A lactation crisis means a temporary decrease in breast milk production during a period when it would seem that lactation has already been established. Crises occur regardless of which child you are feeding, repeating every 1.5-2 months, and are quite understandable from a physiological point of view.
In the past, due to a lack of information about breastfeeding, some women, during the onset of a crisis, mistakenly believed that “milk was running out” and transferred their babies to supplementary feeding, and then even to artificial nutrition. However, modern mothers, armed with existing knowledge and support from loved ones, can survive them safely. Let's look at how.
Signs of a lactation crisis
To determine a lactation crisis, a loving mother needs to pay attention to the behavior of her baby, namely, monitor the following signs:
- The baby is mischievous and refuses to take the breast. He does this in different ways: he refuses to suck, he does not eat enough of the usual portion of breast milk, he grabs the nipples, but does not intend to suck out the contents.
- The child is openly starving, for the first time trying to insist on his own, crying to the point of debilitating hysteria. Sometimes it seems that it is impossible to break the vicious circle of hunger and screams, the little one is so persistent.
Of course, you can try to break the baby’s whims, but it is extremely undesirable for him to starve - just a couple of days or a week, and the newborn will lose weight. A starving child is not in good health; what you sow in the first year of your daughter or son's life is what you reap.
Knowing about the peculiarities of the lactation period, mothers look forward to it like fire. But it happens that it comes earlier or later - there is no need to worry, because each little person develops in his own way, and it is difficult to adjust individuality to standards.
It is better, of course, that this anxious and restless period does not occur at all - this, by the way, although rare, does happen.
Psychologists advise happy parents to rejoice - this means the baby is in complete harmony with his mother, he lives happily and calmly.
How to easily overcome the 3-month crisis in infants
In order to quickly overcome the lactation crisis in 3-month-old infants, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules of behavior, which have been outlined by experienced psychologists and neurologists:
- Only with breastfeeding (breastfeeding) does a child have the opportunity to receive the highest quality nutrition, if, of course, the mother follows a certain diet and adheres to a diet. The exception is when the mother does not produce milk - then the children are bottle-fed and can bypass the lactation crisis. Remember that breast milk is the only way to form and maintain good immunity. Despite the crisis and the whims of the child, continue to insist on breastfeeding. Even the most zealous and persistent kid will give in sooner or later; hunger will still take over. Very soon, the little baby will forget how actively he pushed away his mother’s breast, and will again appreciate tasty and rich milk.
- What you should not do is yell at your child, spank him or use force. Not only will you not force the baby to take the breast, but you will cause him a nervous breakdown, which will result in prolonged crying and hysterics. Be reasonable - this is a child, not a conscious adult. Be patient for just a week, lull your baby to sleep with lullabies, read rhymes and jokes, give preference to gentle intonations, pretend as if nothing unusual is happening, and the baby will stop his rebellion.
- If a child begins to become hysterical and chokes on sobs, switch his attention to another state, mood, show him interesting objects, occupy his thoughts with something else, positive and beautiful. Games, walks, pleasant rest - no one canceled the usual grandmother’s methods.
- You can experiment with eating positions.
- While paying attention to your baby, don’t forget about yourself. You need to eat rationally and properly, then the milk will be fat enough and will not cause bloating or diarrhea.
How long does the 3-month crisis last for infants? From a couple of days to 1 week, so you don’t have to wait long.
Crisis 3-4 months. Difficulties of GW. USEFUL ARTICLE
HELLO GIRLS!!!!!
I think that for many people the article will be interesting and useful...
Thank God it didn’t affect us... Ttt
About the crisis of 3 months
According to perinatal psychologists who study the behavior of infants, at 3-4 months the first stage of separation of the baby from the mother is observed - the baby first declares itself as an individual. He does this to the best of his abilities: while in his arms, he rests against his mother with his arms and legs; turns away and resists when she gives him the breast; screams, barely taking the breast and making several sucking movements; takes one breast but refuses the other. The child seems to be provoking the mother: how will she behave in such a situation? Is she really a reliable protection for him? If, in response to such a change in the child’s behavior (it is called “false breast refusal”), the mother provides him with additional “evidence” of her reliability - she does not stop offering the breast, feeds the child at night, does not use bottles and pacifiers, does not give water and complementary foods, she is ready feeding the baby in different positions that are convenient for him - the crisis of 3-4 months passes quite quickly. The most important thing: only the mother should take care of the child at this time, and all other family members should take care of her. This best helps strengthen the contact between mother and child, which the baby so needs during this period. However, if the mother does not know about the crisis for 3-4 months, does not understand the baby’s behavior, or from the very beginning breastfeeding caused difficulties or was organized incorrectly, a false breast refusal can turn into a genuine one. Sometimes it is accompanied by some kind of ill health of the child (digestive problems, dysbacteriosis, PEDs, etc.), but without establishing psychological contact with the child, treatment may be ineffective, and pediatricians are not always well acquainted with the psychology of the infant. ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– If all mothers knew about such a natural phenomenon as a crisis 3-4 months, breastfeeding children up to a year, or even longer, would be preferable. The fact is that at three to four months of age the child begins to refuse the breast. Most mothers, without further ado, transfer their babies to artificial formulas, and this is fundamentally wrong. A mother should not indulge the child, but act for his benefit. A child, refusing to breastfeed, does not require artificial formulas (he does not know about them yet), but tries to declare himself as an individual. His actions are instinctive and unconscious, but they are aimed at understanding or rather even feeling the reliability of his mother, her love and care. At this age, a child can express himself as an individual in several ways: start sucking at the breast during feeding and immediately stop doing so, suck only one breast and refuse the other, and completely abandon the breast. All these actions are accompanied by crying and sudden movements, which can enrage even the calmest mother. How to overcome this crisis? 1. Try to remain calm, because your emotional mood is transmitted to the child. Talk to your baby or sing a song. Stroke your baby and touch him gently. 2. Let the child take a comfortable position. Experiment. Show your baby that you care. You may have to feed your baby in a position that is uncomfortable for you, but it is comfortable for him. But isn’t his peace of mind the most important thing for you now? 3. Offer your breast continually to your baby. Do not replace it with artificial bottles and pacifiers, refuse complementary foods. In the end, the child, deprived of choice, will happily eat what is offered. 4. Feed your baby at night if he is hungry. Don't let him start crying, demanding a portion of food. Watch your diet to ensure that your milk has enough fat to meet your baby's needs. At the time of this crisis, it is important to carefully monitor the baby's weight in order to be sure that he has enough milk. Otherwise, false breast refusal can provoke very unpleasant consequences. With due patience from the mother, the crisis passes easily and quickly and then you can begin to introduce various complementary foods into the baby’s diet, according to age. Mothers who overcame the 3-4 month crisis in their children helped their babies not only remain on healthy natural feeding, but also laid the foundation for the development of a psychologically correct personality. The child felt that his mother was reliable protection and support, she could be trusted. Now it will be easier for the baby to calm down in the presence of his mother, fears will evaporate without a trace if he hears his mother’s quiet, gentle and so familiar voice.
