Ekaterina Smolnikova
Practicing endocrinologist (10 years of experience). He has extensive experience working in private and public clinics in Russia.
Ask a Question
Platelets are blood cells on which quality such as clotting depends. With a small number of them, even minor injuries can cause heavy bleeding. But they should not be allowed to increase either - it can cause the formation of blood clots. Platelet counts need strict monitoring, this is especially important for women.
What is thrombocytosis?
When the number of platelets in the blood increases, a disease called thrombocytosis . The reason for its appearance may be an increase in the production of such cells in the bone marrow, a decrease in their decay, and problems with movement in the bloodstream.
If left untreated, the disease can progress to thrombosis, which is characterized by blockage of blood vessels due to poor blood circulation. For treatment, it is necessary to work with the underlying disease that caused the increase in platelet levels, and take measures that will prevent their formation.

Thrombocytosis in a child
If a child’s platelets are elevated, this means the same thing as an adult’s: blood viscosity increases and there is a risk of intravascular thrombus formation.
There are many reasons why platelet platelets are elevated in children:
- inflammatory diseases;
- infections;
- hormone therapy;
- slowing down the destruction of old cells;
- bone marrow oncology.
In children, after physical overexertion or stress, false thrombocytosis may develop, when there is an uneven redistribution of red plates in the bloodstream. In this case, a finger prick test will show elevated platelets, and when examining venous blood, the values will be normal. The resulting condition is not dangerous and goes away on its own after rest.
Norm of platelets in the blood of women by age
In women, the normal platelet count in the blood depends on age and physiological state. Also, values may fluctuate depending on the time of day. The highest levels are recorded in the evenings, and the lowest in the mornings.
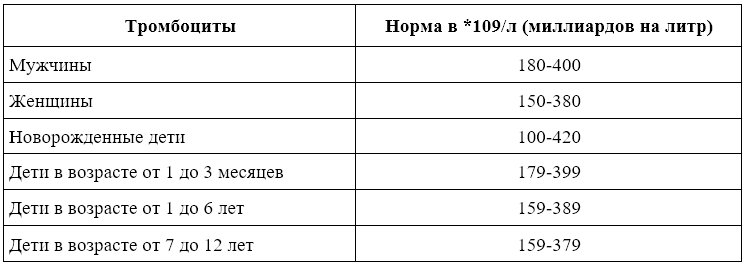
Optimal platelet counts:
- In healthy newborn girls – 150,000-420,000.
- In infants of the first year of life, the indicators are 150,000-350,000.
- In girls from one to one and a half years old, the number of platelets corresponds to the norm for adult women - 80,000-320,000.
- During menstruation, the normal values decrease and amount to 70,000-170,000.
- During pregnancy - 100,000-420,000.
- During the postmenopausal period, the normal platelet count is 110,000-349,000.
Article on the topic:
Symptoms and treatment of hormonal imbalance in women
Reasons for deviations
An increase in platelet concentration in the blood is most often explained by hematological diseases. These include pathologies of the blood and hematopoietic organs (the main one being red bone marrow). If its functioning is disrupted, the synthesis of blood cells changes. Degeneration of stem cells and myeloproliferative processes lead to such disorders.
Adults
Thrombocytosis is a complication of polycythemia vera and leukemia. The functioning of the bone marrow may be disrupted due to the growth of malignant tumors, when metastases appear in the bones (basophils and platelets often increase). The synthesis of blood cells changes with a lack of vitamins and minerals. Iron deficiency and aplastic forms of anemia can provoke thrombocytosis.
If platelet concentrations exceed normal limits, they can cause acute and chronic disturbances in the functioning of the body. The first include:
- injuries (necrosis, burns, cuts, fractures);
- poisoning (chemicals with massive damage to blood vessels by toxins);
- bleeding;
- surgical operations (persistent disorders accompany splenectomy - removal of the spleen).

Chronic provocateurs of thrombocytosis include sluggish parasitic, viral, fungal and bacterial infectious diseases (manifested by increased platelets, monocytes, ESR), autopathologies (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, ulcerative colitis).
