The birth of a child is always a joy, which brings with it certain troubles. During this period, a woman pays special attention to her health, as well as her diet. This is understandable, because the health and well-being of the baby depends on her daily menu. What cereals can young mothers eat while breastfeeding? What should you pay attention to and what do doctors say about this?
Porridge is useful for feeding. Vitamins, minerals and fiber from them, together with breast milk, enter the baby’s body and give him everything he needs for growth and development.
Oats and porridges made from them: all the benefits and warnings
Oats contain many nutrients: magnesium, potassium, iodine, vitamins A, B, E. Therefore, oatmeal should be present in the diet of a nursing mother. It improves lactation and makes breast milk healthy.
Oatmeal contains a lot of iron, which improves blood composition and fights anemia. Improves intestinal motility, relieves inflammation due to its enveloping effect. Strengthens the immune system and increases the body's resistance to colds.
Oatmeal normalizes the functioning of the nervous system. Eating oatmeal helps prevent stress and depression.
Oatmeal is contraindicated for those who have celiac disease, as well as for women and children predisposed to allergic manifestations.
How to cook porridge
Despite the huge number of tasty and healthy cereals for nursing mothers, not all young mothers know how to prepare dishes based on these cereals. Porridge recipes for breastfeeding will help make the daily menu of women in labor balanced and varied. How to properly prepare nutritious and healthy porridge for a young mother?
In the first months of a baby’s life, it is better for a nursing mother to eat porridge cooked in water or with the addition of whole milk - half and half. However, fermented milk products are also considered beneficial for the body of a young nursing mother, including milk porridge. Therefore, porridge with milk is introduced into the mother’s diet gradually in small quantities. And if the child’s body is well tolerated, you can treat yourself to delicious cereals with a small amount of milk and a small amount of butter.
You can cook delicious porridge using water and oatmeal. The oatmeal must be washed and then cooked over low heat until it boils. After this, reduce the heat, collect the resulting foam and cook for about 5 minutes until fully cooked.
Also, barley groats are considered the most harmless porridge for young breastfeeding mothers. However, barley grains require more cooking time than buckwheat or oatmeal. The porridge is cooked for thirty minutes over low heat. If you pre-soak the porridge, it will cook much faster and will turn out crumbly and fluffy.
Rice porridge is also very useful in the diet of mother and baby. You can also cook pilaf from it, add it to salads, soups and puddings for dessert. But you should not overeat too much rice porridge, as cereal is quite difficult for the body to digest and can cause constipation in a child.
Almost all porridges go well with fruits, dried fruits and vegetables. You can also flavor the porridge in small proportions with butter or vegetable oil. You can diversify the taste of porridge by adding banana, apple, pear, prunes, dried apricots, and pumpkin or zucchini among vegetables. If these ingredients do not cause allergies in your child, then you can eat them without fear.
Dish from childhood
Semolina porridge has no less set of useful substances. She is always associated with childhood.
- It is recommended to eat semolina porridge in the morning. It removes harmful substances, fats and mucus from the body.
- Semolina is useful for diseases of the digestive system, relieves inflammation and spasm from the intestinal and stomach mucosa.
- Semolina porridge does not contain protein, so the dish can be eaten by those who have kidney disease.
But semolina should be used with caution. This is due to some of its features.
- Cereals contain a special substance that prevents the body from absorbing calcium, iron and vitamin D.
- Frequent use leads to the development of a disease in a child such as rickets.
- Semolina contains gluten, which often causes allergies.
- Children with gluten intolerance may develop celiac disease. With this disease, the intestinal mucosa becomes thinner and poorly absorbs nutrients. The child begins to gain weight weakly and muscle mass decreases.
- Semolina porridge is high in calories, which affects not only excess weight, but also intestinal function. The risk of developing colic and increased gas formation increases.
Semolina porridge is not recommended to be included in the menu until the child is 2-3 months old. The first time you need to cook it in water, but not in milk, without adding sugar or salt.
