Isn't pregnancy an amazing condition? Inside a woman, a new life is born, growing and forming. The expectant mother herself changes. Changes in her body are absolutely natural, but they can also cause fear and a lot of anxiety.
Colostrum is normal during pregnancy. However, especially during the first pregnancy, this phenomenon makes you panic and worry about your health. Whether there is a reason for concern and how what is happening can affect the condition of the breast should be clarified in detail.
How do nutrients arrive?
Nature has arranged for the newborn to get used to extrauterine life gradually. In accordance with its needs after childbirth, the mother’s body also “works,” including the arrival of milk:
- Colostrum appears first - immediately after birth, in the last weeks of pregnancy, on the first day;
- then it gradually transforms into transitional milk - for first-time mothers on days 3-6, for repeat mothers - on days 2-4;
- and then the mature one appears, the real one - on the 6-10th day.

, Colostrum is super milk, high in calories (1500 kcal), which provides the baby with many nutrients, antibodies that promote the excretion of meconium and bilirubin - the substance that leads to jaundice. You don’t need a lot of this milk after birth; the volume of a newborn’s stomach is only 5-7 ml.
Gradually it becomes transitional - the volume increases, the fat content increases, the protein content decreases, and there is more water. Hot flashes can lead to breast enlargement, swelling, and a feeling of fullness.
Then the mature one appears, containing 88% water. On what day after birth such milk comes in is in many ways very individual.
There are several rules that after childbirth will help a mother solve the problem of how to develop breast milk:
- attach the baby as soon as he shows signs of anxiety (at least every 15 minutes);
- let him suckle until he lets go of the breast, especially early in the morning. This is the best way to quickly establish lactation - the mother’s body receives signals about the baby’s needs and works in accordance with them. Cracks in the nipples do not appear from prolonged sucking, but from improper grip. There is a reliable way of what to do after childbirth so that milk appears faster. This means not skipping pre-dawn feedings, when prolactin is most intensely produced;
- do not use any substitutes - nipples, pacifiers, bottles. A child who is simply thirsty can suckle at the breast for five to ten minutes; if he is hungry, he will do it longer. Exceptional cases when ordinary water is required can be solved using a spoon, pipette, or syringe without a needle, but not with nipples;
- if milk comes in when the mother does not have the opportunity to feed on demand after giving birth (she needs to leave the house, etc.), she will have to use constant pumping.
Also find out what week maternity leave starts and the whole truth about increased bilirubin in newborns.
The only cause for alarm should be crying under the breast or immediately after sucking. This means that either the quantity is really small, which is quite rare, or the most unpleasant thing begins - breast refusal.
Why pacifiers, pacifiers and shields should not be used
In the case of natural childbirth, when born, the baby immediately becomes familiar with the mother’s breast. After a planned operation, when separated from the mother, the child is often first introduced to formula and a pacifier, and later breastfeeding is practiced. The technique of obtaining food from the female breast and its artificial analogue are fundamentally different. Breastfeeding consultants call the process of a baby acquiring skills in sucking a breast or pacifier and remembering the object of sucking - imprinting. Sucking a pacifier does not require the baby to exert the same amount of effort that he needs to make when receiving food from his mother's breast. As a result, when alternating such different means of obtaining food, the baby chooses a simple and easy method that was familiar to him from the beginning - by receiving food from the nipple, refusing the mother's breast. Therefore, it is important, if the separation from the child is long, to choose other ways of feeding the baby:
- supplementary feeding from a spoon;
- supplementary feeding from a syringe on the finger;
- supplementary feeding from a pipette and other methods.
Such feeding is carried out by medical workers or loved ones after a preliminary agreement. It’s great if mommy can express valuable colostrum and pass it on to the baby. This will help the baby get stronger faster, and the mother will thus be able, by maintaining lactation, to prevent the problem of milk deficiency.
The danger also lies in the fact that the baby, using the technique of grasping the nipple to the mother's breast, can grasp the breast incorrectly, injuring it. As a result, the mother experiences discomfort when feeding, and the baby may not receive the required amount of valuable milk. Using breast pads for cracked breasts can also disorient the child.
The baby who initially received a bottle of formula gets used to feeding according to the schedule, sleeps longer, and takes the breast in his usual position. However, restoring full breastfeeding after a cesarean section is also possible. The child's heredity determines the way in which he receives food from the mother's breast. As soon as the mother begins to establish the feeding gifted by nature, the baby’s genetically programmed program is activated.
The baby’s body begins to produce endorphins (hormones of happiness) only with close contact with the mother, with the baby in the correct position and subject to feeding on demand (you can get more information). Compliance with these principles will also help to establish lactation faster: the gland will produce the amount of valuable product necessary for the baby.
Don't be too insistent about offering your breasts. It is important to act gently, gradually reducing supplementary feeding and the time the baby stays with breast substitutes. You can offer the breast to a sleepy baby 1–1.5 hours from the start of sleep, immediately after it. Be sure to practice co-sleeping and establish night feedings. At the same time, do not forget about the correct sucking technique and positioning of the baby.
On what day after the operation the milk will come depends on the time interval between birth and the baby’s first attachment to the breast, on how actively the baby empties the breast, on the mother’s readiness to breastfeed on demand, etc.
How to do it correctly?
It is advisable for a woman to prepare for pumping, as far as the conditions of the maternity facility in which she is located allow. You will need a small container for pumping (for example, a plastic cup with a wide neck and thin walls). The container must be clean. If there is no boiling water for sterilization in the room, ask your relatives to buy and bring a small convenient sterilizer for bottles and nipples; you can easily process the pumping container in it. It works from a regular electrical network.
Before pumping, be sure to wash your hands - the process is carried out exclusively with clean hands. The mammary glands should also be washed with warm water and baby soap to prevent pathogenic bacteria from penetrating into the microcracks of the nipple. The napkin or small towel that a woman will use to dry her hands and absorb drops of colostrum should be clean and ironed.
To begin pumping, place your thumb over the nipple and your index finger under it. There is no need to pull off the pinched nipple with your fingers; the correct thing to do is to press on it with progressive movements towards the sternum. If this is accompanied by pain, then something was done wrong. Try a more comfortable grip on the nipple with your thumb and forefinger and repeat the movement again.
Women after childbirth do not have enough colostrum to express it with a breast pump, and judging by the reviews, such a device is not convenient for everyone. But the most common medical disposable syringe turns out to be quite convenient. If you cut off its sharp nose, located on the opposite side of the piston, you get a convenient device for expressing. The nipple is placed inside the cut part with the piston closed, checking how tightly it is there and whether it allows air to pass through. Then pull the piston in the direction opposite to the nipple.
This method is definitely not suitable for stagnation (“stone breasts”), with very thick colostrum, as well as for the first pumping (if the breasts have not yet developed, such pumping into a syringe is traumatic, it is better to start with manual pumping).
