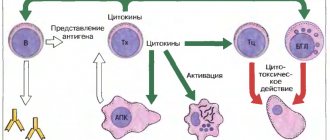
Important components of immunity include lymphocytes, which are a separate subgroup of lymphocytes. They are produced in the bone marrow; the main task of the elements is to identify foreign pathogens and formulate an immune system response to them. An increase in the number of lymphocytes is associated with pathologies that need to be determined to select the correct therapy.
Normal lymphocyte count for women
In adult patients, the component indicators have a conditionally stable value. Measurements of the number of lymphocytes are carried out according to two parameters:
- by absolute value - indicates the number of cells in the blood;
- relative - the percentage of lymphocytes in the total number of leukocytes is calculated.
The norm for the female body is considered to be 1-1.45 billion cells per liter of blood, which is equal to almost 40% of the leukocytes contained. Differences from the specified value may indicate hidden pathologies.
Normal levels of leukocyte cells in urine in men
The unit of measurement of colorless blood cells in the general analysis of urine is a digital indicator (the number of elements in the field of view - n/z). For an adult man (of fertile age), the standard leukocyte count in a general urine test is considered to be ≤ 3 in the urine (for women – ≤ 6).
Reference values for boys under 6 years of age are from 0 to 2 in p/z. In male infants (up to one year of age), the content of colorless blood cells in the urine up to 7 p/w is not abnormal. This is due to the insufficiently developed ability of children's leukocytes to protect the body (more of them are required).
In men 60+, it is allowed to exceed the normal limit by 1.5 times, which is associated with age-related changes in sexual functionality and the functioning of the renal apparatus. The norm of leukocyte cells in urine samples according to Nechiporenko and Amburge for men is ⩽2000 per 1 ml of sediment (for women – ⩽4000).
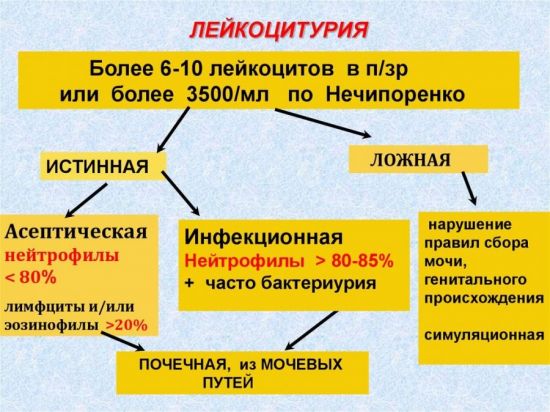
Why are women's urinary white blood cell counts twice as high as men's? This is explained by the anatomical differences of the genital organs. Penetration of bacteria from the outside into the male body is difficult due to the size of the urethra (long and narrow), in contrast to the wide and short female urethra, where germs from the vagina easily enter.
Influence of factors on indicators
An increased number of cells in a woman’s bloodstream is caused by many triggers, including:
- unbalanced diet, prolonged fasting;
- passion for tobacco products, stressful situations;
- hormonal imbalance, including pregnancy and the menstrual cycle;
- physiological characteristics of the body, taking medications, including contraceptives.
These reasons lead to non-critical fluctuations in indicators in absolutely healthy women.
Features of lymphocytosis
The term indicates disturbances in the functioning of the female body, the activity of the immune system to combat intrusions:
- bacteria, viruses;
- protozoa, parasites.
Other reasons for an increased concentration of lymphocytes include their damage or death due to:
- burn disease;
- tissue necrosis;
- inflammatory processes;
- allergies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncological pathologies.
Cells reach problem areas, but with further progression of the disease they begin to die en masse.
The chronic form of lymphocytosis is the result of diseases of the blood or hematopoietic system, lymphatic department. Taurus do not fully mature and cannot fully perform the functions assigned to them. To normalize the balance, the bone marrow produces even more lymphocytes, but the benefits from the increased work are minimal.
The accumulation of protective cells may be due to problems with their utilization in the spleen. Doctors believe that it is not deviations in tests that are of greatest importance, but the sources of their occurrence. Dysfunction of the immune system leads to the development of chronic infections, autoimmune diseases with attacks on one’s own cells, the formation and further proliferation of atypical structural units.
