In the first stages of the disease, feeding milk will not harm the baby, and will help the mother recover faster - because Stagnation of milk during mastitis contributes to the proliferation of infection and only intensifies the inflammatory process. Treatment of diseases should begin immediately so as not to trigger the disease. In the final stages, the milk will change its composition and may harm the baby.
It is important to know! In mothers whose baby sucks almost all the milk from the breast, lactostasis does not occur.
In addition, the temperature may rise due to common illnesses. Such as:
- colds;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- poisoning.
If a nursing mother's body temperature rises and does not decrease between feedings, treatment must be started (you should contact your local doctor and undergo an examination). In some cases, you need to stop feeding your baby. Also, breastfeeding can be harmful if the mother has a very high temperature and needs to be lowered.
High temperature in the mother: Komarovsky’s opinion, how to treat it and whether it is possible to breastfeed the baby
An elevated body temperature indicates that the immune system has begun an active fight against disease, infections, and bacteria.
Many girls want to know whether it is possible to breastfeed at high temperatures, and whether this will affect the baby.
If such a symptom occurs in the first month after the birth of a child, then there is a possibility of complications developing.
An elevated body temperature of up to 38 degrees often indicates an inflammatory process in the scars or genitourinary system.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to objectively assess the condition of the nursing mother and the advisability of maintaining lactation.
Is it possible to feed a baby while sick?
Another question that concerns a nursing mother is whether it is possible to feed the baby breast milk. Doctors recommend not to stop breastfeeding.
After all, along with milk, the baby receives useful elements and protective substances. Thanks to milk, the baby will not get infected.
Also, to keep your newborn safe, wear a gauze bandage or mask.
Research also shows that high temperature
does not affect the taste and quality of milk
. Under no circumstances should milk be boiled. This treatment kills protective antibodies.
Is it possible to breastfeed a baby if the mother has a high fever?
There is no clear answer to this question for women. If your body temperature rises sharply, it cannot be reduced with the usual pills. They may be contraindicated during feeding.

After receiving the results of the examination and diagnosis, he will be able to prescribe a drug. They may be compatible with breastfeeding or completely contraindicated.
Sometimes a nursing mother's breast milk may contain a large number of pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
In such a situation, the baby is transferred to formula milk. But first you need to consult with your pediatrician and inform him.
Thanks to such measures, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of diarrhea in the baby, as well as the penetration of microbes into the child’s body through breast milk.
Its amount can decrease significantly because the mother's body gradually weakens.
Fever affects not only quantity, but also quality. If you consult a doctor, he will give recommendations on how to maintain lactation.
If there are no contraindications, then antibodies will enter the child’s body. Mothers need to wear a bandage to prevent bacteria and infections from coming into contact with their baby.
If this disease progresses, you should consult your doctor. He will evaluate the form of the disease, as well as drugs that are approved for use during lactation.
How to relieve a fever: Komarovsky’s opinion
Also, a well-known pediatrician notes that Paracetamol can be alternated with Ibuprofen
.
Temperature does not affect the quality of breast milk and does not force the baby to refuse the mother’s breast, and modern medications can alleviate the mother’s condition even in such a difficult period. A woman will protect both herself and her child from more serious problems if she is as attentive as possible to her health, listening to the recommendations of specialists. Be healthy!
How can you lower a nursing mother's temperature?
Before lowering the temperature, you need to measure it correctly. It is best to hold the thermometer in the crook of your elbow.
This is due to the fact that when milk stagnates in the breast, the skin temperature may increase and the readings will be inaccurate.

The temperature begins to drop when it rises above 38.5. In other cases, treatment is not recommended so that the body can fight viruses and bacteria on its own. To help him, you can drink tea with lemon or raspberries.
There are other ways that will help quickly reduce the body temperature of a nursing mother:
| Way | Description |
| Medicines based on paracetamol, ibuprofen | You can also take children's Nurofen, but calculate the dosage correctly and do not exceed the norm. |
Numerous studies have confirmed that these medications are completely safe for children and can be taken during lactation.
These medications are sold in the form of rectal suppositories, so the chemical components will not pass into breast milk.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion on the temperature of a nursing mother
Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky is a pediatrician and a candidate of medical sciences. He argues that every mother should be interested in maintaining breastfeeding.
For this reason, it is important to correctly identify the disease and the cause that contributes to the increase in body temperature.

They can only be used when necessary. Adjustment of medication intake is required. It is better to take Paracetamol and Ibuprofen after breastfeeding.
The next time a young mother feeds her baby, the amount of chemicals in the milk will be minimal.
Due to illness, you should not adjust or change your baby’s feeding schedule. If your body temperature does not decrease, you can take the medicine again.
Useful video
Source
“Should I feed at night?”