Crises happen not only to adults. Doctors say that young children also experience emotional swings; parents will either be able to survive these periods with dignity, or they will break down.
After a woman has become a mother and has more or less recovered from depression, she will have to go through the first baby crisis at the age of 3 months. Doctors call it lactation and advise you to be vigilant. Inexperienced mothers try not to pay attention to the child’s unusual behavior, but how correct and effective is this?
The consequences will not keep you waiting, time is lost and it is no longer possible to reverse the situation. Forewarned is forearmed, so sit back and learn the peculiarities of infants growing up with us.
Crises in the first year of a baby's life
A child has quite a lot of crises in the first year of life - 3 months, six months, 9 months and, finally, 1 year. To survive this time with minimal losses, use the recommendations of psychologists:
- Follow the correct daily routine. During the day, the child must be physically exhausted - walk, jump. Make it a rule to follow a bedtime ritual - read a book every day, put on nice pajamas, etc. Children who follow the regime are more mentally balanced.
- There should be a lot of toys - educational and multifaceted, from different materials. Play is always development.
- It is useless to prohibit something, because the more prohibitions, the greater the desire to touch it and taste it. Curiosity is a great way to understand the world, otherwise how else will a child learn what life is. Respect his wishes and provide freedom of choice.
- To avoid prohibitions and conflict situations, put away things that the baby should not touch - matches, detergents, medicines. When a child begins to crawl and then walk, he looks into all the cabinets that can be opened. Therefore, install reliable latches on all drawers that will not fall off at the first effort.
- You should not overprotect an infant - by the end of the first year of life, the baby is trying to show independence, and this should be encouraged. He coats it with a spoon, bringing it to his mouth - it doesn’t matter, he grunts, but he’ll do it. By anticipating his mistakes and helping with everything - dressing, eating - you thereby do not give the baby the right to make mistakes, says Dr. Komarovsky, you allow him to do nothing at all and not even try. Do not be surprised if after such actions the child grows up phlegmatic and remains forever small, lacking initiative, and does not show interest in hobbies and self-development.
- Praise the baby. Psychologists recommend approving girls, regardless of what they did or did not do. Then the girl will grow up and turn into a girl with her own dignity. Raising boys involves praise for actions - this is how they develop an incentive for future achievements. If your son is under 1 year old and cannot cope with his task, offer your help, but do not rush to do it for him if he himself wants to bring the matter to its logical conclusion.
- Learn to say “No” correctly and at the right time. There is no need to shout, it is much more effective to explain.
- Don't force your child to do something he doesn't want to do. Dress him up by saying rhymes and distracting him with foreign objects.
- Talk about your feelings more often.
Source: https://malyshuhod.ru/ot-3-do-6-mesyacev/chto-delat-kogda-nastupaet-krizis-3-mesyacev-u-grudnichkov.html
A child has a crisis of three months - what to do?
New mothers, in anticipation of the birth of a child, study a lot of literature, which is a kind of preparation for upcoming motherhood.
They enthusiastically read literature that describes in detail the development of the baby, the changes that occur in one or another period of his life.
But when women encounter such a word as “crisis,” they begin to worry about whether they will be able to overcome it.
The first crisis that new parents have to face is lactation. This crisis occurs when the child is three months old and is handled individually in each case.
What it is
When the baby reaches three months, their mothers may encounter such a problem as a lactation crisis, the manifestation of which can begin at the age of 2.5 months and even after 4 months.
But you shouldn’t assume that this fate will definitely befall every breastfeeding mother. Not at all. In some cases, neither the baby nor his parents face this, so you need to set yourself up for the best. But we should not forget about how a lactation crisis that overtakes a child at the age of 3 months can manifest itself.
The main signs that a crisis has arrived are:
- A sharp change in the child's behavior during feeding. If previously the baby enjoyed this process, now he turns it into a kind of protest.
Revitalization complex
The main result of the newborn crisis is the revival complex. This is a set of baby’s reactions to external stimuli. It is a combination of the following actions:
- reaction of freezing and visual concentration on the object of attention in the first seconds of communication;
- lively movements of the legs and arms, arching of the back;
- a smile as a response to an adult’s speech;
- vocalizations (loud cries and prolonged hums) during communication.
With the totality of these reactions, the child takes the initiative to communicate with an adult.
It is important to know!
The child's revival complex begins to manifest itself towards the end of the first month of life. It becomes more pronounced at the age of two months. Scientific studies have shown that it appears earlier in those children whose parents not only satisfy the child’s vital needs, but also communicate with them.
With their attention, love and care, adults stimulate the formation of new emotions, needs for cognition and communication in the baby. With a lack of communication and attention from parents, the revival complex may linger or deviations in its expression may be observed.
What to do
Breastfeeding mothers whose children have experienced a crisis of 3 months are interested in the question of what needs to be done in this situation in order to alleviate the symptoms that have arisen and maintain breastfeeding. Therefore, let's look at this issue in more detail.
