Why take hormone tests when planning a pregnancy?
The content of the article
Hormones serve as the main element in ensuring and realizing the reproductive function of every woman. Therefore, proper pregnancy planning must necessarily include undergoing basic hormone tests. The doctor will tell the expectant mother their exact list, in most cases these are FSH, LH, progesterone, DHEA-S, testosterone, estradiol, prolactin, as well as thyroid hormones (TSH, free T4, and so on).
The gynecologist usually tells what hormonal tests a particular patient needs to undergo, but in European practice a range of mandatory measures has been defined.
Types of tests to take before pregnancy
As part of pregnancy planning and during the current pregnancy, the expectant mother is recommended to undergo the following hormonal tests: T3, T4 free, TSH, FSH, LH, estradiol, prolactin, progesterone, DHEA sulfate, testosterone.
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
. This substance, produced by the pituitary gland, is one of the main regulators of follicle (egg) growth in the ovary; in addition, it is responsible for the formation of estrogen, under the influence of which the endometrium grows in the uterus. An FSH test must be taken before pregnancy. - Luteinizing hormone (LH)
. This substance is also produced by the pituitary gland, ensures ovulation, egg maturation, is responsible for the formation of the corpus luteum, and stimulates the secretion of estrogen. At the time of ovulation, the maximum concentration of LH occurs in the female body. During the pregnancy stage, luteinizing hormone ensures the production of progesterone, the main pregnancy hormone. By the way, it is the ratio of LH and FSH in the results of blood tests that doctors primarily rely on when identifying the cause of infertility. - Prolactin.
Ovulation is directly dependent on prolactin; if its level in the female body in a blood test does not correspond to the norm
,
the development of the egg is impossible, because ovulation is absent. And conception without ovulation is impossible. - Estradiol
. The role of this substance in the development of the uterus and its preparation for pregnancy is extremely important. The hormone is responsible for the development of the egg, the formation and regulation of menstrual function. The day before ovulation, the maximum concentration of estradiol is present in a woman’s body. - Progesterone
. This hormonal element is also called pregnancy hormone or motherhood hormone. It is he who is responsible for attaching the fetus to the uterus and creating the conditions for pregnancy to occur. The substance is formed in the ovaries and adrenal glands. - Testosterone
. Testosterone is produced in a woman's body in small quantities, secreted by the ovaries and adrenal glands, and its peak occurs at the ovulation stage. A testosterone test is very important, since its excess can lead to early miscarriage; it must be tested in case of infertility. - DEA sulfate
. Like testosterone, this hormone belongs to the male category, but the female body also needs it in small quantities. Its excess is equivalent to malfunctioning of the ovaries and infertility.
Mandatory pre-pregnancy tests for both partners
Preparing for pregnancy allows you to solve a lot of problems that may arise when trying to conceive a child, during pregnancy and childbirth. However, all over the world (including in Russia), on average, only 6 out of 10 pregnancies are planned. And only 4 out of 100 occur after the so-called “preconception preparation,” which includes tests when planning pregnancy, lifestyle and nutrition adjustments. Of course, in such families the percentage of successful pregnancies and healthy children is higher. Therefore, if a couple is planning to have a child, she needs to think about it and get tested before pregnancy:
- A general urine test is an indicator of kidney function and the condition of the urinary tract.
- The study requires an average portion of morning urine. Collect it in a sterile container immediately after waking up and having an intimate shower, which is necessary to avoid the entry of leukocytes into the urine from the genital tract.
- On the eve of the analysis, exclude coloring foods (beets, carrots, oranges), spicy and sweet foods from your diet, and do not abuse sour and meat foods.
- A general (clinical) blood test informs about the content of hemoglobin, leukocytes, platelets, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the blood. Thanks to this study, one can judge the state of the body, the presence of inflammatory processes and many diseases.
- Blood is taken on an empty stomach from a vein or finger.
- Before taking the test, refuse food for 8 - 12 hours. You can only drink water.
- Analysis of blood type and Rh factor makes it possible to assess the likelihood of an immune conflict between mother and fetus. Women with a negative Rh factor are primarily at risk (provided that the potential father has a positive Rh factor and the child will inherit it).
