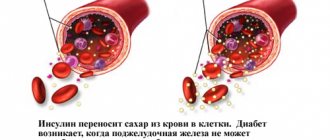
The fourth blood group, according to statistics, is the rarest. No more than nine percent of people with this type of blood live worldwide. Even with modern medicine and the development of blood substitutes, a lot of problems arise due to the rarity of such donors. At all the world's transfusion stations, people with the fourth group are specially registered as donors.
When did it appear?
The history of group 4 is associated with the long development of society and gene mutations. This group is considered the youngest. People with AB blood first appeared in the world about 10 centuries ago. Scientists are considering several hypotheses about the origin of this group.
Researchers found that blood stains of the fourth group were found on the Turin remains. This means that, most likely, Christ was the carrier of such rare blood.
A hypothesis has been put forward that AB (IV) appeared due to interethnic marriages. It is assumed that for the first time children with similar blood characteristics appeared in marriages between Mongols and Europeans. It was not previously allowed to create such families, therefore there was no mixing of blood types giving this group.
Attention! AB (IV) can be inherited by children if the parents have group 2 or 3, but this is not possible if the father or mother has the first group.
There is another theory about how human blood group 4 came about, related to food. Presumably, the composition of the blood is formed and changes according to the principle of mutation. Some geneticists are confident that due to the introduction of new products into the daily diet, such irreversible changes appeared. This means that food that has been chemically processed is responsible for the fourth group. However, this hypothesis does not explain why there are very few such people.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Gastritis
Damage to the gastric mucosa. In acute development, the process is accompanied by inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane and progressive atrophy in the chronic course of the disease.
Predisposition: owners of A (II) and AB (IV) are predisposed to the so-called anacid gastritis, as well as to gastritis associated with reflux (reflux of contents) from the duodenum. Holders of blood group 0 (I) suffer from gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection (H. pylori).
Ulcer
Damage to the mucous membrane of the walls of the stomach or duodenum, which leads to the formation of open wounds (ulcers).
Predisposition: owners of blood group 0 (I), who have the highest acidity of gastric juice compared to other groups.
Crohn's disease
A disease of unknown etiology, accompanied by irritation and damage to various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. It manifests itself in obstruction of certain sections of the small intestine, inflammation of the submucosal layer of the intestinal lining up to its complete blockage with impaired absorption, digestion and defecation.
Predisposition: 0 (I).
What kind of blood is allowed for transfusion?
Fresh blood is prohibited from being transfused to anyone. Only the use of red blood cells or other blood components in specially prepared preparations is allowed. However, in medical practice there is an emergency need for transfusion in case of too intense bleeding, dangerous injury, when the life of the recipient depends on the speed of blood replenishment. Therefore, sometimes direct blood transfusion is completely justified.
As soon as an emergency occurs, all supplies of blood substitutes are prepared at the transfusion station, and donors are invited.
Since it is extremely difficult to find a donor for the minus fourth group, it is permissible to use any blood with minus Rh for transfusion. In this context, people with blood group 4 differ from others, since both B and A agglutinogens are present on their red blood cells, and there are no agglutinins in the plasma. Therefore, when transfusing blood of any group, there is no reaction with the antibodies contained there.
Tests for personal blood compatibility must be established, even if the transfusion is unscheduled.
Allergic diseases
Bronchial asthma
An attack of suffocation develops as a result of bronchospasm or heart failure, mainly left ventricular failure.
Predisposition: 0 (I) and A (II).
Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is an inflammation of the nasal mucosa caused by increased sensitivity to irritating substances.
Predisposition: 0 (I) and A (II).
Arthritis
This is an inflammation of a joint or several of its elements. Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease of connective tissue primarily affecting the joints (polyarthritis). Arthritis and osteoarthritis are primary or secondary degenerative changes in articular cartilage that bear a static load.
Predisposition: 0 (I), A (II) type is predisposed to a more acute rheumatoid form of the disease.
Gastroenterocolitis
A combination of acute inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract with damage to the small and large intestines. The causative agents of the disease are adenoviruses.
Predisposition: 0 (I), A (II) and AB (IV).
Pregnancy with group 4: specifics
For a pregnant woman whose blood is AB positive, some troubles may arise only if she bleeds during labor. This is due to difficulties in choosing a donor.

During pregnancy, special conditions may appear only when the mother is Rh negative and her spouse is Rh+. In such a situation, the child can adopt the father’s Rh factor, and the pregnant woman’s body will begin to actively synthesize antibodies to the blood of the fetus. If the baby chooses the mother’s genes, then this does not affect the course of pregnancy in any way, and she can give birth to a healthy offspring for continuation of the family.
This reaction is called “Rh-conflict”. This condition poses a threat to both mother and child. In the process of its development, intrauterine pathologies arise, systems and organs are formed incorrectly, and indications for early abortion (termination) may appear.
When a woman is pregnant for the first time, the required amount of antibodies in her body accumulates only towards the end of the term, and they do not affect the child’s body. The case of a second and third pregnancy is especially dangerous, even if the woman decides not to give birth to a baby. As soon as conception occurs, a large number of antibodies are already produced in the body of a mother with Rh-negative blood. They attack the body of a defenseless child, he falls into a coma, and rejection begins.
Infectious diseases
Cholera
Acute intestinal infection. It is characterized by a fecal-oral mechanism of infection, damage to the small intestine, watery diarrhea, vomiting, rapid loss of fluid and electrolytes by the body with the development of varying degrees of dehydration up to hypovolemic shock and death.
Predisposition: owners of blood group 0 (I) are especially sensitive to cholera vibrios, although representatives of other groups remain quite susceptible to this dangerous infection.