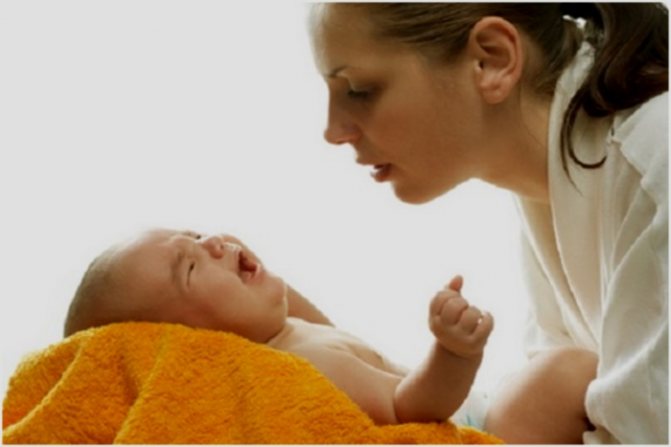

If your baby has a lactation crisis:
- Under no circumstances should you stop breastfeeding, no matter what tantrums your child throws. First of all, you need to understand that it is necessary both for the baby and for the woman herself.
Explaining this behavior by the fact that mother's milk is extremely beneficial for the child's body and the formation of immune defense, breasts should be offered to the baby at any time of the day or night. Yes, this can be a grueling and difficult period, but still, the work done will not be in vain.
At first, there will be a categorical refusal to accept the breast offered, which will disappear over time, because the baby will get hungry and he will not have to do anything else but enjoy his mother’s milk again.
- The crisis of 3 months is difficult to bear not only for children, but also for parents. A mother who does not get enough sleep at night and spends her days busy with her baby may be close to a breakdown during this period, which must be prevented by all possible means.
Taking it out on a child is not the best option, nor is punishing him for refusing to breastfeed. Despite the fact that in some cases this is extremely difficult to do, you need to try to remain calm, not shout at the child, but, on the contrary, wrap him in affection and care.
Affectionate maternal speech and tactile contact will certainly help to overcome the crisis.
- Throughout the day, the child needs to be given maximum attention, including communication, walks in the fresh air, massage, performing gymnastic exercises and other things.
The task of parents during this period is to establish contact and trust with the baby. Regular attention from the person closest to you will reduce the manifestation of a lactation crisis to zero.
- Refusal to breastfeeding may also occur due to discomfort that occurs during feeding. Associated discomfort may be due to incorrectly selected breastfeeding technique, which complicates the feeding process and causes negative emotions in the baby.
In this case, the woman needs to reconsider this issue and choose the position in which her child will feel comfortable drinking breast milk.
- Review mom's diet. Very often, children refuse to breastfeed due to the fact that they do not receive enough milk necessary for development and growth. The quality or composition may also not suit the kids. It is clear that low-fat milk cannot satisfy hunger, and fat milk cannot satisfy thirst.
Therefore, with the onset of a lactation crisis, the menu of a nursing mother should be reviewed and adjusted. From this moment on, the menu should contain exclusively natural and healthy food that promotes milk production and does not affect the change in its taste and quality.

These are the main recommendations that will help if your baby refuses breastfeeding. The duration of this period depends entirely on the parents, who, with maximum effort, will be able to reduce the signs of a lactation crisis to a minimum and soon completely overcome it.
Some children can protest and achieve what they want for a week, while others will torment their household members with hysterics, disobedience, and stubbornness for 2 or even 3 months. But every mother will certainly find an approach to her baby and do everything possible to help him and maintain breastfeeding.
Source: https://razvitie-vospitanie.ru/otveti/krizis_trex_mesyacev_u_rebenka.html
How to behave as parents
Of all the living creatures inhabiting our planet, man is the most helpless at birth. Only the human baby needs its parents the most and for the longest period of time. With all his behavior he signals his needs.
But parents must also be able to recognize these signals. The task of parents is to establish a sense of security and basic trust in the world. Thanks to trust, the child will feel happy and protected, and only this will give him confidence.
To help a newborn go through a crisis less painfully, you can adhere to the following recommendations:
- maintain a comfortable temperature in the baby’s room;
- feed the baby on demand until full;
- talk to the child in a gentle tone during feeding, bathing and while changing clothes;
- surround with calm, attention and warmth;
- do massage and gymnastics;
- during bathing, use some kind of base so that the baby feels it and does not experience a feeling of insecurity and anxiety;
- in the design of a newborn’s room, use light pastel colors, add bright colors very dosed and gradually;
- build a daily routine and stick to it.
Features of the lactation crisis
What signs will become beacons for a woman, announcing that the crisis of 3 months has arrived? Loving, caring, attentive mothers will not be able to help but notice them:
- the child begins to refuse the breast, and in different ways: he may refuse to suck at all, he may not suck enough, he may grab the nipples without sucking anything out of them;
- the baby is starving, trying to emerge as an independent personality, sometimes driving himself to the point of hysterics: since he wants to eat, he will be capricious, cry, scream;
- by starving, he can lose weight;
- his sleep will be disturbed.
Young mothers should take into account that the development of children occurs very individually, so that someone will be ripe for a lactation crisis at 2.5 months, and someone will experience it after 4 months of their life outside the womb. And there is absolutely no need to worry if you have not noticed anything like this in your baby at this period of time. Such a turn of events will only speak in your favor: it means that the harmony between mother and child is ideal, and he does not find it necessary to destroy it.
Diagnosis: “adulting crisis”
But hysterics do not go away in a day or a week. Then moms and dads get angry and look for reasons for disobedience in the little one’s bad character, and conduct an audit of upbringing methods.
Real panic begins when neither the stick nor the carrot method works with the child. By this point, parents are mentally at their limit. They are torn by mixed feelings when anger, tears and irritation border on growing anxiety for the health and future of the baby.
Here, many adults turn to pediatric neurologists for help. And this is correct, since behavioral deviations can be a sign of diseases of the nervous system and more. But it is more likely that the doctor will examine the child and reassure the parents by making a “crisis diagnosis.”
Doctors say that a child’s three-year crisis is a stage of growing up necessary for his full development. And you need to worry more quickly when a baby at this age is phlegmatic, submissive and lacking initiative.

How to overcome the crisis of three months?

But what to do if a crisis does occur? Many who do not know about its existence draw their own conclusions and make typical mistakes, which they later regret for a long time. Try to behave in a certain way, as psychologists and pediatricians advise: this will help smooth out all the rough edges of this period.
- You cannot give up breastfeeding when you see the baby’s refusal to take the breast and switch him to artificial formula. This will have the most negative impact on his immunity and health in the future. Offer your breasts to him during this period at any time of the day or night, keeping in mind the crisis. You can easily restore your diet later: the main thing now is to get out of this three-month crisis. The feeling of hunger will soon take over, and in a couple of days he will again with pleasure empty his mother’s beloved breast. In any case, it will be easier than teaching the baby to breastfeed again.
