If you stop a random passerby on the street (although this is not so easy to do now) and ask what his blood type is, he most likely will not be able to answer this question. Unless you were in the hospital, had a special test, or have a good memory. But knowing your blood type in an emergency can save a life: if you tell the doctor your blood type in time, he will be able to quickly select the appropriate option for transfusion. Moreover, some groups can be mixed with each other, while others categorically prohibit this. What is a blood type, and what determines the transfusion of different groups?
There are 4 recognized blood groups in the world
- 5.1 What blood type will the child have?
Human blood groups
For a hundred years now, one of the most important mysteries of our circulatory system has remained without a solution. We never knew why we have different blood types. However, the fact that groups really exist is beyond doubt - the groups are determined by special molecules (antigens) located on the surface of blood cells, these are the “balls” that blood consists of.
It is the antigens that determine the blood type , and if blood with a different type of antigen enters the human body, it will be rejected. If the antigens are different, then the body will recognize foreign red blood cells and begin to attack them. That is why it is so important to take into account group compatibility when giving blood transfusions. However, why is blood divided into types? Wouldn't it be simpler to have one universal group?
Blood is made up of these “pills” - red blood cells.
Of course it would be easier. But while scientists cannot answer the question of why many people have different blood types, it is impossible to create a universal group. Last year, scientists from the National Defense Medical College tested the first universal artificial blood on 10 rabbits. All animals were injured and suffered severe blood loss. During the study, 6 out of 10 rabbits survived and were transfused with universal artificial blood. Survival among rabbits transfused with normal blood from their group was exactly the same. At the same time, experts noted that no side effects from the use of artificial blood were found. But this is not enough to talk about the creation of some kind of “universal” blood.
So for now we are working the old fashioned way with different blood groups. How are they determined?
When and how were blood groups discovered?
Attempts to save the life of a patient by transfusing him with the blood of another person were made by doctors long before the concept of blood grouping appeared. Sometimes this saved the patient, and sometimes it had a negative effect, even leading to the death of the patient.
In 1901, a scientist from Austria, Karl Landsteiner, during his experiments, noticed that mixing blood samples taken from different people, in some cases, leads to the formation of clots from sticky red blood cells. As it turned out, the process of adhesion is caused by an immune reaction, while the immune system of one organism perceives the cells of another as foreign and seeks to destroy them.
In the course of his work, Karl Landsteiner was able to identify differences and divide people's blood into 3 different groups, which made it possible to select compatible blood and made the transfusion process safe for patients. Subsequently, the most rare, fourth group was identified. For his work in the field of medicine and physiology, Karl Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1930.
How to determine blood type
Current methods for establishing blood type are far from perfect. All of them involve delivery of samples to the laboratory and take at least 20 minutes, which can be very critical in certain conditions. Three years ago, China developed a rapid test that can determine your blood type in just 30 seconds, even in the field, but it is not yet widely used in medicine because it has a strong error.
To determine the group, blood is taken from a vein
The speed of blood group tests is one of the main problems. If a person gets into an accident, if an accident happens to him, his blood type will need to be determined in order to save his life. If there is no data on the victim, you will have to wait another 20 minutes, and this is provided that the laboratory is at hand.
Therefore, doctors strongly recommend either remembering your blood type (this test is at least done in childhood, in hospitals, and even at the army draft board), or writing it down. There is a “Health” application on your iPhone, where you can enter information about yourself, including height, weight and blood type. In case you find yourself unconscious in the hospital.
