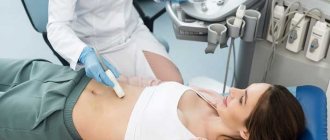
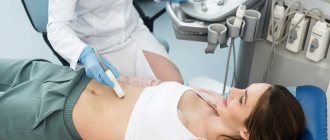
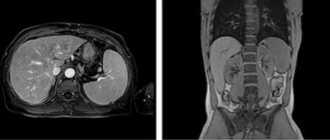
Abdominal MRI is a method for diagnosing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, pancreas and large blood vessels, based on magnetic resonance. This is a safe and precise procedure that does not involve the use of x-rays or other harmful physical factors. What does an abdominal MRI show? Magnetic resonance imaging is a universal method that is successfully used to diagnose a wide variety of diseases due to the ability to “see” the abdominal organs in clear and detailed images.
Anatomy of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum
The abdominal cavity serves as a container for the stomach, intestines, liver and bile ducts, and spleen. Some organs, such as the kidneys or pancreas, are located in the retroperitoneum, which is separated from the abdominal cavity by a thin serosa and lies behind the gastrointestinal tract. The retroperitoneal space also contains the abdominal aorta and ureters, tissue and lymph nodes.
For the convenience of studying anatomy, the abdomen is divided into three parts. In the upper part there is the epigastrium (the area immediately below the sternum, corresponding to the position of the stomach), the right (corresponding to the liver and gall bladder) and left (in the projection of the spleen) subcostal regions. In the middle part of the abdominal cavity there is a periumbilical region (it contains the transverse part of the large intestine, small intestine), right (ascending part of the large intestine) and left (descending part of the large intestine) lateral areas. In the lower part of the abdomen there are the suprapubic region (corresponding to the bottom of the abdominal cavity, partially encompassing the bladder and other pelvic organs), the right (cecum) and left (sigmoid colon) ileal regions.
The retroperitoneal space is filled with connective tissue rich in lymph nodes and fiber. Here, on the sides of the spine, there are the kidneys (their position corresponds to the right and left lateral areas of the abdomen), as well as the renal arteries and veins, the abdominal part of the aorta (in the center from the epigastrium to the suprapubic region), which is divided into two parts (into common iliac arteries) at the border of the suprapubic and periumbilical regions. Most of the pancreas is also located in the retroperitoneum, just behind the stomach.
Abdominal check-up: is it necessary or not?
The now fashionable Check-up medical service is actually not a new thing at all. This is a planned preventive examination, which we used to call medical examinations. The Check-up program may include various types of diagnostics, including MRI of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space. Is it necessary to undergo it if you feel absolutely healthy, have no bad habits, have good heredity, and eat right? Yes, definitely.
More than 95% of the adult population have gastrointestinal diseases. Gastritis, reflux disease, stones in the gall bladder or ducts, pancreatitis of the pancreas, fatty liver hepatosis, benign tumors, cancer - these are just some of the possible pathologies that can develop in anyone, and are often not associated with heredity or lifestyle.
Diseases of the abdominal organs
There are a huge number of different diseases of the abdominal organs:
- Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, enterocolitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis, Crohn's disease;
- Surgical pathologies: appendicitis, cholelithiasis, perforation of a gastric ulcer, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis;
- Fistulas and fistulas;
- Diverticulosis, intestinal polyposis;
- Cysts, liver abscesses, echinococcosis;
- Cirrhosis, portal hypertension;
- Benign and malignant tumors of the stomach, intestines, liver and other gastrointestinal tract organs;
- Vascular diseases: aneurysms, atherosclerosis;
- Congenital anomalies.
Alternative diagnostic methods
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a highly informative diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases at an early stage of development.
- X-ray of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space - performed using barium; diagnosis of pathology of the stomach and esophagus.