- You just need to endure the whims of your little man associated with fasting, no matter how difficult it may be. Spanking and yelling will not work here, but will have the exact opposite effect. And therefore, try to be calm during these 2-3 days, soothe the baby with lullabies, gentle intonations, gentle strokes and kisses. Once he is convinced that he is loved, the baby will also calm down and stop rebelling.
- Distract your child from his condition: devote more time to him, walk, play, entertain him. This will make him forget and quickly take the breast again.
- If the baby does not want to take the breast, experiment with positions: perhaps you will find one that he likes, and he will resume his feeding as before. You can see some more tips here: how to properly attach your baby to the breast.
- Watch your own nutrition: it should be complete and rich in vitamins, so that the milk is moderately fatty and not too liquid, since this can also provoke this crisis.
How to overcome the milk crisis: what to do
Psychological methods
The main rule is not to worry. Remember that if the baby’s health is fine, everything is fine. Sufficient lactation is progressing.
Milk crises during breastfeeding are short-lived phenomena. And the deficiency will stimulate increased sucking, therefore, there will be good milk production. Do not forget that the mother’s anxious state can affect the child and aggravate the problem.
Maintaining a daily routine and improving the life of a nursing mother
Milk crises are a consequence of an irrational or incorrect regimen for a nursing mother. Frequent lack of sleep, fatigue, worries and bad mood are a direct consequence of the crisis.
Solution to the problem:
- focus on the correct daily routine for yourself and your baby;
- regular good sleep. It is advisable to put everything aside and sleep a little while the baby sleeps;
- if possible, involve loved ones in helping with housework;
- put the baby to the breast as soon as required. The more the baby eats, the more milk will be produced.
Sometimes, for psychological satisfaction and to lift your spirits, you need to arrange an interesting walk or meeting.
Massage
To calm the nervous system and stimulate blood circulation, a course of massage is recommended, as a result of which lactation also increases. Exercises in the chest and neck area are recommended. Even light massaging strokes are enough to smooth out the symptoms of the milk crisis during breastfeeding.
Warm baths
Warm treatments help some. They are recommended for pronounced deficiencies.
Warm, relaxing baths will improve blood circulation and promote lactation.
You can also practice a warm wrap: wrap your breasts in a warm towel before feeding.
Nutrition
A very important factor in a mother’s regimen during a milk crisis during breastfeeding in order to stimulate lactation is proper, balanced nutrition and plenty of drinking. Meals should be varied, high in calories, contain a lot of protein and at least five times a day. Since the baby may often wake up for night feedings, it is advisable to drink more nutritional fluid at night. This could be tea with milk, compotes.
But the choice of food products should be approached carefully so as not to cause an allergic reaction in the child. There are natural lactation stimulants: carrot juice with milk or cream, anise seed decoction, anise, fennel and oregano tea, caraway seed decoction.
Increased number of applications
Putting the baby to the breast as needed is the first rule for stimulating lactation. It is even recommended to give to both breasts, but to apply to the second only when the first is completely empty. You should not resort to mixtures. The crisis is short-lived, and the child will become accustomed to formula.
There are cases that children even refuse to breastfeed. It's easier to suck on a bottle than to breastfeed. The baby will be full longer, require breastfeeding less often - lactation will decrease. Therefore, complementary feeding can aggravate the problem of lactation.
Night feedings
Night feeding is a period of intense production of the hormones prolactin and oxytocin, which directly stimulate lactation. In the morning, every mother knows the feeling of a full breast. A good result is achieved by sleeping together and feeding the child frequently at night. It is night application that helps solve the problem without drug intervention.
Milk crisis (lactation crisis) during breastfeeding
— Polina Aleksandrovna, what should we understand by the breastfeeding crisis?
Breastfeeding crisis (or lactation crisis) is a condition in which the mammary glands produce less breast milk than the baby needs.
— Breastfeeding crises can overtake a mother at any period of lactation. Milk production has a wave-like course: sometimes there is a lot of it, at other times - as much or as little as is needed. For each woman, such conditions arise individually, more often in the first month and about six months after the start of feeding, but the “milk” crisis is not directly related to the specific age of the child.
What is a lactation crisis?
In medical practice, a crisis is a situation when milk production decreases. The problem is temporary and occurs already during mature lactation. There is a certain period of time when this phenomenon occurs, usually the period from the third to the sixth week after childbirth or the third and subsequent sixth and twelfth months. But in some cases, young mothers are lucky; their feeding occurs without such disturbances. A lactation crisis can be determined by the following symptoms:
- The baby practically does not leave the mother's breast, sucks too often and for a long time.
- During feeding, the child becomes nervous, cries and is capricious due to hunger.
- A nursing woman does not seem to feel the flow of milk.
Mature lactation, hello!
By 3 months, if this has not happened earlier, mature lactation is finally established with an autocrine process of regulation (i.e., no longer due to hormones, but in response to stimulation of the breast by the child). Autocrine regulation manifests itself in the fact that the breast ceases to be very full and between feedings can be completely soft and not full. That is, lactation is tidal in nature, and milk begins to actively flow immediately during breastfeeding. This is perceived as a sudden tingling and swelling of the mammary gland, especially thin women.
However, in women with congenital hyperlactation or those who regularly pump their breasts, excess milk production may stop much later, sometimes only closer to a year or longer.
Subjectively, you may get the impression that there cannot be a lot of milk in a soft breast, especially if you try to express the breast in between feedings. Women may begin to think that the baby has grown and is no longer getting enough milk. There is a desire to supplement with formula or drink lactogenic tea, and sometimes to do both together. Naturally, these measures do not increase the volume of milk, and the mother, unnoticed by herself, can completely transfer the baby to artificial nutrition by the age of 4 months.
Remember that if the baby is gaining weight well and goes to the toilet often enough, then there is no reason to worry - everything is fine with your milk.