Frequency of pumping
Each situation is individual. The best solution would be to contact a lactation consultant who will develop a special pumping plan and introduce you to the technique of expressing colostrum.
- To normalize the lactation process, if the baby after birth for certain reasons cannot suck, you need to start pumping as soon as possible. It is advisable to do this within 6 hours after birth. Initially, it will be a few drops of colostrum, then its amount will gradually increase.
- Next, you need to express the colostrum approximately in the rhythm of the baby applying to the breast. At least every 2-3 hours, including at night. You need to try to have at least 8 pumpings per day.
- If expressing at night is difficult to do, it is possible to take one break every 4-5 hours. But this procedure at night is very important for sufficient milk production. Thus, you need to have at least one pumping session between 2 a.m. and 8 a.m.
- Rare pumping or its absence, if the baby is not latched to the breast, can interfere with the development of the lactation process and provoke insufficient milk formation in the future.
- To maintain the required amount of milk, it is advisable to express at the same rhythm in which the baby suckled the breast or even more often, since no breast pump or manual expression can stimulate the mammary glands as effectively as a baby.
- Regardless of how much time has passed since the last pumping, colostrum should be expressed until a feeling of relief occurs if the woman feels a strong filling of the glands. And this must be done even when the time has not yet come.
- If you cannot pump as often and for as long as planned, it is important to remember that breast stimulation is a manipulation for milk production. Even a few minutes of pumping is much better than nothing. If it is not possible to adhere to a certain rhythm, you need to do this at any opportunity convenient for the woman.
- To normalize the lactation process, if the baby after birth for certain reasons cannot suck, you need to start pumping as soon as possible. It is advisable to do this within 6 hours after birth. Initially, it will be a few drops of colostrum, then its amount will gradually increase.
- Next, you need to express the colostrum approximately in the rhythm of the baby applying to the breast. At least every 2-3 hours, including at night. You need to try to have at least 8 pumpings per day.
- If expressing at night is difficult to do, it is possible to take one break every 4-5 hours. But this procedure at night is very important for sufficient milk production. Thus, you need to have at least one pumping session between 2 a.m. and 8 a.m.
- Rare pumping or its absence, if the baby is not latched to the breast, can interfere with the development of the lactation process and provoke insufficient milk formation in the future.
- To maintain the required amount of milk, it is advisable to express at the same rhythm in which the baby suckled the breast or even more often, since no breast pump or manual expression can stimulate the mammary glands as effectively as a baby.
- Regardless of how much time has passed since the last pumping, colostrum should be expressed until a feeling of relief occurs if the woman feels a strong filling of the glands. And this must be done even when the time has not yet come.
- If you cannot pump as often and for as long as planned, it is important to remember that breast stimulation is a manipulation for milk production. Even a few minutes of pumping is much better than nothing. If it is not possible to adhere to a certain rhythm, you need to do this at any opportunity convenient for the woman.
Benefit
The beneficial properties of colostrum cannot be overestimated. It helps the child’s body gradually adapt to new environmental conditions.

Providing immunity
Colostrum supports important immune function in children's bodies. The intake of colostrum in the first days after the birth of a child protects the child’s body from many dangerous pathogens that are found in large quantities in the external environment.
The immune function of colostrum is due to the entry into the body of a newborn baby of special protein molecules - antibodies. They are also called immunoglobulins.

The colostrum of a nursing woman contains the following important immune substances:
- immunoglobulins A;
- lactoferrin;
- macrophages;
- neutrophils;
- lymphocytes.
The abundance of leukocyte cells enhances the strength of the immune system. It should be noted that these cells are largely not destroyed in the child’s gastrointestinal tract. They remain in the child’s body, are well distributed and can perform the immune function given to them by nature.
Scientists have found that the colostrum of a woman who has just given birth contains a fairly large number of T-lymphocytes. These cells belong to the immune system
They are able to synthesize a very important substance - interferon, which has strong antiviral activity.
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides contained in colostrum are involved in providing antibacterial protection to the child’s body. They negatively affect pathogenic bacterial cells, preventing them from attaching to healthy cells of the child’s body. Thus, these substances help protect the newborn baby from contracting bacterial infections.
Interestingly, colostrum also contains special peroxidase enzymes. They can have a damaging effect on bacterial cells, leading to their death. This effect helps protect the newborn baby’s body from various dangerous infections.
Modern scientific research confirms the fact that colostrum contains a number of special chemicals that protect the baby from the causative agents of some serious diseases - E. coli, streptococci, clostridia, Vibrio cholerae, salmonella, rotaviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, Coxsackie and polio viruses, enteroviruses , herpes simplex viruses and even Candida fungi.
Participation in activating the work of internal organs
The growth factors contained in colostrum help stimulate the baby's gastrointestinal tract. Scientists have found that colostrum contains insulin, cortisol, and epidermal growth factor type I (IGF-I). These substances have a specific effect on the cellular epithelium of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, helping to change the functioning of the digestive organs.
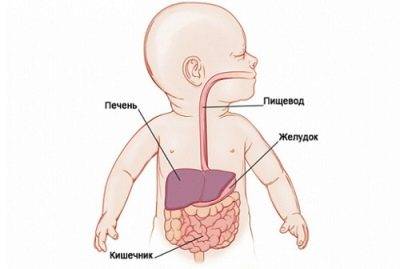
Colostrum has been noted to have a laxative effect.
This property is very important in the first days after the birth of a child, as it ensures the passage of meconium (original feces) from the child’s intestines. After birth, meconium remains in the baby's intestines, but is gradually eliminated. You can improve its removal from the child’s body with the help of colostrum
You can improve its removal from the child’s body with the help of colostrum.
Modern research has proven that colostrum also has a positive effect on baby growth. Scientists believe that growth factors contained in colostrum contribute to this. They stimulate the synthesis of molecular components inside cells, leading to their rapid growth.
Attention: lactostasis
Indeed, it is advisable to express the breast completely when lactostasis develops, when one of the ducts is blocked by a lump of milk, a slight compaction appears and milk ceases to be released from this area. This can be noticed during manual expression, when pressing on a certain area of the areola, liquid does not flow from the nipple.
If a woman notices such a condition and also has a fever, she must quickly see a doctor so that he can confirm lactostasis and rule out more severe breast diseases that can develop due to stagnation of milk and possible infection through an injured nipple.
It is quite simple to determine that the general condition has worsened precisely because of problems with the chest: you need to measure the temperature in the armpit of the arm that is on the side of the inflamed breast, and in the crook of the elbow of the other arm. The thermometer readings will differ with the development of lactostasis.

How much should there be
Feeding your newborn colostrum is very important. The benefit is mutual: the baby receives invaluable drops and learns to digest food, the mother’s uterus contracts, and during these short periods of sucking the breast prepares for full feeding. After all, breastfeeding will place a significant strain on the delicate skin of the nipples, soreness and cracks are possible
This short-term training is needed to adapt to the next period.