- If a Rh-negative woman has had pregnancies in the past or received a blood transfusion, she needs to be tested for antibodies: they can complicate bearing a child.
- Tests for infections before pregnancy.
- A smear on the flora informs about the presence of inflammatory processes and sexually transmitted diseases (ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia, trichomanada). Vaginal or ureteral secretions are used for analysis. 2 weeks before the study, you must stop taking antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal medications, as well as vaginal ointments and tablets. Also, 2 - 3 days before the smear, sexual contact and douching should be avoided.
- Analysis for TORCH infections can detect toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and genital herpes. These diseases are practically asymptomatic, do not pose a threat to an adult, but are very dangerous for the embryo. TORCH infections can lead to serious fetal malformations and miscarriage. The study is carried out in 2 ways. Using PCR diagnostics, an infection is detected, and using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, its type and stage of the disease are determined.
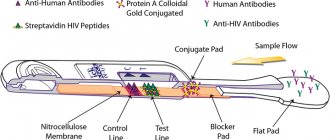
- Test for HIV and viral hepatitis. Taking tests before pregnancy and their timely diagnosis can minimize the risk of infection of the child and complications during pregnancy.
A blood test before pregnancy is especially important for a woman, because she is the one who will bear the child for 9 months. If the doctor deems it necessary, he will prescribe blood biochemistry.
Basic pre-pregnancy tests should be completed 3 to 6 months before the expected conception. If infections are found, they must be treated. If you have not had rubella, measles or chickenpox, it is advisable to get vaccinated and only 3 months after it start planning a pregnancy.
Thyroid hormones
Testing for thyroid hormones is an important part of preparing for pregnancy; pregnant women should also take it. These substances are actively involved in the work of the ovaries; going beyond the norm can create conditions for the development of infertility.
- T3 is free
. This is a substance of the thyroid gland that is responsible for the absorption and exchange of oxygen by tissues. - T4 is free
. This hormone carries out the synthesis of proteins in the body. - Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
. It is responsible for the functioning of the thyroid gland; a change in its concentration level indicates thyroid disease.
This is the main list of hormonal tests that a woman is recommended to undergo in preparation for pregnancy.
Where can I get tested before pregnancy?
Answering the question of where to get tested before pregnancy, let’s say that you can go to a clinic near your permanent place of residence or to your gynecologist, who will help tell you what each woman needs to take specifically when planning her first or subsequent pregnancy.
However, not only the expectant mother, but also the future father must undergo tests and examinations, so it is worth visiting a urologist and therapist. Often spouses are simply looking for a good doctor if previous consultations and examinations have not yielded anything.
If you are planning a pregnancy, we advise you to contact our medical center, where experienced specialists will help you not only prepare your body for pregnancy, but also identify the reasons for its absence. In this matter, it is very important to examine both the man and the woman, since the cause could be in either partner.
In ours, we will prescribe all the necessary tests that need to be taken, as well as the specialists who are best to turn to for help. In addition, sometimes you need to visit a family psychologist, where you can talk about your problems and together find ways to solve them.
How to prepare for tests when planning pregnancy
Each of these tests requires proper preparation. It is usually associated with the day of the cycle, diet and medication. You can learn more about all the nuances from your personal gynecologist.
How to prepare for thyroid hormone tests
Thyroid hormones that need to be checked through analysis before pregnancy are T4, T3, TSH. In preparation for these analyses, the following rules must be observed.
- It is recommended to stop taking thyroid hormones approximately one month before the blood test. Of course, unless otherwise instructed by the doctor.
- Drugs that contain iodine can distort the results of a blood test. It is advisable to stop taking them approximately two or three days before submitting the material.
- The day before the blood test, sports training and other physical activities must be excluded, and it is also recommended to avoid stressful situations. The test rules also require you to stop using cigarettes and alcoholic beverages.
- It is important to donate blood on an empty stomach. It is recommended to remain completely at rest for half an hour before the test.
