Lactostasis is stagnation of milk in the breast, leading to problems with feeding and pumping. Most often, lactostasis is observed in primiparous women on the 5th–10th day after birth. Most often, with timely therapy or a simple change in the feeding rhythm, stagnation disappears on its own. However, in some cases, especially if measures are not taken in time to eliminate stagnation, it can lead to serious consequences for a woman’s health.
Medical is a clinic that helps patients with many health problems, including in the field of mammology. The treatment regimen is drawn up individually, after a thorough diagnosis and taking into account possible concomitant diseases and the general condition of the patient’s body.
What is lactostasis
This is stagnation of milk in the mammary glands. It is observed in almost every breastfeeding woman, especially first-time mothers. Although the number of children is not an indicator, for many mothers the situation repeats itself constantly. Some suffer monthly: having gotten rid of a milk plug in one chest area, they have to solve a problem that arises in another glandular area.
Lactostasis begins with a harmless thickening and heaviness in the chest. Unpleasant sensations increase during and after feeding. The breast hardens, becomes hot and dense to the touch, and turns red at the site of inflammation. The condition often occurs at the beginning of the lactation process, when the baby is still too weak to actively suck milk.
If you do not pay attention to the body’s first signals and do not get rid of the problem in time, the situation will worsen significantly. Stagnation of milk in the breast is dangerous due to a serious complication - mastitis.
Doctor Komarovsky about the treatment of lactostasis
According to the famous doctor, only a child will help solve the problem of milk stagnation. It is he who can remove the milk plug by dissolving the sore breast. The main thing is to position the baby when feeding so that the chin faces the painful area.
To quickly treat lactostasis, Komarovsky advises that the child should be given to the affected breast as often as possible. Use a warm shower, apply cabbage compresses, express milk. All these procedures can only be done without fever. He also warns that it often happens that after lactostasis, a nursing mother becomes low on milk.
Causes
A milk plug does not appear in the breast by itself. Common causes of lactostasis are as follows:
- Infrequent feeding by the hour.
Neonatologists and pediatricians unanimously recommend not adhering to a strict regimen and not limiting the baby to breast milk. A break of more than 3–3.5 hours between feedings is unacceptable.
- No change in body position.
Feeding in one position or constantly falling asleep in an identical position leads to compression of some lobes. The child empties them untimely, the result is stagnation of milk.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Incorrect feeding.
Psychosomatics are a common cause of milk plugs. Stress and nervous exhaustion lead to spasms of the mammary gland ducts and disruption of fluid outflow.

If the child does not latch onto the nipple successfully, the effect of the process is reduced. The breasts become overfilled with milk, which selectively blocks the ducts. This point includes incorrect latching of the breast during lactation by the nursing mother herself. Often, a woman intentionally puts pressure on the nipple area to make it easier for the baby to breathe.
- Uncomfortable underwear.
Purchasing a tight bra is not recommended for nursing mothers. It is not uncommon for women to wear underwear around the clock due to periodic leakage of milk. Constant pressure on the ducts compresses them, causing stagnation. In this regard, sleeping on your stomach is not recommended.
- Viscous milk.
- Constant pumping.
Excessively fatty and thick milk blocks the milk ducts, creates a plug in the glandular lobes, and leads to lactostasis. This occurs due to a small amount of fluid drunk and excessive consumption of fatty foods.
The body of a nursing woman works according to a well-known principle: filling with milk is equivalent to the degree of emptying of the breast. Therefore, when the baby sucks his quota, and the mother additionally expresses the rest, the next time the baby is filled, there will be more fluid. The chest becomes full and stagnation is inevitable.
In addition to the above situations, blockage of the ducts is observed when breastfeeding stops, when a woman bandages her breasts, or when the mammary gland is injured or hypothermia. Sometimes the cause of lactostasis is a genetic predisposition or hormonal disorders.
The essence of the problem
The female breast consists of adipose tissue, in which up to 25 lobules are hidden, which produce colostrum and then milk during lactation. The small ducts of the lobule are collected into one, which opens in the nipple.
