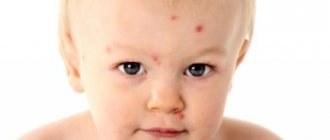
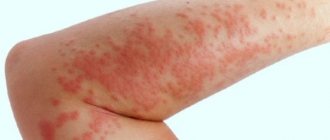
Food allergies in infants are quite common. Many mothers believe that if a child drinks only breast milk, then there can be no allergies, but this opinion is wrong. It happens that allergies in newborns develop due to the fact that allergens enter the body through breast milk if a woman consumes foods that are potentially dangerous to the body. Suitable treatment, as well as diet, is selected exclusively by the attending physician.
What happens with a food allergy?
The causes of food allergies in children under 12 months of age are disorders of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (the baby does not always have the correct production of enzymes, the composition of the microflora is not fully formed), gestosis (late toxicosis) in the mother, infectious diseases that the woman suffered during pregnancy and which were treated with antibiotics. Hereditary factors also play an important role.
Since in children under the age of one year the gastrointestinal tract rarely functions as well as in adults, sensitivity to certain foods is observed. This does not always lead to allergies; there are also so-called pseudo-allergic reactions that require a different approach to treatment. Thus, only a doctor can diagnose an allergy.
Sometimes sensitization to certain foods occurs in utero, through the skin and amniotic fluid. In this case, allergic reactions may appear at a very early age.
How dangerous is an allergic reaction?
We found out how long it takes for allergies to appear in breastfed infants - after 2 days of poor nutrition for the mother. And after the accumulation of allergens in the child’s blood - immediately after the next feeding.
Against the background of the immune system's reaction, excessive cell activity causes damage to body tissues.
- Pustules form;
- Skin sensitivity increases;
- There is burning and itching;
- A purulent-bloody crust appears.
Allergy symptoms
Any allergy, including food, is dangerous due to the phenomenon of anaphylactic shock, which means hypersensitivity to allergens, and this symptom is systemic, since it affects all internal organs. With anaphylactic shock, laryngeal edema and bronchospasm may develop. Due to difficulty breathing, even death is possible, which is extremely rare with food allergies. Anaphylactic shock is possible only when strong allergens such as peanuts and seafood are ingested (in infants this is possible when the mother consumes such products). Sometimes this does not even require the allergen to get inside - contact allergies develop according to the same principle.
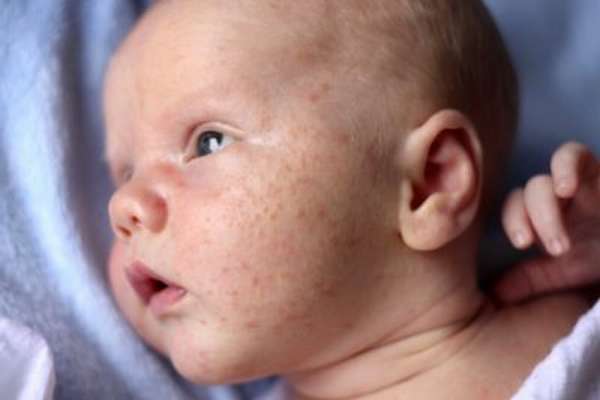
But food allergies more often manifest themselves as local reactions. Symptoms can be very different:
But in babies, skin reactions occur less frequently than gastrointestinal signs, which are observed in 75% of cases. Sometimes several symptoms appear at the same time. For example, stool disorders may well be accompanied by atypical dermatitis. The latter is a skin rash. Moreover, the likelihood of atopic dermatitis is largely due to hereditary factors. Rashes and redness in such cases are often accompanied by itching. This rash is localized mainly on the cheeks, but sometimes it appears on the forehead and elbows. It also appears as diaper rash in the folds of the skin. Atopic dermatitis does not always look like a rash; sometimes it is a so-called “milky crust” on the scalp. During the period of remission, the skin may peel off with characteristic scales. But only a doctor can determine that this is a manifestation of a food or contact allergy.
What does an allergy look like in a newborn baby?
Allergies in newborns initially resemble hives - small red spots all over the face, starting from the cheeks. Then the rashes become more intense and more frequent in location. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the rash spreads to the entire body.
Signs and symptoms
The body's first reaction usually appears after eating. During this period of time, you should be especially attentive to the baby’s behavior. The most common signs of an allergen are:
- Bloating;
- Regurgitation;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Flatulence;
- Increased anxiety;
- Tearfulness;
- Lack of appetite.
