Can a woman breastfeed during pregnancy?
If the pregnancy period proceeds without problems, there is no reason to refuse breastfeeding. The changes occurring in the mother's body favor weaning the child from the breast, but she makes the final decision about this.
Both pregnancy and pregnancy loss require a girl to have additional daily nutritional needs. A woman has to eat for three people in order to provide food for her two growing children. Therefore, it is necessary to consume large amounts of microelements, vitamins and proteins. In such cases, it is recommended to visit a nutritionist for the correct selection of products.
Increased physical activity when combining breastfeeding and pregnancy requires longer rest. Therefore, it is advisable that one of the relatives be with the woman at all times and help in solving everyday issues.
Problems associated with increased breast sensitivity can be compensated for by adjusting the baby's nipple latching. Many mothers suffer discomfort associated with incorrect posture during breastfeeding. Teaching your child the correct grip and choosing a comfortable position reduces this problem.
In addition, when deciding whether to wean an infant, the following factors must be taken into account:
- baby's age;
- psychological need for contact with the breast;
- compliance of the level of development with the age norm;
- the opinion of other relatives involved in caring for the child.
It is undesirable to wean children who are physically weak and often ill early without serious indications. Mother's milk should provide them with nutrients for as long as possible. This will strengthen their health and bring them closer mentally to the brother or sister developing in the mother’s belly.
Question to the expert
When my daughter was 5 months old, I became pregnant again and am breastfeeding. The second child is desired, there is no talk of abortion. Until what stage of pregnancy can breastfeeding be maintained? I really don't want to give up feeding.
If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then you will be able to supplement your baby’s breastfeeding until the birth itself and continue breastfeeding after it. There are no restrictions. The main thing is that your health and the health of your children are not at risk.
Breastfeeding during pregnancy
It happens that a mother finds out about a new pregnancy at a time when the previous baby has not yet weaned. The first question that usually arises in connection with this situation is what to do? Should I continue breastfeeding or should I stop? And if not completed, will breastfeeding harm the pregnancy or unborn child? What can you expect in this situation? We will try to answer the most common questions about the intricacies of breastfeeding during pregnancy in this article.
First, let's try to understand what the chances of getting pregnant while breastfeeding actually are? There are many myths in this area, in particular that breastfeeding always protects the mother from another pregnancy. In fact, research shows that the risk of pregnancy during the first six months of a baby's life when exclusively breastfed on demand is indeed extremely low. [8] The key points here are “the first six months” and “exclusive breastfeeding”, as well as the fact that the mother has not yet returned to menstruation. In this case, the risk of a new pregnancy is about 2%. [2]
If at least one of the conditions is not met - for example, the child is already more than six months old, or he is receiving supplementary feeding or complementary feeding, or menstruation has already resumed - the mother will have to think about other methods of family planning. Suitable methods of contraception for nursing mothers are all non-hormonal methods (condoms, caps, spermicides), as well as non-combined oral contraceptives (mini-pills). Of course, a woman should choose the method of contraception together with her gynecologist.
According to statistics, more than 50% of women around the world still become pregnant while breastfeeding. [4] Upon learning that she is expecting a baby again, a mother usually experiences mixed feelings. Few people plan in advance to combine pregnancy with breastfeeding or initially plan to feed both a newborn and an older child after childbirth. This situation may seem unusual or unacceptable for the society in which the mother lives.
Regardless of whether her environment insists on urgent weaning of the older child or, conversely, on continuing to feed him, first of all, the mother must understand her own feelings about this and make a decision, listening to her heart.
A mother who chooses to continue breastfeeding may potentially face criticism from her family, friends, and health care professionals. Advice from doctors to wean a baby during pregnancy, even in the absence of signs of risk to the mother and fetus, is especially common in developed countries. [4]
When considering the possibility of continuing breastfeeding during pregnancy, factors such as a woman's history of premature birth or repeated spontaneous miscarriages, cervical incompetence, current multiple pregnancies and other risk factors for preterm birth should be taken into account. If such factors are present, then the woman needs to carefully weigh the pros and cons and listen to the opinion of her doctor.