What cereals are recommended during lactation?
What cereals are not harmful to a newborn and can be consumed by the mother in the first, second and subsequent months of lactation? Doctors recommend:
- Oatmeal, rich in vitamins C, A, E and group B, as well as magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, iron and calcium. It is not recommended only for kidney failure and gluten allergies.
- Buckwheat porridge, which contains potassium, iron, phosphorus, sulfur and magnesium, as well as vitamins E and group B. It should be boiled in water, since milk and buckwheat are poorly compatible with each other and are difficult to absorb by the body.
- Egg, rich in proteins, vitamins, phosphorus, calcium, iron and other minerals and trace elements. It also contains plant fiber necessary for normal digestion. Porridge is prohibited only in cases where there are serious problems with the heart, intestines or stomach.
- Corn grits are gluten-free and can be eaten immediately after childbirth. It is not recommended only in case of individual intolerance and in cases where the baby suffers from diarrhea.
- Wheat porridge, rich in vitamins PP, E and group B, as well as calcium, fluorine and sodium, iron, potassium, magnesium, etc. It is hypoallergenic, but should be eaten with caution if there are problems with the stomach and bowel movements.
- Semolina, which contains calcium and iron, sodium, magnesium, vitamins E and group B. The cereal is popular and tasty, but it contains a lot of gluten, and its calorie content is quite high. Porridge has no strict contraindications, but it should be eaten starting from 5-6 months of lactation.
- Rice porridge, rich in phosphorus and sulfur, iron and magnesium, vitamins H, E and group B, but if there are cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure increases and constipation occurs, the consumption of the dish is limited.

Benefits of buckwheat porridge
Buckwheat porridge is on the list of the first products that should and can be introduced to infants. Mothers themselves are no exception. Buckwheat is a must when breastfeeding. It is easily absorbed and digested by the body. Therefore, you can be sure that all valuable substances will enter the baby’s body along with milk.

Buckwheat contains a lot of iron, so this porridge will reduce the risk of developing anemia and improve the condition of hair and skin. It can boost immunity and resist various infections.
Buckwheat contains a lot of calcium, which is responsible for the condition of teeth, nails and hair. Regular consumption of buckwheat minimizes the development of bone diseases such as osteoporosis.
It contains a lot of magnesium, which regulates the functioning of the nervous system. Together with B vitamins, it helps a woman fight postpartum depression, improves sleep, and makes a capricious baby calmer. Thanks to magnesium, normal mental development of the child is ensured.
In what form and with what additives can you eat porridge?
A balanced and varied menu will have a positive impact on a woman’s health and will help the baby actively grow and fully develop. During this period, it is important for a woman not to overeat, but at the same time feel active and cheerful during the day. Healthy and nutritious cereals will help with this, especially in the first month of breastfeeding. What should it be, porridge with milk or water, with or without additives? Doctors' recommendations will help you figure this out:
- Each type of product should be tried separately and introduced gradually. At first, eat no more than 1-2 spoons, and then carefully monitor the child’s reaction. If nothing happens, you can continue to eat the dish.
- If a baby has flatulence, it is necessary to limit the intake of pearl barley. When a child is constipated, it is worth eliminating rice from the diet for a while.
- During the first months of breastfeeding, porridge is prepared in water, because milk contains the strongest allergen, casein. It can not only cause allergies in infants, but also cause indigestion.
- When the baby is 4-5 months old, the product is boiled in water half and half with milk, gradually switching to dairy dishes.
- Semolina and multigrain mixtures are introduced into the menu when the baby is 5-6 months old.
- What serving size is recommended? At first it will be no more than 50 g per day, then the dose is gradually increased, bringing it to 130-150 g per day.
What can be added to cereals during breastfeeding? Allowed products are butter, pears, apples and dried fruits. Salt and sugar should be limited to a minimum, not to mention seasonings and other additives that should be completely excluded.

