A nursing mother may have a fever for several reasons; once they are identified, it is necessary to take immediate action. If a woman has recently given birth, perhaps this is an individual reaction to the formation of lactation; in these cases, low-grade values not exceeding 37 degrees are observed. You should never forget about dangerous mastitis or various infectious processes occurring in the body. Before bringing down a high body temperature on your own, it is imperative to contact a competent specialist who will find out the main causes and prescribe competent treatment. And every mother should remember that even at 39 degrees you cannot stop breastfeeding.
Let's take a closer look at what can affect a woman's temperature increase during breastfeeding, and what measures can be taken in specific cases, what medications are allowed to take, and how to correctly measure the temperature during lactation?
Reasons for rising temperature
Inflammatory processes in the postpartum period.
Both caesarean section and natural childbirth are stressful for a woman’s body, and do not always occur without consequences. It is possible to develop diseases such as inflammation of the uterine mucosa or sutures.
Such conditions are always preceded by elevated body temperature. But the main danger is not this, but the risk of sudden bleeding, in which literally minutes count, and you simply may not have time to get to the hospital.
Therefore, you need to be extremely careful about body temperature above 37.5 degrees in the first two weeks after birth. To be on the safe side and exclude inflammation in the female part, take a general blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula.
If it is not possible to immediately visit a doctor, first, at least try to decipher the results online, on special medical portals and reference books. If they deviate from the norm, very urgently schedule a visit to the gynecologist.
Low-grade fever.
Body temperature up to 37.2 degrees in the absence of other symptoms and undisturbed general condition may be a consequence of increased milk production by the body and is considered conditionally normal.
To make sure there is nothing serious, it is also recommended to take a clinical blood test.
ARVI.
Viral infections are the most common cause of fever. As a rule, in this case, a runny nose, cough, and sore throat are added to the symptoms. These manifestations can occur together, separately, or in various combinations with each other.

Popularly it is also called colds, flu, etc. – this doesn’t change the essence.
In this case, body temperature can increase within varying limits, from 37 to 39 degrees and above.
Lactostasis and mastitis.
Usually, with such problems, elevated temperature is accompanied by pain and severe discomfort in the chest, so the nursing mother, at a minimum, guesses that the cause of the temperature is problems in the mammary glands.
Diseases of internal organs.
As a rule, exacerbation of existing chronic diseases is most often possible. We are talking, for example, about cystitis, pyelonephritis, pneumonia, otitis media, etc.
In such cases, the temperature is usually accompanied by symptoms and pain that are localized in a specific area.
As a result, a young mother can at least guess about the reason for the increase in the mark on the thermometer.
Rules for taking antipyretics during hepatitis B
Taking medications is always accompanied by a certain risk for the baby, therefore, when using antipyretics, certain rules must be followed:
An increase in body temperature is always evidence of an inflammatory process in the body. Therefore, when it appears, it is necessary to contact a therapist or mammologist, depending on the causes of the temperature. The doctor will determine the diagnosis and suggest treatment methods. The nursing mother must strictly follow all recommendations and take medications in accordance with the instructions and prescription. Then the healing process will not take long and will not harm the child.
Source
How to measure correctly
Body temperature is measured in the armpit. The safest way to do this is with a modern electronic thermometer, which should be held for some time after the beep to be sure. It is better to watch the screen and take it out only when the mark stops changing. This indicator will be more reliable.

If you suspect that it is the breasts that are causing the elevated temperature due to active milk production, you can check yourself as follows. Measure the temperature at the elbow while squeezing your hand tightly.
This is exactly the method that was used in the department of postpartum complications, which I visited after my first birth. If the temperature is not due to the chest, then it “rises” in the elbow bend.
How can a nursing mother measure her temperature correctly?
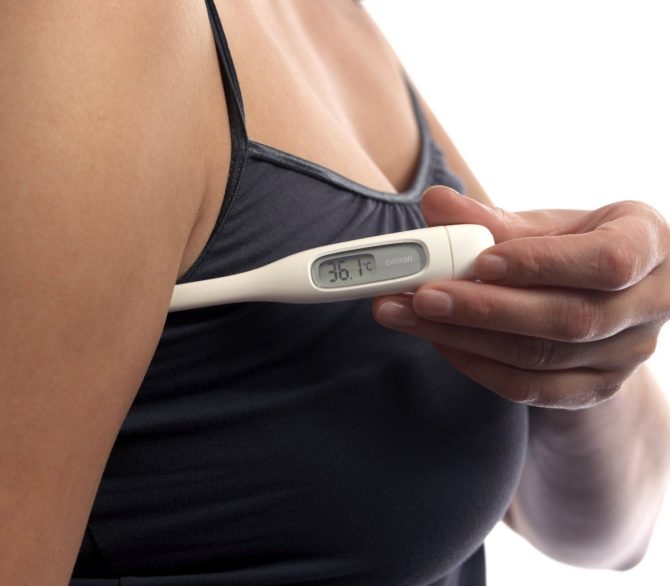
Every third woman's temperature rises to 37.5-37.6 °C during breastfeeding. The indicator is natural and normally decreases after 30-60 minutes. Therefore, it is better to measure the temperature after removing hyperemia from the glands and following the rules.
Recommendations
Swedish scientists came to the conclusion that the most accurate way to find out the body temperature is rectally, since sweat and clothing affect the indicators of the armpit. The study was conducted in 2007-2008 with the involvement of 323 patients (Source: Swedish magazine The Local, unfortunately, published research results could not be found). This method is not excluded for a nursing mother and can be used at will.
Normally, the thermometer stays at 37-37.4 °C, but if the reading is above 37.7 °C, a pathological process in the body is clear. Diagnosis of symptoms and treatment are required.
How does it affect milk?
There are many myths that when the temperature rises, a nursing mother must immediately stop breastfeeding, because the milk curdles, turns sour, goes rancid, etc. Some people advise boiling milk during illness before giving it to the child.
All of this is myths and speculation coming from people who do not understand breastfeeding issues.