That said, the American Academy of Family Physicians states that “breastfeeding during the next pregnancy is not uncommon. If the pregnancy is progressing normally and the mother is healthy, then breastfeeding during pregnancy is the mother’s choice.” [3]
The national strategy for feeding children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation includes a similar opinion: “Breastfeeding during a new pregnancy can continue.” [1]
It is reasonable to assume that a well-nourished woman will have no difficulty meeting the energy needs of both her unborn baby and a child over one year of age. Therefore, a mother who continues to breastfeed during pregnancy will need a nutritious diet, as well as additional vitamin complexes on the advice of a doctor. One study [6] notes that the majority of pregnant nursing mothers rated their general health and, subsequently, the health of their newborn babies as good.
During breastfeeding, a pregnant woman may experience uterine contractions, which are a normal part of pregnancy. Stimulation of the nipples causes the secretion of small amounts of the hormone oxytocin, which in turn can cause contractions of the uterus and alveoli in the mammary glands. The same uterine contractions occur during sexual activity, which most couples do not stop during pregnancy. As a rule, such contractions do not pose a danger to the baby in the womb and do not increase the risk of premature birth. [5]
Often mothers also worry about hormonal changes in the body; will pregnancy hormones harm the nursing baby? There is no reason to worry; the hormones that accompany pregnancy are found in breast milk in very small quantities and are not dangerous for the baby. The baby in the womb is exposed to these same hormones at much higher levels. [5]
What, besides medical aspects and contraindications, do mothers usually focus on when deciding to continue breastfeeding? Important circumstances that may influence such a decision usually include: [5]
- age of the infant;
- the child’s physical and psychological need for attachments;
- the presence of any discomfort associated with breastfeeding (for example, sore nipples), and the degree of this discomfort;
- The opinion of the baby's father and relatives about feeding during pregnancy.
Many mothers say that the main motivation for continuing breastfeeding during pregnancy is the emotional need of their babies to latch on to the breast and confidence in the possibility of self-weaning.
When making a decision, a mother should know that many infants are weaned before the birth of their little brother or sister. According to two different studies, the incidence of such weaning is 57% [6] and 69% [7]. This happens, apparently, due to a decrease in milk volume, a change in its taste and/or due to the fact that the mother creates all the conditions, pushing the baby to complete breastfeeding. The child can wean from the breast without any special actions on the part of the mother, or, for example, if the mother gives the breast only at his request, but does not offer it herself, as happened before. In addition, after 9 months, a baby may simply outgrow his need for breastfeeding naturally, regardless of factors associated with the pregnancy itself.
In any case, if a mother chooses to continue breastfeeding, she should understand that her and her baby's comfort level during breastfeeding can change unpredictably as the pregnancy progresses. Flexibility and sensitivity to your baby's and your changing needs are key to making the experience of combining breastfeeding and pregnancy a positive one.
What are the features of breastfeeding during a new pregnancy? Often mothers who have gone through this note: [4]
- Nipple tenderness and breast tenderness. Hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy can cause sudden attacks of pain in the nipples or breasts, and conventional remedies for this pain or correction of attachment are often ineffective;
- Fatigue and fatigue. Early pregnancy hormones often make women sleepy, although it can be difficult for moms of runners to find time to nap. Fatigue in this case is associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy, and not with continued breastfeeding, and will decrease as pregnancy progresses. A pregnant woman with a small child (no matter whether he is breastfeeding or no longer) needs to have time to rest at those moments when the child is sleeping;
- Reduced number of feedings and milk production. About 70% of mothers say that their milk supply decreased during subsequent pregnancies. By the time a new pregnancy occurs, most children do not nurse nearly as often as they did in infancy. As pregnancy progresses, milk supply usually decreases. Sometimes children are weaned during this period. If a breastfed baby can already speak, he may complain that “the milk is gone” or “it is coming too slowly”;
- Changes in the taste of milk. As pregnancy hormones begin to affect the glandular tissue of the breast, the amount of lactose in the milk decreases and the amount of sodium increases, changing the taste of the milk. “Talking babies” can quite clearly explain what milk tastes like, or simply show with gestures that it is not the same as it was before;
- Uterine contractions. Women may feel uterine contractions while breastfeeding. However, there is no documented risk to the mother or fetus from the fact that the mother continues to breastfeed during a healthy, normal pregnancy, not complicated by the threat of premature birth. [6] However, if the contractions become painful or regular, you should consult a doctor immediately!