Lymphocytes in blood tests
A general blood test is prescribed for the diagnosis of many diseases, as it helps to understand how the body functions and what abnormalities there are in its functioning. When its results are deciphered, the number of leukocytes is most often displayed as a percentage. This is a relative indicator - the so-called leukocyte formula. When the increase in the number of white blood cells is absolute, the number of all white blood cells increases. If the number of only lymphocytes increases, this is relative lymphocytosis. Usually their percentage increases due to a decrease in the number of other leukocytes, mainly neutrophils. This blood condition is called leukopenia.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of men and women is usually the same. It makes up from 20 to 40% of all blood cells. Children and teenagers should have more white blood cells. The number of lymphocytes depends on age and ranges from 30 to 70%. The most lymphocytes should be contained in the blood of children under 2 years of age – up to 60–70%. It increases even more in the first days of life, as well as at 4–5 years, when the hematopoietic system is rebuilt. After 9 years, indicators gradually approach adult norms.
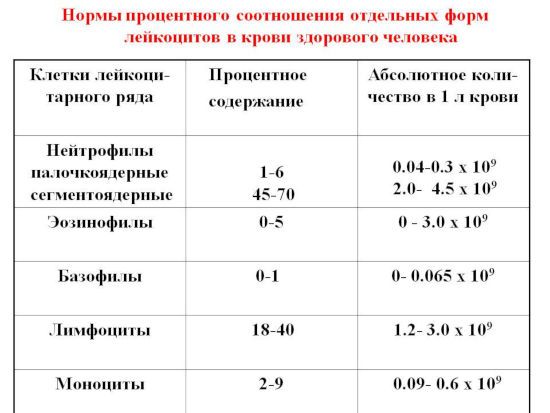
Among all leukocytes, lymphocytes make up about 40%
Typically, the pathological condition when interpreting tests is lymphocytosis - an increase in the level of lymph in the blood. But sometimes these indicators can be lowered. This happens with pathologies of the bone marrow or severe viral diseases. Such blood levels can also be caused by kidney or heart failure, severe immunodeficiency, or taking certain medications that suppress the immune system.
When the level of lymphocytes in the blood is elevated, it rarely shows any external signs. This condition is observed in infectious diseases and cancerous tumors. Therefore, there are no specific symptoms. But lymphocytosis can occur in a latent form. Most often, this pathology is indicated by an enlargement of the lymph nodes and spleen. But this can also be understood by the presence of such symptoms:
- unexplained weight loss;
- frequent colds;
- pale skin;
- low-grade fever;
- increased fatigue;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent allergic reactions;
- indigestion.
Attention! Abnormalities of lym can only be detected by a blood test. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo such an examination in case of any unclear deterioration in health.
Correct interpretation of blood test results will help make an accurate diagnosis. This analysis is taken from the fingertips, and the results form usually indicates the percentage of lymphocytes opposite their Latin designation - lym or lymph.
Causes of lymphocytosis
An increase in the number of lymphocytes in the female body with a normal number of other immune cells is a sign of certain pathologies. A list of common abnormalities and diseases is presented:
- ARVI - lymphocytes belong to the mechanisms of protective properties in the body, which are the first to encounter pathogenic microflora. During the acute phase of the disease, the maximum number of cells is observed, with no activity in other immune structures.
- Rheumatic pathologies - systemic or local lesions of connective tissues are associated with unknown triggers. Experts agree that the main source of their development is bacterial.
- An excess of hormonal substances from the thyroid gland - a disorder provokes the development of autoimmune diseases. The defense system stops recognizing its own and foreign cells and attacks them equally.
- Chronic adrenal insufficiency is a pathological process that is a consequence of bacterial infections or chemical poisoning.
- Abnormal size of the spleen - the problem is directly related to the root causes of the deviation. Minor changes occur due to infection or autoimmune disease, serious changes occur due to malaria and other diseases.
Not all sources of disorders that provoke pathology have been fully identified. These reasons are considered the most common.
Types of lymphocytosis
An increase in the number of lymphocytes in women is associated with a major source of dysfunction. Experts identify several types of pathology:
- Reactive – provoked by diseases that cause disruption of the functionality of the immune system. The list is presented: infectious mononucleosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, HIV infection, severe depletion of the body. To normalize test results, it is necessary to carry out therapy for the infectious disease.