After all, breastfeeding will place a significant strain on the delicate skin of the nipples, soreness and cracks are possible. This short-term training is needed to adapt to the next period.
It is difficult for a woman to independently determine whether her baby has enough colostrum or not. Moreover, during this period, colostrum does not flow from the breasts, like milk in the very first days of the establishment of lactation, the breasts do not swell every 3 hours.
It is believed that a newborn eats up this amount of food if he sleeps a lot, does not cry, and often empties his intestines. In addition, in the first days of life, he is not yet able to suck for a long time; he needs to regain strength after childbirth.
Separation from mother.
Most maternity hospitals use the practice that the mother spends the first 24 hours after a caesarean section in the intensive care unit. If the mother has the opportunity to ask the baby to be next to her, this is, of course, better. Keep in mind that the practice of delaying the start of feeding during a cesarean section leads to the fact that the mother’s milk comes later - just about a day than if the mother immediately breastfed her baby.
After a cesarean section, the mother is usually prescribed antibiotics. If the operation went without complications, then antibiotics compatible with breastfeeding are selected, and the mother can feed her baby. There is no need to be afraid: the antibiotics used in such prescriptions either do not get into the milk at all, or get into microscopic quantities, having virtually no effect on the baby. Moreover, the beneficial factors in breast milk immediately neutralize or mitigate the likely effects of antibiotics, so milk is much preferable to formula.
Unfortunately, in some cases, the specific features of a cesarean section require the prescription of serious antibiotics, during which doctors prohibit breastfeeding. Usually this is the first three to four days of the baby’s life. The greatest danger that awaits the mother during this period is not to take into account that to maintain lactation in the absence of feeding the baby, regular pumping is needed.
After all, milk is produced precisely in response to stimulation of the breast, so if there is no sucking of the baby and no pumping, milk production will also be difficult! And although usually milk still comes in such cases, this may already be the seventh to tenth day of the baby’s life. And very often it turns out that when on the fourth or fifth day the mother is asked to put the baby to the breast for the first feeding, he tries to take the mother’s breast, but not only does he not cope with this after feeding from a bottle nipple, but the breast turns out to be almost empty. The baby already needs mother’s milk in significant volumes, but it’s not there!..
To avoid such a sad situation, you must definitely express milk if you cannot feed your baby. Clinical electric breast pumps help very well with this. Ask the medical staff about them! A combination of manual expression and expression with a clinical breast pump works best for milk production in the first few days. It is best to start 6 hours after birth, in extreme cases - if the mother feels completely exhausted - a day after birth. You need to express each breast for 10 minutes every three hours, with the exception of the night break. This must be done even if nothing is secreted from the breast at all - after all, the purpose of such pumping is not to get milk, but to give a signal to the body that it needs to actively begin producing it.
To pump or not?
During pregnancy, expressing and squeezing out colostrum is strictly prohibited. Mechanical impact on the nipples causes the release of the hormone oxytocin, which “brings” the smooth muscles of the uterus to full “combat readiness”, the tone increases, premature labor may begin, and placental abruption may occur. Therefore, the issue of pumping should not be raised before giving birth.

Expressing colostrum after childbirth, contrary to popular belief, does not in any way affect the rate of lactogenesis processes. Therefore, there is no need to express it. The only exceptions are cases when a woman cannot put her baby to her breast in the first hours and days after childbirth.
Expressing colostrum makes sense if:
- the child is in intensive care, he is not brought in for feeding due to his weak and painful condition, colostrum must be expressed so that the process of lactogenesis is not inhibited;
- the child was born weak, with a poorly developed sucking reflex; in order to “get” colostrum, the baby needs to try hard, and such children get tired quickly (expressed colostrum in this case is handed over to the medical staff so that the baby can take it from a bottle);
- the birth was difficult, the woman was given a large number of drugs, including antibiotics (especially the ototoxic Gentamicin, Neomycin and others); if there are a lot of medications in the mother’s body, doctors themselves may recommend that she refrain from breastfeeding for several days until the drugs are excreted in the urine, then;
- during pregnancy, a woman with a negative Rh factor had a high titer of antibodies; pumping should be carried out until doctors determine the baby’s blood type and Rh, and also make sure that he does not have hemolytic disease (in this case, breastfeeding is allowed, but if the disease is detected, the decision regarding breastfeeding is made on an individual basis);
- a long break unexpectedly occurred between feedings (the mother or child was taken away for examination, a feeding was missed due to transfer to another hospital, etc.), “stagnant” colostrum must be expressed;
- the child refuses the breast for various reasons (anatomically uncomfortable nipple, too strong nipple, the child is used to eating from a bottle, etc.); There are many ways to “defeat” a stubborn person and solve the problem of establishing breastfeeding, but temporarily it is still worth resorting to expressing colostrum.
All other mothers (and 90% of them or more) do not need to express colostrum. This is extra hassle, additional worries, and besides, expressed colostrum cannot be stored for a long time even in the refrigerator, and therefore it is completely unreasonable to “stock up” it for future use.
Antenatal (prenatal) expression of colostrum
Patient Information Leaflet*.
Colostrum is a fatty, nutrient-rich substance that is excellent for nourishing and protecting your baby from infection in the first days of life. It is especially rich in immunological factors that promote the growth and development of the baby’s immune system, and protect him from allergies and various diseases. Colostrum also helps the newborn pass meconium (original feces), which helps prevent jaundice.
This first milk begins to be produced at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy. Some women notice milk leakage during pregnancy, while others may not. In both cases, this is normal and does not in any way affect a woman’s ability to breastfeed successfully.
The importance of exclusive breastfeeding for all newborns has been proven in many studies. Some babies may have difficulty breastfeeding as well as regulating their blood sugar levels in the first few days after birth. By hand expressing and preserving colostrum during pregnancy, your baby will still be able to get your milk, no matter what difficulties you may have. Research data shows that colostrum can stabilize blood sugar levels in newborns much better than artificial formula.
You can start expressing colostrum from 36 weeks pregnant, although if you notice milk leaking earlier, you can collect it in a sterile syringe. You can discuss this with your midwife or other healthcare professional. They can offer you the tools and guidance to get started with colostrum collection.
Benefits of collecting colostrum during pregnancy.
When women start storing colostrum during pregnancy, research shows that they:
-gain more confidence in how their breasts work before the baby is born; reach “full milk production” faster
- their confidence in their ability to breastfeed their baby increases
-they gain manual pumping skills.
Most women can pump during pregnancy, although there are several groups of mothers and babies who may benefit from antenatal colostrum expression:
-Infants at risk for hypoglycemia or possible difficulty sucking
-Children of mothers with diabetes
-Very small and low birth weight children
-Newborns of mothers taking beta blockers, eg Labetalol
-children with a cleft lip or palate, or other congenital anomalies such as Down Syndrome
-when it is known even during pregnancy that the child will need special care in the neonatal unit
-Twins or triplets.