Contraindications Preparation
the prices for services in the price list or check by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Preparation for MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum
| Bowel preparation | not required | |
| Diet on the day of the study |
| |
| Drugs | not required | |
| Take with you |
| |
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
The following symptoms may serve as a reason for examination:
- Pain and discomfort, discomfort of various nature and localization;
- Dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, vomiting, bloating, belching of food or air, heartburn;
- Lack of appetite, aversion to meat foods, sudden weight loss;
- Loose stools, diarrhea or constipation;
- Jaundice, heaviness in the right hypochondrium.

Sources and literature
- Akberov R. F., Yaminov I. Kh., Safiullin R. R., Puzakin E. V. The effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of brain tumors. [Electronic resource] // Kazan Medical Journal. 2011
- Kremneva E. I., Konovalov R. N., Krotenkova M. V. Functional magnetic resonance imaging. [Electronic resource] // Annals of Clinical and Experimental Neurology. 2011
- Kotlyarov P. M., Lagkueva I. D., Sergeev N. I., Solodkiy V. A. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of lungs. [Electronic resource] // Pulmonology. 2021
Contraindications for MR imaging of the abdomen
Contraindications to MRI examinations of the gastrointestinal tract are divided into two groups. Absolute contraindications are conditions in which MRI can lead to serious consequences with a risk to life. Relative contraindications allow MRI if certain conditions are met, without risk to health.
Absolute contraindications:
- The presence of electronic implants in the patient’s body - cochlear implants, pacemakers, insulin dispensers, defibrillators and neurostimulators (magnetic fields generated during the study can lead to breakdown of such devices or serious injuries);
- The presence of metal in the patient’s body in the form of vascular clips, shot, fragments of bullets and shells. Even the smallest metal particles, such as steel shavings in the eyeball, pose a danger (the displacement of such foreign bodies can lead to bleeding or loss of vision).
Relative contraindications:
- Pregnant women during the first 12 weeks - MRI is not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy due to the lack of large-scale studies of the effect of magnetic fields on the developing fetus (however, in case of emergency, the study is carried out in a specialized clinic). However, in more than 30 years of using magnetic resonance imaging, there has not been a single case of MRI causing harm to the health of the mother or child;
- Children under 5 years of age - MRI requires that you remain completely still during the examination. Small children are not able to follow these instructions, which is why the procedure must be performed in a specialized clinic under anesthesia;
- The patient's weight is more than 130 kg and body circumference is more than 150 cm - the study is impossible due to the physical discrepancy between the patient's parameters and the equipment for MRI.
Contraindications
An abdominal MRI is not performed if the patient has the following devices in the body:

pacemaker, cochlear implant - a magnetic field can damage the device and cause a deterioration in the condition;- metal clips of brain vessels, foreign objects inside the body - the movement of metal parts can cause damage to blood vessels and important anatomical structures;
- endoprostheses containing a large amount of ferromagnetic metals - during the examination, large metal objects are heated and displaced;
- patient body weight over 120-150 kg - the design of tomographs is not designed for heavy weight.
The presence in the patient's body of implants made of titanium, chromium, aluminum, intrauterine devices, ceramic prostheses is not a contraindication to MRI. The materials do not interact with the magnetic field and remain unchanged throughout the entire procedure.
In addition to absolute contraindications, there are a number of relative ones:
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- severe claustrophobia;
- mental illness, alcohol and drug intoxication;
- convulsive syndrome;
- the patient's serious condition, severe pain that does not allow him to remain motionless.
Relative contraindications can be addressed after appropriate patient preparation if the procedure is of vital importance. There are tomographs with an open body type, in which people with claustrophobia, children, and obese people can undergo MRI.
The procedure for administering a contrast agent is contraindicated:
- pregnant women;
- with severe renal and liver failure;
- people who are allergic to the components of the contrast agent.
Lactation is not a contraindication to MRI with contrast. A woman is recommended to stop breastfeeding for two days after administration of the drug, replacing the milk with an artificial formula or her own expressed milk.
How to Prepare for an Abdominal MRI
Normally, the intestines and stomach are in constant motion, contracting and moving food through the gastrointestinal tract (this phenomenon is called peristalsis). In addition, gas can accumulate in the intestines, causing displacement of surrounding tissues. These factors significantly degrade the quality and clarity of images, making diagnosis difficult and reducing the value of research results. To reduce the influence of peristalsis on tomography results, mandatory preparation is required.