A blood test for thyroid hormones before pregnancy is allowed regardless of the day of the cycle.
How to prepare for sex hormone tests
Preparing to conceive a child also requires passing important tests for sex hormones; they are also taken in case of infertility. You need to properly prepare for the tests.
- LG
. Sports activities are excluded three days before blood sampling. It is advisable to start abstaining from cigarettes at least a couple of hours beforehand. It is important to calm down before taking material; blood is donated on an empty stomach. If the attending physician does not indicate special dates, it is recommended to schedule the test on days 6-7 of the cycle. - Progesterone
. A blood test for progesterone is recommended to be taken on days 22-23 of the cycle, unless the doctor sets a different time frame for the patient, this will ensure correct results. Blood is taken on an empty stomach (12 hours without food), water is allowed to drink. It is highly advisable to conduct the study in the morning. - Prolactin
. Before taking tests for this hormone, thermal exposure (taking a hot bath, going to the bathhouse and sauna), and sexual contact are prohibited. The concentration of prolactin in the body can change due to stress and physical exertion. The prolactin test is carried out only 3 or more hours after getting up; the patient should relax and rest 10-15 minutes before the test. Prolactin levels are also affected by alcoholic beverages, chest surgery, and drugs or procedures affecting the mammary glands. - Free testosterone.
The most important rule for correctly conducting this analysis is taking it on an empty stomach. For 12 hours, not only food is excluded, but also any sweetened drinks (coffee, tea, juice), only water is allowed to drink. The day before, it is better to remove heavy, fatty foods from your diet. - Estradiol
. This study can be carried out regardless of the specific day of the cycle. Approximately 2 days before blood sampling for analysis, you should stop taking thyroid and steroid hormones, unless otherwise instructed by your doctor. The day before the test, you should avoid emotional stress and physical activity. It is enough to start abstaining from food three hours before the blood drawing procedure; you are allowed to drink clean still water. - FSH.
Distortion of the results of this analysis is possible in connection with radioisotope drugs and hormonal oral (taken orally) drugs. It is recommended to conduct the study on days 6-7 of the cycle.
Tests for women in preparation for pregnancy
When preparing for conception, it is necessary to be examined, and the health of the child depends not only on the woman, but also on the spouse. Therefore, the couple must come to the consultation and check the tests before pregnancy together. At the appointment, a specialist will examine the woman, take smears, give directions for general laboratory tests, blood tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis, and ultrasound. Before pregnancy, internal foci of infection must be eliminated, so the woman is referred for in-depth diagnostics.
List of mandatory tests during preparation for women:
- Smears from the vagina, cervical canal to determine the degree of purity, cytology; colposcopy (if the woman has previously had cervical erosion cauterized or had cervical ruptures).
- A blood test is taken for glucose, HIV, syphilis, blood group, Rh, hepatitis, and a general blood test is also performed.
- PCR study for latent sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood test for TORCH infections (rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes, toxoplasmosis).
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvis.
- Breast examination.
- External examination of the external genitalia reveals rashes, varicose veins, and pigmentation of individual areas of the mucous membrane. An examination of the anus is carried out to detect hemorrhoids and fissures, since these diseases worsen during pregnancy.
- A mirror gynecological examination and colposcopy can assess the condition of the cervix, identify inflammation of the cervical canal, erosion, polypous formations, and endometriosis. Colposcopy may also indicate cervical cancer. Any of these pathologies can interfere with natural conception.
- Swabs for analysis are taken from the cervical and urethral canals. Microscopic examination of the biomaterial can reveal leukocytosis, indicating an inflammatory process, fungal and/or bacterial infection. Inflammation can occur latently without manifestations, but during pregnancy there are hormonal changes and a decrease in immunity, which provokes the activation of infectious agents. Therefore, all infections must be treated before conception. A smear is also taken from the cervical canal to be analyzed for atypical cells (oncocytology). Cytological analysis makes it possible to detect cancer, which in the early stages may be asymptomatic. But if a woman with cancer of the genital organs manages to become pregnant, then the cancer process will become more active and worsen.