It often happens that an already grown child suddenly begins to breastfeed very often, as if “hanging” on the mother’s breast. Naturally, this is very stressful and nerve-wracking for a nursing mother. At such a moment, it is also important not to rush into supplementary feeding. Know that the situation with a temporary shortage of milk is not critical for a healthy and full-term baby; nature has prepared him for such changes in the volume of breast milk from the mother and provided him with the necessary protective resources. Therefore, within 2-3 days the baby can normally survive such a “lactation crisis.” Monitor your baby's urination and offer your baby the breast as often as he asks.
Relax and get some sleep
A lactation crisis at 3 months is often caused by lack of sleep. After all, it is at this time that the baby becomes more active, his daily routine changes. If previously the baby only ate and slept most of the time, now he needs to play and stay awake. Mom may simply not be able to cope with all the workload.
To eliminate this cause, you may need outside help. Ask your dad or grandparents for a little help. Take them for a walk with the baby. In your free time, don’t bother with washing and cleaning. Lie down and get some sleep. A nursing woman's nightly sleep is constantly interrupted.
Reasons why milk production decreases
A temporary lack of milk or decreased production is more of a pathology than a norm, since it does not occur in all nursing mothers. The main reasons for this condition:
- Incorrect attachment of the baby to the mammary glands or insertion of pacifiers and feeding bottles.
- Natural feeding by the hour, not on demand.
- Increased nervous excitability and stress, as a result of which milk fades. Here we can talk about lack of sleep, and fatigue, as well as depression from the constant repetition of “Groundhog Day”.
- Periods of active growth of the newborn. The child grows, which means his need for food increases. But the mother’s body is not always able to react so quickly to the baby’s rapid growth. The woman thinks that there is not enough milk and takes all possible measures to feed the baby. In fact, you just need to be patient a little - in a couple of days lactation will improve and there will be as much milk as the baby is ready to eat.
What to do if a lactation crisis occurs
Lack of milk during a period of rapid growth of a child or a lactation crisis is a non-pathological condition of the mother-child organism when a woman’s breasts do not have time to adapt to the baby’s sharply increased needs for milk. A situation where a mother’s mammary glands temporarily “lag” and produce insufficient milk to meet the baby’s growth spurt.
This typically occurs at the end of the fourth week and third month of breastfeeding. Although any period of lactation is “not immune” from this situation. For many women, this crisis lasts no more than two or three days, causing virtually no anxiety. But for some, it can last for a longer period - 7-9 days or more, becoming a period of great trials for the mother and child, requiring certain measures.
The mechanism of the lactation crisis
The main function of the mammary gland of a nursing mother is milk production. It is regulated using a feedback mechanism: as much as the child’s body requires it, it will produce as much. That is, according to the “request-offer” principle.
Rare and short-term breastfeeding and lack of night feeding lead to a decrease in lactation. This mechanism is realized through the factor of suppression (inhibition) of milk production by a protein molecule that is present in milk.
As a result of inadequate milk output, which overfills the breast, the amount of this factor in it increases, which leads to suppression of fluid formation. When milk leaves the breast in a timely manner and does not overfill it, the amount of inhibitory factor in the mammary gland decreases, which forces it to produce intensively.
How to recognize a lactation crisis
A situation where there is a lactation crisis may not be immediately recognized by a young mother. Key signs, which are conventionally divided into objective and subjective, will help her with this.
Objective signs:
- Decreased frequency of urination (the child urinates less than 12 times, but more than 6 times a day). Rare urination (less than 6 times a day) in combination with severe weakness are symptoms of serious dehydration in a child that requires immediate help.
- Inadequate weight gain (less than 125 g per week for the first 3 to 4 months).
Subjective signs:
- The child often asks for the breast and “it is difficult to tear him away from it,” and often cries.
- The child has stool once every few days, hard, green.
- There is no sensation of milk flow.
Baby growth spurts and lactation
It is unfair when a woman, having adjusted her feeding schedule, receives such a gift from nature: the baby suddenly changes his feeding hours and begins to latch on to the breast every hour.
However, a nursing mother must understand that her baby's growth spurts are a normal, natural process. Panic is inappropriate here, rushing around with the thought “Is the baby getting enough milk?” not worth it. This is the first growth spurt, and it can be repeated more than once during the year. The main task of a child’s body in the first year of life is to grow as quickly as possible. However, this occurs unevenly, with short, intense bursts.
Although growth spurts can occur at any time, growth spurts most often occur between the first and third weeks, and the sixth and eighth. They are then typically expected at three, six and nine months. This is why lactation at three months can go into crisis.
The good news is that growth spurts usually last only 2-3 days, the crisis passes, and life for the child and mother returns to normal.
Lactation crisis at three months
Lactation at 3 months, if this has not happened earlier, becomes mature and is no longer regulated by hormones, but with the participation of an inhibitory factor (switches to breast stimulation by the child). Feeding takes on a tidal character: the breasts stop filling strongly between periods of latching the baby, and milk begins to actively flow directly during latching.
The baby’s growth spurt is combined with the development of mature lactation at 3 months, when a woman notices between feedings that her mammary glands are not full as usual, and the baby begins to demand the breast more often.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of a lactation crisis
The lactation crisis can be influenced not only by the child’s growth, but also by external factors. These include:
- The baby does not attach well enough to the mother's breast. This may be due to pain in the nipple or damage to it.
- Long intervals between feedings. In a healthy child, the frequency of feedings should be from 8 to 12 times within 24 hours.
- Using pacifiers and bottles.
- Long intervals between feedings.
- No night feedings.
- Incorrect introduction of complementary foods.
- The mother had a history of mastitis or breast surgery in the recent past.
- Taking oral contraceptives that contain estrogen.
- Smoking.
- Some medications, including over-the-counter ones.
- Some maternal diseases.
What to do if a lactation crisis does occur
It should be understood that lactation is subject to the principle “demand creates supply.” Hanging on the mother's breast, the baby constantly stimulates her with sucking movements, which leads to an increase in milk production. Therefore, you should extend the time your baby stays at the breast and offer it to him more often.
It is also worth adhering to the “skin to skin” principle. This can be facilitated by a sling and other devices for carrying a baby. The husband, relatives, and older children can take on part of the mother’s household chores, which will allow her to arrange a “nesting” period during the lactation crisis. It is necessary to constantly offer your baby your breasts, even if they seem empty. The number of night feedings needs to be increased.