There are also women for whom, due to their general medical or gynecological history, it will be difficult to achieve exclusive breastfeeding of their babies. Others suffer from certain diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, for which breastfeeding has a very beneficial effect:
- any form of diabetes
-polycystic ovary syndrome
-hypoplasia of the mammary glands
-previous breast surgery
-planned Caesarean section
In mothers with diabetes and allergies, or with a family history of dairy intolerance, inflammatory bowel disease or diabetes, babies are more likely to also suffer from these diseases if they are fed cow's milk protein-based formula from the first days of life.
For mothers with diabetes, it is especially important to avoid formula completely, or at least not use it until the baby is 6 months old.
Women with gestational diabetes are less likely to develop the disease after childbirth if they breastfeed.
Women with diabetes should be especially careful to monitor their blood sugar levels if they express colostrum before giving birth. They may need insulin dose adjustments and dietary changes.
Are there women for whom expressing colostrum during pregnancy is contraindicated?
There is no scientific evidence that daily hand expression of colostrum activates labor for women who are not at risk for preterm birth.
However, we would advise some women not to actively express colostrum until their pregnancy is well advanced:
-women who are at risk of/have previously experienced premature birth
-women with a short cervix
-women who have had several births before 36/40 weeks
-women with stitches placed on the cervix to prevent premature birth
If you feel uterine contractions while pumping, you should stop pumping. If contractions continue, contact your midwife.
How can I express colostrum during pregnancy?
Preparation.
To prevent cross infection, please:
-wash your hands thoroughly before pumping
-breasts should be washed no more than once a day (avoid using detergents that can irritate or dry out the skin on the nipples, causing pain).
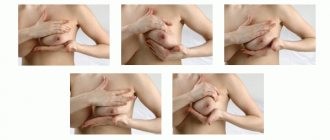
Have a sterile container available to collect the milk, such as a cup, bottle, wide-mouth container, or syringe (may be better suited for collecting small amounts of colostrum while ensuring minimal wastage). Activation of the release of OXYTOCIN (milk ejection reflex) can facilitate the outflow of milk. Find a quiet, private place where you can truly relax. You can gently massage your entire breast before pumping (you can see some massage techniques in the picture), be careful to avoid sliding your fingers across your breasts as this may cause damage to the skin. You can gently roll the nipple between your index finger and thumb. Some women find it helpful to apply a warm diaper (moistened with warm water) to the breast before pumping.
Make light circular movements with your fingertips.
Make gentle rolling movements with a clenched fist towards the nipple
Determination of the location of the milk ducts.
Place your thumb on top of your chest and your index finger opposite it on the bottom. Place both fingers as far from the base of the nipple as you can comfortably do. Gently “walk” your fingers across the chest until you find structures that feel different to the touch.
This means that you have felt the milk ducts (usually they are located 2-3 cm from the nipple).
Expression positions.
It may help if you lean forward slightly. Place your thumb and index finger in the area where you notice changes in the gland tissue. The thumb should be positioned at 12 o'clock and the index finger at 6 o'clock, as shown in the picture (your hand is positioned in a C-shape), covering the chest.
Pumping.
Without moving your thumb and index finger, gently press your chest towards your ribcage (if your breasts are large, you should lift them first). While still applying pressure, make a rolling motion with your fingers towards each other (toward the nipple, approx. per.) to remove milk from the ducts. You should then reduce the pressure to allow the ducts to refill with milk. At first, you will only be able to get a few drops, but with practice, the amount of colostrum will increase. You can move your hand in a circle, alternating the position of your thumb and index finger, or switch hands as needed to express milk from your entire breast. Collect drops of your colostrum into a sterile syringe or cup with a lid if the amount is larger. You may find it easier to deal with this if you have help from your husband or other family members. Write your name, due date, time and date of pumping on each syringe. Colostrum is usually produced in small quantities, so don't expect to be able to express a lot at once, although you may have better luck! You may only need 1 or 2 servings, but don't despair...every drop counts and the more often you pump, the greater your chances of increasing your milk supply. Hand expression is generally more effective than using a manual or electric breast pump.
Colostrum can vary greatly in color from dark orange/brown, yellow/green to pale/clear. Don't worry if your colostrum changes color or consistency after a few pumping sessions. This is fine. Rest assured, the colostrum is not “over”. You continue to produce colostrum until your milk comes in (about 3 days after your baby is born). You can pump as often as is comfortable for you.
What to do if colostrum is not released?
Do not panic! For some mothers, pumping is not so easy. Keep trying, it may take a few days before you see the first drops of colostrum. If you're ready to continue, try pumping every day. Remember that you don't have to pump during pregnancy, but it can be very helpful if you do. Rest assured that when your baby is born, you will definitely be able to get colostrum.
Guide to help you pump:
- try pumping after a hot bath or shower
- place warm diapers on your chest to improve circulation
- relax!
- Gently massage your breasts before pumping
— keep an ultrasound scan of your baby handy
What might you need?
You can ask your midwife for some sterile syringes for the first portions of colostrum. You can then purchase them at a pharmacy or online. 1 ml syringes work best.
How much colostrum should I collect?
As much as you want and can. Remember that a newborn's stomach is the size of a small ball.
Storing colostrum.
Besides preparing colostrum for your baby, there are other benefits to expressing your first milk. Many women feel more relaxed and secure knowing they have an “extra reserve” of colostrum in case their newborn needs it.
Place the syringe you used to collect the colostrum back into the package and place it in an airtight plastic container (such as a lunch box or freezer container). Freeze this portion of colostrum immediately.
Transportation of colostrum.
It is best to freeze the colostrum after you collect it at home and take it to the hospital when needed. Use a cooler bag with ice when transporting colostrum to the hospital and ask medical staff to place it in a special cooler as soon as possible after delivery. Once thawed, colostrum should be used within 12 hours, so to avoid wasting colostrum when it is already thawed but not used, it is better to thaw only a few syringes for each feeding.
When the child was born
Immediately after birth, continuous skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby should be provided as early as possible to encourage the initiation of breastfeeding (usually within the first 90 minutes after birth). Ideally, your baby will breastfeed well soon after birth and will latch on frequently, so you won't need to use the expressed colostrum! However, some babies need regular supplementation to keep their blood sugar levels stable or the baby has some difficulty sucking. In this case, you will be provided with ongoing support to help resolve any difficulties that arise, and in this situation you can use previously stored colostrum. Your health care team will teach you how to feed your newborn colostrum. You will also need to ensure that you continue to express colostrum regularly until your baby is able to breastfeed effectively, to help establish milk production and supply for your baby. We hope you enjoy the process of expressing colostrum during pregnancy, as it will give you additional confidence and an invaluable reserve if difficulties arise in establishing breastfeeding. We hope you now know more about how your breasts work and that pumping during pregnancy will help you feel more confident when you start breastfeeding your baby!