During feeding, the thin muscle fibers surrounding the lobules reflexively contract, promoting the flow of milk. At the same time, the ductal muscles relax so that their lumen expands and adequate drainage occurs. As soon as a woman thinks about the upcoming feeding, this well-coordinated mechanism is launched. This is how nature makes it easier for the baby to suck milk.
Lactostasis is caused by blockage of the excretory ducts of one or more lobules with a milk plug formed as a result of stagnation of milk. The secreting cells continue to produce milk, and the lobules become overcrowded and increase in size. This leads to compression of the nerve endings. The process continues until the milk begins to flatten the acini cells, after which their function fades away.
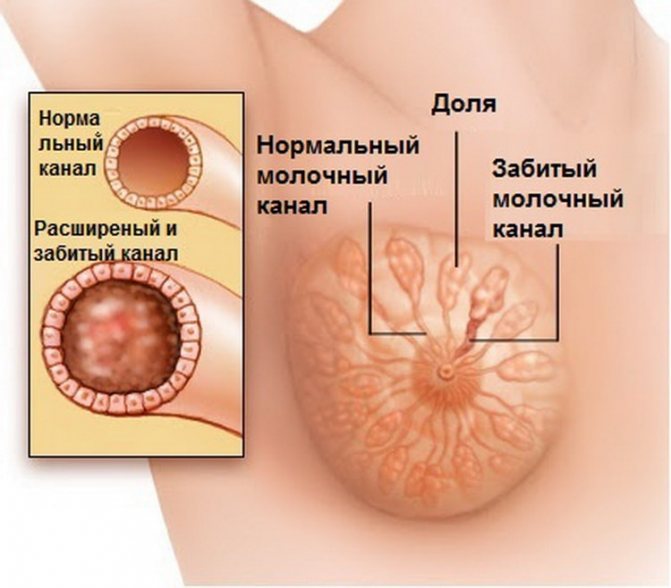
With a ductal block, the milk stagnates and thickens. Subsequently, the body tries to get rid of it, and reabsorption of the changed milk begins, triggering the inflammation mechanism. This ultimately leads to non-infectious mastitis.
Symptoms and external signs
Signs of lactostasis are easy to identify even for a new mother:
- Pain at the site of blockage.
- Increase in size of the affected breast.
- Local redness of the skin.
- The appearance of compactions.
- Fever, chills.
Regarding the last symptom, it is worth clarifying: if the thermometer is 39 or higher, this is a reason to sound the alarm, since perhaps an inflammatory process with the formation of pus has joined lactostasis. In this case, when expressing, unnaturally yellow milk may appear, which is not absorbed into the napkin and looks like mucus. You can definitely find out the diagnosis at an appointment with a mammologist and during an ultrasound scan.

Lactostasis in the mother has an adverse effect on the child. It is difficult for the baby to suck out the milk, the stream becomes thinner, so the baby behaves restlessly.
Diagnostics
Are tests needed for milk stagnation, you ask? Only for differential diagnosis with mastitis. In this case, the doctor may prescribe:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examination of milk.
If an inflammatory process is suspected, the specialist will offer an ultrasound and possibly a biopsy of the lesion.
Differences between lactostasis and mastitis
Untreated lactostasis inevitably leads to mastitis. One disease can be distinguished from another by a number of specific signs. Uninfected mastitis symptoms are similar to lactostasis, but they manifest themselves much more intensely. The temperature rises above 38 degrees, chest pain is felt when walking or feeding. A simple test will help differentiate lactostasis from uninfected mastitis. Measure the temperature in the groin, armpits and elbow. In the second case, the indicator is different - in other places it is lower.
Infectious mastitis is a dangerous condition that requires immediate medical intervention. The disease develops due to the penetration of bacteria through microcracks in the nipples and prolonged blockage of the milk ducts. Significantly different from lactostasis in symptoms. It is characterized by a severe course, prolonged fever (up to 40 degrees), and severe discomfort. The inflamed area is hyperemic, sharply defined, painful, and hot to the touch.