During the lactation crisis, pacifiers and pacifiers should be put aside. There is no need to rush into supplementary feeding of the baby, even if grandmothers with extensive experience and other “experts” advise it. There is a simple pattern: as much as supplementary feeding increases, milk production will decrease. Therefore, if you do not control the amount of infant formula, the lactation crisis can be resolved by stopping breastfeeding.
Panic in this situation is inappropriate; stress has a detrimental effect on milk production.
It is necessary not to overwork, try to get enough sleep, and eat well. And do not forget about the amount of fluid consumed, it should be sufficient for the daily norm. To improve lactation, you can drink decoctions of fennel, cumin, and anise.
If a child cries, is restless, and breastfeeding has almost stopped at three months, it is necessary to help him cope with this dissatisfaction. A wide variety of methods are appropriate here to help distract the baby, which largely depend on the mother’s imagination. Beautiful music, sounds of nature, carrying, rattles - all this can solve the problem. But the main thing that is important not to forget is that it is necessary to offer the baby the breast as often as possible.
The above measures, patience, and attentiveness of the mother will help cope with the lactation crisis. You shouldn't wait for him, but if he appears, don't panic. As a rule, it does not last long.
Any crisis is a great chance to direct the process in the right direction. If a woman listens to herself and the desires of her child, breastfeeding her baby will become a fruitful and joyful process for her.
GrudInfo.ru
Duration
How long does a lactation crisis last? This question arises for every woman faced with a similar problem. In fact, everything is individual. It is impossible to specify exact dates, because a lot depends on your desires and actions.
If you try to increase the amount of milk produced and comply with all the conditions described below, the crisis will end after a few days. Usually it takes three to four days. When a woman lets everything take its course and categorically does not want to fight, the crisis can last up to a week (provided that breastfeeding continues).
How does a lactation crisis manifest at 3 months?
When the child reaches three months of age, the lactation process is completely normalized and enters the most active phase. But sometimes that very crisis happens when the baby behaves nervously at his mother’s breast. He cries, is capricious, moves away from the mammary glands. Or she doesn’t allow her mother to rest at all and suckles almost all day long, without getting enough to eat.
During this period of its development, the baby changes its lifestyle.
He begins to show interest in the objects around him, sleeps less, and at the same time his diet changes. Longer periods of wakefulness appear when the baby is more active. The baby takes the mother's breast after or before sleep, as well as at night. This behavior of a baby is quite natural and there is no point in correcting it or force feeding it. But you should make sure that when the baby falls asleep, he sucks on the breast and not on a pacifier. After all, when he wakes up, he may find himself hungry, and the mother’s milk will decrease, as the baby sucks out less and less of it.
The 3-month crisis in breastfeeding infants can also occur for another reason - when the care of a loving mother is excessive.
That is, when taking care of her baby, the mother carries him in her arms, instead of letting him lie quietly in the crib. Or she constantly rocks the baby in her arms, afraid that the baby will cry again. A child suffers from such excessive care no less than a woman. He gets used to this state and no longer perceives the next portion of delicious milk with as much joy as he could.
Periods and timing of the crisis: from 1 to 6 months
The time of onset and periods of duration of the breastfeeding crisis by month are strictly individual. You should not wait or worry that it will come - this will make the situation worse.
The crisis is usually divided into the first month, 3 months, 4 months and 6 months. How long can a lactation crisis last? As a rule, it has a short period, about 3-7 days. With proper organization of the regime, it passes quickly.
3–7 days is the duration of the crisis.
Crisis in the 1st month of development
This is an important month in a baby's life. There is a shift in the development of sensory perception, the child is already familiar with something. A lactation crisis may occur in the 1st month.
At such moments, the child may behave restlessly and needs something familiar - the close presence of his mother. When the baby is worried, the mother may experience mixed feelings of misunderstanding and fear, worrying whether the baby has enough food, whether he is hungry, or something else is bothering him.
But the baby calms down when applied to the breast, so he may require more than normal. In such cases, many begin to think that a period of lactation crisis has begun: if the baby often requires the breast, it means he is not getting enough. Experts advise putting the baby to the breast as required. A close connection between mother and baby is established, and if there are no other irritating factors, he calms down.
Lactation crisis at 2 and 3 months
A milk crisis may occur in the second or third month. It would seem that milk production has improved, the colic in the tummy has passed, everything is fine. But a child is characterized by a certain leap in development; he already perceives surrounding objects and people with interest and understanding. A breastfeeding crisis may occur during this period.
During feeding, the baby may refuse, distracted by extraneous movements, to hang on the chest. During this period, it is advisable for the baby to fall asleep at the breast, this will stimulate the production of natural food.
The child should be allowed to learn and examine as much as possible, so that he gets tired, bored and eats willingly. If all the rules are followed, the lactation crisis at 2 and 3 months will pass painlessly for both mother and child.
Lactation crisis at 4 and 5 months
The crisis at this stage of child development is similar to the lactation crisis at 3 months. It all depends on the individual growth periods of the child. Certain leaps in development and weight gain require an increase in nutrition.
If the mother and her baby's daily routine is followed correctly, the mother will quickly and without worry cope with the resulting shortage of milk.
Crisis at 6 months of development
A six-month-old child requires more and more attention in matters of feeding and communication, so the nature of the lactation crisis at 6 months is also different. At this stage of development, the child needs additional nutrients.
There are signs to determine whether a baby on breastfeeding needs complementary feeding: the weight has more than doubled, the child is capricious and constantly asks for food. Complementary foods are introduced in a sitting position with the help of an adult. It starts with five grams and gradually increases the volume.
Each complementary food must be supplemented with breastfeeding.
- Do not reduce the number of breastfeedings.
- Do not switch to artificial mixtures.
- Wait time and milk production will be restored.
- In this case, it is necessary to follow certain rules for stimulating lactation, developed for periods of lactation crisis.
Complementary feeding from 3 months while breastfeeding: is it necessary?
Only in the most extreme cases, for example, if due to certain circumstances the child cannot receive sufficient amounts of vitamins, macro- and microelements from mother’s milk. For example, when a woman is prescribed a strict diet with many restrictions for health reasons.
In this case, it is allowed to introduce applesauce and banana puree, very liquid and well-cooked cereals, some vegetable and fruit juices, prepared at home immediately before feeding, into complementary feeding for a breastfeeding child from 3 months. But we should not forget that from the point of view of benefits, nutritional value and digestibility, not a single delicacy can compare with mother’s milk.