Useful Contact Numbers Breastfeeding Midwife 01296 315799 Community Midwives Office (SMH) 01296 316120 Community Midwives Office (WH) 01494 425172
If you require a translation or other leaflet format, please contact our midwife
We continually strive to improve the quality of information provided to patients. If you have any wishes or suggestions regarding this booklet, please contact us:
Head of Midwifery Women & Children's Division Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Stoke Mandeville Hospital Mandeville Road Aylesbury Buckinghamshire HP21 8AL
How can I help reduce the spread of hospital-acquired infections?
Infection control is an important part of the well-being of our patients, which is why we have developed on-site infectious disease control procedures. An effective way to prevent the spread of infection is to wash your hands frequently. We ask that you and your visitors use hand sanitizer, which can be found at the entrance to each room, before and after your patient visit. In some cases, hands must be washed in the sink using soap and water, and not just treated with antiseptic. Hospital staff will let you know if additional hand cleaning is needed.
www.buckshealthcare.nhs.uk Follow us on Twitter @buckshealthcare
Author: L. Randell
Publication date: December 2016
Reissue date: December 2018
Leaflet code: n/a Version: 1
Translation: Tatyana Mamontova
Original: https://www.buckshealthcare.nhs.uk/Downloads/Patient-leaflets-pregnancy-labour-and-postnatal-care/Antenatal%20hand%20expression.pdf
*Attention! Antenatal (prenatal) expression of colostrum should be carried out only when indicated. If you think you need it, be sure to consult with a breastfeeding support group leader or lactation consultant first.
After caesarean section
If childbirth was performed surgically, then usually the change in stages of lactogenesis is somewhat delayed. You usually have to wait a little longer for milk to appear after a caesarean section than after a natural birth.
Expressing itself after surgery does not pose a risk to the health of the young mother. On the contrary, it stimulates the production of oxytocin, which will more intensely contract the smooth muscles of the uterus. This will allow the woman not only to establish lactation, but also to avoid a common problem among women in labor who have undergone surgery - congestion, poor contractility of the uterus, and adhesions.
Before you start pumping, you should definitely talk about it with your doctor. He will tell you how best to organize this process so that mother and child get the maximum benefit.
You will learn more about whether you need to express calluses after childbirth in the following video.
Why is this necessary?
If the baby and mother are healthy and are committed to breastfeeding, expressing colostrum after birth is not required. Colostrum is produced in the most optimal quantity, does not burden the baby’s digestive system and increases his strength. Many women wonder whether they express colostrum. This may only be required in the following cases:
- A woman is unable to breastfeed her baby for a certain period after childbirth due to anesthesia after illness or caesarean section. In this case, to start the lactation process, it is necessary to express colostrum.
- The baby was born weak or premature and cannot fully breastfeed. Expressed colostrum is given to him from a spoon or through a pipette.
- For severe neonatal jaundice and phototherapy.
- With special schemes for caring for a low-weight baby.

How do the mammary glands change?
After washing the mammary glands, use a soft towel to dry and blot. Avoid sudden movements and avoid rubbing
It is important to use moisturizers in the early stages - when colostrum begins to appear during pregnancy. Due to this, you can prevent stretch marks on the chest and reduce the risk of developing cracks.
It is important to maintain a balanced diet, which reduces the consumption of simple carbohydrates, and increase the consumption of fats a month before giving birth. With the help of nutrition, a woman’s overall health improves, the future baby receives useful substances, and colostrum will become saturated in composition
Fats are essential for colostrum and breast milk to be nutritious.
With the onset of pregnancy, the female body begins to rebuild. First of all, the uterus enlarges. This process is accompanied by frequent urination, especially at night. The woman’s breasts do not remain unchanged. The mammary glands become larger, and heaviness and discomfort may appear in the chest area.
One of the most common phenomena is colostrum in pregnant women. When it appears and what causes it, you need to find out from your obstetrician-gynecologist. But it’s worth mentioning right away that there are no exact dates - it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
Sometimes colostrum appears in the early stages of pregnancy, when the woman does not yet know that she will soon become a mother. For first-time mothers, this fact is especially alarming and forces them to consult a doctor.
Women often discuss this topic with each other - when colostrum appears in pregnant women. Reviews from expectant mothers vary. But statistics show that only in 20% of cases fluid is released immediately after conception (at 3-4 weeks of pregnancy). This can be caused by the following factors:
- Visiting the sauna.
- Hot shower.
- Breast massage.
- Orgasm.
- Increased body temperature.
All these nuances can provoke the early appearance of colostrum.
As we found out earlier, one of the most common phenomena in the 3rd trimester is colostrum in pregnant women. When liquid appears, you need to follow some recommendations and rules:
Maintain hygiene. Wash your mammary glands with warm water at least 2 times a day. Use only special underwear - maternity bras are made from natural materials, they do not have wires that would squeeze the breasts
It is important to choose the right size. It is not recommended to wash nipples with soap to avoid cracks. But nourishing cream is allowed
This will moisturize your skin and get rid of stretch marks. During this period, it is recommended to use a soft towel so as not to irritate the nipples. If colostrum flows in large volumes and oozes through clothing, you can purchase special breast pads.
“When does colostrum appear in pregnant women?” - a question that interests many women. Experienced doctors will help you understand the nuances, but, as a rule, this happens after the 32nd week of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the structure of the gland undergoes changes, this is due to preparation for lactation (the appearance of milk). The blood supply to the gland becomes intense, and under the influence of hormones, proliferation of both glandular tissue and ducts occurs. This process begins as early as three weeks after conception.
Before a woman gives birth to milk, the mammary glands undergo a number of transformations. The first symptoms of changes in pregnant women appear in the first month, when they notice heavier and swollen breasts. Moderate soreness lasts until childbirth and does not go away after a few days, as during premenstrual syndrome.
How to express colostrum after childbirth?
There are two ways to express colostrum - using a breast pump or by hand. If a woman has never breastfed before, her nipples have a very dense and elastic structure, so using a breast pump is not recommended, since using this device can easily injure the nipple. In this case, fluid from the chest is poorly released. This is due to the fact that the breast pump expresses the contents of the gland under vacuum pressure, and to remove colostrum, a mechanical effect on the entire gland is necessary. Colostrum is very thick, and the breast pump is not able to remove it in sufficient quantities. In this case, it remains to express it manually. To do this, you need to knead and prepare the breasts; you can lubricate them with oil or baby cream.
If a woman has already breastfed her children before, the process of expressing colostrum will be much easier. This is explained by the fact that such a woman’s nipples are softer, the milk ducts are wider, and colostrum is expressed quite easily. In this case, you can use a breast pump, or you can express with your hands.