Corn on the menu
Corn porridge has the following beneficial properties:
- normalizes peristalsis, eliminating constipation, as it contains fiber;
- cleanses the body of toxins;
- selenium contained in corn prolongs youth;
- has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin, hair and nails.

Corn porridge should be included in the diet no more than twice a week. It can cause allergies, so it should be introduced into the diet with caution. Those who are prone to diarrhea should not eat it either. Women with gastritis and duodenal ulcers should not eat corn porridge.
Can a nursing mother eat this product?
In order to replenish lost strength during pregnancy and childbirth, it is necessary to eat healthy, nutrient-rich food. Porridge is suitable for such purposes. The list is multifaceted, for every taste and color:
- Buckwheat.
- Barley.
- Wheat.
- Oatmeal.
- Manna.
- Rice.
- Corn.
- Pearl barley.
Cereals can be cooked in either water or milk. They are healthy and nutritious. It is advisable to minimize the amount of sugar and salt when cooking.
IMPORTANT! If there is no allergic reaction to the protein, then they are safe to eat in the diet for mother and child. The optimal time for consuming cereals is the morning hours, in order to monitor the baby’s reaction to the product eaten.
When to include it on the menu?
Milk porridge can be added no earlier than a month after the baby is born.
Cow's milk is a very strong allergen that can harm a child's health. It should be introduced into the mother's diet gradually and not in large portions.
Eat only one type of cereal a day and observe the child’s reaction . If after a while a rash, peeling or other changes in the skin appear, you should temporarily exclude this product.
Benefits for women
Eating porridge is necessary for the full growth of the child, as well as for the health of the mother in general. Each of them has its own beneficial properties.
- Buckwheat is a necessary product for a nursing mother and will help with anemia. Contains a large amount of iron and minerals, and also has a beneficial effect on lactation.
- Millet – contains vitamin D, useful for jaundice in a child. Will help get rid of constipation.
- Oatmeal contains a large amount of vitamins and minerals, and also removes waste and toxins. Contains zinc, iodine, magnesium and vitamin complex A, B, E.
- Rice contains fiber, which helps cleanse the body. Helps overcome diarrhea.
- Semolina is beneficial for its properties for bones and the digestive system. It is very high in calories and contains a significant amount of gluten, to which allergies can occur.
- Corn – contains a vitamin complex and a lot of selenium. Removes toxins and loosens stool, improving digestion, and also improves the condition of the skin and hair.
- Barley - contains fiber, which improves intestinal function and is also useful for stomach pain. Improves the condition of skin, hair and nails.
- Barley – a group of vitamins B, E, PP and useful elements: calcium, sulfur, iron, magnesium. Improves immunity and digestive functions.
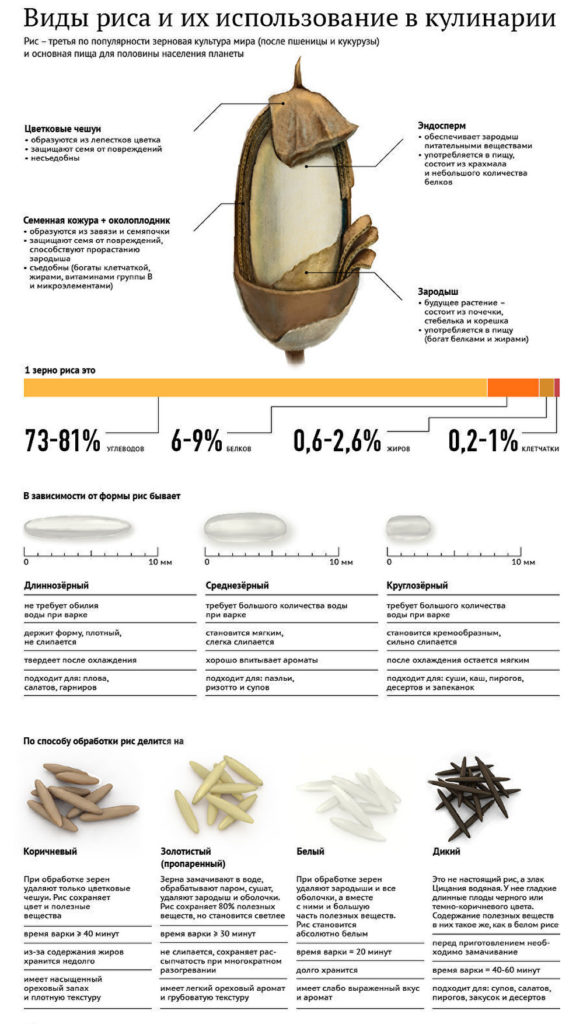
Benefits of rice
Rice contains complex carbohydrates in large quantities, so the cereal is classified as a dietary product. And what’s important is that it is gluten-free. Therefore, rice in limited quantities during breastfeeding can bring many benefits. In addition to enriching the body with nutrients, it improves lactation. One rice dish is allowed per day, for example, only rice porridge, but not more than three times a week.
