Ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) is detected in 50% of patients in the early stages of cancer and in almost all patients in whom the cancer process is at the last stage.
The Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest diagnostic equipment from the world's leading manufacturers, with the help of which oncologists identify the early stages of oncological pathology. Chemotherapists, radiologists, and oncologists treat patients with ascites in accordance with international standards of medical care. At the same time, doctors take an individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient.
Reasons for development
Ascites is a serious complication of stomach and colon cancer, colorectal cancer, malignant tumors of the pancreas, and oncological pathology of the mammary glands, ovaries and uterus. When a large volume of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, intra-abdominal pressure increases, and the diaphragm moves into the chest cavity. This leads to disruption of the heart and lungs. There is a violation of blood circulation in the vessels.
In the presence of ascites, the patient's body loses a large amount of protein. Metabolism is disrupted, heart failure and other imbalances in the internal environment of the body develop, which worsen the course of the underlying disease.
There is always a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity of a healthy person. It prevents the sheets of peritoneum from sticking together. The produced intra-abdominal fluid is reabsorbed by the peritoneum.
With the development of cancer, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted. The secretory, resorptive and barrier functions of the peritoneal layers fail. In this case, either excess fluid production or disruption of its absorption processes may be observed. As a result, a large volume of exudate accumulates in the abdominal cavity. It can reach twenty liters.
The main reason for damage to the peritoneum by malignant cells is its close contact with organs that are affected by a cancerous tumor. Ascites in the presence of oncological pathology develops under the influence of the following factors:
- A large accumulation of blood and lymphatic vessels in the peritoneum through which cancer cells spread;
- Tight fit of the folds of the peritoneum to each other, which contributes to the rapid spread of malignant cells to adjacent tissues;
- Germination of a cancerous tumor through the peritoneal tissue;
- Transfer of atypical cells to peritoneal tissue during surgery.
Chemotherapy may be the cause of ascites. The accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum occurs due to cancer intoxication. If the liver is affected by a primary cancerous tumor, metastases of malignant cells from tumors of a different location, the outflow of blood through its venous system is disrupted, and portal hypertension develops - an increase in pressure inside the portal vein. The lumen of the venous vessels increases, plasma sweats from them and accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
The cause of ascites may be peritoneal carcinomatosis. In the presence of a cancerous tumor of the abdominal organs, atypical cells settle on the parietal and visceral sheets of the peritoneum. They block the resorptive function, as a result of which the lymphatic vessels do not cope well with the intended load, and lymph outflow is impaired. Free fluid gradually accumulates in the abdominal cavity. This is the mechanism of development of carcinomatous ascites.
Make an appointment
Causes
The causes of ascitic disease are unexpected, the most common among them are presented below. This:
- malignant neoplasms and metastases;
- liver cirrhosis and increased blood pressure in the portal system;
- thrombosis (narrowing of the hepatic, inferior vena cava and portal veins);
- acute and chronic inflammatory kidney diseases;
- nephrotic syndrome (protein begins to be excreted in the urine);
- chronic renal failure;
- inflammatory lesion of the serous membrane of the heart;
- acute and chronic heart failure;
- some infectious and inflammatory bowel diseases, in which diarrhea and protein loss are observed;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- tuberculosis;
- pseudomyxoma (mucus accumulation);
- anasrka.
This disease is a complication of liver cirrhosis and more. It progresses gradually in the body; at first it does not manifest itself in any way. Abdominal ascites is difficult to treat successfully. However, healing occurs if the main pathogenic factor is eliminated.
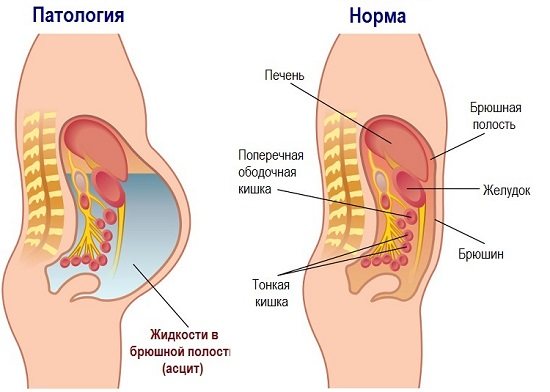
Stages of severity
There are three stages of abdominal hydrops depending on the amount of accumulated fluid:
- Initial stage - up to one and a half liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity;
- Moderate ascites - manifested by an increase in the size of the abdomen, edema of the lower extremities. The patient is concerned about severe shortness of breath, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, constipation;
- Severe dropsy - from 5 to 20 liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. The skin on the abdomen tightens and becomes smooth. Patients experience heart failure and respiratory failure. When the fluid becomes infected, ascites-peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneal layers) develops.
