Coccobacilli are a consequence of the occurrence of sexually transmitted infections in a woman or the development of bacterial vaginosis. Also, such bacteria may be present in the feces, which will soon lead to the appearance of dysbacteriosis.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a gynecologist with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Extended colposcopy | 1500 rub. |
| Amino test for bacterial vaginosis | 300 rub. |
| Medical abortion (all inclusive) | 4500 |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
Composition of normal vaginal microflora
The gold standard for diagnosis in gynecology is the examination of a smear taken from the posterior vaginal vault and cervical canal. Normally the following can be found:
- 1Döderlein acidophilus bacilli (lactobacteria). Normally, their number should be at least 85-95% of the entire flora or 106-108 copies in the sample.
- 2Bifidobacteria (about 10%).
- 3Peptostreptococci, eubacteria, prevotella, bacteroides, fusobacteria and other anaerobic bacteria (5%).
- 4Other cocci and fungi (in small quantities).
- 5Epithelium (not much, its quantity depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle).
- 6Leukocytes (up to 10 cells).
This ratio of microorganisms can maintain a slightly acidic environment for a long time, allows you to fight pathogenic bacteria, provides natural hydration and local immunity. The state of the vaginal microflora is assessed using laboratory methods and has its own conditional classification.
Degrees of vaginal cleanliness
The concept of degrees of purity was introduced in order to promptly identify women at risk for inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, and so on). You can read more about this in our other article (follow the internal link). They are identified based on the results of a simple smear for flora and GN:
- 1First degree (second name - normocenosis): acidic environment. Normal number of lactobacilli, few epithelial cells, no cocci. It is rare, usually observed immediately after treatment or the use of antibiotics.
- 2Second degree: acidic environment. The number of lactobacilli is slightly reduced, leukocytes (up to 10) and small diplococci appear. The number of cocci is insignificant (one or two pluses).
- 3Third degree: the environment becomes slightly acidic or alkaline. The number of Doderlein rods is significantly lower than normal, there is a lot of epithelium, leukocytes 10-30, coccal or bacillary flora predominates, fungal mycelium can be detected. This condition is called dysbiosis (dysbacteriosis). Such women need to be monitored and receive timely treatment.
- 4Fourth degree: alkaline environment. Lactobacilli may be completely absent, a large number of epithelial cells, leukocytes (above normal), many cocci or other pathogenic bacteria. This degree corresponds to vaginitis, therefore, treatment of the woman is mandatory.
As the pH shifts toward the alkaline side, the quality and quantity of flora changes. The level of acidophilus bacilli gradually decreases, cocci multiply, then fungi and other bacteria join.
An alkaline environment is detrimental to Doderlein's bacilli, which leads to the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
It is worth noting that the following microorganisms can be found in normal smears: hemolytic streptococcus, aureus, epidermal and saprophytic staphylococcus, peptococci, micrococci, green streptococcus and others. All of them in small quantities do not pose a threat to health and are opportunistic representatives of the vaginal flora.
With 3-4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness, the following types of cocci can most often be detected:
- 1Streptococci. As mentioned above, these microorganisms are allowed in small quantities, but their increased proliferation leads to the occurrence of an inflammatory process - vaginitis.
- 2Enterococcus fecal. Often found in the intestines, if it enters the genitourinary tract it can cause cystitis or colpitis. Detection of it in large quantities in smears indicates a violation of the rules of intimate hygiene, including during sex.
- 3Staphylococcus is an opportunistic microorganism that normally lives on the skin. With increased reproduction, it can cause serious inflammation with damage to the external and internal genital organs.
- 4Diplococcus occurs in vaginal dysbiosis with disruption of the normal composition of the microflora of the mucous membrane.
There are other cocci, they usually cause nonspecific colpitis.
Important! If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in a gynecological smear, then there is a possibility of its detection on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract (oropharynx, nasal cavity).
Reasons for the appearance of cocci in a gynecological smear
Coccal flora in a smear in women can be observed for several reasons:
- Failure of a woman to comply with personal hygiene rules. This may include improper and irregular care of the genitals, rare changes of underwear, constant use of panty liners, and the use of alkaline soap.
- Long-term uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, refusal of barrier methods of contraception, improper alternation of anal, oral and vaginal sex within one sexual act, non-compliance with the rules of sexual hygiene.
- Abuse of douching, especially with antiseptics (washing out normal microflora).
- The onset of sexual activity before the age of 15, lack of literacy in intimate hygiene.
- Hormonal changes in women during menopause, pregnancy, and menstrual irregularities.
