What are adenoids and where do they come from?
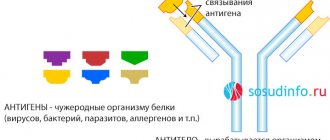
Adenoid vegetations (nasopharyngeal tonsil) are lymphoid tissue in the vault of the nasopharynx. It is present in all children without exception and is a peripheral organ of the immune system, part of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring. The main function of this anatomical formation is to fight bacteria or viruses that enter the child’s body. Its main difference from other tonsils is that the surface is covered with a special epithelium that produces mucus. An increase (hypertrophy) of adenoid tissue is provoked by frequent allergic and respiratory diseases of viral or bacterial etiology. Therefore, the peak of hypertrophy of adenoid tissue occurs precisely at the age of 3-7 years. Then the lymphoid tissue is gradually reduced at the age of 10–12 years. By the age of 17, only fragments of tissue often remain; in healthy adults, adenoid tissue is absent. Hypertrophy of adenoid tissue is usually divided into several degrees according to its volume in the nasopharynx, from the first, where the adenoids close the nasal passages (choanae) by 1/3, to the third or fourth degree, when complete obstruction of the nasopharynx occurs with the impossibility of nasal breathing.
Causes of adenoids
The growth of adenoid vegetations can lead to:
- heredity;
- persistent colds;
- “childhood” diseases affecting the nasal cavity and pharynx: scarlet fever, measles, rubella;
- weak immunity;
- non-compliance with ventilation standards, room humidity, dust;
- allergic manifestations;
- unfavorable environment (exhausts, emissions).
The baby's body, constantly attacked by viruses, in combination with an undeveloped immune system, leads to hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, as a result of which a complex disruption of the process of nasal breathing occurs, mucus in the nose stagnates. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrating from the outside “stick” to this mucus, and the adenoid vegetations themselves turn into a focus of infection. From here, bacteria and viruses can spread to other organs.
Clinical manifestations
Inflammation of the adenoid tissue is called adenoiditis. Its course can be acute, subacute and chronic. Let's briefly touch on the main symptoms that parents should pay attention to:
1. Runny nose, most often it has a protracted course.
2. Predominant breathing through the mouth. Caused by difficult nasal breathing. The degree of difficulty directly depends on the degree of hypertrophy of the adenoid tissue. Nasality often appears. With a long course of chronic adenoiditis and breathing through the mouth, changes in the facial skeleton are possible, which later manifests itself as a persistent violation of speech pronunciation.
3. Night snoring, restless sleep.
4. Morning cough caused by choking on mucus draining from the nasopharynx overnight.
5. Hearing loss, recurrent otitis due to mechanical obstruction of the auditory tubes by adenoid vegetations. In this case, hypertrophy can be 1-2 degrees, when the adenoids are located near the mouths of the auditory tubes, which are responsible for ventilation of the middle ear through the auditory tube. The child begins to constantly ask questions or watch cartoons too loudly.
6. Fatigue, apathy. Caused by constant oxygen starvation of the brain, especially in chronic adenoiditis. There may be a lag behind peers in mental and physical development.
Symptoms and treatment of adenoids in children
- difficult or impossible breathing through the nose;
- the child breathes through his mouth;
- adenoids in young children (infants) cause problems with the sucking process (the baby does not eat enough, is capricious and does not gain weight well);
- anemia;
- problems with smell and swallowing;
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- the child speaks quietly;
- nasal voice;
- snoring during sleep, sleep disorder;
- recurring otitis media, chronic runny nose;
- hearing problems;
- complaints of headaches in the morning;
- overweight, excessive activity, decreased performance at school.
Methods for studying adenoid vegetations
In its normal state, it is impossible to see this tonsil without additional optical devices. There are a number of studies that help determine the extent of adenoid vegetations: digital examination, posterior rhinoscopy with a mirror, radiography of the nasopharynx, endoscopy of the nasopharynx, three-dimensional X-ray examination or CT scan of the nasopharynx. The most modern methods today are:
- endoscopy of the nasopharynx and nasal cavity. The procedure is performed in our clinic under local anesthesia during an appointment with an ENT doctor. It is completely painless and allows you to assess not only the degree of adenoid vegetations, but also the nature of inflammation, the condition of the mouths of the auditory tubes, and also examine the posterior parts of the nasal cavity.
