Atypical lymphocytes in a blood test: should you panic?
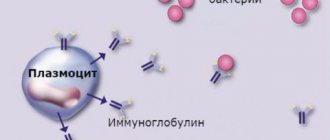
It's no secret that tiny bodies called antibodies are responsible for fighting diseases in our body.
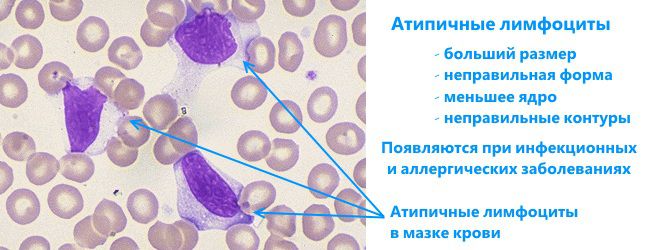
The red bone marrow, a hematopoietic organ, is responsible for their production, in the depths of which new immune cells mature: lymphocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. The main agent of the immune response are lymphocytes - their number in the blood prevails over all others, and it is with their help that the body fights infection. Most lymphocytes have a regular round shape and clear contours, but there are cells whose parameters are slightly different from the “original”. Scientists call such cells atypical.
Atypical or reactive lymphocytes are special immune bodies that appear during allergic reactions, infectious and other diseases. The irregular shape and size of cells are caused by the influence of pathogenic microorganisms, which completely change their structure. Normally, atypical immune bodies should not appear at all, and their presence may indicate the development of various diseases.
In this article, we will tell you what to do if atypical lymphocytes are detected in your blood test, and we will tell you about the reasons that could trigger their growth.
general information
Lymphocytes are the types of blood cells responsible for the body’s defense processes when it is affected by various diseases.
Atypical lymphocytes are a modification of “standard” white blood cells, differing in size and “working” properties.
Ideally, in a healthy adult or child, the number of lymphocytes in the blood should fall within the reference norm limits.
The number of cells increases significantly when the patient’s body begins to fight any problem that affects tissues, organs or the immune system.
A condition in which lymphocytes are elevated is called lymphocytosis. Sometimes pathology can be observed in apparently healthy people who do not have complaints about any problems with their well-being.
In this case, if lymphocytosis is detected and confirmed by repeated tests, patients should visit a specialized doctor - a hematologist who studies blood pathologies.
Atypical lymphocytes come in different types. These species are named after doctors who studied blood diseases and first discovered one or another type of atypical cell.
The first group of atypical bodies is called Downey cells. They were first identified in the first third of the twentieth century in patients suffering from pathologies caused by the presence of cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus.
The second group of atypical lymphocytes is named after the famous hematologist Rieder, who studied various blood pathologies of his patients.
Reeder found that many of those who suffered from acute leukemia had a different lymphocyte structure.
In particular, the nuclei of such lymphocytes seem to be divided in half and have an unequal contour. Sometimes the bodies of this group are called amitotic.
READ Prescribing a test for bladder cancer in a blood test
The third group of atypical lymphocytes is called Botkin-Klein-Gumprecht cells. The main disease that provokes the appearance of these atypical bodies is lymphadenosis.
Cells of this type do not possess any useful functions, but are constantly present in the blood of patients suffering from pathologies. In some medical sources you can find an alternative name for these atypical lymphocytes, sounding like “Botkin-Klein-Gumprecht shadows”.
What is the manifestation of atypicality of lymphocytes?