Boiling milk generally destroys almost completely all the beneficial substances in it.
Elevated body temperature itself does not affect the quality of milk.
Therefore, when the mark on the thermometer rises, it is recommended not only not to interrupt breastfeeding, but moreover, to actively continue it. Why? Read on!
Normal temperature during breastfeeding
With the first influx of transitional milk (on the 3-4th day), the endocrine system is rebuilt to a new regime. Now the body's resources are aimed at the growth, development of the baby and recovery after childbirth. Due to the increased load, the immune system reacts with a low-grade fever - the thermometer shows 1-2 degrees above the individual norm (37-37.5 °C).
The temperature of a healthy person (without lactation) varies during the day from 36.5 °C to 37 °C. The indicator varies depending on the time of day, physical and psychological stress. Low-grade fever after childbirth is a normal state of the body, which is influenced by 2 factors: postpartum stress and hormonal changes.
The temperature of a nursing mother can normally be up to 37.5 °C.
The greater the accumulation of breast milk in the glands, the more local immunity is loaded, and the higher the temperature rises. If a woman is diagnosed with mastitis (complications of blocked ducts), the indicator increases to 39 °C.
It is recommended to measure the temperature an hour or 30 minutes before feeding. As the milk flows in, the thermometer rises, and after the sucking stops it returns to normal.
Research results
Breast skin temperature was measured during breastfeeding in 11 mothers a total of 47 times using Coretemp CM-210 (Terumo Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) to study changes in breast skin temperature during breastfeeding. In both breasts, breast skin temperature was significantly higher than baseline skin temperature from the start of suckling to 5 minutes after suckling ended, and mean breast skin temperature before breastfeeding from 4 days to 8 weeks postpartum was significantly higher than in the first 1-2 days after birth. These results indicate that breast skin temperature increases during the first 1–2 days and 4–5 days postpartum, and that breast skin temperature remains high during suckling and up to 5 minutes after suckling ends.
Is it possible to breastfeed
The answer to this question will depend on what is causing the increase in body temperature and what treatment will take place.
If the cause is a viral infection, flu, or cold, then the doctor will prescribe symptomatic treatment.
Milk is formed from blood and lymph. Viruses do not penetrate the blood and lymph. Therefore, breast milk is not contaminated with ARVI and influenza.
On the contrary, it contains antibodies produced by the mother's body to fight the virus. It is these antibodies, if the baby feeds on the breast, that will help him either completely avoid infection by airborne droplets from the mother, or suffer from a mild form of the disease.
Therefore, during a viral infection, breastfeeding is simply necessary.

If the mother has a bacterial disease (inflammation of the uterine lining, mastitis, cystitis, pneumonia, otitis media, etc.), the treatment of which requires a doctor to prescribe antibiotics, then the question arises as to whether the latter are compatible with breastfeeding.
Antibiotics are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, who must be aware that we are a nursing mother.
In the modern world, there are antibiotics approved for use in nursing mothers. A competent doctor will certainly select for you the option of medication that is effective and at the same time approved for use during breastfeeding.
If the prescribed antibiotic is not compatible with breastfeeding, the newborn will need to be switched to artificial feeding for the period of its use.
You should express milk 6-7 times a day to maintain lactation. This will be a signal to the body that milk is being removed from the breast, and therefore it needs to continue producing it.
After you are treated, you will be able to breastfeed your baby again.
If you have mastitis, you can feed anyway as long as it does not cause you obvious pain. If the pain is unbearable, you should feed from the healthy breast and pump the sick one.
What to do in case of high temperature
So, with a reading of up to 37.4 °C, there is no reason to panic. In this case, it is recommended to monitor the temperature for 3-4 days. An increase can be triggered by simple stress or lack of sleep. Normally, the temperature returns to normal within a day. If there is an increase in the indicator, then it’s time to take action.
General algorithm of actions
If the temperature is not critical, it is recommended to monitor the condition for 1-2 days. Diseases in which feeding stops appear sharply and acutely, accompanied by fever and fever. Urgent hospitalization is required only for such symptoms.
To eliminate the risk of complications, it is better to call a doctor within 24 hours after detecting a symptom. Breastfeeding mom and baby are vulnerable to outbreaks of colds and flu. Due to weakened immunity, viruses “go down” within 3 days without treatment. The result is pneumonia, severe laryngitis, meningitis, cessation of breastfeeding.
If the temperature does not exceed 38 °C, recommendations are limited to drinking plenty of fluids and semi-bed rest. It is important to continue breastfeeding, since the best immunomodulatory agent for the baby is breast milk.
If the temperature is 38-39 °C

