The appearance of foamy stool in a breastfed baby is considered by many parents to be an alarming symptom. And not in vain, because against the background of liquid feces, the baby’s condition can sharply worsen - he cries, eats and sleeps poorly, disturbing his loved ones with his well-being. However, foamy feces can also be caused by non-serious reasons that parents can eliminate on their own, without the help of doctors. Today we will talk about the types of foamy stools, what problems they may indicate, and how to improve the functioning of the digestive system in accessible ways.
What does foamy stool look like in a baby?
Normally, babies' bowel movements are mushy and have a yellow tint. In order to determine what foamy stool looks like in a breastfed newborn, it is better to visit a specialist. The pediatrician will more accurately explain what may be causing the disorders, evaluate the smell and consistency of stool, and detect the presence of blood streaks or mucous impurities.
Such symptoms will help the doctor more clearly determine the diagnosis, conduct a high-quality diagnosis and select a treatment method. In most cases, foamy stools are liquefied. If there is not much foam, the stool is mushy, and the symptom appears once a week, this can be considered as normal.
What is considered normal?
Mucus in the feces of infants is not a pathological sign, so its appearance must be assessed in conjunction with other symptoms. If the child is active, has an excellent appetite, sleep corresponds to age standards, nothing threatens the baby’s health.
Mucus is present in certain quantities in the intestines of all children, including newborns. It performs a protective function, preventing the aggressive effects of acids and alkaline elements entering the child’s body. Normally, mucus should be mixed with fecal matter before bowel movement. This means that even a small amount of mucous content should not be detected externally in the stool.
Stool containing mucus becomes light in color and its consistency becomes jelly-like or watery.
Mucous stool in a newborn
After the baby is born, the bladder and intestines are emptied. In the first 1-3 days, the baby's feces are a viscous and sticky mass of dark green color with a brownish tint.
This stool is called meconium. It consists of epithelial cells, mucus, amniotic fluid that surrounds the baby throughout the 9 months of intrauterine life, bile and hair.
The amount of mucus in meconium is about 70-80% of the total mass of feces. This is considered normal. Already at 3-4 years of age, the transition period will pass, and the baby’s stool will become thicker (the consistency of it resembles a yellow or yellowish-brown pulp).
How to determine the presence of mucus?
To understand whether children's stool contains mucus or not, as well as to determine its quantity, it is necessary to take a stool test, which is called a coprogram. Using a coprogram, you can detect not only mucus, but also fatty acids, soaps, starch, muscle fibers, leukocytes, etc. Based on the results obtained, you can judge the presence of a pathological process, as well as its stage.
mucus of different colors: pink, transparent, white, yellow, green
Not only the amount of mucus, but also its color is important for diagnosing the disease.
- Transparent slime. It is a sign of catarrhal phenomena (inflammatory processes on the mucous membranes, for example, sore throat, otitis media, etc.).
- Green or yellow mucus. This color means the growth of bacterial (pathogenic) flora, the addition of an infection and the development of a purulent focus.
- White slime. May be a sign of vaginitis in girls.
- Pink slime. Usually appears with hemorrhoids in the inflammation stage and anal fissures, as well as various injuries to the anus.
- Mucus streaked with blood. A dangerous phenomenon indicating internal bleeding, ruptures or the formation of ulcers on the intestinal mucosa. In severe cases, it can be a symptom of malignant diseases of the anus and intestines.
Types of foamy stools
In many cases, studying the color and consistency of the baby’s stool helps to independently carry out the initial diagnosis. Against the background of the appearance of foam in it, the shade changes and a specific smell appears. And such changes are caused by various reasons.

The color of a baby's stool can tell a lot about the baby's health.