As you know, lymphocytes participate in the processes of the immune response - that is, they are among the first to rush to fight dangerous microorganisms. As a result of this struggle, they can acquire the following parameters:
- Non-standard appearance
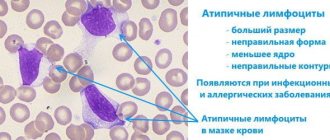
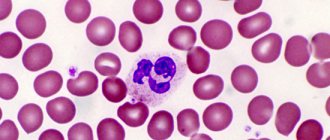
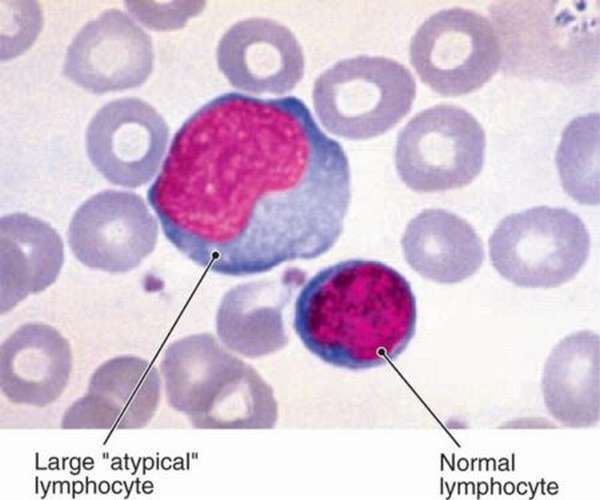
Typically, a lymphocyte has a round shape and smooth borders. Atypical lymphocytes are characterized by jagged contours and irregular polygonal structure.
- Increased size
In a normal state, the size of a lymphocyte does not exceed 12 microns. An increase in this indicator indicates its atypicality.
- Modified core
The impact of pathogenic organisms also extends to the cell nucleus - if you look at an irregular agranulocyte through a microscope, you will find that it is elongated, elongated, and dotted with elongated cracks.
- Cell color
Atypical lymphocytes also have a brighter color when hematoxylin dye is added to the analyzed blood - this is also one of the ways to identify unusual cells.
Did you know that a person’s character traits affect his level of resistance to disease? There is research confirming that active and confident people produce more immune response cells, which helps them fight disease. Thus, an optimistic and positive person has less reason to worry about his health.
External differences of atypical leukocyte cells
Leukocytes are the main agents of immunity. They represent a large class of cells that differ from each other in structure and function. The peculiarity of leukocytes is that they come from different types of precursor cells, which results in their high polymorphism.
In the process of differentiated maturation, leukocytes of different types acquire characteristic morphological characteristics and are released into the blood. They remain in the bloodstream for a short time, up to two days, then enter the tissues. Therefore, when examining blood for the level of leukocyte cells, only those cells that were in the bloodstream at the time of analysis are subjected to microscopy.
During the analysis, the size of each population of the leukocyte group (granulocytes and agranulocytes) and their morphological characteristics are assessed. In the body of a healthy person, leukocytes morphologically do not differ from standard shapes and sizes. But under certain conditions (allergies, infections, tumors) atypical leukocytes with pathological morphological signs are found in the blood.
Using a microscope, an experienced laboratory technician will immediately identify atypical cells based on the following characteristics:
- Non-standard form. Normal lymphocytes are round. The atypicality of the cell manifests itself in a ragged outline or multifaceted shape.
- Increased or decreased size. The usual size of a lymphocyte is about 12 microns. Atypical forms can reach the size of monocytes (up to 30 microns).
- Modified core. When assessing cell morphology, they look at the ratio of the size of the nucleus to the volume of the cytoplasm. Immature neutrophils do not have a segmented nucleus, and the nucleus of an atypical lymphocyte, on the contrary, may consist of several segments. Atypical lymphocytes have increased plasma; they are called plasmatized. The basophilicity of plasma indicates the youth of these cells.
- Atypical staining of cells with dyes, granularity of the cytoplasm. When atypical lymphocytes are treated with eosin dye, they turn blue. The kernels turn purple. Normal lymphocytes after tinting become pearly, grayish or yellowish.
Reasons for the appearance of atypical lymphocytes
Many people, frightened by various articles on the Internet and medical reference books, already at a reflex level begin to panic at the sight of the words “atypical”, “abnormal” and “mutagenic”, associating them with cancer. I don’t argue that an increased number of lymphocytes, as well as the appearance of atypical lymphocytes, can be an indirect symptom of cancer, but this is only one of the possible causes, and not the most common.