Treatment at home
Before treating the disease, it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis. To do this, pay attention to temperature indicators and the intensity of unpleasant sensations - with mastitis of any kind they are much more pronounced. Having decided on the diagnosis, the first thing you should do is remove the unpleasant symptoms. It will not be possible to fight the temperature with antipyretics - as long as there is stagnation, the fever will not go away for a long time.
Treatment at home is possible for lactostasis and uncomplicated mastitis. Compresses, ointments, pumping, massage are used. Nutrition is adjusted and physiotherapy is applied.
Massage rules
The first rule is not to use force. Knead your chest carefully and carefully. You cannot put pressure on the lumps or try to break them - this can injure the mammary gland. It is better to massage your breasts under a warm shower in parallel with pumping, especially if the procedure causes pain. The direction of movement is from the outer edge to the nipple. The rules for performing a massage are as follows:
- Wash the hands.
- Apply a little massage oil to your palms.
- Knead your chest in a spiral, moving towards the areolas, for about 5 seconds.
- Bend down and shake your chest slightly.
- In the same position, pull back and massage the nipple (if there is no hypersensitivity or cracks).
- Straighten up and stroke your chest in a spiral manner, as in step 3.
- The massage ends with a warm shower.
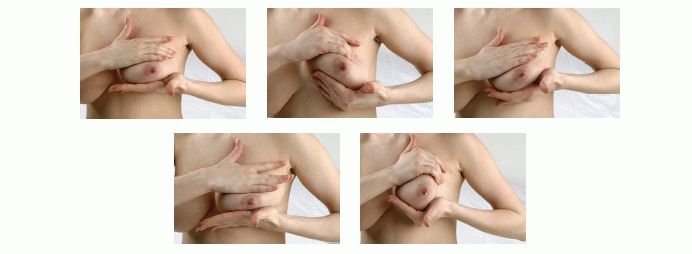
The procedure is carried out both before and during hygiene measures. Warm streams of water are directed alternately to each breast.
Compresses
You can cure lactostasis at home using compresses. They are applied for a period of 20 minutes to 2 hours.
- Cabbage leaf.
The product quickly relieves pain and inflammation. The sheet is kneaded and fixed with a bandage or bra to the sore breast. The duration of the procedure is 2 hours.
- Chamomile application for lactostasis.
Brew 2 tablespoons of chamomile flowers in a glass of boiling water, cool, filter, moisten a clean cloth in the solution and apply to the chest until the application dries completely. To quickly relieve swelling and pain, it is better to cool the healing liquid moderately.

- Honey and onion cake.
The onion is finely grated and mixed with honey in a 1:1 ratio. The formed pancake is applied to the affected breast, covered with a piece of polyethylene so as not to stain the bra, and underwear is put on. The holding time of the compress is an hour.
- Compress with cottage cheese.
Take a clean napkin and spread mashed low-fat cottage cheese on it. After fixation, it is permissible to keep the compress for 2 hours. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day, it perfectly relieves swelling and pain.
- Flax with flour.
Flaxseed is ground in a coffee grinder and diluted a little with water until a paste is obtained. The mixture is evenly distributed on gauze or a napkin and applied to the chest without insulation. You can keep the compress from 20 minutes to two hours.
These recipes are variable, for example, honey is mixed in equal parts with flour. For lactostasis, applications are made using baked onions, raw grated potatoes or beets, combining the components with crushed flaxseed.

Lotions made from eucalyptus, Japanese sophora and sweet clover are effective. The plants are mixed in equal parts (adjusted to 4 tbsp), poured with boiling water (a glass). After cooling and straining, half a stick of cow butter is added to the mixture, heated and mixed. Warm compresses are applied to the affected breast.
Lotions made from tangerine peel and licorice root are effective for lactostasis. Grind the ingredients finely (2 tablespoons to two teaspoons), pour in three glasses of boiling water. After cooling, divide the infusion into parts, one of which is used for applications, and the second is taken orally in parts throughout the day.