Breastfeeding litmus test
Three months is like a litmus test that shows how the relationship with the baby developed before. If there were any serious mistakes in organizing breastfeeding and caring for the child, they will always manifest themselves in the child’s restless behavior and refusal to breastfeed. It is at 3 months that abandonment of the mother's breast becomes the number one problem for many parents.
But, oddly enough, sometimes breast refusal can be provoked by overprotection on the part of a woman, when the mother constantly carries the child in her arms or in a sling and constantly offers the breast. Very often this happens to those mothers who were unable to breastfeed their older child, or in case of fanatical adherence to any methods for raising and caring for the child. The child is simply drowning in “mother’s love” and is trying by any means to break free.
Therefore, try to alternate between carrying the baby in your arms and placing the baby near you. Do your homework, giving the baby the opportunity to watch you - in my opinion, there is no point in carrying a baby in a sling or in your arms around the clock.
As for other educational aspects, at 3 months the mother can already begin to regularly take the child with her to the table, if she has not done this before. This is how we shape the child’s eating behavior, or, more simply, we accustom him to the look of a common family table.
In addition, if the baby has previously bathed in a small bath, which is more appropriate for a newborn, then from 3 months you can try to move to a large bath; joint bathing with the child is especially welcome.
Also, from 3 months we begin to actively carry it on the hip and sit it by the arms for a couple of seconds on the changing table. This is important for the proper formation of hip joints and the prevention of dysplasia. Children usually signal this themselves by their reluctance to remain in a horizontal position while awake.
If you keep your baby without diapers and practice dropping him off, then at 3 months you should start making sure that your baby doesn’t pee on you. “Mistakes” happen even among experienced parents, but if the baby starts peeing on you, you need to interrupt him and take him off your hands, thereby demonstrating disagreement with what he is doing...
As you can see, 3 months is a difficult time in the development of your baby, when he begins to change his behavior and slowly “separate” himself from his mother. It is important not to miss these changes and to be sensitive to your child's signals. Due to inexperience, many mothers are tempted to give up breastfeeding for one reason or another. Those who manage to “cross the Rubicon” are usually fed happily for up to a year or longer (provided that complementary feeding is introduced no earlier than 6 months and in a volume that does not replace breastfeeding).
Successful GW to you!
How to deal with a lactation crisis
To correct the problem and eliminate the lactation crisis, a nursing woman needs to take a number of measures, all in combination.
Emotional component
Negative emotions have a detrimental effect not only on lactation, but are also transmitted to the baby. Therefore, a caring mother should be nervous, worried and worried as little as possible. A woman’s stable emotional state leads to full lactation and the absence of a crisis. But if the problem already exists, then the correct breastfeeding technique and a favorable emotional background can speed up the process of restoring milk production.
All possible help, support and understanding of the young father are very important for the mother during the milk crisis.
Increasing standard of living
A favorable environment for the development of a lactation crisis can be considered lack of sleep, excessive fatigue and excessive physical activity. A young mother should allocate enough time for sleep - at least 9 hours. If you were unable to sleep well at night, you need to rest with your baby during the day. When a crisis occurs, it is better to delegate most household chores to relatives.
The mother herself should take care of herself and the baby - put her to the breast more often, caress and take care of the newborn.
Physical exercise
A nursing woman can influence the level and quality of milk through massage. Light kneading, stroking with the palm of your hand or rubbing the mammary glands can increase blood supply. Breast massage frees the milk ducts, resulting in the outflow of milk faster and in greater quantities. You can supplement the beneficial procedures with a warm shower, cream or oil for the delicate skin of the breast.
What should a mother do to overcome the crisis of the third month of a child’s life during breastfeeding?
The crisis of 3 months in breastfeeding infants can be overcome in 3-4 days, provided that the woman follows the recommendations of breastfeeding consultants.
Psychological methods
Meditation is considered one of the most effective psychological ways to normalize the condition of a young mother. It should be performed before bed or immediately after waking up, when the woman is as relaxed as possible. It is recommended to meditate in absolute silence with dim lighting.

The work algorithm should look like this:
- Lie down or sit down in a position that is comfortable for you.
- Close your eyes and then concentrate on your inner sensations. For convenience, you can record your own voice, voicing tips and instructions during the meditation process.
- Imagine yourself as a bird flying in the blue sky among the clouds. Stay in this state for 3-4 minutes.
- Next, the bird heads to a tall tree standing in the forest or on a mountain (in a place where the young mother feels calm and confident). On a tree she has a nest with a small chick (child).
- The bird sits down next to its baby, hugs it with its wings, strokes it, caresses it. He responds to her with the same tenderness. A light fresh breeze blows over them and the sun warms them.
- It is important to feel how the baby’s reciprocal tenderness responds in the body of the mother bird (and the real mother). The chick is grateful to her for what she does, he is happy that he has such a mother. He accepts and loves the bird for who it is.
- Concentrate on these emotions for 10-15 minutes.
Maintaining a daily routine and improving quality of life
The first months of a child’s life usually radically change the way of life of the parents. A woman worries a lot, doesn’t get enough sleep, stops playing sports, and forgets to take care of herself.
The above factors add up to the reason why hormonal imbalance occurs in the weakened female body - the amount of prolactin rapidly decreases, which is why the production of breast milk slows down.
To normalize the condition, psychologists and lactation consultants recommend that young mothers:
- introduce small pleasant rituals (for example, take a hot bath with fragrant foam every evening and listen to your favorite music);
- agree with your husband on the distribution of responsibilities (for example, while the mother cooks, the father goes for a walk with the child);
- allocate time for yourself every day (this should be at least 40 minutes, during which a young mother can do whatever she wants - sit with her family or go for a walk alone, sing songs loudly or read her favorite book in silence);
- devote at least 8 hours of sleep per day (ideally, nighttime sleep should be 8 hours, but if you can’t sleep that much, it is recommended to rest with your baby during the day);
- eat at least 3 times a day (due to fatigue and the inability to correctly allocate time, young mothers consider it sufficient to simply have a snack during the day, not realizing that their diet directly affects the formation and maintenance of lactation).