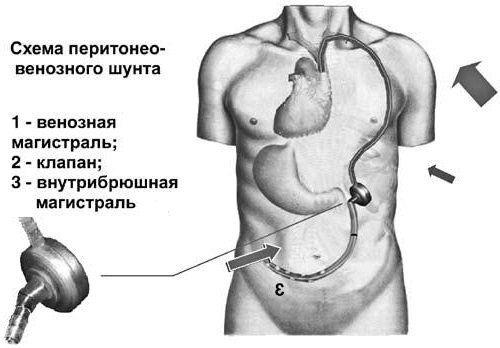
Peritoneovenous shunt (Levine shunt)
Sometimes used to treat refractory ascites, i.e. one that does not respond to drug therapy and quickly returns after puncture. The operation consists of increasing the volume of circulating blood through the constant flow of fluid from the abdominal cavity into the general bloodstream system.
A Levine shunt is a long plastic tube that is inserted into the abdominal cavity, reaching the pelvic floor. Next, the shunt is connected to a valve and a silicone tube, which passes subcutaneously to the neck area for subsequent connection to the internal jugular and superior vena cava. The valve opens with the help of the resulting displacement force of the diaphragm and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Thus, there is an unimpeded flow of fluid into the superior vena cava.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of ascites is a significant increase in size and pathological bloating of the abdomen. Signs of abdominal dropsy can increase rapidly or over several months. Ascites is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- Feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- Pain in the abdomen and pelvis;
- Increased gas formation (flatulence);
- Belching;
- Heartburn;
- Digestive disorders.
Visually, the patient’s abdomen enlarges, in a horizontal position it hangs down and begins to “blur” on the sides. The navel gradually protrudes more and more, and blood vessels are visible on the stretched skin. As ascites develops, it becomes difficult for the patient to bend over and shortness of breath appears.
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic evaluate the clinical manifestations of the disease and carry out a differential diagnosis of cancer with other diseases, the manifestation of which is ascites.
Diagnostics
Doctors identify ascites during an examination of the patient. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients, which allows them to identify the cause of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity. One of the most reliable diagnostic methods is ultrasound. During the procedure, the doctor not only clearly sees the liquid, but also calculates its volume.
In case of ascites, oncologists necessarily perform laparocentesis. After puncturing the anterior abdominal wall, the doctor aspirates fluid from the abdominal cavity and sends it to the laboratory for testing. Computed tomography radiology scans are used to determine the presence of malignant tumors in the liver that cause portal hypertension.
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to determine the amount of accumulated fluid and its location.
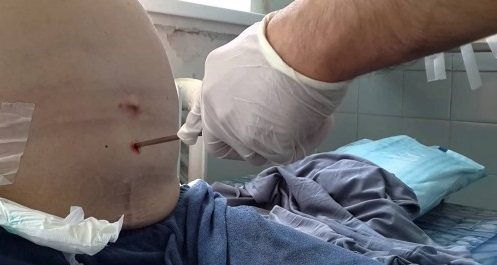
Abdominal laparocentesis
For ascites, abdominal laparocentesis is a surgical procedure in which fluid is removed from the abdominal cavity by puncture. You should not pump out more than 4 liters of exudate at a time, as this threatens the development of collapse.
The more often a puncture is performed for ascites, the higher the risk of developing peritoneal inflammation. In addition, the likelihood of formation of adhesions and complications from the procedure increases. Therefore, for massive ascites, it is preferable to install a catheter.
Indications for laparocentesis are tense and refractory ascites. The liquid can be pumped out using a catheter, or it simply flows freely into a previously prepared container after the trocar is installed in the abdominal cavity.
Treatment
Drug therapy for ascites is not carried out due to low effectiveness. Aldosterone antagonists and diuretics normalize water-salt metabolism and prevent excess secretion of peritoneal fluid. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital offer palliative surgery to patients with ascites in the late stages of cancer:
- Omentohepatophrenopexy;
- Deperitonization;
- Installation of a peritoneovenous shunt.
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic carry out traditional or intracavitary chemotherapy for ascites - after removing the fluid, a chemotherapy drug is injected into the abdominal cavity. Laparocentesis is performed to remove fluid. The procedure is not performed if the following contraindications are present:
- Adhesive process inside the abdominal cavity;
- Severe flatulence;
- Perforation of the intestinal walls;
- Purulent infectious processes.
Laparocentesis is prescribed in cases where taking diuretics does not lead to a positive result. The procedure is also indicated for resistant ascites.
Laparocentesis is carried out in several stages using local anesthesia:
- the patient is in a sitting position, the doctor treats the subsequent puncture site with an antiseptic and administers painkillers;
- An incision is made in the abdominal wall along the linea alba at a distance of 2-3 centimeters below the navel;
- The puncture itself is performed using a trocar using rotational movements. A special flexible tube is attached to the trocar, through which excess fluid is removed from the body. The fluid is pumped out quite slowly, and the doctor constantly monitors the patient’s condition. As the exudate is removed, the nurse tightens the patient's abdomen with a sheet to slowly reduce the pressure in the abdominal cavity;
- After the fluid is pumped out, a sterile bandage is applied to the wound.
Using laparocentesis, up to 10 liters of fluid can be removed from the patient’s body. In this case, it may be necessary to administer albumin and other drugs to prevent the development of renal failure.