Allergy symptoms may appear within two days. This time is quite enough for the allergen to begin to manifest itself due to the cumulative effect.
- Rash, redness on the face, neck, chest, arms, buttocks, groin;
- Bloody and purulent crusts on the cheeks, neck, head.
With these symptoms, you should urgently contact your pediatrician to rule out more serious diseases:
- Diathesis;
- Hyperemia;
- Dermatitis;
- Diaper rash;
- Prickly heat;
- Hives.
In very rare cases, dysfunction of the respiratory system may occur, developing into bronchial asthma.
Main allergens
Children in the first year of life are more likely to be allergic to cow's milk. It is observed, according to statistics, in 2-3% of children under the age of 3 years. The reaction develops to cow's milk protein. Dr. Komarovsky believes this may be due to the fact that it is the first foreign protein that babies encounter. Moreover, they receive it in quite large quantities - if the children are bottle-fed. But even if the mother breastfeeds the baby and eats dairy products herself, the baby may develop allergic reactions to them, which manifest themselves in the form of colic or eczema. All of these signs disappear immediately after the mother refuses milk.

The most common sign of a cow's milk protein allergy is vomiting after feeding. But there are other reactions. In addition to colic, this is increased gas formation and a red rash. Breathing problems may also occur. If a child is allergic to cow's milk, he may react the same way to goat's milk. So, contrary to popular belief, there is no need to replace one milk with another.
This also applies to soy protein. That is, formulas for artificial feeding in which cow protein is replaced with soy protein can also cause allergies. In such cases, the pediatrician will help you choose food so that a reaction to the mixture does not occur. Typically these are products based on deeply hydrolyzed proteins - they do not cause such reactions.
As the immune system matures, food allergy to milk goes away; it rarely persists into primary school age.
Food allergies to eggs, or more precisely to egg whites, also develop. Moreover, this also applies to those cases when egg whites are consumed by a nursing mother. Another source of danger is some vaccines, for the production of which egg white is also used. Therefore, before getting vaccinated, you need to clarify this issue with your doctor. Vaccines against rubella, measles and mumps (mumps) are safe for allergy sufferers. Egg whites are used to make the flu vaccine and some other vaccines, but it would still help to clarify.
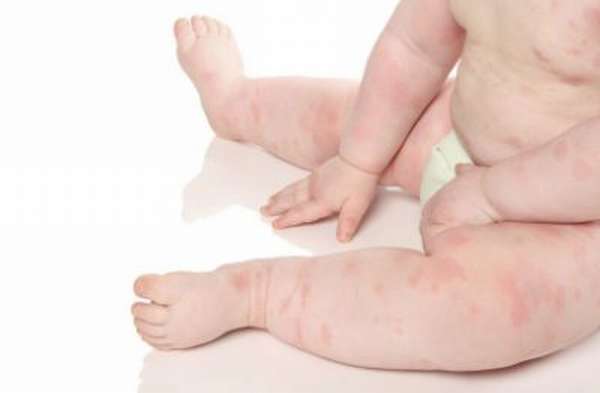
Although theoretically only the protein causes allergies, and the yolk is harmless, eggs are completely excluded from the diet, since it is almost impossible to separate the white from the yolk so that no traces of the protein remain. For this reason, eggs are introduced into complementary foods carefully. In addition, they are not the only source of protein; they can always be replaced with those products to which there is no allergic reaction, for example, meat, grains and dairy dishes.
When introducing complementary foods, you need to be very careful when consuming fish. Almost all children with food allergies have a reaction to seafood, including shrimp, fish and shellfish (such as mussels), that a nursing mother eats. And if a child outgrows most types of food allergies, fish causes the same reactions in adolescents and even adults.
Preventive measures
Allergies last longer and are more severe if additional triggers are present. To reduce the risks of allergic reactions or speed up the treatment of existing symptoms, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- In the nursery, a comfortable air temperature should be maintained, not exceeding +20 degrees.
- The permissible humidity in the room where the baby lives must be at least 50%.
- It is advisable not to use household chemicals when washing the floors in the nursery and for washing the baby’s clothes.
- Bathing water must be filtered and boiled.
- For care, you must use only hypoallergenic hygiene products without fragrances or bright dyes.
- Regular wet cleaning.
- In the nursery there should be no carpets with thick and long pile, flowers, or soft toys. Dust quickly accumulates in them.