Komarovsky claims that if the child is gaining weight well, then there is no need to wake him up for night feeding. From birth, children can easily withstand a night feeding break for 4-5 hours, and from three months - 5-6 hours.
It’s another matter if the baby wakes up at night and demands food. In this case, there is no need to refuse him.
Everything changes when the baby is six months old. At this age, Komarovsky believes, the toddler physiologically no longer needs a night meal, and therefore he can be gradually weaned from the habit of eating in the middle of the night. To do this, according to the doctor, you need to have a late bath (at 10-11 p.m.), then feed the child tightly and put him in a well-ventilated room, where it is not stuffy and not hot (the air temperature is about 19 degrees).
If, after six months, the baby is indulged in his desire to wake up in the middle of the night and scream until breastfeeding, then, according to Komarovsky, you can achieve the opposite effect - the child will begin to suffer from overeating, wake up and cry no longer from hunger, but from gluttony, from pain in the stomach, distension. The mother, of course, immediately offers the crying baby the breast, he will take it to calm down, the result will be a vicious circle that will not lead to anything good.
Evgeniy Olegovich also reminds mothers that not every child’s awakening at night is caused by hunger. Before giving him the breast, you need to figure out whether the baby is experiencing discomfort - is he dry, is he comfortable in the crib, is it hot. Perhaps it is not necessary to feed him this time.
And here is Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on how long breastfeeding should be maintained.
Elevated temperature during breastfeeding in the mother: is it necessary to bring it down and is it possible to feed?
During the entire period of breastfeeding, almost every woman experiences noticeable discomfort at least once. Often - with a rise in temperature. What an elevated temperature in a nursing mother may indicate, how it can be normalized, and whether it is worth urgently switching the baby to formula - we will talk about this further.
Causes of mother's temperature during breastfeeding
They may be different. Most often, the mother’s temperature during breastfeeding indicates:
In addition, if an increase in the body temperature of a nursing mother occurs in the first few days or weeks after childbirth, we may be talking about inflammatory processes in the uterus or other gynecological diseases.
In order to correctly determine why a nursing mother has a fever, and to develop tactics for further treatment and feeding, it is necessary to consult a doctor. It is advisable to call him at home so as not to aggravate your condition by visiting the clinic.
Is it necessary to wean a child from the breast if the mother has a fever and breastfeeding?
Contrary to popular belief, it is not always advisable to do this. For example, if a woman simply has a cold, she should continue to feed: during this period, her body produces specific antibodies, which, entering the baby’s body with milk, take an active part in the formation of its immunity. Of course, if a nursing mother has a fever due to an acute respiratory infection or acute respiratory viral infection, she should take precautions during contact with her baby: wash your hands thoroughly and wear a disposable mask.
With lactostasis and mastitis, feeding is even more indicated - it will reduce milk stagnation and alleviate the general condition. But if the temperature during mastitis in a nursing mother is accompanied by purulent discharge from the mammary gland, the process should be temporarily stopped, transferring the child to formula until the pathology is completely eliminated. At this time, the woman is strongly recommended to express milk.
It makes sense to interrupt feeding in case of acute intestinal infection - there is a possibility that pathogenic bacteria can enter the baby’s body along with the milk.
In all other cases, it is quite possible to breastfeed if the mother has a fever. True, several points should be taken into account here: the drugs used for treatment should not affect the quality and composition of breast milk.
In this context, a reasonable question arises: what about antibiotics? Will they cause resistance in the child? To avoid the risk and at the same time not stop feeding, you should, firstly, consult a doctor, and secondly, carefully study the instructions. If the drug withdrawal period is, for example, 6 hours, then after this time, before taking the next dose, it is quite possible to feed the child. Or express the milk and use it in one of the subsequent feedings.
How to measure temperature correctly?
There is no need to panic if a nursing mother's temperature is 37.2 or so. There may be several reasons for its rise:
To avoid this, you need to know how to correctly measure the temperature of a nursing mother. This should be done 15-20 minutes after finishing the child’s meal, after wiping the place where the thermometer will be placed with a cool, damp cloth.
It is important to eliminate sweat from the measurement area - it can, on the contrary, reduce the values, since, like any liquid, it can absorb heat. By the way, it is measurement in conditions of a sweaty body, and not overwork, as is commonly believed, that is one of the common causes of low temperature in a nursing mother.
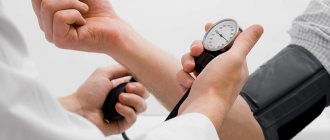
Traditionally, most people measure their temperature in the armpits. However, doctors say that this is not the best place to obtain objective information about your health. Therefore, we, together with specialists, recommend measuring the temperature of a nursing mother in the elbow crease. This will reduce the likelihood of error to a minimum.
How to measure correctly
Body temperature is measured in the armpit. The safest way to do this is with a modern electronic thermometer, which should be held for some time after the beep to be sure. It is better to watch the screen and take it out only when the mark stops changing. This indicator will be more reliable.