Preparations: ointments and tablets
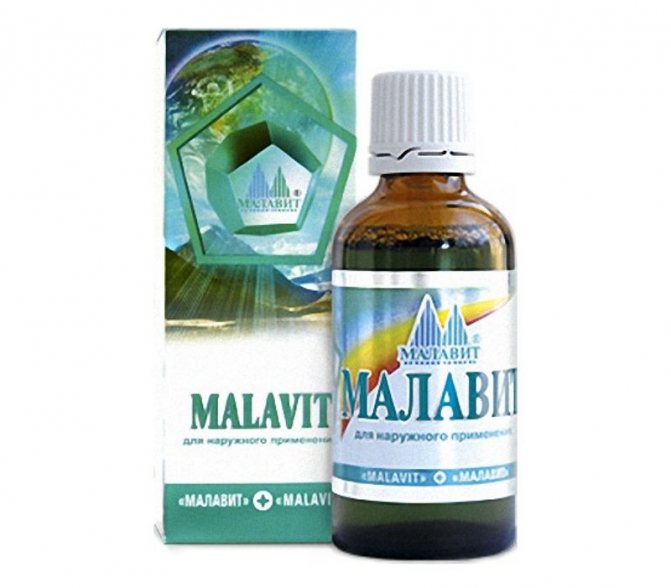
Therapy for lactostasis is complex. The first cure for milk congestion in the chest area is ointments. But preparations based on camphor alcohol are contraindicated, Vishnevsky ointment is not recommended, and you should not rub your chest with products containing ethylene. External agents such as Arnica, Chlorhexidine, Progestogel (if mastitis has occurred), Traumeel, and Malavit are prescribed. With regular use of ointments, according to the instructions, pain goes away, swelling is relieved, and lactation is improved.

Tablets for lactostasis are used as a last resort, antibiotics - strictly as prescribed by the doctor. The most popular are antispasmodics, which help milk pass unhindered through the milk ducts, and painkillers (with the doctor’s permission) - “No-Shpa” (taken half an hour before feeding), “Paracetamol” (effective for hyperthermia, practically safe for babies), “Nurofen” . To fortify breast milk and correct its fat content, the dietary supplement “Lecithin” is used.
Ultrasound
You can mechanically stimulate the passage of milk through blocked ducts. For this purpose, ultrasound treatment of lactostasis is used. The procedure is painless and short (quarter of an hour). The principle of operation is a soft, non-traumatic massage with ultrasonic waves, after which independent pumping is greatly facilitated.
An important nuance: you cannot feed the baby this milk - just pour it out.
Ultrasonic massage is carried out in a course of up to 8 procedures. After this, the outflow of milk improves and blood flow normalizes due to the heating of the gland. Contraindications are mastitis in the acute stage or purulent inflammation, hormonal imbalance, cyst, breast cancer, central nervous system disorders.
Physiotherapy
Lactostasis can be successfully treated with other hardware methods. Physiotherapy for congestion in the breasts of a nursing woman includes magnetic therapy and wave exposure (decimeter, centimeter). In the first case, inductors are placed on the patient’s skin in the affected area, avoiding the areola area. The course of treatment is ten days. The procedure is carried out once a day for 5 minutes.
In the second case, emitters with a power of up to 10 W are used, which are installed over the inflamed area. The effect lasts 10 minutes and is repeated for eight days in a row. Contraindications to these physiotherapeutic procedures are the same as for ultrasound exposure.
Nutrition
Diet will help cope with stagnation. There are no serious restrictions, but you need to pay special attention to your drinking regime in the summer. With insufficient fluid intake, milk becomes thicker, which will aggravate the situation with lactostasis. But in everything you need to observe moderation - drinking too much will contribute to an excessive flow of milk, so balance is necessary. Nutrition is adjusted according to the child’s age so that the baby does not have bloating, allergies, etc. But if a nursing mother is prone to the formation of plugs in the milk ducts, she should not eat a lot of nuts and animal fats.