- Malignant – cancerous tumors provoke the formation of acute or chronic lymphocytosis. The phase of the disease directly depends on the stage of development of the neoplasm.
- Post-infectious – deviations in tests are caused by previous infections. Lymphocytosis is accompanied by influenza, chickenpox, rubella, hepatitis, scarlet fever, and measles.
A sharp increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood should alert a woman. Sometimes deviations make it possible to timely detect latent pathological processes or the initial stages of malignant neoplasms. Small changes should not be ignored; patients need to reconsider their usual diet, eliminate bad habits, and do not forget about seasonal vitamin therapy.
Treatment with medications
Before answering the question of how to reduce lymphocytes in the blood of women or men, you should accurately determine the cause of the increase. There are no specific drugs in medicine that can affect the level of blood cells. Accordingly, to correct the pathology, it is necessary to identify and treat the underlying disease.
Infectious and viral diseases
In viral and infectious diseases, lymphocytosis is most often accompanied by leukocytosis, an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), and a decrease in hemoglobin levels. In addition, they are manifested by characteristic symptoms - fever, cough, runny nose, deterioration of health. Antibiotics are the basis for treating infections, and anti-inflammatory, expectorant, and vasoconstrictor drugs are used to eliminate symptoms. In addition, the patient needs to take vitamins and drink more fluids to reduce intoxication and prevent dehydration.
Hematopoietic diseases and oncology
The most dangerous causes of lymphocytosis are diseases of the hematopoietic organs and malignant processes. Lymphocytes are elements of the blood and reflect the state of the hematopoietic organs, therefore, in diseases of the lymphatic system, bone marrow and cancer, an increase in their concentration is observed. Pathologies that cause changes in blood counts include:
- all types of leukemia;
- multiple myeloma;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- metastasis to the bone marrow.
Therapy for such diseases is determined taking into account their clinical course and the characteristics of the patient’s body. Most often, radiation and chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, etc. are performed, followed by drug therapy. The prognosis for patients depends on various factors, but with proper treatment it is usually favorable.
Autoimmune processes
Another common reason for an increase in the level of lymphocytes is autoimmune processes in the body. Their mechanism and causes have not been sufficiently studied - it is known that under the influence of a number of factors, cells of the immune system begin to attack their own tissues and organs.
Such diseases include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Hashimoto's disease, etc.
An alarming sign is a sharp increase in the concentration of lymphocytes, which may indicate malignant tumors with metastases.
Symptoms of autoimmune disorders can vary. Most often, these are causeless changes in weight and psycho-emotional state, pain of different localization, and constant fatigue. In the blood, along with the appearance of specific antibodies, an increase in the concentration of lymphocytes is observed. Therapy includes glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs and symptomatic agents.
Endocrine diseases
All diseases of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis, thyroiditis, etc.) are accompanied by an increase in the concentration of lymphocytes in the blood. Other symptoms include hand tremors, severe drowsiness, emotional disturbances, severe fatigue and drowsiness. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to donate blood to analyze thyroid hormones (hormonal panel).
After intense physical exertion, the level of lymphocytes increases 2-3 times, but returns to normal on its own after a few hours.
Therapy for thyroid diseases is selected individually. Most often, conservative therapy is carried out using medications that correct hormonal levels.
Therapy for thyroid diseases is selected individually. Most often performed in severe cases, radiotherapy and surgery are used.
| Diseases that cause lymphocytosis | Associated symptoms | Treatment |
| Viral and bacterial infections | Intoxication, fever, headaches, manifestations from the respiratory system | Antibiotics, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Disorders of hematopoietic processes | Severe fatigue, unmotivated weight loss, the appearance of bruises and bruises on the skin, decreased immunity | Radiation and chemotherapy, bone marrow transplant |
| Autoimmune diseases | Pain of various localizations, spots and rashes on the skin, weight changes, psycho-emotional disorders | Immunosuppressive drugs, glucocorticosteroids, symptomatic drugs |
| Thyroid diseases | Severe fatigue, dry skin, hair loss, menstrual irregularities in women, causeless anxiety and restlessness | Medicines containing thyroid hormones or drugs that suppress their excessive production |