Mother's milk is an ideal food for a child in the first year of life, which helps the baby develop properly and increases the body's defenses. Unless absolutely necessary, you should not give up breastfeeding, but for various reasons, breast milk production may noticeably decrease or disappear completely.
Restoration of lactation is possible even after a long break from breastfeeding. To achieve success, it is important to follow the rules and be patient if the process threatens to drag on.
It is important to understand that the percentage of “non-dairy” women, who naturally have an extremely low ability to lactation, is quite small, so it is worth fighting to feed the baby with your milk.
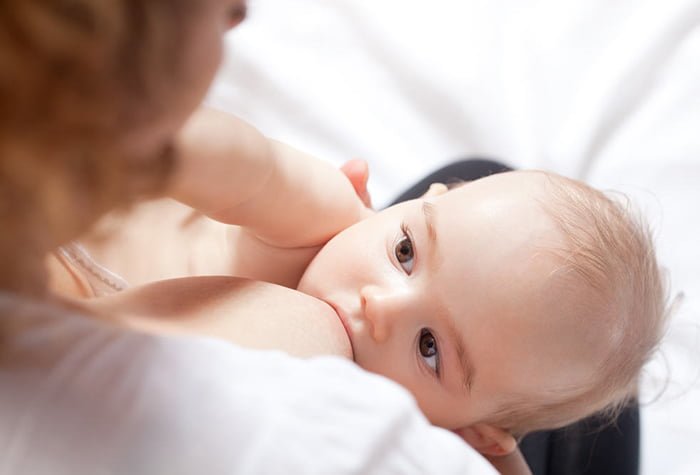

Reasons for decreased lactation
The decline of lactation occurs for various reasons, including those related to the health of the mother or child. First of all, it is necessary to understand what prompted the deterioration or cessation of milk production and, if possible, eliminate the causes of decreased lactation.
Restoration of lactation is required in the following cases:
- lactation crisis;
- a break in breastfeeding for medical or other reasons;
- improperly organized breastfeeding;
- loss of milk due to overwork or stress;
- low milk production due to the child’s poor appetite.
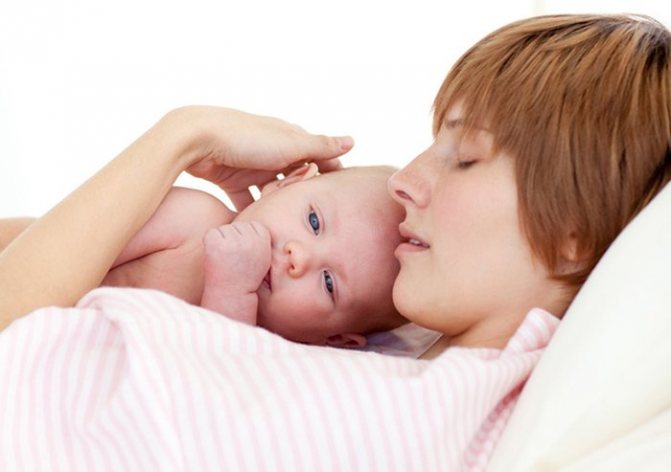

How to resume lactation after a forced pause due to illness of the mother or baby
Young parents have to face various problems regarding the upbringing and development of their child. During the first year of a baby’s life, the main question remains breastfeeding – whether he receives enough mother’s milk to fully develop.
But in life all sorts of unforeseen circumstances can arise. Sometimes, at the insistence of doctors, you have to give up breastfeeding due to the health of the young mother or the baby itself.
Lactation experts advise not to panic in such a situation. When a woman wants to continue breastfeeding after some time, certain measures are required to help maintain lactation.
Lactation crisis
Breast milk production may decrease markedly from time to time. The reason is hormonal changes in the mother’s body, including the restoration of the menstrual cycle, sudden growth spurts in the baby associated with an increase in the need for food.
The duration of the crisis does not exceed two to three days if it is monitored and milk production is additionally stimulated.
During a lactation crisis, do not be nervous and switch your baby to formula. It is enough to drink more warm water, massage your breasts and put your baby to it more often. Breast milk volumes are restored within three days, after which feeding can be continued as usual.