Rice contains many B vitamins, as well as PP, E. It contains magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, silicon, and iron. This composition determines the following benefits of cereal for the body:
- The functioning of the nervous system improves, sleep normalizes.
- The skeletal system is strengthened.
- The choline content (vitamin B4) has a beneficial effect on brain activity.
- Rice porridge is able to remove harmful waste, salts, and toxins from the body, cleansing it.
- Rice improves the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- The growth of hair and nails improves, and the skin gets rid of inflammation.
To prevent rice porridge from having a strong fixing effect, you need to add other products with a relaxing effect during the cooking process. You can add apples, plums, prunes, bananas.

If the rice is of poor quality, there is a risk of health problems. Blood pressure increases, vascular diseases (atherosclerosis), diabetes mellitus appear, and stones form in the kidneys and gall bladder.
How to eat corn porridge correctly
Cereals during breastfeeding should be introduced in stages. First try eating a few spoons and observe the reaction for 2-3 days. If the latter is missing, you can continue.
For the first 3-4 months, consume water-based corn porridge; cow's milk is an allergen; in subsequent months, increase the proportion of milk. You can add soy or goat.
Not every child is able to accept this particular type of cereal. This depends on the characteristics of metabolism and heredity. If an allergy occurs, the stool changes (it becomes too thin or thick, the color changes), colic appears, you must not eat corn porridge for a month, and then try again.
If you have constipation, you should limit the use of this product due to the high starch content. You need to monitor your child's stool.
There are certain cooking rules. Consumption of fried soups is not allowed. You should also not overuse the quantity, as this can cause a feeling of bloating and heaviness in the abdomen.

You should avoid eating fresh corn, but you can always treat yourself to corn sticks or flakes. Fresh corn can cause bloating and colic in your baby. You can start using it from the age of at least 3 months, and increase the amount gradually.
We recommend reading: Garlic during breastfeeding
It is strictly forbidden to eat canned food; it contains preservatives. It's not common to eat popcorn.
The main thing is not to overdo it. It is optimal to alternate the different types of dishes that are allowed during this period.
How to introduce porridge with milk into a child’s diet?
In the first months, the child does not need complementary feeding in the form of porridge . His main food is mother's milk or a special formula for feeding up to a year of age. Opinions differ between the older and younger generations - semolina can be given from birth, as grandmothers and great-grandmothers used to do.
Everyone makes decisions for their little one on their own, whether to give the baby porridge or not. Cereals are a valuable storehouse of useful minerals and substances, and should certainly be present in the complementary feeding of babies up to one year old.
For the first complementary feeding, use cereals cooked in water, or purchased dairy-free ones intended for complementary feeding.
From what age?
Complementary feeding begins at four months.
Many experts recommend speeding up the process if the baby is not gaining weight well. The first thing your baby will try is dairy-free and low-allergenic cereals, such as:
- buckwheat;
- oatmeal;
- rice.