Certain medications can also cause deviations. Medicines that increase platelet levels include chemotherapy, corticosteroids (a shift in indicators is noted after Dexamethasone, Prednisolone), and oral contraceptives. Sometimes abnormalities in clinical blood tests occur after long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Thrombocytosis in children can be provoked by both serious diseases (such as blood cancer) and any past infections. It is important to ensure that the level of corpuscles returns to normal within 2 weeks after recovery. Children in the first year of life have higher platelet counts than adolescents and adults. This is explained by the body’s increased need for corpuscles during its active growth.
Pregnant women
Mild thrombocytosis during pregnancy is considered normal. It is associated with a slowdown in metabolism and increased stress on the body, and a deficiency of certain substances. However, expectant mothers should regularly undergo blood tests in order to notice significant abnormalities in time.
Thrombocytosis in the third trimester is considered physiological. This is due to the fact that the body “stores” formed blood elements, including platelets, thus preparing for the upcoming birth and blood loss (the minimum for a natural birth of a child is about 300 ml, during a cesarean section - at least 500 ml).
Severe thrombocytosis and increased blood viscosity can adversely affect fetal development. Violation of the permeability of the placental barrier leads to hypoxia; in addition, under conditions of increased stress, the brain and kidneys of the expectant mother are at risk of ischemic processes.
Thrombocytosis in a pregnant woman can signal late gestosis, antiphospholipid syndrome, eclampsia, iron deficiency anemia (accompanied by decreased hematocrit and red blood cell counts).
To distinguish physiological changes from pathological ones, in addition to platelets, other indicators are examined - coagulogram, INR (international normalized ratio, which indicates how high the risk of thrombosis is). If necessary, medication correction is prescribed.
Causes of increased levels of thrombotic cells in the blood in women
Depending on the cause of its appearance, the following types of thrombocytosis are distinguished:
- Primary – a pathological process begins in the red bone marrow, resulting in increased platelet production. This pathology is typical for people over 60 years of age.
- Secondary thrombocytosis can begin with the development of any disease. More often it begins in pediatric patients.
- Relative - in this case, a decrease in the number of platelets is associated with a decrease in the level of blood plasma.
Primary thrombocytosis can be caused by the following reasons:
- Formations in the bone marrow or penetration of metastases into it.
- Leukemia is the appearance of malignant processes in the blood. The most dangerous are congenital forms.
Secondary thrombocytosis can occur in the following cases:
- Inflammatory process in liver tissues.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Inflammation of various organs and systems.
- Chronic or acute course of infection.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Anemia.
- Tuberculosis.
- Neoplasms in the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- The appearance of parasites in the body.
- Purulent diseases of internal organs and skin.
- Relative increase in platelet level, reasons:
- Intoxication.
- Not enough fluid enters the body.
- There are problems with the kidneys that increase fluid secretion.
- Due to dyspeptic disorder, dehydration began.
What are platelets in a blood test?
The beginning of the study of platelet morphology and functions is not known for certain. This is due to the lack of precise written facts, photographic techniques and imprecision in the terminology of the early stage of microscopy. Donne is considered to be the discoverer of platelets, but there is information that they were studied by the creator of the microscope, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, a century and a half earlier.
- What does an increase in the average platelet volume in the blood mean?
The now obsolete name “blood plates” was introduced in 1881 by the Italian doctor and researcher Bizzocero. He also took part in establishing the relationship between platelets and the processes of homeostasis and thrombosis. Later, in 1901, Dekhuizen introduced the established designation of cells “platelets”.
In Russian-language literature, the concept of “platelets” is accepted, while in foreign literature this term describes only a narrow group of platelets with a nucleus, which are not found in mammals. In English-language literature, cells are referred to as “blood plates.”
Platelets are blood cells without a nucleus or color. In the human body they perform the following functions:
- form a primary plug when the integrity of blood vessels is damaged;
- participate in phagocytosis reactions (reducing the risk of infection when a vessel is damaged);
- participate in thrombus stabilization;
- accelerate blood clotting reactions;
- participate in the further dissolution of the blood clot.