- Difficulty choosing a position for feeding. In the last stages of pregnancy, the mother’s belly may be so large that it becomes difficult for the baby to reach the breast. In this case, you can experiment with feeding the baby in a wide variety of positions. If an older baby is determined to continue to breastfeed, then he can certainly find a way to do this.
To summarize our review, it should be noted that if a mother chooses to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy, then two options await her further. In the first option, this is the end of breastfeeding, which (in the absence of medical or other contraindications) most often occurs closer to the end of pregnancy, and in the second option, this is tandem breastfeeding, that is, a newborn and an older baby at the same time. You can learn about how such feeding can be organized and what the peculiarities of this process are in our following articles on this topic.
Call a consultant Do you have any questions? +7 (812) 956-3-954
Literature:
- Borovik T.E., Ladodo K.S., Yatsyk G.V., Skvortsova V.A., Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Kon I.Ya., State Scientific Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences , National Strategy for Feeding Children of the First Year life in the Russian Federation. Natural feeding // Pediatrician practice, Baby nutrition. March, 2008
- Breastfeeding counselling: training course , WHO, Secretariat, Diarrheal and Acute Respiratory Disease Control Unit, Geneva, 1993.
- American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) . Position Statement on Breastfeeding 2002. Leawood, Kansas; American Academy of Family Physicians, 2002.
- Breastfeeding and Human Lactation (Jones and Bartlett Series in Breastfeeding/Human Lactation) by Jan Riordan Publisher: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 3rd Edition, 2004. Pages: 819.
- Mohrbacher N., Stock J., La Leche League International, The Breastfeeding Answer Book, Third Revised Edition, 2008.
- Moscone SR, Moore MJ Breastfeeding during pregnancy. J Hum Lact 9:83–88, 1993.
- Newton, N. and Theotokatos, M. Breastfeeding during pregnancy in 503 women: does a psychological weaning mechanism exist in humans? Emotion & Reprod 1979, 20B:845-49.
- Wijden C, Kleijen J, Berk T. Lactational amenorrhea for family planning. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD001329, 2003.
Alena Lukyanchuk, psychologist, lactation consultant, member of ILCA (The International Lactation Consultant Association)
Alena Korotkova, clinical psychologist, lactation consultant
Pregnancy and breastfeeding at the same time: contraindications
The maternal instinct is the strongest in women, therefore during pregnancy and pregnancy it maximally mobilizes the physiological and material resources of the body for children. As a result, individual organs may not be able to cope with increased loads, which will ultimately lead to pathologies. The progression of diseases can force a choice between the life of the mother and the supply of nutrients to two children at the same time.

Conditions that require weaning a baby from a pregnant woman's breast include:
- Toxicosis, accompanied by frequent vomiting, loss of consciousness and the need for hospitalization. Sometimes the baby may experience the same symptoms as the mother.
- Weight loss with proper nutrition.
- Nervous breakdowns due to chronic fatigue.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- A history of miscarriage or threatened miscarriage.
- Weakness of the cervix and other pathologies that can lead to miscarriage.
- An increase in the level of oxytocin in the blood, threatening to provoke premature labor.
- Continuous drop in maternal hemoglobin levels.

Pashkova Alla Valerievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences.
Ask a Question
If voluntary termination of breastfeeding is within the competence of the mother, then weaning for medical reasons is the responsibility of the doctor. At the slightest threat to the health of the fetus, he must convince the woman of the need to stop breastfeeding.
Pregnancy while breastfeeding
Lactational amenoria is a postpartum condition of the female body in which ovulation is suppressed and menstruation is absent. This is a natural and quite effective contraceptive that reduces the risk of a new pregnancy to 1-2%. However, the natural method only works if certain feeding rules are followed:
- Frequent breastfeeding. The baby should be fed once every two hours and at least four times at night;
- Position your baby correctly. It is important that when feeding he captures both the nipple and areola. Proper attachment of the baby is the key to successful lactation, good health of mother and baby, and complete nutrition of the baby;
- Feed your baby according to requirements, not according to a schedule;
- Feed your baby until he is full. When the baby is full, he releases the nipple on his own. Do not limit the time of attachment and do not interrupt feeding;
- Do not over-feed or over-hydrate your baby for at least the first six months. Breast milk contains all the necessary elements and vitamins for the full growth and development of the baby;
- The first complementary foods can be introduced at 5-7 months.
Tips from the article about ideal food for a newborn will help you establish breastfeeding.