The process of milk appearance
First, a woman produces colostrum and only then milk. The production of secretion begins in the last months of pregnancy and is episodic. Moreover, it can be released in minimal quantities. Already during gestation, a woman’s mammary glands enlarge due to the growth of special tubules, through which milk secretion will later begin to flow.
If a pregnant mother's colostrum has a yellowish tint and thickness, then on the eve of labor, it thins out and becomes transparent.
The expectant mother may feel the colostrum moving through the ducts, causing slight itching. By the way, neither discharge from the breast during pregnancy nor the absence of this phenomenon is a pathology. And even more so, it is impossible to judge by these signs whether a young mother has milk or non-milk breasts.
We recommend: How to increase breast milk lactation
In fact, from the moment of conception, the female body prepares to feed the baby. In some cases, early breast discharge may be caused by the following factors:
Changes in mood, outbursts of emotions, naturally leading to changes in hormonal levels, and it does not matter what feelings a woman experiences - positive or negative; Drinking hot tea, compote or other liquid; Massaging the mammary glands, sometimes prescribed by a doctor, often leads to this situation; Hygiene procedures using hot water.
Do not underestimate the properties of colostrum, because it contains many useful substances and is high enough in calories to satisfy the appetite of a newborn.
Beneficial properties and functions of colostrum:
- Thanks to the secretion of the mammary glands, the child’s intestines are populated with beneficial lactic bacteria necessary for strong immunity;
- The substance promotes the removal of primary feces from the body;
- Prevents infection from entering the baby’s body, thanks to the protective cells contained;
- Nourishes tissues and blood with essential vitamins, microelements and minerals;
- Fills the blood with antioxidant elements that play a role in the adaptation of respiratory function.
In addition, colostrum prepares the newborn’s body to absorb full-fledged mother’s breast milk.
We recommend: Step-by-step instructions on how to properly bathe a newborn
Women should know that there are cases when colostrum discharge, accompanied by pain, may indicate the onset of a purulent process. Mastitis threatens the health of the mother in labor and can make healthy breast secretions harmful to the baby.
When the production of colostrum is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, as well as in the lumbar region during the last months of pregnancy, there is a threat of labor occurring ahead of schedule. In addition, colostrum mixed with blood or an unpleasant odor should also alert a woman and be a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Such symptoms indicate tumor growths or the presence of an infectious infection. If childbirth is imminent, the danger is that bacteria may enter the mother's milk.
Answering the question of women interested in what day milk comes after childbirth, we can say that colostrum first begins to be intensively released - within three days, maximum, a week after childbirth. And only then does the mother produce milk.
The importance of colostrum for the baby
- Material for building the body's immune system.
- A complex of beneficial bacteria (they are the ones who will create favorable microflora in the child’s intestines in the near future).
- Accelerator for getting rid of original feces - meconium.
- A natural obstacle to the development of jaundice.
- The only and complete nutrition in the first 2-3 days of the baby’s life until the mother’s breast milk appears.
Expectant mothers, when discussing at what stage of pregnancy colostrum appears, most often mention a period of 10-12 weeks of pregnancy.
Another name for colostrum is “ first milk ”. This breast fluid is nutritious and fatty, contains many useful substances and is indispensable for the baby.
Until milk production returns to normal, this substance from the breast will become its temporary replacement in the baby’s diet. Despite the small amount, its high calorie content can completely satisfy the modest appetites of a child.
Lactation crises: what they are and how to cope with them
When breastfeeding is established, milk is produced clearly and on time without unexpected hot flashes and other nuances. But every woman is individual, so many nursing mothers experience a sharp decrease in nutrient fluid at a certain time. Such phenomena are called lactation crises.
There are several periods when lactation may decrease:
- two weeks after birth. Some people may lose valuable liquid altogether. At this time, the crisis is associated with stress and emotional overstrain. Difficult childbirth, health problems for the baby, fatigue (especially if the baby does not sleep at night and does not allow the mother to sleep), the appearance of cracks in the nipples and, as a result, a painful feeding process. Not all women are able to cope with so many difficulties, so they begin to experience problems with milk production;
- a month after delivery. Most often this is due to the fact that the body has begun to adapt to lactation and is learning to regulate and produce as much milk as the baby needs, and no more;
- three and six months. The baby grows, shows more attention to the world around him, shows character, strives to learn and see something new. The sleep and wakefulness patterns change, so the frequency of breastfeeding may decrease, and with it the production of nutrition for the baby.
What to do to overcome lactation crises
- The psychological attitude is very important. You need to be calm, tune in to success and a positive breastfeeding experience. Talk to your baby more often, calming him and yourself. The child feels the mother’s mood: if the woman is happy, joyful and balanced, the baby will feel the same way.
- Get plenty of rest. Of course, getting a good night's sleep in the first months of your son or daughter's life is very difficult. But you can fall asleep during the day when the baby is sleeping.
- Massage the mammary glands. Such actions stimulate blood circulation, which is useful for the movement of fluid through the milk ducts.
- Follow the diet and drinking regime. Eat foods that increase lactation, and also drink more fluids.
- Feed your baby on demand.
- Increase the number of breastfeedings at night.
Video: what is a lactation crisis
Breastfeeding a child is a natural desire for most women. Experts insist that this valuable liquid contains all the necessary vitamins, minerals and immunoglobulins, which are so necessary for the full development of the baby. There is no need to panic in advance and be afraid that problems may arise with lactation. Lactation consultants and gynecologists will definitely answer any questions that arise, and latching will bring pleasure to the young mother and baby.
Stimulating lactation
If you and your baby are not together right away after surgery, you will still have enough milk. To do this, you need not only to express, but also to stimulate your nipples from time to time. Stroke them, massage them lightly, pinch them. Do this in a calm environment. And the milk will come!
Instructions
Several decades ago, when women after a cesarean section were in intensive care for 2 weeks, and children were brought to them only for feeding, many actually lost breast milk. Today, the baby is often put to the breast right in the operating room, and by the end of the first day after a caesarean section, the woman is already in the general ward next to the baby. Stimulation of the nipple and sucking activate the production of prolactin, a hormone responsible for sufficient lactation.
Colostrum and mature milk may actually arrive a couple of days later. There is no harm in this; adequate supplementary feeding should not be abandoned if the child is really hungry. The child will retain strength and will not lose weight. Milk is often delayed in women who did not receive parenteral nutrition on the first day after surgery; if the woman was given intravenous nutrient solutions and the operation went without complications, the milk will come on time. With large blood loss, breast milk is also retained. If the mother feels unwell, first of all you need to restore her condition, and then establish breastfeeding. A hungry, tired and unwell woman will not be able to breastfeed. If a child is forced to stay in the children's department, he needs to use a breast pump: the staff will be able to feed him expressed milk, and the mother will be able to stimulate lactation.