If you suspect that it is the breasts that are causing the elevated temperature due to active milk production, you can check yourself as follows. Measure the temperature at the elbow while squeezing your hand tightly.
This is exactly the method that was used in the department of postpartum complications, which I visited after my first birth. If the temperature is not due to the chest, then it “rises” in the elbow bend.
Reducing a mother’s temperature during breastfeeding to normal: choosing remedies
However, imagine that all the conditions are met, and the thermometer shows a high temperature in the nursing mother: how to bring it down and when should it be done?
The values at which the temperature needs correction are the same for mothers undergoing breastfeeding as for all other people. Indicators below 38-38.5 degrees do not need any intervention: it is advisable to give the body the opportunity to deal with the virus, infection or other pathology on its own.
If a nursing mother's temperature is above 39, urgent measures are necessary. Here's what doctors recommend doing in this case:
Finally, some useful advice: sometimes a nursing mother has a high temperature without symptoms. This can be either a consequence of overwork or a dangerous sign. The fact is that hormonal changes that occur as a result of pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding often dull pain and other discomfort. That is why, in such conditions, you should always consult a doctor and, if indicated, undergo all examinations necessary to establish a diagnosis.
Source
Which doctor treats breastfeeding women?
In the case when a nursing mother is still in the early postpartum period, that is, less than 6 weeks have passed since the birth of the baby, her condition is monitored by an obstetrician-gynecologist, and, if necessary, consults with related specialists (surgeon, therapist, infectious disease specialist and pediatrician ). After 1.5-2 months of the lactation period, the woman should contact her local physician, who will coordinate a further plan of examination and assistance. In the case of a high temperature of an inflammatory nature, most likely, the nursing mother will need to stay in a hospital under the supervision of doctors and take antibacterial therapy, which is an indication for interrupting lactation and temporarily transferring the child to adapted milk formulas.
Why can the temperature rise during lactation?
When the postpartum period (6 weeks) is over, some diseases are added to the causes of fever. Among them:
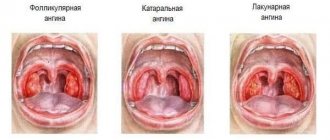
Acute respiratory diseases do not occur so often during lactation. Infection can occur from any family member living in the same house as the nursing mother. Everyone knows the symptoms of this disease very well - loss of energy, nasal congestion and snot, sneezing, sore throat (see also: how to treat a nursing mother’s throat while breastfeeding if it hurts?). The temperature rises above 38 degrees. By observing bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids and taking antipyretics, on the fifth or sixth day you can completely rid yourself of the unpleasant ailment.
Lactostasis is a violation of the outflow of milk in the mammary glands. The milk duct becomes clogged, swelling appears, followed by inflammation. Naturally, with such processes the temperature rises and pain occurs in the mammary glands, and if the problem drags on, then after 3-4 days it can be complicated by a bacterial infection and mastitis will develop with an even more serious temperature - up to 39-40 degrees. Preventing lactostasis is not very difficult. It is necessary to ensure the prevention of milk stagnation, which is achieved by frequently putting the baby to the breast, expressing the remains and massage. If there is too much milk in the breast for the baby, some mothers use a manual breast pump. True, with this method small lumps appear in the chest, but they are easily eliminated with massage.
When it comes to infectious mastitis, you will have to be treated with antibiotics, and in the most advanced cases, surgical intervention will be required.
In the case of poisoning and intestinal infection, in addition to high temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, severe headache, and severe weakness are observed (we recommend reading: what should a woman take for headaches during lactation?). Treatment requires enveloping drugs and sorbents, as well as a strict diet. You should definitely consult a doctor, since intestinal infections are very dangerous, and they should be treated during breastfeeding only under the supervision of a specialist.
Algorithm of actions at elevated temperatures
When the temperature during breastfeeding suddenly becomes higher than usual, you should not panic under any circumstances - this will aggravate the mother’s painful condition and have a worse effect on the baby.
The first thing is to determine the cause.
If you know the symptoms of all of the above diseases, determining the cause will not be particularly difficult. In any case, even when you have correctly diagnosed yourself, consult a doctor. This is important when breastfeeding, as a specialist may notice signs that escaped your attention. The help of an experienced doctor will never be superfluous.
Second - continue lactation
There is a common belief that you should not continue to breastfeed your baby if you have a fever, but there is growing evidence to the contrary. Doctor Ruth Lawrence, an expert in her field, in a methodological guide for doctors “Breastfeeding” lists diseases in which the process should not stop:
Nowadays, there are drugs that can be used by a nursing mother without harm to the baby. If breastfeeding is stopped during illness, the child will lose antibodies that are produced in the blood and pass into breast milk; and if he himself is sick, then this is even more unhelpful.