- three-dimensional X-ray examination / CT scan of the nasopharynx. The methods are significantly more informative than conventional X-rays of the nasopharynx, since they allow one to determine not only the size, but also the ratio of adenoid vegetations to other structures of the nasopharynx (the mouths of the auditory tubes, choanae, etc.). The radiation dose is almost 3 times less (0.009 m3v), and the duration of the study is no more than 2 minutes. You can undergo this study at the clinic on Usacheva.
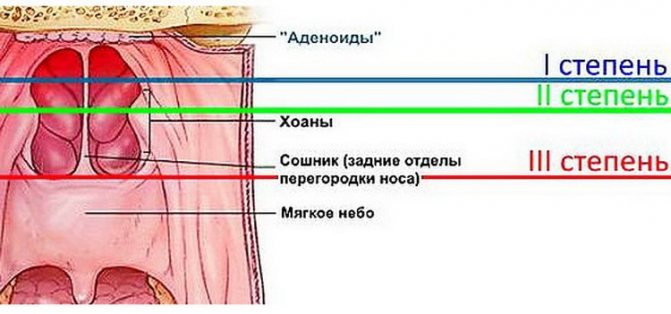
Classification of adenoids
Adenoids of the I degree: the initial stage, characterized by a small size of vegetation. At this stage, the upper part of the vomer (posterior part of the nasal septum) is closed. The child feels uncomfortable only at night, when breathing becomes difficult during sleep.
In children with grade II adenoids, the vegetation covers more than half of the vomer. They are medium in size. Distinctive features of this stage: the child constantly snores at night and breathes with his mouth open during the day.
At stage III, the growths reach their maximum size: they occupy most of the space between the tongue and palate. Breathing through the nose becomes impossible. Children with stage III inflamed adenoids breathe exclusively through their mouths.
Treatment of adenoiditis
Treatment of adenoiditis is usually divided into conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment requires from parents, first of all, a lot of patience (you need to teach the baby to blow his nose correctly, use the nasal cavity with him, sometimes several times a day!), attend procedures (rinsing the nose by an ENT doctor, physical therapy, etc.), and strictly follow all doctor's orders. This is far from a quick process, but if the parents and the doctor are at the same time, and act as a cohesive team, then the result will not be long in coming! But there are cases when conservative treatment is ineffective, then the doctor decides on surgical intervention, and this does not always depend only on the degree of the adenoids. Most often, indications for surgical treatment are: complete absence of nasal breathing, recurrent otitis (tubo-otitis), night apnea, persistent hearing loss.
“If they are involved in the immune response, why remove them? There is nothing superfluous in the body!”
Indeed, adenoid tissue is part of the lymphoid ring of the pharynx, as mentioned above, but only a part! Here it is important to assess the balance of harm and benefit to the body. In the case of chronic adenoiditis, the tonsil itself becomes a place of residence and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which clearly does not benefit the child, and frequent exacerbations lead to an increase in adenoid tissue in size, causing parallel ear disease, followed by persistent hearing loss.
“If you remove them, they will grow back!”
At this stage of medical development, this opinion is erroneous. The adenotomy operation is performed under general anesthesia using endoscopic techniques. Modern equipment allows you to remove adenoid tissue completely under visual control, thereby ensuring the absence of relapses. With adenotomy under local anesthesia, as was previously performed everywhere, the risk of repeated adenotomies is really high, since most often part of the tonsil is not removed the first time, which causes a relapse.
Why are adenoids dangerous?