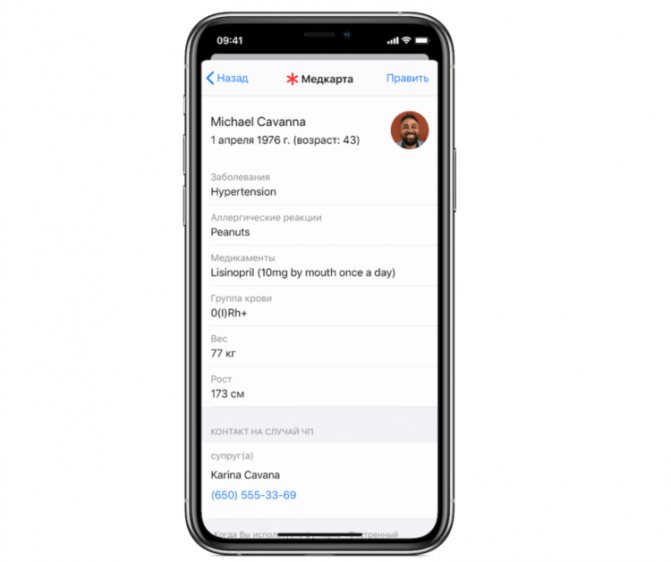
“Medical card” section in the “Health” application
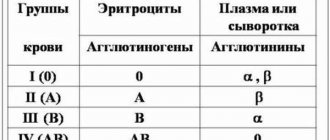
Today, 35 blood group determination systems are used in the world. The most widespread, including in Russia, is the ABO system. According to it, blood is divided into four groups: A, B, O and AB . In Russia, for ease of use and memorization, they are assigned numbers - I, II, III and IV . Between themselves, blood groups differ in the content of special proteins in the blood plasma and red blood cells. These proteins are not always compatible with each other, and if incompatible proteins are combined, they can stick together red blood cells and destroy them. blood transfusion rules exist to only transfuse blood with a compatible type of protein.
To determine the blood type, it is mixed with a reagent containing known antibodies. Three drops of human blood are applied to the base: anti-A reagent is added to the first drop, anti-B reagent is added to another drop, and anti-D reagent is added to the third drop. The first two drops are used to determine the blood type, and the third is used to determine the Rh factor. If the red blood cells did not stick together during the experiment, it means that the person’s blood type matches the type of anti-reagent that was added to it. For example, if in a drop to which the anti-A reagent was added, the blood particles do not stick together, then the person has blood type A (II).
If you are interested in science and technology news, subscribe to us on Google News and Yandex.Zen so as not to miss new materials!
1 blood group
First (I) blood group, also known as group O. This is the most common blood group , it is found in 42% of the population. Its peculiarity is that there is no antigen A or antigen B on the surface of blood cells (erythrocytes).
The problem with the first blood group is that it contains antibodies that fight both antigens A and antigens B. Therefore, a person with group I cannot be transfused with blood of any other group except the first.
Since there are no antigens in group I, for a long time it was believed that a person with blood type I is a “universal donor” - they say that it will fit into any group and “adapt” to antigens in a new place. Now medicine has abandoned this concept, since cases have been identified where organisms with a different blood group still rejected group I. Therefore, transfusions are performed almost exclusively “group to group”, i.e. the donor (from whom the transfusion is given) must have the same blood type as the recipient (to whom it is transfused).
A person with blood type I was previously considered a “universal donor”
2 blood group
The second (II) blood group, also known as group A, means that only antigen A is found on the surface of red blood cells. This is the second most common blood group, 37% of the population has it. If you have blood type A, then you cannot, for example, be transfused with blood of group B (third group), because in this case there are antibodies in your blood that fight against B antigens.
3 blood group
The third (III) blood group is group B, which is the opposite of the second group, since only B antigens are present on the blood cells. It is present in 13% of people. Accordingly, if you transfuse type A antigens to a person with such a group, they will be rejected by the body.
4 blood group
The fourth (IV) blood group in the international classification is called group AB. This means that there are both A and B antigens in the blood. It was believed that if a person has such a group, he can be transfused with blood of any group. Due to the presence of both antigens, blood group IV does not have a protein that glues red blood cells together - this is the main feature of this group. Therefore, the red blood cells of a person receiving a transfusion do not repel the fourth blood group. And a carrier of blood group AB can be called a universal recipient. In fact, doctors try to rarely resort to this and transfuse only the same blood type.
The problem is that the fourth blood group is the rarest, only 8% of the population has it. And doctors have to resort to transfusions of other blood types.
In fact, for the fourth group there is nothing critical in this - the main thing is to transfuse blood with the same Rh factor.
It is believed that blood type can also influence a person’s character.
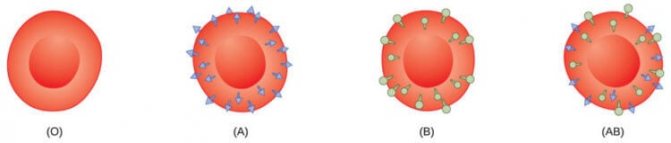
Visual difference between blood groups
Blood type - what does the child inherit?