If necessary, temporary catheters can be installed in the abdominal cavity, through which excess fluid will gradually be removed. It should be noted that the use of catheters can lead to a decrease in blood pressure and the formation of adhesions.
There are also contraindications to laparocentesis. Among them:
- pronounced flatulence;
- adhesive disease of the abdominal organs;
- stage of recovery after surgery on a ventral hernia.
Diuretics are prescribed to patients with developing ascites in cancer over a long course. Such drugs as Furosemide, Diacarb and Veroshpiron are effective.
When taking diuretics, medications containing potassium must also be prescribed. Otherwise, there is a high probability of developing disturbances in water and electrolyte metabolism.
Dietary nutrition primarily involves reducing the amount of salt consumed, which retains fluid in the body. It is also important to limit the amount of fluid you drink. It is recommended to include more foods containing potassium in your diet.
After removal of fluid from the abdominal cavity, patients are provided with a balanced and high-calorie diet. This allows you to meet the body's needs for proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Fat consumption is reduced.

Drug treatment
The main drugs that help remove excess fluid from the body are diuretics. Thanks to their intake, it is possible to achieve the transition of excess fluid from the abdominal cavity into the bloodstream, which helps reduce the symptoms of ascites.
- To begin with, patients are prescribed the smallest dose of diuretics to minimize the risk of side effects. An important principle of treatment with diuretics is a slow increase in diuresis, which will not lead to significant losses of potassium and other important metabolites. The most commonly recommended medications are Aldactone, Veroshpiron, Triamterene, and Amiloride. In parallel, potassium supplements are prescribed. At the same time, hepatoprotectors are introduced into the treatment regimen.
- At the same time, doctors monitor the patient’s diuresis on a daily basis and, if treatment is ineffective, increase the dose of drugs or replace them with stronger drugs, for example, Triampur or Dichlorothiazide.
In addition to diuretics, patients are prescribed drugs aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels (vitamin C, vitamin P, Diosmin), drugs that prevent fluid from leaving the vascular bed (Reopoliglucin). The introduction of protein preparations improves the metabolism of liver cells. Most often, concentrated plasma or an Albumin solution in a 20% concentration is used for this purpose.
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed if ascites is bacterial in nature.
Non-cancerous ascites
Ascites is a consequence of various disorders that occur in the body. Treatment tactics depend on the pathological process that caused the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity:
- To treat acute heart failure, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe metabolites, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors to patients;
- For infectious and toxic liver lesions, therapy with hepatoprotectors is carried out;
- If ascites has developed due to low protein levels in the blood, albumin infusions are performed;
- Ascites that develops as a result of peritoneal tuberculosis is treated with anti-tuberculosis drugs.
To remove fluid from the body, patients with ascites are prescribed diuretics. The main method of eliminating ascites is to remove accumulated fluid by puncturing the abdominal wall, followed by installing drainage. For persistent ascites, peritoneal fluid is reinfused after filtration. A peritoneovenous shunt for abdominal ascites ensures the flow of fluid into the general bloodstream. To do this, surgeons form a structure with a valve, through which fluid from the abdominal cavity enters the superior vena cava system during inhalation.
Omentohepatophrenopexy for abdominal ascites is performed to reduce pressure in the venous system. The surgeon sutures the omentum to the diaphragm and liver. Then, during breathing movements, the veins are unloaded from blood. As a result, the release of fluid through the vascular wall into the abdominal cavity decreases. As a result of deperitonization (excision of areas of the peritoneum), additional outflow pathways for peritoneal fluid are created.
How to remove water from the body through diet?
Increasing the volume of fluid you drink makes metabolic processes and the functioning of the excretory system run smoothly. Adequate hydration means that the body does not protect itself from dehydration and does not retain water as a protective reflex.
Noticeable effects can be achieved by reducing dietary salt intake. Sodium is an osmotically active element, which means it promotes water retention. If we have problems storing water in the body, a low sodium diet can be used. Cooked and highly processed foods should be avoided, and seasoning should be done using herbs (preferably natural rather than pre-made spice blends that contain extra salt), and choosing low-sodium mineral water.
One way to accumulate water in the body is to increase the amount of vegetables, fruits and herbs consumed, which improve the process of removing excess water from the body. These include, but are not limited to: cucumber, cranberry, strawberry, parsley, nettle infusion and green tea.
Physical activity helps get rid of excess water. It doesn't have to be a competitive sport, regular daily walks are enough.
Konstantin KAZANTSEV
Forecast
Ascites in cancer significantly worsens the general well-being of the patient. As a rule, such a complication occurs in the later stages of oncology, in which the survival prognosis depends on the nature of the tumor itself and its distribution throughout the body.
Life expectancy with ascites depends on the following factors:
- Functioning of the kidneys and liver;
- Activities of the cardiovascular system;
- The effectiveness of therapy for the underlying disease.
The development of ascites can be prevented by an experienced doctor observing the patient. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in dealing with various types of cancer. Qualified medical personnel and the latest equipment allow for accurate diagnosis and high-quality, effective treatment in accordance with European standards.