis.
Evgeniy Vasiliev, a radiologist of the highest category, chief expert at Dr. MC, tells the story. Spin :
What to pay attention to when making an appointment for an MRI
- Manufacturer of the MRI device: it is important that the device is not “made in China”, but of a well-known brand, for example Philips
- The power of the device must be at least 1 Tesla. Ideally – 1.5 Tesla
- Choose closed MRIs rather than open ones. Even though closed MRIs look scarier, make more noise and have a closed tube, still do MRIs for yourself and your loved ones only on closed machines! According to their principles of structure and operation, open MRI devices cannot be more powerful than 0.5 Tesla, and this is very important for effective research.
Magnetic resonance imaging is highly informative for cardiac pathologies. The heart is not a stone: 4 ways to examine it
- Electrocardiogram. Prescribed for arrhythmia, tachycardia, as well as for active sports.
- Holter monitoring. Threat of heart attack, heart rhythm disturbance.
- Echo KG. Congenital heart pathologies, murmurs, microinfarction. Diagnosis is necessary after heart surgery, in the presence of defects and tumors.
- MRI. Monitoring the condition during and after treatment, myocardial pathology. Problems with blood vessels (plaques, stenosis).
All of these types of studies are painless and safe, but they require prior consultation with a doctor.
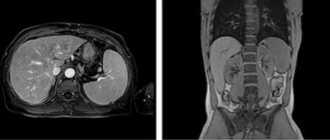
What is a CT scan of the lungs?
Computed tomography (CT) is a type of diagnosis based on the use of X-rays. Unlike conventional x-rays, it gives a more accurate picture - the device rotates around the patient and takes a certain number of pictures, which help to study sections of organs, tissues, and bones. The results are processed on a computer, and decoding allows us to establish the following violations:
- Malignant tumors and metastases in the lungs.
- Pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis.
- Pathologies of the chest.
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, CT allows one to determine the extent of damage to lung tissue. Diagnostics is prescribed for moderate and severe cases of the disease, but with mandatory consideration of contraindications.
“Focus on medical centers where doctors have the first or highest category,” says Evgeny Vasiliev. — Good clinics have a quality control system. Doctors and ongoing research are supervised by a highly professional expert who will not allow hackwork. In good centers, you can get a consultation with a doctor or an expert and discuss with him the issues that concern you, and not just get an opinion.”
Which is better CT or MRI of the lungs: pros and cons
Only the attending physician can correctly determine which procedure is required in your case. A computer scan is carried out using x-rays, which helps to obtain images of the progressing disease in specific sections. Diagnostics visualizes all the nuances of the course of the anomaly, different parts of the lung tissue and bronchi. The main advantages of the study are:
- modeling of spiral slices;
- the ability to change the viewing angle;
- the results obtained are provided in 3D digital format;
- a quick scan is a decisive point if the patient has a hemorrhage;
- the device can detect bleeding and hematomas;
- prescribed in case of injury (fractures, disturbances in the structure of the pulmonary region).
MR examination uses a safe magnetic field, which provides images also in three-dimensional projection. The main advantages include:
- safety;
- there is a high probability of detecting the disease at the initial stage of development - which effectively helps to detect oncological tumors;
- scanning is allowed at any frequency.
Use the search service mrt-v-spb.ru, where you can make an appointment at any clinic in the northern capital online in a few clicks. On the portal you will find information about the location and contact numbers of medical centers, current price lists, the number of vacancies and reviews from visitors.
The difference between CT and MRI of the lungs
Both studies are informative and the choice is made taking into account the expected diagnosis, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
| Preferably CT | MRI preferred |
| Chest injuries | Pneumonia |
| Lung tissue pathologies | Neoplasms larger than 3 mm |
| Lung examinations that require contrast administration | |
| Assessment of the condition of the pulmonary vessels | Assessment of the pulmonary aorta (with contrast) |
| Circulatory disorders | |
| COVID-19 in severe stage with respiratory failure | |
| Aneurysms |
Benefits of MRI
- No radiation (can be used for pregnant women and children).
- The results are in the form of a three-dimensional image.
- There are no restrictions on the number and frequency of procedures.
- High accuracy.
Disadvantages: not suitable for patients in serious condition, people with fear of confined spaces.
What does a CT scan of the lungs show and what are its advantages:
- The examination takes about 2 minutes.
- Minimum radiation dose.
- Ability to identify internal bleeding and tumors.
- The result is a three-dimensional image.
- Allowed for people with implants and electronic devices.
Disadvantages: limited number of procedures (due to increased radiation dose), inability to detect abnormalities in the functioning of organs (only changes in the structure are visible in the image).
What is examined using MSCT
Multislice computed tomography is used:
- for examining the spinal column after severe injuries and severe bruises;
- for planning an operation;
- to detect tumors, determine the boundaries of their spread, quality and presence of metastases;
- for diagnosing spinal pathologies;
- to assess lung volume;
- to assess the patency of the coronary arteries;
- to detect blood clots;
- for diagnosing diseases of the ENT organs (ear, throat, nose).
Using an examination, the need for surgery is determined for complex bone injuries and a prognosis for recovery is made. The list of study areas includes:
- brain;
- pelvic organs;
- abdominal organs;
- chest organs;
- ENT organs;
- spine;
- joints.