According to the latest research, they also take part in the process of restoration and healing of damaged tissue. The mechanism of action is due to the ability to secrete specific protein molecules (growth factors), which enhance the processes of cell growth and division.
Clotting
A characteristic feature of platelets is their ability to undergo rapid and irreversible transformation. To start this process, exposure to external or internal factors, including simple physical overstrain, is sufficient. The main activating factors include:
- fibrillar protein collagen;
- clotting factor II (thrombin);
- adenosine triphosphate, which is released when the walls of blood vessels are destroyed.
After activation, platelets attach to the site of vessel destruction and also stick to each other. As a result, a plug is formed that closes the damaged area. Subsequently, the active substances contained in platelets help stabilize the blood clot.
Platelets also contribute to the activation of a further cascade of blood coagulation reactions.
What does an elevated platelet level indicate during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, a woman's blood may experience an increase in the number of platelets. This factor is considered negative; it is caused by the following violations:
- Varicose veins
- Blood diseases.
- Fluid deficiency.
- Iron deficiency.
- Oncological problems.
- Fungal, viral diseases.
In the early stages of pregnancy, thrombocytosis may be noted due to toxicosis. An accurate result can be obtained by performing a blood test. An increase in platelet levels is dangerous for the development of the fetus and can cause miscarriage. Indicators need to be checked regularly.
If the indicators are 400,000, it is necessary to begin treatment. If the platelet count increases slightly, this is considered a physiological problem.
Why might platelet levels be elevated in women after childbirth?
If platelet deviations from the norm are observed in the postpartum period, this most often means that the body is trying to replenish blood loss. Therefore, increased cell production begins in the bone marrow. If a woman does not have serious diseases or pathologies, after some time the normal composition of the blood is restored. During childbirth, blood loss within normal limits is not considered a pathology, but the body will in any case try to eliminate the lack of blood cells.
Article on the topic:
What is ACTH hormone? Normal blood levels in women and interpretation of tests
If it is necessary to treat a poor blood condition, the dosage of medications for a woman who is independently feeding a child must be chosen carefully. The drugs must not cause harm to the health of the mother or newborn.
High platelets and low hemoglobin
Most often, high platelets and low hemoglobin in women indicate iron deficiency anemia, when the hematopoietic function is impaired due to insufficient intake of ferrous compounds into the body.
The reasons for the combination of thrombocytosis and a decrease in hemoglobin levels may be associated with diseases of the digestive tract:
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- acute and chronic processes in the intestines.
Sometimes the cause of a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in platelets in women is varicose veins, complicated by vitamin deficiency. This condition is also typical for patients who have undergone major surgery, accompanied by large blood loss.
Why is an increase in platelet levels dangerous?
When the number of platelets in the blood increases, complex therapy is necessary. It is prescribed to avoid adverse effects on the body. In the absence of timely treatment, blood clots may form in the arteries, vessels and veins, which will gradually increase in size and clog the channel, causing swelling and inflammation.

Diseases that can cause an increase in platelet count:
- Heart attacks.
- Strokes.
- Vascular thromboembolism.
The latter disease can cause death. Regular blood tests will help to detect the disease in a timely manner and select adequate therapy.
Thrombocytosis and its consequences
An increase in the level of anucleate colorless cells is medically called thrombocytosis. It can be primary and secondary. If the process was started against the background of impaired hematopoietic functions, then it is called primary. The following diseases can become a provoking factor in this case:
Secondary thrombocytosis can be triggered by chronic diseases and inflammatory processes. The most common of them are:
- rheumatism in older people;
- ulcerative colitis;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- tuberculosis.
In some cases, an increase in platelets goes unnoticed, since this condition does not produce specific symptoms. If the level of these cells in the blood is not controlled, then in the vessels they can
blood clots form. They are blood clots that interfere with circulation. With minimal physical activity, blood clots break off from the walls of blood vessels and can clog them or get into the heart.