Chicken pox
Acute viral disease with airborne transmission. Usually characterized by a febrile state, papulovesicular rash with a benign course.
Predisposition: A (II).
Salmonellosis
In case of salmonellosis, the sources of the infectious agent are domestic animals - cattle, pigs, poultry, etc. Salmonella can be found in poultry eggs. Infection occurs when food processing technology is violated and it is stored improperly. The disease develops 6 hours (latent period up to 3 days) after consuming contaminated products.
Predisposition: people with blood groups A (II) and AB (IV) suffer especially often from salmonellosis.
Dysentery
Acute intestinal infection. The first symptom of the disease is a fever accompanied by stool disorder. Since dysentery pathogens primarily affect the large intestine, signs of the onset of the disease are regularly recurring pain in the lower abdomen, most often in the left iliac region.
Predisposition: those with blood group B (III) suffer from dysentery more often than representatives of other groups.
Diet features
A theory has been put forward according to which, depending on your blood type, you need to build your diet correctly. Let's look at the main product tips for representatives of the fourth group:
- It is especially important to use fish dishes in the diet. The most useful types of fish: sturgeon, tuna, trout. You can eat shellfish and other crustaceans in limited quantities,
- Among the varieties of meat, it is better to give preference to turkey, rabbit, veal and offal,
- It is permissible to consume no more than 4 eggs per week,
- Products made from sour milk with a low fat content are perfectly digestible. It is better to exclude fresh milk,
- Among the cheeses, you should choose only hard varieties,
- Vegetables and fruits are necessary every day in any form. The only thing you should limit yourself to is citrus fruits and pomegranates,
- It is important to eat porridge: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal,
- It is worth paying attention to the need for vegetable oils and fats in the form of nuts. It is better to use olive oil rather than sunflower oil,
- Among the drinks recommended are teas, juices from vegetables and fruits, but you need to be careful with coffee,
- The diet excludes the consumption of seeds, corn and beans.
Important! Men and women with group 4 tend to be overweight. So they need to monitor their blood sugar and cholesterol levels regularly.
In addition to a proper diet, do not forget about sufficient physical activity.
Skin diseases
Pyoderma
Painful skin conditions, most of them hereditary. This name refers to all dermatoses that are caused by streptococci, staphylococci and other pathogens and are characterized by purulent inflammation of the skin.
Predisposition: A (II) and AB (IV).
Psoriasis
Chronic recurrent dermatosis of unknown etiology, manifested by the appearance of plaque-papules on the patient’s body.
Predisposition: primarily affects those with blood group 0 (I).
Kaposi syndrome
Dermatosis in the form of multiple grouped blisters, accompanied by general intoxication of the body.
Predisposition: more often registered in those with blood group A (II).
Lyell's syndrome
It is a dermatosis of a medicinal nature. It is characterized by rapid necrosis of superficial areas of the skin and mucous membranes. Usually accompanied by the formation of large, rapidly opening blisters and severe intoxication of the body.
Predisposition: an allergic skin reaction to certain medications is typical primarily for those with blood groups A (II) and AB (IV).
Atopic dermatitis
Allergic inflammation of the skin, accompanied by redness, swelling, exudation, crusting and peeling.
Predisposition: A (II).
Eczema
One of the most common skin diseases. It is expressed by redness, itching and rashes in the form of spots, blisters and pustules. Eczema can be a manifestation of phenylketonuria, a hereditary disease characterized by a deficiency of the enzyme responsible for the transformation of amino acids.
Predisposition: A (II) and AB (IV).
Hives
The disease occurs when taking certain medications or foods and is characterized by a sudden rash of itchy blisters on the skin surrounded by an area of redness.
Predisposition: A (II) and AB (IV).
Autoimmune diseases
Lupus nephritis
Inflammation of the kidney, primarily the glomeruli (glomerulonephritis). The disease is characterized by the appearance of protein and blood cells in the urine, accompanied by edema and the development of arterial hypertension. Previously, the term "lupus" was used to describe skin erosions that resembled wolf bite marks. Currently used to refer to various diseases, for example, lupus vulgaris, systemic lupus erythematosus, tuberculous lupus, etc.
Predisposition: holders of blood group B (III) are predisposed to this disease to a greater extent than representatives of other groups.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Rheumatism
Systemic inflammatory disease of connective tissue with a predisposition to relapses and predominant lesions of the cardiovascular system. Accompanied by multiple lesions of the articular and pleural membranes.
Predisposition: holders of blood group AB (IV) are predisposed to diseases of the musculoskeletal system, group A (II) - to rheumatism.
Character of people
People with this rare fourth blood group are considered creative, emotional, and with a rich inner world. The character of these people is characterized by impulsiveness and a tendency to extremes. They can be both great leaders leading nations and religious fanatics ready to do anything for the sake of an idea.
Negative qualities include absent-mindedness and lack of discipline. People of the fourth plasma group are very susceptible to criticism and easily hurt. Due to their harsh nature, they are prone to a pessimistic mood, which, however, does not bother them for a long time.
Interesting facts about people with blood type IV:
- have an increased level of adrenaline, which significantly increases physical endurance and speeds up reflexes;
- at the same time, they are susceptible to unmotivated depression and apathy;
- due to their impulsiveness and penchant for adventure, they can get involved in bad company, get carried away with alcohol and drugs;
- often have elevated platelet levels and may suffer from blood clots and strokes.
- among them there is a large percentage of asthmatics and allergy sufferers;
- With irregular nutrition, they quickly develop diseases of the digestive tract.