- General somatic diseases, chronic infections, taking glucocorticoids, which weaken the immune system.
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane (violation of the natural barrier function).
Routes of infection
Diplococci are more often found in smears during biological studies. Their presence may already indicate disturbances in the microflora of the genital organs. The route of infection depends on the pathogenicity of the bacterium:
- Intracellular gonococcal bacteria enter the body through unprotected sex, through the sharing of individual objects and in utero. Gonorrhea is one of the most unpleasant diseases, which, if left untreated, can lead to unpleasant consequences.

- Meningococcal bacteria are pathogenic and can appear on a smear. The main route of infection is airborne and household. The infection affects the lining of the brain and the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. Without appropriate treatment, serious complications with irreversible processes may occur.

- Pneumococcal bacteria are a common cause of pneumonia, especially in young children and the elderly. Pneumococcus is transmitted by airborne droplets and household contact. In the presence of pneumococcus, extra- and intracellular diplococci can be detected in the patient.

To determine this or that type of diplococcus, when visiting a doctor, all women must accurately describe their sensations, the process of urination, the presence of unusual discharge and unusual anxieties.
What symptoms may be observed?
Active reproduction of coccal flora will sooner or later lead to the appearance of clinical symptoms of the disease. Signs of an inflammatory process in the vagina are nonspecific, that is, they cannot be used to determine which cocci are multiplying in the genital tract.
A woman may suspect a change in the composition of the microflora based on the following symptoms:
- Itching, irritation, burning of the genital tract - these symptoms may be absent.
- Change in the nature of vaginal discharge (yellow, white, gray or greenish, copious, thick).
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse and in the lower abdomen.
- Unpleasant and pungent odor, but may be absent.
The symptoms of colpitis are quite vivid, it is impossible not to notice them. If you ignore the signs of the disease, the infection can lead to the following complications:
- 1Nonspecific cervicitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix).
- 2 Endometritis, salpingoophoritis (appear when local or general immunity decreases).
- 3Cystitis and pyelonephritis often develop against the background of vulvovaginitis and have a chronic course with frequent relapses. They are associated with sexual intercourse, during which flora is carried from the genital tract into the urethra.
- 4Attachment of pathogenic flora (Trichomonas, Candida fungi, chlamydia). Disruption of the microflora contributes to the transmission of STIs in the presence of an infected sexual partner.
- 5Complications of normal pregnancy.
conclusions
Remember that timely diagnosis, medication and folk therapy can cope with this disease. But self-treatment will lead to chronic pathologies.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Smears during pregnancy
Recently, the number of inflammatory diseases and dysbiosis of the genital organs in pregnant women has been increasing.
This may be due to uncontrolled use of certain antibiotics, hormones (contraception before planning or for the treatment of infertility), poor diet, lifestyle, and decreased immunity. The appearance of coccal flora in smears of pregnant women sharply increases the likelihood of the addition of pathogenic flora, which is facilitated by:
- Changes in hormonal levels.
- Weakening of local immunity during pregnancy.
In addition, many drugs are not recommended for the treatment of pregnant women, therefore, when excess coccobacillary microflora appears, the possibilities of therapy are significantly reduced.
Active reproduction of opportunistic bacteria entails the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, and bladder. Their danger lies in the increased risk of intrauterine infection with delayed fetal development, miscarriage and other complications.
If there is no flora at all
The absence of microorganisms in the smear indicates improper preparation for the test. Most often, this situation occurs if a woman used antibacterial suppositories or douched before visiting a doctor. Some patients use douching because they believe that they need to go to the doctor “clean.” But such purity makes taking tests pointless.
The second reason for the lack of flora is the use of antibiotics. Modern antibacterial drugs kill beneficial bacteria throughout the body. If measures are not taken, the woman will develop dysbiosis and instead of the normal flora, a pathogenic flora will appear, most often coccobacillary. Therefore, patients are prescribed probiotics in suppositories to treat dysbiosis.
However, the absence of flora does not indicate the absence of hidden STDs. In such cases, on the contrary, various sexually transmitted diseases are often detected, so you need to undergo a PCR test and retake a smear.
Detection of trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma and chlamydia in analyzes does not bode well. Such a woman requires serious examination and long-term treatment with repeated tests.
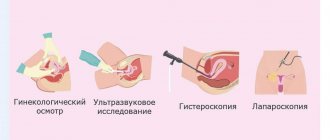
Diagnostic methods
Detection of cocci in the vagina in women is possible using three laboratory tests: a simple smear for flora, the Femoflor test modified by Femoflor 8 (10) or Femoflor 16 (17) and bacterial culture.