Please note that the lactational amenorrhea method only works in the first six months after birth and provided that the baby is fed only breast milk. After six months, milk production begins to decline, and mothers begin to introduce the first complementary foods. This dramatically increases the risk of pregnancy, even in the absence of menstruation. When your period comes after childbirth, read here.
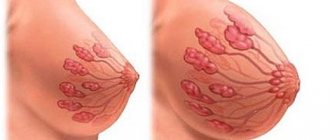
Does a nursing mother lose milk during pregnancy?
At month 5, uterine myocytes begin to respond to oxytocin, released into the blood during breastfeeding. From this period the risk of premature birth begins to increase. Therefore, this period is considered optimal for starting to quit breastfeeding.
Also, after the 20th week of pregnancy, the amount of milk in a nursing woman begins to decrease. Then its taste and structure of the main components change. These factors must be used to start weaning the baby from the breast, if such a decision has been made. It is advisable to completely complete breastfeeding if there are medical risks by the end of the 7th month of pregnancy.
If no measures are taken to limit breastfeeding, milk will continue to be produced, and after childbirth, its quantity will even increase.
Doctor's advice
Some women mistakenly believe that while they are breastfeeding, they will not be able to get pregnant again. However, the risk of unplanned reconception increases when the baby is 6 months old, even if lactation continues. Doctors recommend that if a couple does not plan to give birth to a child, use contraception throughout the entire feeding of the baby with breast milk.
If conception does occur, it is worth assessing the resources of your body, on which the load will increase. A doctor observing the pregnancy will help you make the right decision in this situation. If any disturbances are recorded during pregnancy, and the woman does not feel very well, it is better to switch the child to formula, especially if he is already six months old and can use complementary foods.
Feasibility of tandems
Not every pregnancy is worth setting up for tandem feeding, as situations vary. The age of the child at the time of the new pregnancy is key.
If pregnancy occurs when the older child is six months to a year old, then it is worth continuing to fully breastfeed the older child while carrying the younger one and taking full care of your health. When the second child is born, the eldest will not be so old, about one and a half years old, and he will still very much need breast milk and breastfeeding for psychological comfort.
If pregnancy occurs when you have a baby at the age of one and a half years, then during pregnancy you will have time to gently prepare the baby for weaning and stop feeding by the time of birth. It is also possible that there will be a chance to feed the eldest after the birth of the youngest for just a couple of months and gradually reduce his feeding in favor of the youngest.
Each specific situation has its own way out, but what you shouldn’t do is force things with the elder (excommunicate abruptly and quickly) for the sake of a new pregnancy.
At the same time, you should not specifically plan the birth of the same age and tandem feeding. This is too much stress on a woman’s body, it is physically difficult, but the choice is always up to the woman herself.
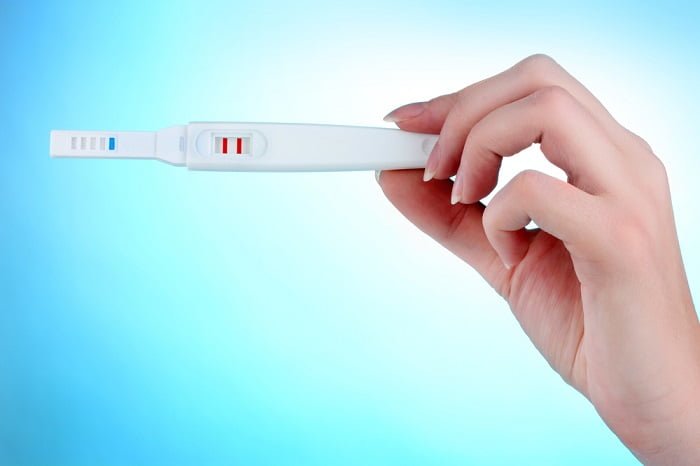
Signs of pregnancy during lactation
- The baby's behavior has changed. The baby does not want to breastfeed and has become capricious. Most often, the reason for this behavior is a change in the composition and taste of milk. Milk is affected not only by the nutrition of the nursing mother, but also by a new pregnancy;
- Decreased lactation for no apparent reason;
- Pain in the chest and nipples;
- Delayed menstrual cycle if menstruation has already returned;
- Manifestation of toxicosis, vomiting and nausea, general malaise and fatigue, low blood pressure.