Third, measure your temperature correctly.
This is not surprising - even in the absence of illness in a nursing mother, the temperature in the armpits is slightly higher than normal - 37.1-37.3 degrees. Hyperthermia is explained by the high milk content in the mammary glands. A reliable result can be obtained only half an hour after feeding, by washing and drying the skin of the armpits well.
Fourth - use an antipyretic
Medicines that lower fever are oral (tablets, powders, syrups) and rectal (suppositories).
The only difference is the speed of action. Oral medications begin to act faster, since the stomach has a larger area of mucous membrane with which the substance interacts.
Fifth - drink plenty of fluids
It doesn’t matter whether the mother has a cold or simply has an excess of milk in her breasts; at elevated temperatures she needs to drink plenty of fluids. It is advisable to drink at least a glass of water every hour. In addition to the fact that the body will replenish lost fluid, the milk will not thicken and will flow easily - this will help normalize the temperature and reduce the risk of lactostasis.
Mom's actions at home
There is no need to immediately rush to the hospital if, while breastfeeding, the mother’s temperature rises due to a runny nose, sneezing and body aches. Mom can try to solve an increase in temperature caused by viral diseases or a cold on her own, using traditional medicine in the form of decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, lemon balm, linden and rose hips). Such decoctions contain a lot of vitamins and minerals that will help quickly restore a woman’s body and increase the amount of breast milk produced. Tea with honey and lemon can be consumed along with herbal infusions, provided that the baby is not allergic to these products.
Self-treatment consists of drinking plenty of fluids and bed rest.
It is recommended to lower the temperature only when the mercury column exceeds 37.8-38 degrees. Earlier use of antipyretic drugs can cause decreased immunity and frequent infections in the mother. To lower a high temperature, a nursing mother is allowed to take the following actions:
- take a paracetamol or nurofen tablet, taking into account the recommended dosage indicated in the annotation;
- during lactation, the temperature during breastfeeding decreases if the mother rubs a solution of vinegar in half the composition with water, starting with the feet and palms;
- put a compress with vinegar (1:1 with water) on the temples, armpits and groin area, they act on the main vessels of the woman’s body in case of a critical rise in temperature;
- severe hyperthermia is considered an indication for intramuscular injection of a lytic mixture, that is, the mother is allowed to inject 2 cubes of analgin, papaverine and 1 cube of diphenhydramine in one syringe, even at home, which will quickly and effectively reduce the temperature;
- During hyperthermia, it is not recommended to wrap yourself up or use warm compresses, mustard plasters and rubbing.
In cases where persistent rises in temperature continue for more than 3 days, and other symptoms increase in the form of a severe dry cough, weakness, lack of appetite, shortness of breath with slight exertion, the woman should urgently seek help from a medical institution or call a doctor at home. The infection reaches the lower respiratory tract and we are talking about bronchitis or pneumonia, which is considered a serious complication requiring antibacterial therapy.
Acceptable means to reduce temperature during lactation
Not every temperature is worth lowering. If it has risen slightly above 37 degrees, it is better to leave the immune system the opportunity to fight and produce antibodies. It is recommended to drink antipyretics when the thermometer reaches 38.5.
What medications are allowed if a nursing mother needs help? The list in this case consists of only 2 items:
According to clinical trials, Paracetamol crosses the placental barrier during pregnancy and is concentrated to a fairly high degree in breast milk (up to 24%). However, researchers claim that it is not capable of harming the baby either during intrauterine development or after birth during breastfeeding. Even versions of Paracetamol have been developed for children from 2 months due to its safety. To normalize the temperature, a nursing mother needs to drink 325-650 mg of the product and repeat the dose every 4-6 hours until a stable result.
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal drug. It acts comprehensively: reduces temperature, eliminates inflammation, relieves pain and calms feverish conditions. In the international classification of medicines, Ibuprofen is among the medicines compatible with breastfeeding. The duration of its antipyretic effect reaches 8 hours. This drug is taken 200 mg 3-4 times a day. In an emergency, it is allowed to take 400 mg, but further intake should be reduced to 200 mg. You can take 400 mg 3 times a day, but no more.
What can't be used?
You will have to forget about the beloved “Aspirin” for a while. Its active ingredient - acetylsalicylic acid - does not have the best effect on the functioning of the heart, digestive system and other organs of mother and child. It can cause topical damage to the baby’s liver and brain (Ray’s syndrome). The international classifier E-LACTANCIA classifies “Aspirin” as a dangerous drug, which is not recommended to be taken during lactation. Only one-time use is acceptable, when everything else is even more undesirable. In this case, it is better not to feed the child, express the milk, and resume breastfeeding after some time (see also: how can you effectively cure a cough while breastfeeding?).
It is unknown what side effects may occur, so it is better to take the active substance in its pure form.