The Burnout Myth
A common misconception when milk production decreases is that it has “burned out.” From a physiological point of view, this term has nothing to do with lactation. When the breast remains full for a long time, some of the milk is absorbed back into the blood. Under no circumstances do processes occur in a woman’s body that could be associated with this word.
Sometimes, deciding that the milk has suddenly disappeared, women stop breastfeeding their baby as usual. Instead, they try to pump, measure the volume of fluid received, worry and begin to think about introducing supplementary feeding.

Break from breastfeeding
Stopping breastfeeding may be necessary for medical reasons, which include the recovery period after breast surgery, or taking medications that are unsafe for the child.
Breastfeeding is interrupted for some time and when mother and baby are separated. The cause is illness of the child or mother, or the mother’s high employment. The baby can receive expressed milk, but lactation decreases due to insufficient stimulation of the mammary glands, which requires further restoration of breastfeeding after a forced break.
Incorrect organization of natural feeding. Common breastfeeding mistakes that lead to the extinction of lactation include feeding the baby by the hour rather than on demand, lack of night feedings, supplementing with water, and using a pacifier.
Relactation - what is it?
Relactation is a technique for resuming lactation. It includes complex actions, the purpose of which is to organize breastfeeding after a forced pause.
Often, the reason for refusing to breastfeed a baby lies in the mother’s treatment with drugs that are prohibited during lactation.
In addition, the source of the problem may be pathologies of the mammary glands, which require immediate treatment, sometimes in a hospital setting, or other diseases that require the mother to stay in the hospital for a certain time.
How to restore lactation?
The decline or complete cessation of breast milk production is in most cases a solvable problem. Resuming natural feeding is easier the younger the child is. For a baby up to three months old, solving the problem takes 1-2 weeks; older children will have to work longer, but the result will come if you don’t give up.
A favorable psychological climate for a nursing mother and help with household chores are very important, since maximum time will be devoted to the baby. If you have any questions, it is recommended to contact a breastfeeding specialist, who is better to find in advance.
If milk has completely disappeared or is produced in insufficient quantities, the following actions should be taken:
- ensure constant physical contact with the child;
- avoid overwork and stress;
- stimulate baby's breastfeeding;
- gradually reduce supplementary feeding;
- monitor your own nutrition;
- use means to increase lactation (herbal remedies, massage, etc.).

What you need to know about tablets and teas
In an effort to establish breastfeeding as soon as possible, some mothers are ready to resort to any methods and means. Such an active position is commendable. But there are a number of tips that cannot significantly help a woman in this matter.
- Special teas for lactation. Store-bought teas labeled “to increase lactation” contain various herbal mixtures. The effect of most herbs on the body of a nursing mother and her infant has not been studied. Moreover, nettle, fennel, anise and caraway, which are often included in such mixtures, have the first (nettle) and second (other plants) level of risk for a lactating woman and her child.
- Drink plenty of fluids. You can often hear that mothers are advised to drink two to three liters of fluid a day to increase lactation. This is an unnecessary measure. You should drink according to thirst, on average a liter and a half per day. It is worth remembering what exactly affects the formation of milk. And for its production to stop due to a lack of water in a woman’s body, she must have a severe stage of dehydration.
- Pills . They also include plants and herbs whose effects have not been studied in nursing mothers. Some components may cause individual intolerance or an allergic reaction. Their use in isolation from the basic recommendations for increasing lactation will not bring results.
If a nursing mother is faced with a decrease in milk production, she has the power to resume this process. This statement is true for any age of the baby. If you clearly and diligently follow the advice on how to restore lactation after a break or other circumstances, in a few weeks the mother will be able to again enjoy the harmonious process of breastfeeding.
Body contact and psychological comfort
In order to restore lactation as quickly as possible, mother and baby need to be together around the clock. Constant skin-to-skin contact helps the mother's body produce prolactin and oxytocin, hormones that promote lactation.
The baby is in the most comfortable environment, awakening instincts - this is facilitated by the warmth of the mother’s body and the smell of milk. He develops better and begins to suck more actively.
For constant physical contact, the child should spend most of his time in his mother’s arms or in a sling. Sleeping together at night with the opportunity to sit comfortably for feedings is also important. In this case, the mother will not have to regularly get up to the child, experiencing additional stress.
Household chores will have to be transferred to the husband and relatives, since milk can only be returned by completely switching to the child. It is important to avoid overwork and stress to prevent the production of hormones that interfere with lactation.