A nursing mother is pregnant - possible health consequences
If a nursing mother becomes pregnant, this usually happens six months after giving birth. Despite the significant period, this is sometimes not enough to fully restore the body from stress, which is usually the period of pregnancy and childbirth for a woman’s body.
According to many doctors, pregnancy occurring within the first two years after birth increases the risk of developing many complications, among which the most common are an increased risk of miscarriages, the development of severe anemia, postpartum complications, and placental insufficiency.
However, if a nursing mother is pregnant, this is not a reason to think about an abortion. In addition to psychological stress, abortion can also have quite strong negative consequences for a woman's health.
To avoid such problems, as soon as the first worries associated with the birth of a baby subside, you should select adequate contraceptive methods that can provide reliable protection for the young mother.
Pregnancy and lactation: should you combine them?
Many doctors recommend stopping breastfeeding immediately. However, such a drastic method is not justified and can harm a nursing baby. Breastfeeding does not affect pregnancy and does not cause premature birth. The hormone that is produced during lactation has no effect on the functioning of the uterus.
In the first year of a baby's life, you can continue breastfeeding. However, after a year, feeding should be stopped. Therefore, as soon as you find out about pregnancy, start introducing complementary foods so that the transition to regular food goes smoothly.
If you decide to continue breastfeeding, be sure to monitor your well-being and pregnancy progress. For any deviations, be sure to consult your doctor. It is necessary to stop breastfeeding during pregnancy in the following cases:
- Two to three months before giving birth. During this period, the uterus becomes sensitive, and the volume of breast milk decreases sharply;
- With severe toxicosis and increased uterine tone;
- When the first baby turns one year old;
- Severe chest pain.
If a nursing mother decides to stop breastfeeding prematurely, she should be prepared for the problem of excess milk accumulating in the mammary glands. Stagnation leads to lactostasis, and then to mastitis. Therefore, it is important to complete lactation correctly. Read how to do this here.

Are there enough nutrients for two?
Another important question when combining pregnancy and breastfeeding is the following: will the fetus have enough necessary substances for full development, and at the same time, will there be enough good, high-quality milk for the older baby? But there is also your own body, which needs to recover after the first birth and fully endure a new pregnancy that occurs during breastfeeding.
During pregnancy, the mother's body is reconstructed to a new level of work, and the main task for it will be the formation and full development of all organs and systems of the new, born baby. Therefore, the main forces of the mother’s body will be included in the work for the full development of the fetus. This will be his priority.
The second priority task will be for the female body to produce breast milk for the child who is still being fed by the mother. He will secondarily take nutrients, microelements and vitamins from the mother’s body.
And finally, in last place will be providing your own body with everything necessary, which needs strength to feed the older one and bear a new child. All forces will be devoted to the benefit of their own children, and we can figuratively say that the work of the body will be as if a woman was carrying two children. Naturally, in such a situation, the mother’s health is not going through the best of times, and it is extremely important that the mother takes full care of her health and nutrition so that she does not need anything. The diet should be varied, containing all the necessary components, vitamins and minerals, including those additionally taken in the form of multivitamins. If a woman wants to eat, she should eat as much as she wants, there are no restrictions. She should also drink when thirsty; fluid cannot be limited while she is pregnant and breastfeeding at the same time. In this case, the phrase “eating for two” may be quite relevant - there are two kids and they consume a lot!
Carrying a baby in your arms during pregnancy
You can often hear advice not to carry heavy objects during pregnancy, so as not to harm the baby. But what to do if you have an older child who is still very small and needs his mother’s hands, including during breastfeeding? Naturally, the child needs to be in your arms and you need to take him in your arms if you feel well and the child asks to be held. But during pregnancy you need to do this not as often as before, and not for as long as you are used to. You can help yourself a little: take the child in your arms while sitting on the sofa, or involve your dad or grandmother in this. In addition, in the first months of pregnancy, while the tummy is not yet in the way, you can carry your elder in a sling or ergo-backpack. This will evenly distribute the baby’s weight over the shoulders, back, and lower back, and make life easier for the mother. When the tummy grows, you can put the older one on your hip. You can replace mom's hands with games on the sofa and sitting on her lap when she is sitting, games on the floor on the rug, and you can rock the baby to sleep while sitting or even lying down, using a stroller and other devices.