- Analysis for TORCH infections is a mandatory minimum, since any of these infections can be fatal to the fetus or lead to its abnormal development. If a woman does not have any infectious diseases, then during pregnancy she must take care to prevent infection. The same applies to sexually transmitted infections, then tests are taken by both partners.
- If the expectant mother had rubella as a child, she has lifelong immunity to it. In other cases, a woman may be offered a rubella vaccination, after which at least three months must pass before the expected conception.
- Women who have pets should be careful when interacting with them, since animals can become infected with another dangerous infection - toxoplasmosis. According to statistics, 15% of women have had this disease; for the remaining 75%, this virus is potentially dangerous. Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, during the gestation period it is necessary to limit communication with pets, and meat should be subjected to thorough heat treatment.
- Cytomegalovirus can be infected through airborne droplets. If, in preparation for pregnancy, a high level of the virus is detected during the analysis, then antiviral therapy is prescribed. If the result is negative, preventive measures must be taken.
How to decipher test results when planning pregnancy
A gynecologist or endocrinologist will also tell you about the names of the tests that a particular patient needs to undergo in preparation for motherhood. Below are the normal values for the tests that are most often prescribed. Of course, only a professional doctor can give a correct assessment of the test results, but a woman can identify general points on her own.
To understand the interpretation of blood test results, you need to know the normal concentration of a particular hormone in the body. In women, normal values are usually determined by the phase of the menstrual cycle.
- FSH
is
follicle stimulating hormone
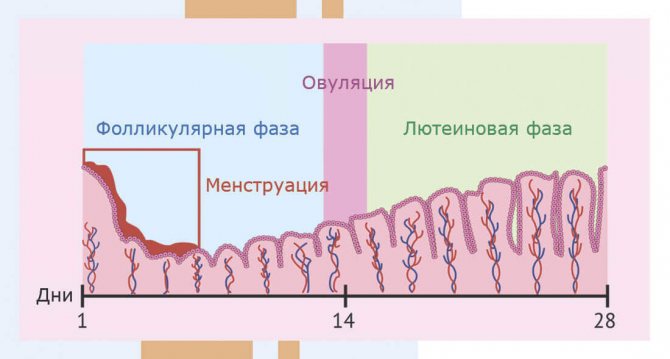
. The FSH substance is responsible for the enlargement of the egg and the growth of the endometrium, therefore its concentration in a woman’s body changes depending on the phase of the cycle in which the blood test is performed. For the menstrual phase (1-6 days) and for the follicular phase (3-14 days) the norm is values in the range of 3.5-12.5 mIU/ml, for the ovulatory phase (13-15 days) - 4.7-21.5 mIU/ml, for the luteal phase ( 15 – beginning of menstruation) – 1.7 – 7.7 mIU/ml. - LH is luteinizing hormone. The normal level of this substance in the female body is also determined by the phase. Menstrual and follicular phases - 2.4-12.6 mIU/ml, ovulatory - 14 - 96 mIU/ml, luteal - 1 -11.4 mIU/ml.
- Progesterone
. The results of tests performed before pregnancy for this hormone should also be interpreted depending on the specific phase of the menstrual cycle. For the menstrual and follicular phases, normal values are 0.6 - 4.7 nmol/l, for the ovulatory phase - 2.4 - 9.4 nmol/l, for the luteal phase - 5.3-86 nmol/l. - Prolactin
. The concentration of prolactin in a woman’s body in test results is important information for infertility; this indicator must be checked as part of pregnancy planning. The normal level of prolactin in the blood of non-pregnant women is 102-496 µIU/ml. - Estradiol
. Normal levels of this substance are also directly dependent on the patient’s menstrual phase. The norm of estradiol during the menstrual and follicular phases is 12.5-166 pg/ml, during the ovulatory phase - 85.8-498 pg/ml, during the luteal phase - 43.8-211 pg/ml. - Free testosterone
. Despite the fact that this sex hormone is considered “male,” it is also necessary for the female body, and its concentration is included in the list of routine tests when planning pregnancy. The norm for a woman over 18 years of age is 0.5-4.1 pg/ml. - DEA-S . If the level of DHEA-S in a woman’s body is outside the normal range, infertility and ovarian dysfunction are possible. The day of the cycle on which the study for this substance will be carried out does not play a special role. The norm for a woman is 7.2-100 nmol/l.