Errors
Wrong actions for lactostasis can not only negate all treatment, but also aggravate the problem. I'm telling you about the most common mistakes.
- Don't knead your chest roughly. There is an opinion that with lactostasis you need to massage your breasts until it hurts, with effort. But glandular tissue is very delicate and can be easily injured. This approach can easily lead to an abscess.
- You can't heat your breasts. Heating in a sauna or hot shower can cause swelling and increase inflammation. But at the same time, it is worth provoking a surge of oxytocin, which helps empty the breast. Oxytocin is released when you relax. In this sense, a warm shower on your back while pumping your breasts is good and safe.
- Use any warming ointments and compresses. Warming up the breast tissue using any traditional methods aggravates the condition and provokes mastitis.
- Alcohol lotions. Alcohol reduces the sensitivity of oxytocin receptors, complicating the normal flow of milk.
- Limit drinking. At the same time, the milk flow does not decrease, but its outflow only worsens.
- Do not give the baby a sore breast. Many mothers ask me: “Has the milk in the breast spoiled due to lactostasis? Will it be harmful to the baby? Of course not! The milk in the mother’s breast is always beneficial for the baby; you can continue feeding even with mastitis.
And we tell you how to do it correctly in a special course in our online school “Easy Childbirth”.
Lactostasis in a nursing mother is a serious problem. You should not delay treatment and hope that the situation will resolve itself. The easiest way to deal with this problem is within the first 4 hours after it occurs. If you do everything correctly and in a timely manner, lactostasis will recede, and lactation will become much easier and more enjoyable.
Did you like the post? Share it on social networks!
Telegram
Tweet
We recommend that you read similar articles:
- How to properly organize the postpartum period
- How to deal with the symptoms of postpartum depression
- 8 main fears during pregnancy
Expressing during milk stagnation
Straining the plug is the first aid for lactostasis. It is most correct to express milk with your hands, and not with the help of a special suction. In this way, stagnant liquid is extracted better and faster. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Before pumping your breasts, you need to take a warm shower.
- Create a calm environment.
- Convenient location.
- The chest is grasped with a nearby hand.
- With the right hand, take the right mammary gland so that the thumb is on top and the rest are under the breast.
- Moving radially towards the nipple, you must constantly change the position of your fingers.
- A sign of correct pumping is a powerful, energetic stream of milk.
This manipulation during lactostasis often provokes pain. To avoid it, take anti-inflammatory drugs. Pumping helps break up any lumps of milk that have stagnated in the breast.
Should I feed the baby?
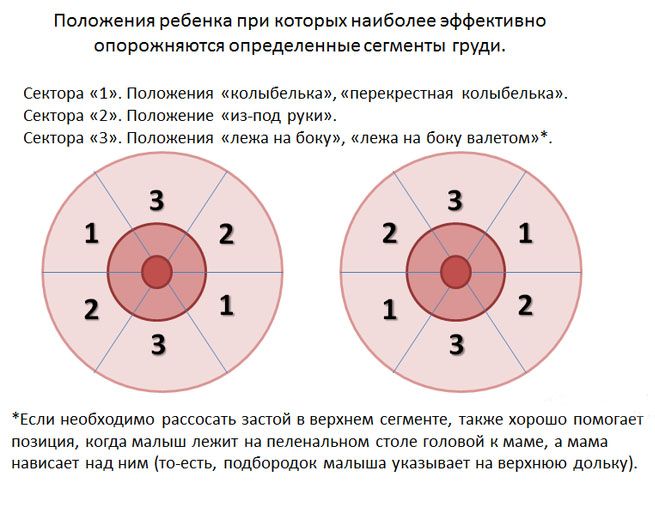
It is possible and necessary to feed a child with lactostasis. Moreover, no pumping will help remove congestion better than the baby will do. There is a rule - whichever thoracic lobe the baby’s chin rests on will be emptied faster than others. Based on this postulate, select positions for feeding. Universal provisions:
- The baby's head lies on the mother's elbow. The lateral and upper lobes of the chest are emptied.