The effect of stress on lactation
The favorable course of pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding largely depends on the woman’s hormonal levels. Estrogens and progesterone are largely responsible for carefree pregnancy. Immediately after childbirth, their number drops, but the level of prolactin increases sharply. Thanks to it, even during pregnancy, a transformation of the mammary gland ducts occurs, aimed at producing milk. And after the baby appears, it is the “trigger” moment for the start of lactation.
Oxytocin also plays an important role, the formation of which increases in response to stimulation of the nipples. That is why for the first day or two the baby simply “hangs” on the chest, thus increasing the concentration of oxytocin in the blood. And the hormone is already responsible for contracting the ducts and releasing milk.
The production of all these hormones and active substances is regulated by the pituitary gland of the brain. And then the dominant “breastfeeding” is created, all processes in the body are aimed precisely at this.
Stress, worries, fear and any other situations, usually of a negative nature, lead to the activation of the body's defenses.
At the same time, adrenaline begins to intensively form and enter the blood. It stimulates an increase in blood pressure, causes spasm of blood vessels and smooth muscles of the intestines, and promotes the formation of another dominant in the brain - “how to solve the problem.”
As a result, the intensity of all processes associated with lactation (and most of the mother’s strength and energy is allocated to them) drops sharply. And this leads to a decrease in milk production, and if nothing is done, in ongoing stressful situations, lactation will stop altogether. The likelihood of lactostasis and mastitis also increases due to uneven contraction of the ducts and disruption of the outflow of secretions.
So, the following points are necessary for normal breast milk production:
- Relaxing and carefree atmosphere in the house and maximum limitation of household chores. In such situations, the woman’s body is completely concentrated on the process of lactation.
- Mechanical nipple stimulation. The more intensively this happens, the better the ducts of the mammary glands contract, and all the milk comes out to the last drop. And empty breasts are a signal for greater milk production.
Adrenaline, figuratively speaking, counteracts these processes, redirecting the body’s work in a different direction. This is why stress during breastfeeding leads to a decrease in milk production.
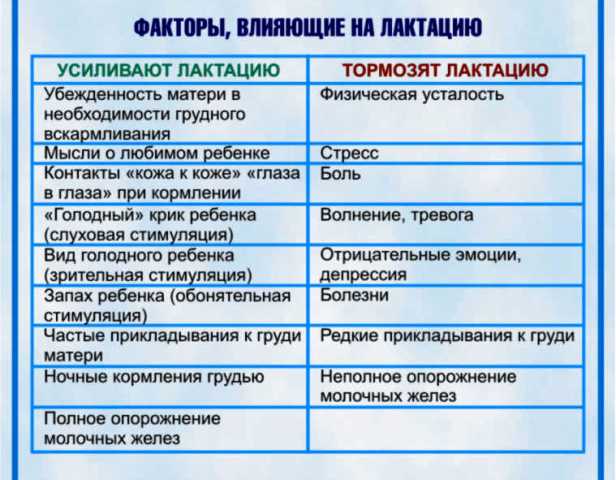
Stimulation of breast milk production
The main assistant in restoring lactation is the baby himself, since he is the one who regulates milk production. The more actively the baby suckles, the more intensely the hormone prolactin is produced.
If your baby is offered the breast frequently, he will eventually learn to suckle. It is necessary to put the baby to the breast without waiting for his desire; it is important that the baby satisfies not only hunger, but also the sucking reflex.
To restore lactation, you must stop using pacifiers and bottles with nipples for supplementary feeding. Sucking soft rubber does not require effort from the baby, and babies often make a choice not in favor of the mother's breast, from which it is much more difficult to obtain food.
If you do not use a pacifier to supplement formula or expressed breast milk, the baby will quickly learn to extract milk from the mother's breast. It is recommended to supplement the baby's feeding using a soft spoon or a special supplementary feeding system (more about it below).
If little milk is produced, but even then the baby does not completely empty the breast, it is necessary to express regularly - at least 8 times a day. Manual expression is not always effective, especially without the proper skill, so it is recommended to purchase a breast pump.
It is important to monitor the condition of the nipples - if cracks occur, you will have to take a break during the process of restoring natural feeding.