Much more often, an infection or an allergic reaction leads to increased production of lymphocytes. This phenomenon is called lymphocytosis. Doctors distinguish three types of this disease: reactive, post-infectious and malignant. The first two are associated with weakening of body functions as a result of infection, the third - with the presence of a tumor process in the body.
Lymphocytosis inevitably leads to the formation of abnormal lymphocytes, or rather, it is one of the factors accompanying this pathology. There may be several reasons for this:
- Taking a certain range of medications (for example, immune serums of organic origin);
- Infectious diseases: pneumonia, chickenpox, hepatitis, etc.
- Brucellosis is a disease that affects domestic animals. Entering the human body through food, it can cause disruption in the functioning of various systems, including the immune system;
- Toxoplasmosis is a disease without an obvious clinical picture, which, however, affects the body’s immune cells and leads to the appearance of reactive lymphocytes;
- Lymphocytic leukemia is a malignant lesion of the lymph nodes, characterized by the accumulation of cancer cells in them;
- Whooping cough is a respiratory disease accompanied by a convulsive cough. Most often found in children;
- Serum sickness is an allergy to drugs of animal origin;
- Syphilis at some stages.
The level of agranulocytes in the blood is determined by a general blood test (for platelets, erythrocytes and leukocytes). This test is usually taken in the morning and on an empty stomach.
It is worth noting that atypical lymphocytes can be found in the blood of an adult even in the absence of a pathological process in the body, so it is so important to consult a doctor about the results of your analysis - he will be the first to notice that something is wrong and advise what to do in the current situation.
Another important factor in the development of atypical agranulocytes is allergy. Doctors around the world say that allergic reactions will become one of the main problems plaguing urban residents in the 21st century. The fact is that in conditions of environmental disasters and air pollution, the human immune system begins to work incorrectly and “fail.” Official statistics show that the number of children with allergies is already 15%!
Types of atypical leukocyte cells and causes of appearance
Reactive leukocytosis occurs due to increased leukopoiesis. This process is activated in the body by cytokines, active components of complement, in response to the appearance of toxins. Under such extreme conditions, not all cells mature correctly, and atypical forms of reactive lymphocytes inevitably appear. In the laboratory, atypical cells are counted for every 100 cells of a certain group
Degenerative changes
This atypical form of cells appears during prolonged and intense intoxication of the body. Deposits of toxic substances accumulate in leukocytes, and the cell loses the ability to divide and perform its functions. These substances can be of different nature (fatty, pigmented). Such cells are characterized by an increase in the number and size of vacuoles (vacuolization), and toxogenic granularity of the cytoplasm appears. Changes in size can be larger or smaller (wrinkling). Such changes are usually associated with severe sepsis, abscesses, and liver dystrophy.
With vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency, hypersegmented neutrophils are found in the blood. Their cores can contain up to 6 segments.
Atypical mononuclear cells
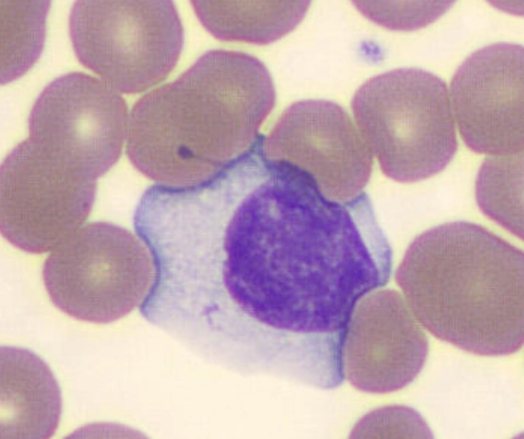
They are called Downey cells or lymphomonocytes due to the morphological similarity of atypical lymphocytes of this type to monocytes. They are larger in size than ordinary lymphocytes and have a monocytic nucleus. These cells are most often found in the blood.
Varieties
The structure of the cell changes under the influence of microorganisms. As a result, its functions and parameters completely change.
Degenerative
A period of prolonged intoxication leads to the formation of degenerative cells that are unable to divide and function due to accumulated toxins. Their size decreases or increases. The culprits of the changes are liver dystrophy, sepsis, and abscess.