Massage
To stimulate lactation, it is recommended to use simple massage techniques, which must be performed before putting the baby to the breast:
- Lubricate your hands with natural oil or rich cream.
- Place your hands below and above your chest, turning your palms back to each other.
- Lightly pressing on the chest, perform several rubbing movements away from you. Movements should be gentle but sensitive. If excessive compression of the breast occurs, a woman risks damaging the milk ducts, causing lactostasis.
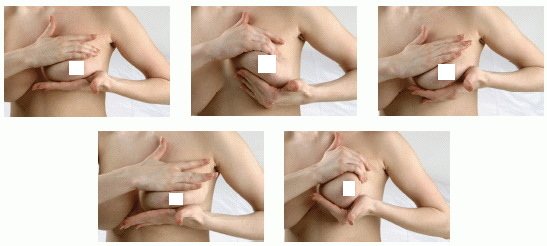
- Place your hands to the right and left of your chest, as if holding it between your palms.
- Lightly pressing on the chest, perform several rubbing movements away from you.
- Place your hands below and above your chest, turning the backs of your palms towards each other.
- Perform several light chest crunches in a clockwise direction.
- Place your hands to the right and left of your chest. Knead the chest with stroking movements back and forth for 2 minutes.
- Grasp the breast in the areola area, placing the nipple between the index finger and thumb. Massage your breasts with light pressure without changing the position of your fingers for 5 minutes.
Warm baths
The 3-month crisis in breastfeeding infants can be overcome more quickly if the mother takes a warm bath at least once a day. It is important that the water temperature does not exceed 38-40 degrees Celsius. Otherwise, a woman’s weakened body may react to such procedures not only by increasing pressure, but also by opening uterine bleeding.
Taking baths is permitted only after the approval of a gynecologist who conducts a thorough examination of the woman during the postpartum period.
The doctor must not only see the current state of the young mother’s reproductive system, but also have an idea about the characteristics of her health (presence of diseases preceding pregnancy, how the pregnancy went, and so on).
Nutrition
To maintain lactation, a woman needs to eat a balanced diet. It is not recommended to adhere to a strict diet, as this may subsequently lead to the inability of the child’s gastrointestinal tract to adapt to solid food (the child is diagnosed with acquired allergies).

This does not mean that a young mother can include foods that are objectively harmful to the body in her diet. to build eating behavior to prevent a crisis, as well as normalize lactation when it occurs, based on the rules below:
- minimize the consumption of fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- exclude hot seasonings, sauces, and additives containing large amounts of salt (regardless of its type);
- don't eat a lot of sweets;
- minimize consumption of flour products;
- eat as many fermented milk products as possible;
- include fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet (ideally, these should be products whose surface has not been treated with chemicals that enter the child’s body through breast milk);
- exclude alcoholic drinks, carbonated waters, and packaged juice products (as an alternative to tasty drinks, you can use natural fruit drinks and compotes prepared at home).
Increased number of applications
Infants aged 3 months who are on breastfeeding are recommended to be applied to the breast at least 5 times a day. When a lactation crisis occurs, it is optimal to increase the number of feedings to 8-10. The more often a child sucks breast milk, the more the body is forced to produce it, adapting to the needs of a particular child.
It is considered normal during this period if the child almost constantly requires the breast. It is strongly not recommended to refuse him or feed him by the hour, as this can lead to complete suppression of lactation and the baby’s forced transition from natural to artificial feeding.
Night feedings
During the period from 2 to 4 am, the mother’s body produces the maximum amount of prolactin and oxytocin - hormones responsible for the formation and maintenance of lactation, regardless of the existing crisis.
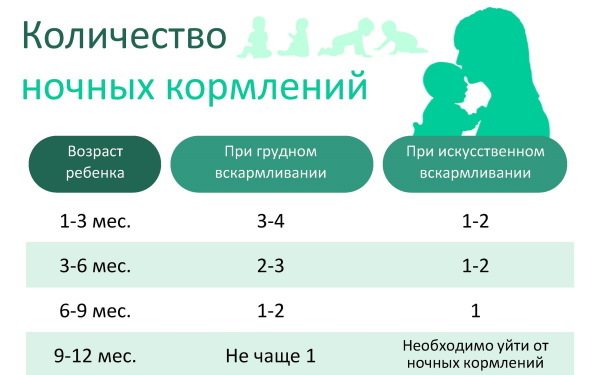
Therefore, avoid night feedings, in the absence of the mother’s desire to complete breastfeeding, in children under 9-12 months. highly not recommended. During the crisis period of 3 months, the number of meals from 12 to 5 am must be increased by 2 times, focusing on the norms:
| Child's age | Number of feedings |
| 1 – 3 months | Up to 4 times per night |
| 3 – 6 months | Up to 3 times per night |
| 6 – 9 months | Up to 2 times per night |
| 9 – 12 months | No more than 1 time |
Eliminate stress
Often a lactation crisis develops due to a nervous breakdown. This can happen due to fatigue, lack of sleep, moral exhaustion, and so on. Therefore, a nursing woman needs mandatory support from close relatives. Never refuse help. Walk and spend more time in the fresh air. Long-term confinement within four walls only aggravates your condition. Don't isolate yourself.
If you feel constant anxiety, get nervous a lot and realize that you can’t cope on your own, go to the doctor. The doctor will prescribe you safe herbal medications, for example, Tenoten, Persen and others. They will not harm the baby, but will be able to normalize your condition. Remember that it is unacceptable to take medications on your own.
Let's summarize...
Any lactation crisis, periods whose timing is known to you, is not such a serious problem for a woman who wants to continue breastfeeding. Keep in mind that this situation usually resolves in about a week. If you follow the above conditions and tips, you can cope with a lack of milk in just a few days. If you can easily overcome the first lactation crisis, which occurs about a month after the birth of the child, then the rest will not pose any particular danger or difficulty.
An important point to remember is that bottle feeding should never be substituted. Don't think that your baby is starving. Check if the baby has enough milk. To do this, count how many times a day he urinates. If the number of wet diapers exceeds 12, then the child has enough nutrition. Please note that this rule is only valid for babies before complementary feeding is introduced. We wish you normalization of breastfeeding as soon as possible!
Source: https://kcdc.ru/zabolevaniya/krizis-pri-gv.html