Light and liquid
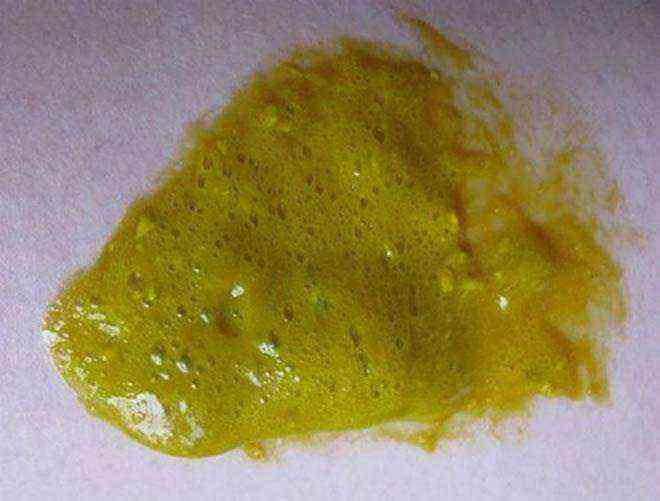

Normally, the color of feces in infants is yellow-brown. The substance stercobilin, which is a pigment, is responsible for color. Also, what shade the stool may be colored depends on the set of foods consumed the day before by the nursing mother. If a woman eats a lot of plant foods and regularly drinks cow's milk, loose, foamy stools in a breastfed baby are not uncommon.
Advice! Also, clarified feces can signal problems in the gallbladder area or rotting processes in the intestines. Therefore, if you notice the appearance of light, foamy stools in your child, it is better to visit a pediatrician and consult on a disturbing topic.
Green

If a breastfed baby has green, foamy stool with a pungent odor, this is a sign of an improper feeding process. In this case, the balance of milk being received by the baby from the anterior and posterior chambers is disrupted. When a baby does not receive enough substances contained in hind or fore milk, disruptions occur in the digestive system, leading to changes in the color and consistency of stool.
The anterior portion contains more water and less fat, so frothy greenish stool in infants is often called “hungry”, because. the baby only manages to quench his thirst, but is not fully satisfied. To eliminate the problem, you should contact a specialist and adjust the feeding process. The baby needs to be latched to the breast for a long time so that he has time to receive not only fore milk, but also hind milk (which contains more fat and nutrients). It is also not recommended to place the baby on one or the other breast during feeding.
Yellow chair
Transient dysbacteriosis is a disease characteristic of infants up to six months and occurs against the background of foamy yellow stool. You can protect your baby from this borderline state by regular breastfeeding - mother's milk contains a lot of immunoglobulins. Thanks to them, the baby’s immunity and intestines become protected.
A newborn baby has a sterile intestine, and it begins to be populated with beneficial microorganisms and bacteria as it passes through the birth canal. The digestive system has a hard time adapting, causing the intestines to become stressed and react by producing yellowish, foamy stools. Usually this condition is accompanied by little weight gain and requires a visit to the doctor.
Foamy stool streaked with blood
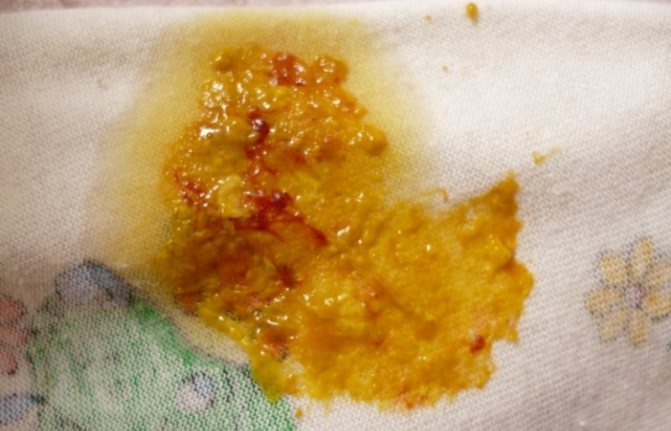
Often the cause of this condition is lactase deficiency, when the baby’s digestive system does not have enough enzymes to break down milk. If a nursing mother consumes a lot of dairy products, the fragile stomach is not able to cope with the load, which is why blood streaks and foam appear in the stool.