What is prohibited during relactation
During the relactation process, you must adhere to some rules:
- There is no need to worry or panic or assume that reintroducing breastfeeding is impossible. You need to be optimistic and not be afraid to seek the help of specialists; they will be able to tell you how to improve lactation.
- You should not check your baby's weight more than once a week. According to standards, a child should gain approximately 125 g in a week.
- If possible, during the first weeks of resuming breastfeeding, do not leave your home, but stay close to the baby all the time.
According to experts, the positive result is largely due to how psychologically the mother is ready for relactation, and how strong her desire is to feed the baby with breast milk.
For this reason, before starting the procedure to resume lactation, you should make sure that you really want to continue breastfeeding and you are not afraid of temporary physical and psychological problems that may arise.
Reducing supplementary feeding
When restoring lactation after milk has disappeared, you should not suddenly give up the formula that the child was fed during the break in breastfeeding. Supplementary feeding is removed gradually, according to the “breast - supplementary feeding - breast” scheme: each feeding should begin and end with attachment to the breast.
The supplementary feeding device is a container with a soft thin tube, the end of which is attached to the breast - the baby grabs it along with the mother's nipple, getting used to sucking the breast. The container itself with the mixture is hung on a cord around the mother’s neck.
If supplementary feeding is sharply reduced, the child will develop a deficiency of substances that promote growth and proper development. At the same time, the baby must steadily increase the consumption of breast milk, not only fore milk, rich in lactose, vitamins and microelements, but also hind milk, containing fats and lactase.

Mother's diet
Nutrition should be of high quality, and fluids should be consumed in large quantities, not forcing yourself, but also not leading to a feeling of thirst. In addition, the diet must necessarily contain products for lactation of a nursing mother.
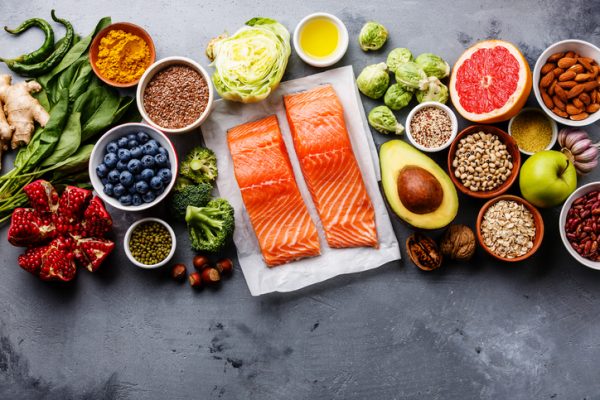

To improve breast milk production, a young mother is recommended to consume:
- warm tea;
- caraway seeds and bread with caraway seeds;
- dried fruit compote;
- clean water;
- nuts;
- dill tea;
- herbal tea;
- nut milk;
- low-fat meat soups and broths;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- hard cheese, Adyghe cheese, feta cheese;
- fermented milk products;
- barley decoction or barley coffee;
- radishes with honey;
- tea to increase lactation with ginger;
- Hercules;
- buckwheat, etc.
Causes of stress in a baby
Despite the fact that a child up to a certain age cannot tell or somehow show his reaction to what is happening, he “absorbs” his mother’s mood. Her facial expression, gestures, tone - all this can bother the baby, which puts him in a state of stress. After all, a calm mother for him is the key to safety and reliability.
The first three months of a baby’s life are the most difficult, sometimes called the “fourth trimester of pregnancy.” Breastfed children form a special relationship with their mother; they are strongly attached to her, and only when they are nearby do they feel calm. At this time, even minor changes for adults can cause stress in the baby. The main causes of discomfort in a baby can be identified:
- Reducing attention to him. The mother may be either busy with other things due to family circumstances, or has not yet learned to respond so quickly to the child’s needs.
- Newfangled movements like baby yoga and swimming for infants are not suitable for all children. The choice of the type of activity and the decision to practice it should be approached with special care, weighing all the pros and cons. Inept movements or inexperienced instructors can even lead to injury or fright.
- Large flow of information. In many families, it is customary to visit the young mother and baby after birth. However, regular guests, noise, unfamiliar voices and the disrupted rhythm of the day - the baby perceives all this more sensitively. What can we say about this little man, if adults themselves sometimes get tired of such celebrations?
- If something is bothering your baby, it is better to seek help from a pediatrician. You should not use gas tubes on your own, even stool suppositories unless indicated. Some parents, if their children are not gaining weight well, start weighing them almost after every feeding. This is also stressful for the baby, in addition to the fact that the child takes on the restless state of the parents.