After transfer to the general ward, hold the baby in your arms and put him to your chest more often, especially at night. Prolactin is more actively produced at night, reaching peak values at 2-4 am. Try to rest more, sleep when you want, and don’t talk on the phone with relatives. The use of disposable diapers already in the maternity hospital allows you to minimize the burden of caring for the child, as a result he sleeps better and longer, the mother does not need to change diapers every quarter of an hour. If you feel unwell, do not hesitate to take your child to the children's department for a few hours. Feed him beforehand and go to rest.
Teas that stimulate lactation, wearing special underwear for nursing women, and often split meals improve milk flow. Fatty nuts, condensed milk, large volumes of butter and other folk methods impair the digestibility of milk, it becomes too fatty, and the child may experience bloating. There are special nutritional formulas for nursing mothers. This is a modern therapeutic food, high in protein. It allows the mother to receive high-quality nutrition, which also affects lactation.
Upon arrival home from the maternity hospital, you should continue to drink tea that stimulates lactation, rest more often, leave some household chores for later and involve relatives. If possible, you can use the services of a visiting assistant. Scientists have proven that co-sleeping improves lactation. If you decide to use this advice, practice co-sleeping during the day, place your baby on your chest or stomach and do not swaddle him so that your baby can move away from you. Choosing a comfortable position for feeding will allow the mother to rest while the baby eats. Breastfeeding centers operating at clinics help women properly manage lactation. They provide free assistance within the framework of compulsory medical insurance; employees have a medical education and have completed the necessary qualification courses.
Cesarean section surgery is performed frequently today. The compelling medical indications for this operation (severe gestosis, absolutely narrow pelvis, etc.) are often accompanied by slightly different reasons. The financial side of the issue is often interpreted ambiguously. Also, delivery in this way is more difficult when the mother’s body is restored, and the baby has a longer period of adaptation.
It can be difficult to establish breastfeeding in such a situation, because mother and baby are often separated or too weak for comfortable breastfeeding. At the same time, at these moments it is important for the newborn to feel the mother’s warmth nearby and receive the most valuable colostrum - an indispensable component for successful postpartum adaptation. It is important for mom to understand that a caesarean section is not a reason to deprive the baby of miracle milk; breastfeeding in this situation must be organized in a timely and competent manner.
Feeding a baby with breast milk is a harmonious process that subtly responds to the child’s needs. As fluid is removed from the mother's breast, milk returns in the required quantity. If the gland is not emptied in a timely manner, its quantity may decrease or the milk may disappear altogether.
Birth is the first important event in a baby’s life. When the process proceeds naturally, the baby is prepared for environmental changes and overcoming the difficult path by interacting with the mother emotionally (hormonally). In the case of a cesarean section operation, the baby simply does not know that he was born. A baby born naturally gets acquainted with the necessary bacteria; his sterile body is populated by the maternal microflora, passing through the birth canal. From this moment on, the child lives in a new environment, and the formation of his own bacterial environment begins, which is important for the development of the baby’s immunity.
Children born through surgery enter the pathogenic microflora of the hospital ward. Moreover, many “local” pathogenic bacteria are invulnerable to the effects of antibiotics. Such an unfavorable environment awaits the baby immediately after birth. This is why lactation after cesarean section is so important for the newborn. After all, the first breast milk (colostrum), in addition to nutrients, water and vitamins, also contains the antibodies and probiotics necessary for the baby, which provide the most valuable immune protection to the child’s body and form the microflora in the intestines. In addition, colostrum does not overload the gastrointestinal tract of children. Small but nutritious doses of this valuable liquid can fully saturate a baby weakened after exposure to anesthesia.
Sometimes you can hear statements that breastfeeding after a caesarean section is impossible or often ineffective. Such arguments are erroneous and are associated rather with some features of the mother and baby’s stay after the operation.
Causes of delayed or lack of milk
What to do in a situation where there is little or no milk? Two hormones are responsible for the process of its production: prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin begins to be produced during pregnancy and enters the bloodstream after childbirth. Oxytocin is produced during breastfeeding. It is these hormones that promote the production of breast milk after childbirth. The presence of colostrum depends on the characteristics of delivery - whether it was through natural birth or cesarean section.
What is the condition and are there any problems in the postpartum period? These are the main reasons why a woman in labor does not have colostrum. For mothers who gave birth by cesarean section, colostrum may come only 2-3 days after birth, and milk on 5-7 days. If there is very little colostrum, but there is some, then simply put the baby to the breast more often.
As the baby grows, its need for breast milk will also increase. A period of shortage may occur - it is called a lactation crisis. At this point, the mother should think about continuing breastfeeding. It usually occurs 2 weeks after birth and lasts about 7 days. Don't panic and start supplementing with formula right away. It is necessary to increase lactation by all means.
To establish breastfeeding:
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day
- Eat healthy and varied
- Avoid stress
- Get more rest
As soon as milk begins to come in, a woman needs to carefully monitor the condition of her breasts to prevent stagnation. Stagnation or lactostasis, i.e. milk retention in the mammary ducts.
Milk stagnation in the first days after childbirth is quite common, especially in first-born mothers. The young mother is not yet experienced and does not know how to properly express colostrum with her hands; the thoracic ducts have not yet developed, so seek advice from your midwife. If stagnation is not resolved in time, a dangerous complication may develop - mastitis, which cannot always be treated conservatively; surgical intervention is often required.
Symptoms of lactostasis:
- Breast pain
- Lump in the mammary gland.
- Local temperature rise
Causes of lactostasis:
- Insufficient expression of remaining milk after feeding
- Hypothermia
- Incorrect attachment to the breast
- Tight bra
Introducing your baby to the breast
A baby born in the wrong way is most often in a state of intrauterine rest in the first hours. His body has not yet had time to adapt to familiarity with the outside world. In this regard, children born naturally are more adapted, since the natural program was completed in full.
How to put a baby to the breast after a caesarean section:
- first, prohibit giving your baby a pacifier;
- first application - no later than 6 hours after birth;
- help the baby latch onto the breast;
- constantly be near him.
Until now, not all Russian maternity hospitals practice keeping mother and newborn together in the same room. This will prevent a woman after surgery from familiarizing her baby with the breast in time. Especially if the woman is in a difficult situation and has not yet recovered from the effects of anesthesia.
Preparing in advance for surgical intervention in the natural process, the pregnant woman agrees with the hospital medical staff that the newborn will not be given a pacifier until he touches the mother's breast. If this condition is not met, the baby, weakened by the operation, may take the path of least resistance and choose artificial nutrition.
A baby who has had a cesarean section may develop a sucking reflex within a few days, but you should not wait that long. As soon as the woman recovers from anesthesia, she tries to feed the newborn. If a child does not latch on to the breast after a caesarean section because he does not latch onto the nipple, the mother helps him.
In this case, you need to squeeze out a little colostrum from the breast so that it gets on the baby’s tongue. Having felt the nutritious liquid in the mouth, the baby will inevitably have to take a sip, and soon it will be followed by a sucking movement.