How are CT and MRI procedures of the lungs performed?
To perform a diagnosis, you need a referral from a doctor. No special preparation is required; the patient must follow the specialist’s instructions, namely:
- Remove jewelry, glasses, shoes.
- Administer intravenous contrast (if necessary)
- Lie down on the CT scanner table and remain still throughout the procedure.
- On command, hold your breath.
For children and people with increased nervousness, mild sedatives may be recommended.
How does a CT scan of the lungs occur, features:
- Performing a test before contrast injection.
- Complete immobility is not necessary.
- The procedure time is 2 minutes.
Like MRI, computer diagnostics are carried out only as prescribed by a doctor, even in the case of coronavirus disease.
Preparing the patient for CT and MRI of the lungs
To resolve the issue of preparation for diagnosis, it is necessary to clarify whether it will be carried out with or without the introduction of contrast. If contrast enhancement is to be used, the following prohibitions must be taken into account:
- It is best to perform the procedure in the morning on an empty stomach; the drinking regimen does not need to be changed. Your doctor will tell you whether you can eat before a CT scan of the lungs without contrast injection. In any case, you should avoid overeating and foods that cause increased gas formation.
- The day before and on the day of CT and MRI, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages.
- Clothing should be loose and not restrict movement. For MRI, it is important that there are no metal parts, be it clothing, jewelry, glasses, etc. They must be removed before the procedure.
CT and MRI with contrast are prescribed only after an allergy test and a blood test for creatinine to exclude possible renal failure.
Contraindications to the procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed for patients with a pacemaker, fixed dentures, or metal implants. The procedure is not prescribed for patients in serious condition, or those weighing more than 130 kg.
The list of contraindications for CT scanning includes: pregnancy, breastfeeding, childhood, possible excess of the permissible radiation dose. If contrast enhancement is necessary, patients with renal failure are excluded.
When is it better to do a CT scan of the lungs and when to do an MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are used in the diagnosis and treatment of coronavirus. Many patients have a question: what is better to do: MRI and CT of the lungs, and which type of diagnosis is more informative?
MRI is prescribed in cases where it is difficult to make a diagnosis and there is a suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis, pleurisy or a tumor. MRI is less capable of visualizing hollow organs and is not always suitable for studying the condition of the lungs.
CT scan shows changes in the bronchi and structural changes in the lung tissue, as well as lesions characteristic of viral pneumonia. When to do a CT scan of the lungs? In the presence of symptoms such as: high fever (more than 3-4 days), respiratory phenomena, cough and increasing shortness of breath.
A CT scan of the lungs gives a clear picture of the disease:
- The so-called “frosted glass” is a noticeable decrease in the density of lung tissue.
- Thickening of the septa between the lobules of the lungs (“patchwork quilt”) associated with hypoventilation and inflammation.
In addition to signs of viral pneumonia, tomography reveals the presence of subpleural foci and tumors in the initial stage.
Indications for MSCT
Indications for multislice computed tomography are:
- oncological diseases of organs and bone tissue, in particular malignant tumors of the abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine and intervertebral discs;
- the need to identify foci of tuberculosis;
- suspicion of tumors in soft tissue fibers outside the organs;
- pronounced pain syndrome;
- multiple injuries.
MSCT of the brain is prescribed after a stroke and injuries to determine the presence of hemorrhages, inflammatory processes and tumors.
Multislice computed tomography is often prescribed to examine the entire vascular system for the presence of cholesterol plaques, aneurysms, calcifications and other diseases of the circulatory system.
Questions for the doctor
How long does a CT scan of the lungs take?
A CT scan without contrast takes 1.5-2 minutes, with contrast – up to 10 minutes.
Fluorography or CT scan of the lungs - what is the difference?
Unlike fluorography, CT allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image and assess the condition of the organ.
How often can CT and MRI of the lungs be done?
Despite the minimal radiation dose, computed tomography can be done no more than 1-2 times a year. There are no restrictions for MRI.
Is it possible to do CT and MRI of the lungs at high temperatures?
A relative contraindication is the general severe condition of the patient, including hyperthermia.
What is more harmful: CT or MRI of the lungs?
Both types of diagnostics, when carried out on the direction of a doctor, are painless and safe.
Use of radiation diagnostics
Multislice tomography is a variation of one of the most modern techniques for visualizing internal organs and tissues - CT (computed tomography). The diagnostic method is based on the technique of scanning the patient’s body using X-ray transmission, which converts the received information into electrical signals.
Multislice computed tomography - what is it?
Further data processing takes place in a computer and, thanks to specially developed programs, a synthesized layer-by-layer image is displayed on the monitor.
Initially, this diagnostic method was intended only for studying the brain, but medicine does not stand still - today there is equipment for scanning the entire human body. Practicing doctors consider the MSCT method to be the most highly effective way of examining a patient.
It allows you to identify pathological processes such as:
- diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- carcinomas;
- injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- internal bleeding.
The MSCT procedure is absolutely painless for the patient and does not cause him fear of confined spaces. Its duration is from 20 to 30 minutes (if there is a need to use contrast). It is in the time during which the patient must occupy a motionless position that there is one of the main differences between the diagnostic methods of MSCT and MRI.
MSCT allows not only to visualize changes in internal organs, but also to obtain detailed images of cross-sections of tissues throughout the patient’s body