The indicator is considered critical and indicates that the body cannot cope with disorders on its own. Antipyretics and targeted drug therapy are recommended. To treat viral infections, a nursing mother can start with traditional methods of treatment:
The use of traditional methods neutralizes colds in 5 days. But if a nursing mother’s fever does not subside for more than 3 days, antipyretic medications are required.
Treatment
If the cause of the high mark on the thermometer is a viral infection (flu, common colds, other acute respiratory viral infections), then the treatment that the doctor will prescribe for you will be symptomatic, since currently there are no drugs with proven effectiveness that can act on viruses.

The following are intended to alleviate the condition of a nursing mother:
- The air in the room is 18-20 degrees. Due to the difference in body temperature and room temperature, the body will be able to lose excess heat, thereby independently lowering body temperature. In this case, you should dress warmly.
- Air humidity is 50-70 percent. Only a special device can cope with this task - an air humidifier (costs from 2000 rubles). As the temperature rises, the body begins to rapidly lose fluid. If at the same time you have to breathe dry and warm air, then the losses are catastrophic, dehydration, rhinitis and bronchitis are guaranteed.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Mineral water, dried fruit compotes, fruit drinks, special solutions for rehydration (sold in pharmacies) are designed to significantly alleviate the condition and reduce recovery time by removing toxins and viruses from the body through urine and sweat. If there are no contraindications, you should drink up to 5-6 liters per day.
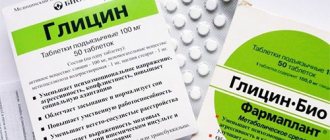
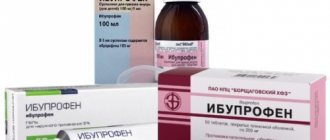
- Antipyretics if necessary symptomatically. If you are wondering how to lower your temperature, then the recommendations are as follows. During breastfeeding, paracetamol and ibuprofen are allowed for use according to the instructions and prescriptions of the doctor.
Antipyretics during breastfeeding
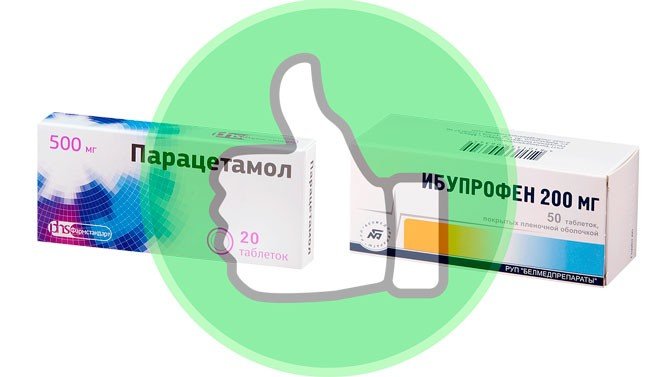
If the temperature is not brought down by folk remedies, therapists recommend remedies based on paracetamol and ibuprofen. The drugs penetrate the lactation barrier, but are safe for the baby’s body.
Approved medications
The drugs act against fever, pain and inflammation. Available in tablets, suspensions and suppositories. Differences in release form - exposure time. Syrups act in 15-20 minutes, tablets - in 30-40 minutes, rectal suspension - within an hour. If the temperature needs to be brought down urgently, it is better to drink a suspension or capsule; rectal suppositories are recommended at night.
Prohibited drugs
The effect of drugs on milk has not been studied, but the list of side effects is a reason to refuse breastfeeding. Complex powders contain substances that depress the functioning of the central nervous system and provoke disturbances in the development of the baby.
Prevention of colds in a nursing mother
Due to the fact that acute respiratory viral infections are one of the most common causes of fever in a nursing woman, she needs to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of infection:
- try not to appear in places with large crowds of people, especially in the autumn-spring period;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- eat well. Make sure that the diet is varied and contains all the necessary substances, vitamins and microelements;
- use adequate physical activity. Physical exercises will help maintain body tone: yoga, dancing, swimming, gymnastics;
- harden yourself, for example, take a contrast shower. Just try not to overcool the mammary glands.
If a nursing mother discovers that she has an elevated temperature, she needs to quickly find out the cause of this condition. First of all, you need to see a doctor, he will make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment, which can be safely used while breastfeeding. But it is best to ensure that this problem does not arise. To do this, you need to follow feeding rules to prevent lactostasis, monitor the quality of food consumed to prevent poisoning, and apply measures to prevent ARVI. It is important to be attentive to your health and well-being so as not to miss the first signs of the disease. In this case, malaise will not overshadow the entire period of breastfeeding.
- Author: Veronika Chudnova
Rate this article:
(3 votes, average: 3.7 out of 5)