Downey cells
The size of atypical mononuclear cells is larger than that of healthy lymphocytes. They are characterized by the presence of a monocytic nucleus. Lymphomonocytes are an indicator of the presence of a viral infection. Most often it is herpes or mononucleosis. Recovery leads to normalization of blood composition. In the blood of children, atypical mononuclear cells are present in an amount of no more than 1%. Indicators may be elevated due to recent illnesses or vaccinations. They are also found in adults. The appearance of such cells is associated with an increased likelihood of infection with herpes or allergies.
Botkin-Klein-Gumprecht shadow cells
This concept includes destroyed lymphoid cells obtained during the preparation of the test material for analysis. This means that blood cells are subject to rapid destruction. Because they are difficult to detect, they are called shadows. Characteristic of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Reader cells
The detection of kidney-shaped cells with nuclei that have a jagged outline signals serious diseases. Most often, a person is sick with leukemia, pernicious anemia, and severe infections.
What causes the appearance
During the examination, atypical lymphocytes are found in the blood test, even in the absence of complaints. As the disease progresses, their number increases, and new atypical cells appear along the way, the main culprits of which are infections of viral origin and allergies. The entry of microbes into the body provokes a protective reaction of the immune system. The production of antibodies begins to fight the pathogen. With reduced immune defense, maturation may not occur; the cell is modified and acquires different qualities.
Exceeding the normal level of lymphocytes in the blood, as well as the formation of atypical cells, can occur in the presence of cancer. Along with it, there are other reasons. The most common are infections, as well as allergies, from which residents of megacities suffer. An increase in the number of lymphocytes leads to lymphocytosis.
The detection of cells with atypical properties is associated with dangerous diseases. There are four main groups of factors influencing their occurrence:
- The presence in the body of infections caused by viruses and bacteria.
- Consequences of intoxication.
- Radiation exposure.
- Oncological diseases, the presence of genetic pathologies.
Atypical lymphocyte cells are formed if a person is sick:
- Brucellosis is a disease of domestic animals that can be transmitted to people. The disease occurs with damage to the nervous system, heart, blood vessels, bones, and joints.
- Lymphocytic leukemia is an oncology in which malignant cells affect lymph tissue.
- Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease affecting the skin and mucous membranes. The disease worsens the condition of bone tissue and complicates the functioning of organs and systems.
- Toxoplasmosis is an asymptomatic infection caused by Toxoplasma. Cats become the source of infection.
Medicines and serums of animal origin also promote the formation of reactive lymphocytes. In a child, this process is caused by meningococcal infection, whooping cough, measles, and a number of other diseases.
Reactive lymphocytes in childhood
The designation of the normal blood composition of children and adults is different. There are no atypical lymphocytes in the body of a healthy child. Often the cause of their appearance is mononucleosis. With this disease, the integrity of leukocytes is disrupted, and the composition of their nucleus changes. As a result, the immune system weakens and the child becomes infected.
The causes of lymphocytosis in children are considered to be:
- viral hepatitis;
- taking medications such as tetracycline;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- problems of the digestive organs;
- chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever.
Early diagnosis helps speed up recovery and avoid complications. A blood test can detect the problem. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky recommends conducting such a study at least once a year. This will allow you to have comparative data on the composition of the blood when the child is healthy, as well as during illness.
Symptoms
Atypical lymphocytes do not appear in any way. Symptoms occur when the disease affects organs. Parents note in their children:

- temperature increase;
- the appearance of drowsiness, weakness;
- spread of infection to the respiratory system.
In some cases, rashes appear and the skin begins to itch. Lack of treatment worsens the condition. Need to get medical help.
Treatment
To normalize the condition, doctors carry out complex therapy:
- Lymphocyte drugs reduce the level of lymphocytes.
- Antiviral, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics fight viruses and infections.
- They choose a diet. A diet high in vitamins and microelements is recommended. Limit the consumption of fats and salt.
- Cancer is treated with a course of chemotherapy.