After compatibility was clarified, that is, which blood is safe to transfuse and to whom, geneticists began studying problems of inheritance. They wondered whether it was possible to calculate what blood type a baby would be born with, or at least predict the probability. For relatives, sometimes it’s just a matter of interest - what color eyes the baby will have, which of their loved ones he will resemble. And for scientists and doctors, the main task is to prevent congenital diseases.
It has been proven that just as a baby inherits the color of its eyes, skin and hair, its blood type follows the same principles. Genetic laws are quite precise, there is only a small probability of exceptions.
How to find out what blood type a child will be born with?
There are some general patterns of inheritance:
- if both parents are owners of the first blood group, then the child will be born with the same;
- if mom and dad have the first and second groups, then the children will also have either one or the other group;
- the same applies to the situation when parents have the first and third groups;
- Do mom and dad have blood type IV? Children may be born with the second, third or fourth group;
- and when parents have the second and third groups, there is a possibility of having a child with any blood type.

All these calculations are based on the teachings of Mendel, a famous geneticist. From the parents you can find out important information about the future baby. It is known that children inherit 50% of their genes from their father and 50% from their mother.
Article on the topic:
Elevated leukocytes in the blood of women - causes and consequences
Positive blood type
The Rh factor (Rh) can be negative or positive. Rh status depends on another antigen - D, which is located on the surface of red blood cells. If the D antigen is present on the surface of red blood cells, then the status is considered Rh positive, and if the D antigen is absent, then Rh negative.
If a person has a positive blood type (Rh+) and is given a negative blood type, the red blood cells may clump together. The result is lumps that get stuck in the vessels and interfere with blood circulation, which can lead to death. Therefore, when transfusing blood, it is necessary to know the blood type and its Rh factor with 100% accuracy.
taken from the donor has a body temperature , that is, about +37 °C. However, to maintain viability, it is cooled to a temperature below +10 °C, at which it can be transported. The storage temperature of blood is about +4 °C.
Negative blood type
It is important to correctly determine the Rh factor of the blood
Negative blood type (Rh-) means the absence of D antigen on the surface of red blood cells. If a person is Rh negative, then when they come into contact with Rh positive blood (for example, through a blood transfusion), they may develop antibodies.
The compatibility of the blood type of the donor and the recipient is extremely important, otherwise the recipient may have dangerous reactions to the blood transfusion.
Cold blood can be transfused very slowly without adverse effects. However, if a large volume of blood is needed quickly, the blood is heated to body temperature +37 °C .
Blood group compatibility table for transfusion
| Donor | Recipient | |||||||
| 0(I)RH+ | 0(I)RH- | A(II)RH+ | A(II)RH- | B(III)RH+ | B(III)RH- | AB(IV)RH+ | AB(IV)RH- | |
| 0(I)RH+ | + | + | + | + | ||||
| 0(I)RH- | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| A(II)RH+ | + | + | ||||||
| A(II)RH- | + | + | + | + | ||||
| B(III)RH+ | + | + | ||||||
| B(III)RH- | + | + | + | + | ||||
| AB(IV)RH+ | + | |||||||
| AB(IV)RH- | + | + | ||||||
Important: Before the transfusion procedure, a test is performed to determine individual compatibility.
To reduce the risk of possible complications, they do not use whole blood, but only its components necessary for the recipient.
Parents' blood types
If blood cannot be mixed , then what to do in case of pregnancy? Doctors agree that it is not so important what group the mother and father of the child have , but their Rh factor is important. If the Rh factor of mom and dad is different, then there may be complications during pregnancy. For example, antibodies can cause pregnancy problems in a woman who is Rh negative if she is carrying a child who is Rh positive. Such patients are under special supervision by doctors.
This does not mean that the child will be born sick - there are many couples in the world with different Rh factors. Problems generally arise only at conception and if the mother is Rh negative .
What blood type will the child have?
Today, scientists have developed ways to accurately determine a child's blood type , as well as his Rh factor. You can find out this clearly using the table below, where O is the first blood group, A is the second, B is the third, AB is the fourth.