Less commonly, congenital dysbiosis is the cause of bloody spots in foamy stools. This pathology is very difficult to treat and the child has to constantly be given medications that maintain the intestinal microflora in a normal state.
Foamy stool with mucus
The appearance of mucus impurities in foamy stool is often caused by taking inappropriate medications or long-term use of medications. But the symptoms are more likely to indicate the development of an intestinal infection. If, against the background of mucus and foam in the stool, the baby’s temperature has risen, and the condition does not improve within 24 hours, it is better not to delay a visit to the doctor.

If, along with changes in the color of the baby’s stool, his behavior changes and the temperature rises, then this is a reason to consult a doctor
When to worry
Young mothers are wondering whether it is possible for a baby to replace the formula or continue breastfeeding in full the next time the color of the stool changes.
When white mucus appears in the baby’s stool, you need to sound the alarm, because such symptoms are considered a sign of pathology (atony, polyp, tumor). It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance when the baby becomes worse, he is restless, anxious, frequent regurgitation occurs, the consistency and color of the stool has changed.
In the menu of a nursing mother, new dishes should not be introduced in the first year. Fermented milk drinks should be included in the diet of new products if a dysbacteriosis diagnosis has been made.
Dangerous colors of stool:
- Pink. Indicates bleeding.
- Black or veined. Characterizes gastric bleeding.
- Transparent. Infections, inflammation, colds, hepatitis.
- White slime. It is possible to detect parasites or rotavirus infection.
- Cloudy green substance. Characterizes a bacterial infection.
Main causes
Foamy stools in infants can be caused by various reasons:
- non-compliance with diet by a nursing mother;
- development of intestinal infection;
- incorrect feeding regimen;
- allergic predisposition;
- lactase deficiency;
- disorders of the digestive system.
Need to know! In bottle-fed infants, foamy stool occurs due to an incorrectly selected formula, or when the baby is fed without following a schedule. Also, the cause may be inadequate hygienic treatment of nipples and bottles from which the baby eats.
Allergic reaction
If the stool of a breastfed baby foams and becomes liquid, the reason may lie in an allergic predisposition. Together with mother's milk, the baby receives substances that can cause irritation of the digestive tract and intestines. To eliminate the problem, a woman just needs to determine which product causes her baby’s allergy and eliminate it.
Foam in the stool often appears when complementary foods are introduced incorrectly and untimely, when the baby is given foods that are not age-appropriate and irritate the baby’s delicate intestines. Infants under six months of age often experience gastrointestinal disorders after drinking cow's milk. Medicines that the mother takes or gives to the baby (even anti-bloating medications) can also trigger allergies and cause loose, foamy stools.

When breastfeeding, it is important for a woman to adhere to proper nutrition
Infectious diseases
When a baby has foamy stools and their color changes to green, you should not hesitate to visit the doctor. It is necessary to take tests for microflora disorders, infection with staphylococcus and other infectious agents.
The development of an infectious intestinal disease occurs against the background of severe symptoms:
- heat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- increased frequency of bowel movements up to 10-20 times a day;
- lack of appetite.
Foamy stool with an admixture of foam, which has an unpleasant odor, also appears with the development of a staphylococcal infection with suppuration of wounds on the baby’s body, the growth of boils and inflammation of the mucous membranes. Therapy is selected by a pediatrician.
Bowel dysfunction
The appearance of foamy stools in infants is often caused by malfunctions of the digestive system. These include:
- dysbacteriosis - manifested by alternating constipation and diarrhea, foamy stool with a strong sour smell, a change in the shade of stool to too light and greenish;
- increased formation of gases - the condition can be eliminated by selecting a diet for a nursing mother, preventing bloating and colic;
- enzyme deficiency - a weakened digestive system, not ready for excessive loads, can react with foamy stools to sucrose, fructose, lactose, and the introduction of complementary foods.