MRI of the abdomen is performed on an empty stomach—hunger reduces peristalsis, improving the quality of the images. A couple of days before the examination, it is recommended to give up legumes, cabbage, carbonated drinks, alcohol, and dairy. The evening before, it is recommended to take a carminative (espumisan) and an antispasmodic (no-spa) - this will help cope with the formation of gas and relax the smooth muscles of the abdominal organs, which also reduces the severity of intestinal motility. It is forbidden to do enemas - such procedures irritate the gastrointestinal tract and increase peristalsis. For the same reason, smoking is not recommended.
How to prepare?
To increase the information content, it is necessary to prepare well for the procedure. This includes a number of rules:
- abstaining from food for 5-6 hours before the analysis;
- for 2-3 days it is good to give up all types of cabbage, beans, sour milk, raw fruits and vegetables, carbonated water, and do not drink alcohol;
- if an MRI is planned under anesthesia (for example, for patients with claustrophobia), preparation will include the avoidance of cosmetics that may interfere with the contact of the sensors;
- as prescribed by the doctor, take antispasmodic medications 30 minutes before the procedure, if required;
- Empty your bowels and bladder before the procedure.
Immediately before an MRI of the abdominal cavity, preparation is simple - remove all metal objects. If necessary, contrast is injected into the vein before the procedure begins.
In our clinic, cavity diagnostics are performed daily. To make an appointment, simply call us or fill out the form on the website. The specialist will advise you about contraindications and the course of the study.
How is an MRI examination of the abdominal cavity performed?
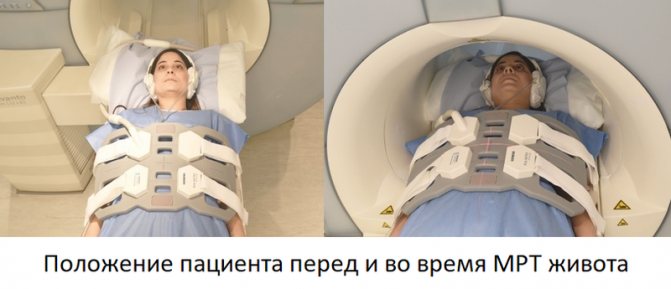
The procedure is carried out using special equipment in the form of a large cylindrical block. It has a through tunnel (the length and width of the tunnel is about 60 centimeters), equipped with guides for the movable table. After the patient is positioned, the table moves to ensure the scanning sequence.
Before starting the examination, the patient needs to wear special headphones - they protect the hearing organs from noise (MRI is a rather noisy procedure) and serve to communicate with the operator. In addition, an array antenna or coil is placed on the patient's abdomen, which serves to read data. Visually, it resembles a grille with thick plastic ribs and is connected to the device with a wire. The coil significantly improves the quality of images of the abdominal organs. The patient is given an alarm button - by pressing it, you can contact the operator and ask to stop the procedure.
The duration of the study is about 45 minutes. In controversial and complex cases, obtaining accurate data requires an additional 15 minutes to administer contrast. Contrast agents are a special class of medicinal substances for intravenous administration that can increase the accuracy and clarity of the resulting images and increase the information content of the method. Most often, contrast is used to diagnose inflammatory pathologies and space-occupying formations.
After completing the procedure, the patient must wait for the examination results - a maximum of 30 minutes. The images themselves are transferred on a CD or on film/flash drive (for the latter you will have to pay a little extra), along with a report from a radiologist. Each patient of our medical center is given a free consultation with an MRI diagnostic doctor - they will show you the images and tell you in detail about the results of your study.