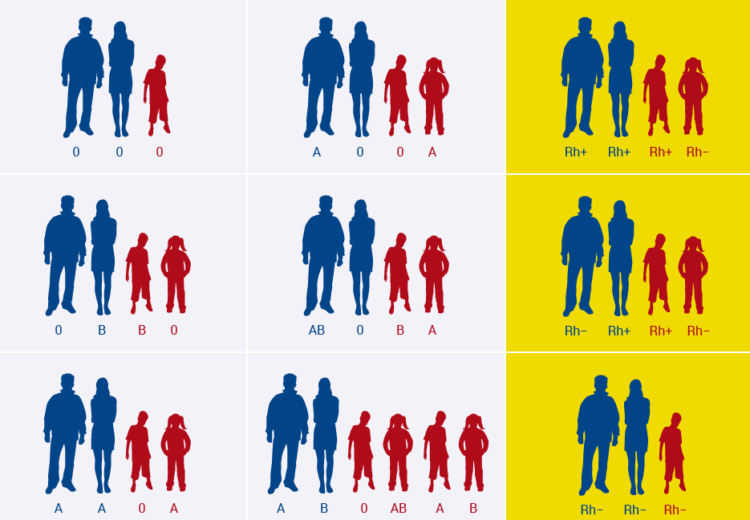
Dependence of the blood type and Rh factor of the child on the blood type and Rh factor of the parents
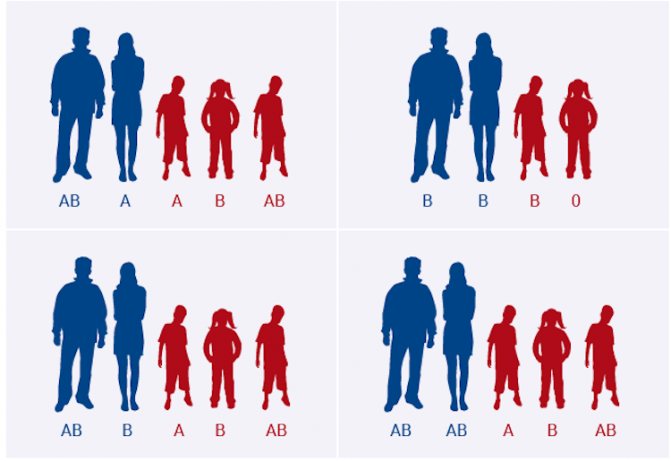
If one of the parents has blood type IV, children are born with different blood groups
The risk of blood group conflict between mother and unborn child is very high, in some cases it is less, and in others it is impossible. The Rh factor does not have any effect on the child's inheritance of a particular blood group. The gene itself responsible for the “+” Rh factor is dominant. That is why if the mother has a negative Rh factor, the risk of Rh conflict is very high.
Did you know that there is a way to cleanse the blood of cancer cells without drugs?
TABLE OF INHERITANCE OF BLOOD TYPE BY A CHILD DEPENDING ON THE BLOOD GROUPS OF THE FATHER AND MOTHER
| MOM + DAD | BLOOD TYPE OF A CHILD: POSSIBLE OPTIONS (IN%) | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | — | — | — |
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | — | — |
| I+III | I (50%) | — | III (50%) | — |
| I+IV | — | II (50%) | III (50%) | — |
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | — | — |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | — | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III+III | I (25%) | — | III (75%) | — |
| III + IV | — | I (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | — | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
Table 2.
Inheritance of the blood type of the Rh system, possible in a child, depending on the blood groups of his parents.
| Mother's blood type | Father's blood type | |||
| Rh(+) | rh(-) | |||
| Rh(+) | Any | Any | ||
| rh(-) | Any | Rh negative | ||
Can your blood type change?
Blood type remains the same throughout a person's life. In theory, it can change during bone marrow surgery, but only if the patient’s bone marrow is completely dead and the donor has a different blood type. In practice, there are no such cases, and the doctor will first try to operate on a person using a donor organ who has the same blood type.
So we advise everyone to remember their blood type just in case, especially since it does not change throughout life. It’s better to write it down and tell your relatives in case of unforeseen situations.
Mendel's law
Based on the discovery of Karl Landsteiner, who discovered the presence of blood antigens, Mendel’s law of inheritance of its group now exists. Although Gregor Mendel lived in the 19th century and was a monk, his teaching about the transmission of biological characteristics from parents to children turned out to be not far from the truth and today they are explained from the point of view of the molecular mechanisms of gene inheritance. And it looks like this. The first blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B. This means that the blood group in which these antigens are present - (the second, has only A, the third - only B, the fourth - A and B) can never be found in a child whose parents have the first group. If a husband and wife have the first and second blood groups, then their children will be heirs of the paternal or maternal group, depending on whether they have dominant or recessive phenotypic characteristics. A similar situation arises in marriage among people with the first and third blood groups. But here