After time, if the child tolerated everything tried well, you can gradually introduce porridge with the addition of milk.
Benefits for the baby
Each cereal has its own beneficial properties for the child and for the mother during lactation . This must be taken into account when adding them to the toddler’s menu, because with the correct selection of complementary foods you can improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and improve the intestinal microflora. The beneficial features of porridges are mentioned above.
Possible harm to mother and baby
The benefits of milk porridge for the mother during breastfeeding are known to everyone, but many do not know about its harmful properties. In children, the gastrointestinal tract does not produce an enzyme capable of digesting milk. If consumed during lactation, health problems may arise for the baby, such as:
- allergic reactions;
- colic;
- stomach upset.
ATTENTION! Allergies can manifest themselves not only by skin rashes and diarrhea, but also by fever and asthma attacks.
Types of rice, their benefits and harms
Rice has been known to mankind for several millennia and is cultivated in Asia, Africa, the Australian continent and America. The number of rice varieties is measured in tens of thousands, divided into groups according to the following characteristics: grain shape and size, color, intended use and cooking features.

Nowadays, it is common to think that brown rice and white rice are representatives of different varieties. However, most often the difference is only in the degree of grain purification. White grain is devoid of shells and has gone through the polishing stage, while brown rice has largely retained its natural appearance.
What's healthy about rice:
- The rough shell of the grain contains fiber necessary for proper digestion. These are dietary fibers that promote a feeling of fullness (prevent overeating), stimulate the contractile activity of the intestinal walls, and are responsible for the absence of congestion. Fiber also acts as an absorbent and feeds beneficial bacteria that live in the intestines and form microbiological balance. Just remember: brown rice has 3-4 times more fiber than polished rice.
- This product is a source of carbohydrates thanks to starch. In some varieties their share reaches 70%. This explains the extraordinary popularity of grain crops among more than half of the world's population. The media and social networks have conditioned people to believe that carbohydrates are evil. This is fundamentally wrong, because this energy supplier should be the main one.
This is important for a beginning mother, because with full breastfeeding (without complementary feeding), the body spends from 500 to 700 kilocalories per day on milk production, but you still need to provide for yourself. In this regard, there is a pleasant bonus for a nursing mother: by staying within the limits of a normal diet without excess, without intensely exercising or going on diets, it is easy to lose weight.
- Rice is rich in vitamins. Unprocessed grains contain substances important for health in greater variety and quantity. Thus, the shell that is removed from white rice contains carotene, which is good for vision, and a whole list of B vitamins, without which the nervous, cardiovascular system and other human organs will not function properly. Nicotinic acid is responsible for metabolic processes and proper cholesterol levels, while vitamin E supports reproductive function and keeps the skin young.
- But one of the prizes is given to rice in terms of the content of microelements beneficial to humans. Rice grain contains more than 20 minerals. Among them are calcium and phosphorus, which not only form a strong bone skeleton and teeth, but also participate in the functioning of the brain and nervous system. Silicon strengthens blood vessels, helps the immune system and slows down the aging process. Potassium removes excess fluid and saves from swelling. Zinc is involved in metabolic processes, ensuring the functioning of many systems: nervous, reproductive, circulatory, etc. But there is also iodine, selenium, sulfur, magnesium, etc.
What's not in rice:
- There are almost no proteins and fats that need to be additionally introduced into the diet of a nursing mother.
- No gluten. However, it is important to know that in fact this protein is dangerous for people with the hereditary disease celiac disease, and there are about 1% of them on Earth. Therefore, the currently popular “gluten-free diet” is nothing more than a tribute to fashion.
- There are no readily available sugars. Gradually breaking down starch, the body releases insulin in small portions. This gives energy, does not overstrain the pancreas and does not contribute to the accumulation of fat.
- Excessive amount of calories: there are about 300 in 100 g of dry grain. But when boiled, this is too large a portion, especially since rice must be supplemented with other products. As a result, a standard dish will have an average of 100 calories.