Attention! If foamy stools appear in the artificial one, one may suspect intolerance to the mixture. Perhaps they contain biologically active substances that the baby is not able to digest, or he suffers from lactase deficiency. He needs to choose the right nutrition with the help of a specialist.
Malnutrition and nutritional imbalances
As a result of malnutrition, when a baby does not receive enough formula or breast milk, a nutritional deficiency develops in his body. In such cases, the color of the stool becomes darker, and an admixture of foam appears in it.
As already mentioned, foamy stools also occur when there is an imbalance of milk from the anterior and posterior mammary chambers. When fed only with foremilk, the baby develops lactase deficiency, which is why liquefied feces with foam appear.
When should you see a doctor?
It is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician if the appearance of mucus is accompanied by other symptoms of various diseases, including:
- foul-smelling diarrhea;
- darkening of urine;
- rare urination;
- profuse and frequent regurgitation;
- smell from the mouth;
- heat;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- sunken fontanel;
- wrinkled and sagging skin.
When is emergency help required?
An ambulance should be called at the first suspicion of intestinal obstruction, as well as signs of intestinal infections. If a child suddenly has a fever, vomits, has frequent and foamy stools or watery stools mixed with mucus, an examination by an infectious disease specialist is required.
Treatment and assistance at home
Treatment of foamy stool in a breastfed baby, if it is not caused by an intestinal infection, is carried out at home and depends on the cause. First of all, it is necessary to identify provoking factors, be it an allergic predisposition, lack of lactase or nutritional imbalance. And then eliminate them together with your doctor. The following describes the algorithm of actions that are needed to stabilize the baby’s stool.
What should parents do?
When monitoring your baby’s well-being during the period of foamy diarrhea, you must follow several rules for home treatment:
- establish breastfeeding - feed every 2-2.5 hours and give the baby the opportunity to get to the hindmilk;
- do not independently prescribe medications for your baby - what works for one child may harm another;
- visit a doctor even for preventive purposes, get tested and make sure that foamy stools are not caused by pathological reasons.
Perhaps foamy stool is caused by problems with the gastrointestinal tract; here, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary. The specialist will diagnose and prescribe treatment.
When to see a doctor?

The development of diarrhea with foam requires a visit to the clinic for consultation with a pediatrician. But if the baby is feeling well and there are no alarming symptoms, a visit to the doctor is not considered urgent. Indications for urgent medical attention:
- heat;
- child's refusal to eat;
- constant vomiting;
- loud crying of the baby, indicating sharp pain in the abdomen;
- lack of urination for 8-10 hours in a row;
- signs of dehydration.
Such symptoms should immediately alert parents and force them to take the child to specialists. Dehydration due to diarrhea is a dangerous condition that develops in young children in a matter of hours.
Primary diagnosis
Judging by the color and consistency of the stool, you can roughly determine at home what causes the appearance of foamy stool in your baby:
- light-colored feces with a rotten smell, increased gas production, skin rash - signs of dysbacteriosis;
- green foamy stool is a symptom not only of dysbiosis, but also of intestinal infection, if it is accompanied by hyperthermia, abdominal pain and vomiting;
- yellow feces with foam - indicates improper organization of breastfeeding and requires elimination of nutritional imbalance;
- white stool - signals poor-quality bile outflow, which requires a coprogram, analysis of the biochemical composition of the blood and ultrasound of the peritoneal organs.
On a note! After the baby has foamy stools, his well-being should be monitored. If alarming symptoms develop, doctors can give directions for the necessary laboratory and instrumental tests for subsequent treatment.