Preparing for magnetic resonance imaging
Examination of the pelvic organs (organs of the female reproductive system, prostate gland, bladder) requires the following measures:
- the procedure is carried out with a full bladder: you should not urinate for several hours, and an hour before the scan you should drink half a liter of clean water;
- It is recommended to cleanse the intestines with an enema or laxatives;
- half an hour before the study, it is advisable for the patient to take an antispasmodic drug (“No-spa”);
- women of childbearing age indicate the day of the menstrual cycle.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach or after a light snack if the procedure is scheduled for daytime or evening hours. A few days before diagnosis, you should exclude from your usual diet foods and dishes that contribute to increased gas formation. These include legumes, whole milk, and sweets. Also avoid foods that cause constipation (flour, rice, chocolate). It is advisable to take enzymes and sorbents (activated carbon) during this period. On the eve of the study, the patient is recommended to take an antispasmodic.
Examination of other parts of the body does not require special preparation. Immediately before scanning, you must remove keys and other metal items from your pockets and remove jewelry.
MRI of the abdominal organs - what the examination will show
Each MRI image is a thin “computer” slice through the area of interest to doctors, 1-2 mm thick, taken in various planes in a manner reminiscent of slicing a loaf of bread or sausage. The computer, carrying out image reconstruction, virtually dissects the patient’s body, obtaining detailed images that allow one to examine the liver, spleen, pancreas and other organs in detail. Each series can contain up to several hundred pictures, which completely eliminates the possibility of missing something really important.
If the study was carried out with contrast, the dynamics of accumulation of contrast agents in various organs and tissues is also assessed. Contrast is absorbed especially intensely by tumors and foci of inflammation. In addition, when deciphering, the structure of organs, their size, volume, position, the presence of anomalies and pathological changes are taken into account. The procedure for deciphering images is similar to sifting sand - any, even the most minor, deviation from the norm will be detected in the images.
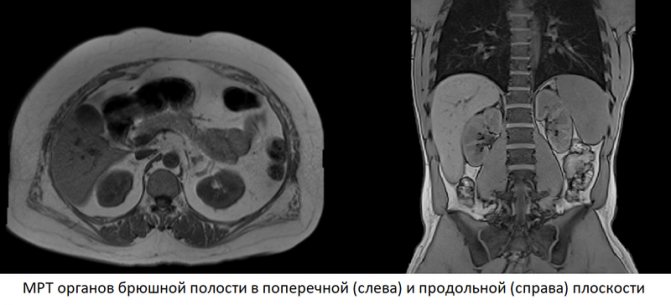
MRI or CT of the abdominal cavity - what to choose
Computed tomography is a well-proven diagnostic method, but unfortunately not without its drawbacks:
- CT scans expose the patient to radiation due to the use of powerful X-ray beams;
- CT “sees” soft tissues worse than MRI;
- Computed tomography of the abdomen is always performed with iodinated contrast, which is often difficult to tolerate by patients;
- Computed tomography itself is cheaper than MRI, but when contrast is used, the cost of the study may be equal to or exceed the cost of the latter.
Meanwhile, computed tomography also has advantages:
- The method is faster - the entire examination takes 5 minutes, which is important when diagnosing acute pathologies;
- Due to the high speed of obtaining images, CT is less susceptible to distortions that occur during intestinal and stomach peristalsis;
- CT is indispensable for acute surgical pathologies and abdominal injuries.
MRI, unlike other diagnostic methods, has increased sensitivity and specificity, which allows for more accurate diagnosis. The procedure does not involve radiation exposure, is safe, and has no side effects associated with the high toxicity of contrast.
The choice of a specific diagnostic method depends on your doctor, the intended diagnosis and the patient's condition. Moreover, CT or MRI cannot be directly compared - both methods have their pros and cons, which are important in each individual case.
MRI preparation process
Before undergoing the examination, the patient is prescribed a diet - do not eat for 6 hours, do not drink liquids for at least 4 hours.
There is quite limited space in the tomograph, so it is better to take care of your wardrobe in advance. Comfortable, loose clothing is ideal.
Some patients begin to worry as soon as they step through the doorway into the specialist’s office. Such people are prescribed sedatives, but there are other methods of reducing stress - headphones with pleasant music, qualified calming behavior from a specialist. Sometimes close people are allowed to be in the room next to such patients.