- Clothes for babies also need to be chosen correctly, the fabric is better natural in composition, and the colors are discreet.
- Only certified toys made from environmentally friendly materials are suitable for play.
- During the feeding period, the mother should carefully monitor her diet.
- It is best to start complementary feeding with high-quality natural products produced without chemicals and preservatives.
- The child should undergo regular routine examinations with a pediatrician.
- If he is still very small, it is not recommended to have pets; it is better to wait until he grows up.
To minimize a child’s tendency to allergies, in the first 2-3 years of his life it is important to completely eliminate or minimize all contacts with potential irritants.
Prevention and regular examinations by pediatricians will help avoid the occurrence of unwanted reactions. If signs of food allergy still make themselves felt, it is necessary to establish the cause as soon as possible and begin treatment.
What other foods cause food allergies?
All products can be divided according to the degree of allergic activity into the following groups:

Guided by this classification, complementary foods are introduced. That is, first the child can be given zucchini and pumpkin in small quantities, then apples and bananas. They begin to give porridge according to the same scheme - first corn, then buckwheat, and only then wheat.
Allergies develop to any products for which yeast fungi were used. Theoretically, these products - kefir, some types of cheese, yogurt and various dairy drinks - are even beneficial for the body. But they can also provoke allergic reactions. In such cases, food allergies also develop to yeast baked goods.
Not only foods, but also food additives can provoke the development of allergies in a child. Usually baby food is produced without them. But sometimes they enter the child’s body along with mother’s milk. Allergies in such cases are caused by products containing flavors, food colors, preservatives, etc.
Diagnosis and treatment
To begin treatment, you need to make a correct diagnosis. First you need to identify the allergen. Allergists advise keeping a food diary, which records everything that the child ate during the day. This is especially important at the complementary feeding stage, when new foods are introduced quite often.
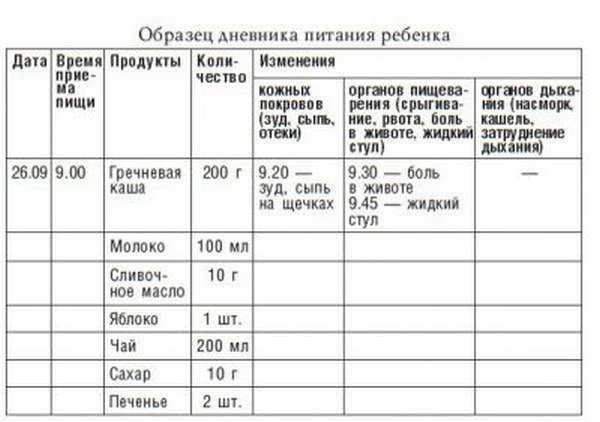
For diagnosis, special skin tests are performed. It is necessary to make incisions on the skin through which specially selected allergens are dripped and the reaction is checked. Such tests are done only after the acute period has passed. During this time, you need to exclude all potential allergens from your diet.
Various immunological methods are also used to diagnose food allergies - ELISA, RAST and others. They are also suitable for children under the age of one year, allowing one to determine the reaction to cow's milk protein, egg white, fish, etc. An open oral provocative test is rarely performed, since it is very dangerous due to the occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
Treatment of food allergies requires following a hypoallergenic diet. Infants are given specialized mixtures based on milk protein hydrolysates, monocomponent hypoallergenic fruit, berry or vegetable purees (based on one particular fruit), dairy-free porridges and monocomponent canned meat.
Nursing mothers also need a special diet. To prevent the baby from developing such a disease, they need to exclude from their diet all vegetables, berries and fruits of red or orange color, mushrooms, nuts, carbonated drinks, fish, eggs, cheeses, marinades, and spices. You need to limit baked goods, sour cream, kefir, whole milk, and pasta.
Sometimes children are prescribed medication. Only a doctor selects medications. They are used for symptomatic treatment. From the age of one month, you can use Fenistil gel, which will help relieve rashes and redness. But if the rash covers large areas of the skin, it cannot be used. Enterosgel helps to quickly remove allergens from the body, and therefore it is also prescribed to eliminate the main symptoms.
It happens that even food allergies manifest themselves as increased lacrimation. In this case, infants aged from one month are prescribed antihistamine drops Zyrtec, and starting from six months - Fenistil drops.
You should not give your child strong antihistamines, especially the second generation - Tavegil or Suprastin due to serious side effects.