- The baby lies on a pillow, under the mother’s arm, in a “jack” position. The upper areas are emptied, closer to the outer edge.
- The mother is on her back, and the child is in the “cradle” created by the bend of the woman’s arm. The pose helps empty the lateral glandular lobes.
- The overhanging position is the best because all areas of the chest are emptied evenly.
Position the child so that the problem area is emptied first. When feeding, be sure to massage your breasts - this stimulates the flow of milk and avoids lactostasis.
When to see a doctor
A mammologist is a doctor whom a nursing woman turns to in case of a problem. If all the measures described above do not help, the condition does not improve, the temperature does not drop, and the compaction remains the same, it means that the local status of lactostasis has not changed and requires the intervention of a doctor.
The mammologist will conduct visual and palpation examinations and determine the status of the localis (the initial state of things, then monitored over time). Based on the initial appointment, the doctor monitors changes in the nursing mother’s well-being. After examination and tests, diagnosis, the doctor prescribes adequate therapy for lactostasis.
Possible complications
Lactostasis occurs both at the beginning of lactation and after a year of feeding. In any case, an untreated disease provokes negative consequences. If there is less milk, the baby is restless and does not eat enough, the woman’s temperature rises, severe pain in the chest appears, local redness is observed on the skin, as shown in the photo - these are signs of lactostasis. The condition quickly develops into a common complication – mastitis.
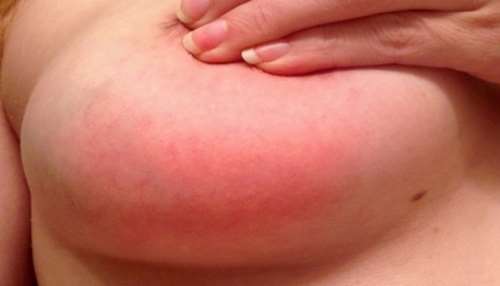
If cracks appear in the nipples, the disease transforms into infectious status and an abscess develops, requiring the prescription of antibacterial drugs. Many of them are compatible with breastfeeding. In exceptional cases, surgical intervention is performed.
Treatment of lactostasis in nursing mothers
As a rule, treatment and control of lactostasis is carried out on an outpatient basis; in rare cases, hospitalization is required if lactostasis occurs with an elevated temperature. After a doctor examines the mammary glands, he gives several recommendations on feeding the baby, the process of expressing milk, and prescribes a course of ultrasound for no more than 7 days. It is not uncommon for a mammologist to perform an ultrasound examination of the gland. Among the medications, homeopathic gel Traumeel and antispasmodics that dilate the ducts (No-spa, Drotaverine hydrochloride) are prescribed for 3-5 days.

Prevention of lactostasis
Competent preventive measures will help to avoid chest congestion. Prevention of lactostasis is as follows:
- Maintain a balance between work and rest.
- Avoid stress.
- Sleep more often on your back or side.
- Do not express milk when breastfeeding is established.
- Feed the baby on demand.
- Change body position during lactation.
- Wear special underwear, do not use tight underwear.
- Establish a drinking regime.
- Don't get too cold.
- When completing breastfeeding, do not bandage the breast.
Regarding the last point, the best option is gradual weaning. Every day they do one less feeding or do not offer the baby the breast at all, but pump until relief occurs. Every day the amount of milk will decrease.
Preventive measures
Lactostasis clearly affects the quality of breastfeeding, breast health and the mood of mother and child.
The following tips can help avoid stagnation:
- feed the baby on demand;
- Always empty both breasts completely;
- change positions to free all lobes from milk;
- Do not pump frequently to avoid producing too much milk;
- do not press your breasts with underwear or while sleeping;
- avoid drafts;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- try to follow the diet of a nursing mother and drink a lot of water;
- If you have any questions, seek the help of a lactation consultant.
Lactostasis often occurs repeatedly, so when faced with the problem for the first time, it is important to determine the cause of its occurrence.