How to interpret thyroid hormone tests
Tests for thyroid hormones are a mandatory part of the test as part of pregnancy planning.
- TSH . For women, the normal level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood is 0.35-4 µIU/ml. Testing for this substance is often carried out during pregnancy. At 1-12 weeks of pregnancy, the normal result is 0.35-2.5 µIU/ml, for 12-24 weeks - 0.35-3 µIU/ml, for 24-42 weeks - 0.35-3 µIU/ml.
- Free triiodothyronine
. The normal concentration of free T3 hormone in a woman’s body can be 2.3-4.2 pg/ml. - Free thyroxine
. The free T4 concentration level can be 0.6-1.76 ng/dl.
If, when studying the transcript of test results, any deviations from the norm are discovered, you should definitely show it to a specialist. Only a doctor can correctly identify the problem, take into account all the necessary factors and select the optimal treatment.
CLICK TO SIGN UP
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Expert opinion of a doctor
Dmitriev Dmitry Viktorovich
Deputy General Director, obstetrician-gynecologist for reproductive health.
The herpes virus is dangerous during embryo development. It circulates in the body constantly and is carried by 90% of the population. Testing for herpes before planning allows you to assess the potential risk of primary infection. During life, the virus may not manifest itself in any way, but in pregnant women it can become more active and turn from opportunistic to pathogenic. Then the virus may cause the development of defects in the fetus. Women who have previously been ill have antibodies to the herpes virus. If herpes worsens during gestation, then treatment and screening of the fetus is necessary.
Expectant parents need to be tested for their blood group and Rh factor. Rh conflict that occurs in women with negative Rh, if the child inherits a positive one from the father, which leads to fetal pathologies (hemolytic jaundice, stillbirth). This risk is minimal during the first pregnancy and increases during subsequent pregnancies. There are cases of conflict not only by Rh factor, but also by blood type.
Transvaginal ultrasound examination before planning is carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. It helps to exclude pathologies that interfere with natural conception or pregnancy. Ultrasound reveals uterine fibroids, inflammation, cysts, polyps, and tumors. The pathological formation must be removed to ensure a normal pregnancy.
According to indications, an analysis is carried out to study hormonal levels, determine the functioning of the blood coagulation system, and genetic examination with consultation with a geneticist. Cycle disturbances, excess body weight, endocrine chronic diseases, infertility for a year with regular unprotected sex require a hormone test.
Typically this is an analysis of:
- Luteinizing hormone, which affects ovulation.
- Follicle-stimulating - causes growth and maturation of follicles.
- Prolactin - affects ovulation.
- Testosterone - increased concentrations in the analysis in women can provoke a miscarriage.
- Estradiol is responsible for the development of the genital organs.
- DHEA sulfate - affects ovarian function.
- Thyroid hormones.
A genetic test is necessary if future parents have or had relatives with hereditary diseases, or if a woman’s previous pregnancies ended in miscarriages.
Then the expectant mother must consult three specialists:
- Dentist - to identify foci of infection, eliminate them, and preserve teeth during gestation.
- Otolaryngologist - to exclude chronic infections of the ear, throat, and rhinoinfections.
- The therapist will give directions for general blood and urine tests and interpret the results.
- Sometimes a visit to an endocrinologist, geneticist, or other specialized specialists is required.
When planning a pregnancy, your partner should also be examined. Mandatory tests include fluorography to exclude tuberculosis, general blood and urine tests, as well as group tests, Rh factor, and syphilis. If a woman is diagnosed with sexually transmitted infections, her partner is also subject to similar tests. If a man is over 40 years old, then he undergoes a consultation with a geneticist. If attempts to conceive a child are unsuccessful, the spouses are tested for HLA compatibility and a spermogram.
Calculate dates suitable for taking tests
Results sent successfully. Please check your email.
Clear results