Most often, a simple smear is used in women. Material for research is collected from 2 or 3 points: the mucous membrane of the posterior vaginal vault, the cervix and sometimes the urethra.
Before taking the material, you should not douche, use suppositories with antiseptics, take antibiotics, or have sex, as the result will be distorted.
The biomaterial is applied to sterile slides and examined under a microscope. If necessary, culture is done on nutrient media to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sometimes examining only smears for flora is not enough to make a diagnosis, so they resort to additional examinations (Femoflor, real-time PCR, ultrasound, PAP test, colposcopy, etc.).
Symptoms
When the number of cocci in the vagina reaches a certain level, the first clinical manifestations of the pathology appear. The symptoms are nonspecific, but some of them may indicate that a woman has a health problem.
Patients visiting a gynecologist complain of copious, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, as well as pain and discomfort during and immediately after sexual intercourse. They experience itching and burning in the vagina, and a feeling of tightness in the perineum. Painful sensations occur when visiting the toilet. The external genitalia swell and the mucous membrane becomes irritated. The menstrual cycle is disrupted - periods become heavy, painful, prolonged, and irregular. Signs of dysuric syndrome are: pain and burning during urination, frequent urge to go to the toilet, dissatisfaction after bowel movement.

Vaginal discharge deserves special attention. They become abundant due to increased secretory processes. Discharge is present on the labia, underwear, and napkins. As the pathology progresses, they become viscous and form clots. The secretion produced takes on a milky, gray or yellowish tint. The secretion of mucus increases after sexual intercourse or hygiene measures. Another characteristic sign of vaginal secretion is the smell. It smells unpleasantly of sour milk or stale fish.
Women in severe cases complain of weakness, weakness, lack of appetite and loss of strength. These manifestations are due to the ability of microbes to produce toxins - the main pathogenicity factors that trigger the entire process of inflammation. Due to existing lesions, patients experience significant discomfort. Such symptoms cannot be ignored. They exhaust sick women, cause a lot of inconvenience, and disrupt the usual rhythm of life. The appearance of even some of the signs from this list is a reason to contact a gynecologist.
In men, coccal infection is asymptomatic. The disorder is discovered accidentally during a laboratory test. Some patients with weakened immune systems may develop a clinically significant disease, manifested by itching of the genital organ, swelling and redness of the head of the penis, and purulent discharge. Such symptoms require contacting a urologist.
Drugs for treatment
Treatment depends on the nature of the identified microflora, symptoms of the disease and the general condition of the woman. If a large number of cocci and leukocytes are detected in the smear, local therapy in the form of vaginal suppositories, ovules and capsules is indicated:
- 1 Hexicon (chlorhexidine in the form of suppositories).
- 2Fluomizin (dequalinium chloride).
- 3Terzhinan, Polygynax.
- 4Clindamycin.
- 5Makmiror (nifurantel).
- 6Neo-Penotran.
- 7Betadine (now used less and less, often causes discomfort, itching, burning).
- 8Local antiseptics in solutions - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine.
In case of severe inflammatory process, systemic antibiotics are prescribed: ceftriaxone, cefixime, amoxiclav, etc.
Additionally, agents may be prescribed to restore normal vaginal microflora. There have been no comprehensive studies on their use, but this issue is being actively studied. Probiotics are not indicated for thrush, as they can trigger its relapse.
Topical probiotics in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets:
- 1 Vaginorm-S with ascorbic acid acidifies the vaginal environment and normalizes the composition of microflora, use 1 tablet vaginally before bed for 6 days.
- 2 Acylact with live acidophilus bacteria, 1 suppository 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
- 3 Laktonorm 1 vaginal capsule 2 times a day for 7 days.
After treatment, smears are taken again to monitor the effectiveness of therapy. If there is no effect, alternative regimens are prescribed or the main course of antibiotics in the form of vaginal forms is extended.
Treatment can be done on an outpatient basis, at home. Among folk remedies, sitz baths with chamomile, calendula, and furatsilin solution can be recommended.
Prevention
To prevent imbalances in the microflora of the genital tract, it is necessary to eliminate, if possible, all provoking factors:
- Eliminate hormonal imbalance (HRT for menopause, oral contraceptives as indicated).
- Maintain daily intimate hygiene, as well as during menstruation and sex. Avoid douching without a doctor's prescription.
- Use condoms.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, be active, play sports or exercise, eat right, avoid frequent use of antibiotics, protect your body from infections.
- One of the methods of prevention is also regular visits to the gynecologist and treatment of chronic diseases not only of the reproductive system, but also of other organs.