The growth of adenoid vegetations can lead to hearing problems, including hearing loss. The human hearing aid has several sections. In the middle section there is an auditory tube, also known as the Eustachian tube, which is responsible for regulating external (atmospheric) pressure with pressure in the nasopharynx. The pharyngeal tonsil, increasing in size, blocks the mouth of the Eustachian tube, air cannot circulate freely between the nasal cavity and the ear. As a result, the eardrum becomes less mobile, and this negatively affects the ability to hear. In severe cases, such complications cannot be treated.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
When normal air circulation is not possible, an infection develops in the ear and inflammation (otitis) occurs.
Constant mouth breathing leads, as mentioned earlier, to deformation of the facial skeleton, as well as a decrease in oxygen saturation of the brain: the child quickly gets tired and cannot withstand the school load, and performance decreases sharply.
The constant concentration of infection in the nasopharyngeal tonsil leads to general intoxication of the body and the spread of viruses to other organs. The baby is exposed to frequent bronchitis, laryngitis and pharyngitis.
Unpleasant consequences also include problems with the gastrointestinal tract, urinary incontinence at night, and coughing.
Advice from the doctor
As a generalization, I want to say that the well-known joke about curing a runny nose in 7 days and a week does not work with children! Those who treat a child’s runny nose as “ordinary snot that will go away on its own” most often face a whole bunch of complications in the future. Therefore, the sooner you consult an ENT doctor and begin competent treatment, the higher the likelihood that the problem of adenoids will bypass you!
Make an appointment with a pediatric otolaryngologist by calling the single contact center in Moscow, fill out the on-line appointment form, or contact the reception desk of the Family Doctor clinic.
Health to you and your kids!
Effective methods of treating adenoids in children
There are two ways to treat children - surgical and conservative. Treatment methods are prescribed only by an ENT doctor, based on the stage of vegetation growth and the child’s condition.
Treating adenoids with a conservative method means using medications in combination with physiotherapy. An integrated approach is the key to effective treatment of adenoids. The doctor prescribes vasoconstrictor drops and antimicrobial drugs.
It is recommended to rinse the nose with a solution of furatsilin, protargol, rhinosept and other medications. It is not forbidden to treat adenoids in children with folk remedies: decoctions of chamomile, oak bark, St. John's wort, string, horsetail, etc. are perfect for washing)
To consolidate the effect of treatment, it is recommended to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures: ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, electrophoresis, etc.
At the same time, it is worth taking antihistamines and vitamin complexes. Children with overgrown adenoid vegetations are recommended to visit our Black Sea resorts.
How is adenoid surgery performed on children?
Adenotomy is performed under general anesthesia, 1 hour including anesthesia. hours depending on the degree of pathology and individual characteristics of the development of the nasopharynx in the child.
What is included in preoperative preparation
The preparation plan before adenotomy includes:
- examination by a pediatrician;
- sanitation of the oral cavity by a dentist;
- consultation with an anesthesiologist;
- examination by a cardiologist.
The following tests will be required:
- UAC;
- test for blood clotting, group and Rh factor;
- blood biochemistry;
- ECG;
- OAM;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- hospital group.
7–10 days before surgery, you should avoid taking medications that affect the rate of blood clotting. For a week, it is advisable to limit children’s contacts with strangers, stay in crowded places, and exclude foods that can cause an allergic reaction from the diet. Measures are necessary to ensure that the operation is as effective and safe as possible for the baby.
How is surgery to remove adenoids performed in children?
There are two options for performing the operation:
- classic adenotomy, in which the doctor inserts a special instrument (adenotome) through the mouth and cuts off the enlarged tissue;
- endoscopic adenotomy, which is performed using an endoscope and special equipment - a ring knife, a microdebrider shaver (an instrument that simultaneously sucks out the cut-off lymphoid tissue).
Endoscopic adenotomy is considered the standard, in which the operation to remove adenoids in children is carried out under the control of video equipment. In parallel with the removal of nasopharyngeal tonsils, in some cases a vasotomy is performed, which significantly reduces nasal swelling, and tonsillectomy, which involves resection of the palatine tonsils. A combined operation is performed only if there are strict indications and it is impossible to solve the problem by other methods.