Symptoms and manifestations of thrombocytosis
At the very beginning of the disease, there may be no signs. The secondary form of the disease has more pronounced manifestations, since they begin against the background of the appearance of chronic inflammation. The presence of thrombocytosis in the blood can be assumed by the following symptoms:
- Fast fatiguability.
- Deterioration in general health.
- Edema.
- Bleeding.
- Problem with the functioning of blood vessels.
- The appearance of hematomas not associated with bruises.
- Hypertension, migraine.
- Painful shortness of breath.
- Feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
Many patients find out that they are sick after a clinical blood test. The primary form can develop into a chronic stage in a short time. When thrombocytosis of the second type appears, patients often complain of unpleasant conditions associated with their main illness. If you quickly diagnose and determine the cause of deterioration in health, treatment will be prescribed in a timely manner. In this case, blood clotting is unlikely.
Normal and thrombocytosis
The physiological parameters of colorless blood platelets change throughout life, which is associated with the gradual development of the synthesizing function of the bone marrow and fluctuations in hormonal levels. Platelet levels also change in some conditions (read all about platelet levels here). For example, when adrenaline is released into the blood, after physical exertion, during pregnancy.
Table - Reference indicators
When the level of platelets in the blood increases above 420*10⁹/l, they speak of thrombocytosis. This is a laboratory term that reflects an increase in the concentration of platelets per unit volume of biomaterial. The mechanism of development of the condition is important. A failure may occur at the stage of formation of formed elements (in the bone marrow), their distribution in the blood, or during disposal. To eliminate a problem, you must first find its cause.
Varieties of the condition
Thrombocytosis can be relative or absolute. The first accompanies dehydration of the body, when the volume of fluid in the bloodstream decreases, but the number of formed elements remains the same. The deviation occurs due to blood thickening. This happens when:
- violation of drinking regime;
- exposure to hot/dry conditions;
- electrolyte imbalance;
- kidney pathologies;
- metabolic disorders accompanied by loss of water (diabetes mellitus);
- against the background of intestinal infections (with profuse vomiting and diarrhea).
Absolute thrombocytosis is said to occur if the concentration of cells changes due to an increase in their number without changes in blood volume, which happens in many pathological conditions. This condition can also be called “thick blood”.
An increase in the level of thrombus-forming bodies may be primary. This means a change in platelet production in the bone marrow. One of its forms is idiopathic; there are many causes of the condition, but it is not possible to determine which one triggered the development of the pathology. Another name is clonal thrombocytosis, which is characterized by a rapid significant increase in the concentration of cells in the blood with a change in their morphology, functions, and the formation of giant structures.
Primary thrombocytosis can also be essential. It is characterized by changes in the number and shape of megakaryocytes and tends to be chronic with a gradual increase in the number of platelets (often up to 3000). Their functions and morphological properties are subject to metamorphosis. The pathology is more often discovered accidentally in older people and is rarely accompanied by specific symptoms. It is characterized by a paradoxical combination of a tendency to thrombosis and at the same time to bleeding. With essential thrombocytosis, spontaneous and repeated hemorrhages from the gastrointestinal tract are recorded.
Secondary thrombocytosis develops against the background of the underlying disease and is not associated with impaired hematopoietic function or changes in the structure of the bone marrow. It is also called symptomatic or reactive. The main prerequisites for development are considered to be activation of thrombopoietin, redistribution of platelets, and massive release of cells from the depot. Characteristics of the reactive form:
- accompanied by a moderate or slight increase in cell levels (up to 800);
- their morphological properties and functional activity are preserved;
- reduced risk of bleeding and vascular thromboembolism.
Symptomatic thrombocytosis can develop against the background of acute conditions (bleeding, surgery, infection) or chronic changes in the body (anemia, cancer, inflammatory, autoimmune processes).
Thrombocytosis is detected in a general blood test (see options for changes in other indicators in the article “CBC: detailed explanation of all positions and causes of deviations”). If there are significant variations in platelets, it is recommended to take the test again (to eliminate errors).
Diagnostics of deviations
Diagnosis of thrombocytosis is performed to identify the pathology that caused the increase in the level of blood cells. With its help, the optimal treatment method is determined.