Drug treatment
If a baby develops foamy, frequent stools, it must be saved from dehydration. To do this, the baby is given solutions containing electrolytes and continues breastfeeding. There are also a number of medications that will help cope with the problem:
- Regidron, Gastrolit - solutions to prevent dehydration, which are diluted with water and given to the child to drink throughout the day;
- Smectite is a drug that helps remove harmful substances and toxins from the baby’s intestines that cause loose, foamy stools;
- Enterol is a remedy that relieves dysbiosis and intestinal infections. After 3-4 days of use, the baby’s intestines will be cleared of microbial flora, and the stool will improve;
- Hilak forte - a drug in the form of drops to restore normal intestinal flora and improve the functions of the digestive system;
- Linex - capsules containing a large number of beneficial bacteria that fight the manifestations of dysbacteriosis and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Lactase Baby - a drug prescribed to children with symptoms of lactase deficiency, it promotes better breakdown of mother's milk or artificial formula.
If taking medications at home does not produce results, and the baby’s condition worsens, you should call the doctor again and get tested. Perhaps an infection was added to a simple digestive disorder.
Other ways to improve bowel movements for babies
If foamy stools are not caused by pathological reasons, the most common advice from doctors for improving stool in children is to adjust the diet of the nursing mother. She needs to exclude fatty, fried, dairy foods, and carbonated drinks. You should also avoid foods that have a laxative effect (plums, apricots, beets) and cause increased gas formation (nuts, cabbage, apples, legumes).
A nursing mother needs to breathe fresh air more often, eat vegetables and greens, but avoid overeating. Your daily diet should include lean meats, fish, soups, and cereals. During the period of treatment for foamy stools in a baby, a woman may need advice from a nutritionist.
How to get rid of mucus inclusions
Before prescribing adequate treatment, the causes of mucus are determined in the laboratory. If it is not possible to visit a doctor, relatives can offer the baby to drink Smecta. For a baby in the first month of life, one sachet is diluted with water and consumed in small portions throughout the day. The course lasts a week, but it is important to visit a doctor and undergo the necessary examination by a pediatrician or prescribe other remedies.
Healthy children should undergo tests at least once every six months for control. With the help of mucus of a characteristic color, an experienced doctor suggests a diagnosis. If there is still pain, colic or vomiting with altered stool, hospitalization is required.
With altered microflora, the intestinal lining is restored by bifidobacteria and lactobacilli - special preparations or fermented milk products. After completing a course of antibiotic therapy, beneficial bacteria are prescribed.
For many young parents, the appearance of mucus in a baby’s stool becomes a reason to go to the hospital and get tested. Changes in stool that occur between the ages of 0 and 6-8 months are certainly important and require close attention, but in some cases, parents' concerns are completely unfounded.
It is important to understand that in the first half of the year, the baby’s intestines continue to develop, and its mucous membranes are populated by beneficial and conditionally pathogenic bacteria that make up the intestinal microflora.
It is for this reason that stool in infants is unstable and often changes its consistency and color. If the stool contains mucus, do not panic ahead of time. Information savvy will help parents stay calm, so it is necessary to know the causes and symptoms of this phenomenon.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of foamy stools in infants, parents should follow preventive measures:
- keep nipples and bottles from which the baby eats and drinks clean;
- do not introduce complementary foods before the due date;
- increase the baby's immunity;
- establish a diet;
- keep a food diary if the baby is prone to allergies;
- do not give medications to your baby unless necessary and on the recommendation of a doctor;
- select the appropriate formula for bottle-fed babies.
If there are constant signs of bloating, colic and pain in the intestinal area, you should visit a pediatrician. This will allow you to identify problems (dysbacteriosis, lactase deficiency, allergies) in the early stages and quickly eliminate them.
Most often, foamy stools appear in infants when fermentation processes begin in the intestines. If you stop pathological changes in time, you can improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate the alarming symptom. If within 4-5 days of treating diarrhea at home there is no change in the baby’s well-being, and even more so if there is deterioration, you should urgently seek help from a doctor. Self-medication can aggravate the problem and cause health complications for the baby.