Both laser and endoscopic removal of adenoids in children occur according to a specific algorithm:
- the child is given general anesthesia;
- An endoscope and the necessary instruments are inserted into the nasopharynx;
- Using a laser, microdebrider or adenotom, excess tissue is cut off:
- assess the condition of the mucous membranes and blood vessels, the degree of opening of the lumen of the nasopharyngeal canal;
- carefully remove the equipment.
To provide a better view, in some cases doctors use a laryngeal speculum, which is inserted through the mouth. The risk of bleeding is minimal and nasal packing is usually not required.
Possible complications
The only dangerous complication after surgery is bleeding. It occurs in extremely rare cases. After the operation, the child is in the hospital. Sometimes after removal of the adenoids, a child may experience:
- dizziness;
- slight increase in temperature;
- short headache;
- slight nausea.
A slight nasal voice, nasal congestion and a slight runny nose may persist for 4–10 days. In most cases, these phenomena go away on their own and do not require medical attention.
Contraindications to X-ray of the nasopharynx
Despite the fact that radiography is a safe method, even minimal doses of radiation can have an adverse effect on the development of the fetus, therefore such diagnostics are not prescribed to pregnant women. It is also not used if a woman has recently given birth and is breastfeeding. In addition, it is not used in the following cases:
- The patient has received a large dose of radiation over the past year;
- The patient is in serious condition;
- The patient is under 16 years of age.
In the latter case there are a number of exceptions. Children are also prescribed an X-ray of the nasopharynx in cases where other methods cannot be used, but a diagnosis and treatment need to be made. In this case, the attending physician compares the risks and chooses the lesser of the evils.
Conservative therapy
How to determine the degree of adenoids in a child? Refer to the description above - individual symptoms are highlighted for each stage of pathology development. As for treatment, the most common would be drug therapy.
For the most part, children are prescribed antihistamines, immunomodulators, vitamin supplements, and other drugs that stimulate the body's immune defense. To relieve inflammation and facilitate breathing through the nose, special nasal drops with anti-inflammatory components are used.
Vasoconstrictors are prescribed with caution - they cannot be used for more than 3-5 days in a row! In some cases, rinsing the nasal passages with salted solutions or similar medications has a good effect.
As for physiotherapeutic procedures, the following are usually prescribed:
- Medicinal electrophoresis (with prednisolone, potassium iodide or silver nitrate).
- UHF therapy.
- High frequency magnetic therapy.
- Mud applications.
- Ultraviolet treatment.
Breathing exercises are also of great importance here. After all, a child, especially at an advanced stage of the disease, gets used to breathing through his mouth. Re-developing the habit of nasal breathing in such cases is very important.
The whole complex of these methods is in most cases enough to get rid of adenoids. But if the disease is at the third stage, the child’s condition does not improve, and surgical intervention has to be resorted to.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Enlarged adenoids. Endoscopic picture
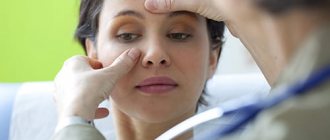
To establish a diagnosis, a simple examination is sometimes sufficient, but often it is necessary to “see” the adenoids. It is best to look directly into the nasopharynx using an endoscope. However, this procedure is possible in children only from 5-7 years of age, when the child understands how to behave when there is an instrument deep in the nasal cavity. At an earlier age, endoscopy is also possible using 2-3 minutes of superficial inhalation anesthesia.
A more accessible method is x-ray examination. The advantage of this method is that everyone can view the image, including parents, and not just one doctor. Therefore, this method is considered the most objective. One of the X-ray diagnostic methods is computed tomography. But using it only to examine the nasopharynx is absolutely irrational and expensive. I would like to warn parents about a very ancient method of examining the nasopharynx, the so-called “finger”, which was used in the “pre-radiological” era and which doctors sometimes use now. It involves feeling the adenoids with a finger bent and placed behind the soft palate through the mouth. Look at the location of the nasopharynx in the diagram, and you can understand what the unfortunate child experiences. We consider this an inhumane, psychologically traumatic, highly subjective, archaic and unacceptable method. Don't let your children get hurt like that.