The following studies help determine how much platelet levels in the blood deviate from the norm:
- CBC with platelet count determination.
- Collection of information about the state of health with the determination of thrombosis that has ever occurred in the patient.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Biochemical analysis of inflammatory markers.
- Chest X-ray to detect inflammation or tumors.
- Conducting a study of the digestive tract.
When conducting a diagnosis, the doctor will listen to the patient, clarify complaints, and try to identify previously suffered diseases. An external examination is also carried out, during which the condition of the skin, the presence of bruises, and bruises are assessed. The area of the spleen and liver is palpated.
Article on the topic:
Calcitonin hormone - what is it? Norm for women and table of values
The selection of therapy is carried out after receiving the results of a visual examination and clinical examinations. If necessary, the patient is referred to more specialized specialists - nephrologist, infectious disease specialist, traumatologist.
Diagnostics
First of all, you should contact a therapist. After an examination and medical history, the general practitioner issues a referral to a specialist. With such a pathology, you may need to consult the following doctors:
- hematologist;
- oncologist;
- cardiologist;
- medical geneticist - if there is a suspicion of a congenital disease.
The diagnostic program may include the following activities:
- general blood analysis;
- detailed biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis and Nechiporenko test;
- analysis of stool for occult blood;
- tumor marker test;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
The specific diagnostic program will depend on what clinical picture is present and on the data that were collected during the initial examination. It should be noted that not only personal, but also family history is collected.
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, it is possible to determine why platelets are elevated and what therapeutic measures to take to eliminate the pathological process.
Diet for thrombocytosis
To stabilize the number of platelets in the blood, it is necessary to follow certain rules when compiling a diet. If you follow all the recommendations, you can achieve a good effect:
- It is necessary to eat food at the same time. When choosing a diet, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his needs. Proteins, carbohydrates and fats should be distributed in accordance with the recommendations of nutritionists.
- It is necessary to avoid consuming foods high in fats and carbohydrates.
- You should add foods to your diet that help reduce and normalize your platelet count.
- Drink enough clean drinking water daily.

Natural foods, green vegetables, seafood are healthy. Drinks include herbal teas and natural juices.
Drug therapy
With the correct selection of medications, it is possible to stably and quickly reduce the platelet count and prevent complications.
The earlier treatment for thrombocytosis is started, the faster it can be dealt with.
For this purpose the following medications are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory, based on acetylsalicylic acid.
- Antitumor - "Hydroxyurea" .
- To eliminate thrombosis, with the effect of slowing blood clotting.
- Immunostimulator "Interferon" .
- Blood-thinning drugs - “Curantil”, “Trental” .
Trental Curantyl Interferon Hydroxyurea
The dosage depends on the stage of the disease, as well as on the age of the patient. The doctor will check your platelet count regularly. If there is no decrease in their levels, medications will need to be replaced.
Traditional recipes for thrombocytosis
Treatment of the disease is sometimes carried out using traditional methods. Natural ginger, garlic tincture, berry infusions and Gingko Biloba are used. Cocoa, which should be drunk in the morning, before breakfast, without sugar and milk, also helps. Experts may recommend hirudotherapy.

Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine offers various recipes for infusions, decoctions and teas to reduce blood clotting. However, it should be remembered that such treatment methods should be carried out only after agreement with the treating doctor. Otherwise, you can harm the body, aggravating the course of the disease.
The most popular and simple traditional medicine recipes:
- Cocoa drink. Cocoa powder must be made from natural cocoa beans; the product is not suitable for instant preparation in this case. The drink is brewed with water. It must be unsweetened, so you should not add sugar or other sweeteners. You need to drink the drink on an empty stomach in the morning;
- Ginger root tea. The root must be grated, take 1 tablespoon and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Boil the tea for 5 minutes. You can add a little honey to the finished drink. This volume must be drunk in parts throughout the day;

- Tincture with garlic. Peel and crush 2 medium heads of garlic. Add 200 ml of vodka to the resulting garlic pulp. The mixture is infused for 30 days, after which the medicine is taken twice a day, 0.5 teaspoon.