On the first visit, the baby may not get enough, so it is important that he is close to his mother. Even in the first hours after birth, children smack their lips in their sleep - you should take advantage of this and give the newborn the breast. As soon as the baby understands what they want from him, the establishment of breastfeeding after a cesarean section will be more active.
Let's summarize
Many people mistakenly believe that the baby is not getting enough colostrum and start pumping to increase the volume of secretions. However, this opinion is wrong. Colostrum is a very valuable and nutritious product. It contains substances that provide strong immunity to the child for several months of life. In addition, in the first days after birth, the baby’s gastrointestinal tract is just beginning to function, and the amount of colostrum is quite enough to provide the baby’s internal organs with the necessary (but not more!) load.
It is also worth noting that expressed colostrum should be fed to the baby immediately. It cannot be stored for a long time even in the refrigerator, so the question of constant pumping disappears by itself.
In any case, it should be borne in mind that sites on the Internet can only give some recommendations. But if you have any problems or questions about breastfeeding, you should contact a specialist so as not to risk your health or the health of your baby.
How to pump your breasts: 3 easy ways
In fact, solving the problem of breastfeeding is not so difficult - there are at least three effective methods to establish lactation and enjoy breastfeeding.

Women in labor who have encountered problems with milk stagnation, the appearance of lumps in the breasts, and lactostasis know that it is much easier to pump the breasts in the maternity hospital with the help of a midwife than to then suffer trying to do it yourself at home. The nurse, doing a special breast massage, presses on the areola (the brown area around the nipple), stimulating the release of milk. Many people note that the procedure is painful, but it is much easier to do it at the very beginning of milk arrival than after the breasts have swelled and hardened. During a round and examination of women in labor, a gynecologist assesses the general condition of the woman, including the breasts, and may ask the nurse to show the woman in labor how to properly massage her and express milk.

You can try to strain breast milk using a special device - a breast pump. Now manufacturers produce them in various types:
- piston;
- pump-action;
- cylindrical;
- mechanical;
- electric, battery-powered and mains-powered.
The principle of operation of pump-action devices is based on creating a vacuum in the middle of the bottle with the help of a rubber bulb, the neck of which tightly clasps the areola of the nipple. Due to the difference in pressure, milk begins to flow out of the breast. But using such a device requires some skill, and there is a high risk of nipple injury. The advantage of this breast pump is its low price.

More convenient are two-phase piston breast pumps that imitate a baby's sucking. With their use, you can express quickly and painlessly. The disadvantage of the device is the rapid wear of its parts and the rather high price.
Simple cylindrical breast pumps are popular: the cylinders are inserted one into the other and by creating a vacuum, milk flows out of the breast. The advantage of this device is that it can be used as a feeding bottle: the set includes a special nipple.
If a woman has a need to constantly pump, if feeding the baby cannot be done naturally, the most convenient model would be a breast pump powered by an electrical outlet or powered by batteries. These devices allow you to adjust the power of the sucking simulation, some of them come with double cups, which allows you to express both breasts at the same time. Electric breast pumps are easy to disassemble, all parts can be washed and sterilized. The only drawback of such models is their high cost.
Before using a breast pump, you need to massage your breasts a little and try to manually express at least a little milk to soften your breasts, otherwise severe pain may occur. The good thing about using this device is that the milk is immediately collected in a special container with a scale, you can track how much milk there is in each breast, and understand whether it is enough for the baby. The collected food can be frozen and then fed to the baby or even prepared for his first milk porridge. Some sets of breast pumps immediately come with special bags for portion freezing of collected milk. They are also equipped with special brushes for washing, nipples, and replaceable bottles.
If a woman in labor is afraid to trust her breasts to the midwife or to mechanical and electrical devices, you can try expressing breast milk yourself. To do this, you need to prepare the mammary glands: wash with warm water and begin to massage, pushing the milk to the nipple. The massage should be done by lightly tapping with your fingertips in the direction from the armpit to the nipple along the lobes of the breast (the breast is conventionally divided into eight lobes, in which there are milk ducts - about 15-20, some ducts unite in the middle of the chest and milk comes out of the milk openings, of which there are from 8 to 15). Then, by pressing on the areola area around the nipple, you need to stimulate milk release. It can flow in a stream or be squeezed out drop by drop. Breast milk can be expressed into a glass, cup or other sterile container for freezing and storage. But when expressing for the first time, it is unlikely that you will be able to collect a lot of milk, so you can simply squeeze it onto a towel. The main thing is to find a comfortable position and make this procedure the least painful.
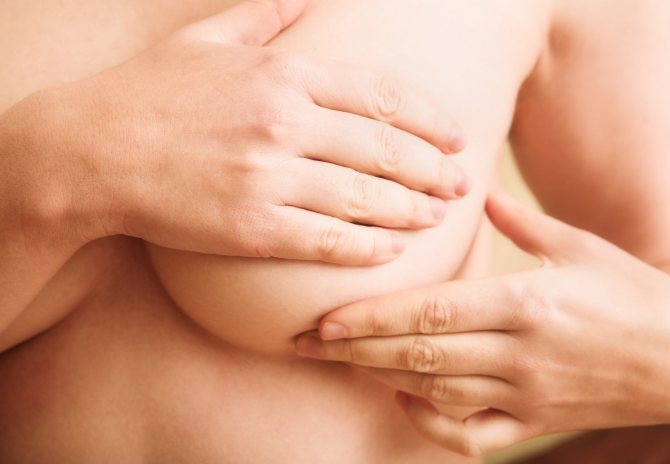
How to quickly pump breasts at home: 5 useful tips
1. Under the influence of hot water, milk flow increases. You can use this phenomenon for quick and painless pumping. Mommy can take a warm shower or give her breasts a warm shower. When pumping, the milk will flow faster
2. You can relieve hardness and relieve the feeling of fullness in your chest using an old proven method - a cabbage leaf compress. You need to wash it, beat it a little and put it in your bra. The breast will become softer and it will be easier to strain.
3. If the baby takes the nipple well and actively sucks, if stagnation or a feeling of fullness appears, you should try to offer him the breast more often. The baby's mouth is ideally suited for sucking; no one can empty the mammary glands and help mommy better than a baby.

4. Some old-school grandmothers advise using your husband as a means of helping to drain your breasts. But experienced lactation consultants recommend not resorting to such services, because there is a high risk of breast infection through possible damage to the nipple area. In addition, a man will not be able to pull milk the way a baby does, due to the peculiarities of the oral cavity. It is better to use a breast pump or express by hand.
5. If the problem of breast distension and lactostasis periodically returns, it means that breastfeeding is not established entirely correctly, perhaps the baby is not latching onto the nipple as it should, perhaps the feeding position is chosen incorrectly, some area of the breast is compressed and milk stagnation occurs. . In such a situation, it would be a good idea to consult a pediatrician, nurse, or lactation consultant.