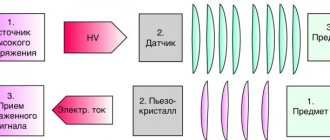
Stereotypes and differences from radiography
Regardless of where the procedure took place, it is important to pay attention to what is written in the direction issued by the attending doctor. If it says that it is required to undergo fluorography, there is no need to go against the instructions. Most people far from medicine believe that a classic x-ray will better show the condition of the lungs. But in reality, ignoring the advice of a specialist will result in the body receiving an unreasonably high dose of radiation.
In addition to the difference in the percentage of radiation, the differences between two similar testing formats also lie in the resolution of the image. Fluorography has a reduced radioactive load, but you will have to pay for taking care of your own body with a “photograph” of lower quality.
This is where the temptation arises to get high-quality results straight away. But in fact, the average quality of an X-ray photograph is quite sufficient to establish a possible pathology even at an early stage of the development of the disease. Because of this, doctors recommend following the instructions, and if you suspect any anomaly, look for where to undergo a traditional x-ray of the chest organs.
People are often interested in the question of how much radiation the patient will receive if he agrees to undergo the procedure. It is believed that one round of conventional radiophotography is equivalent to the dosage that the body receives in ten days in the natural environment.
But here you should definitely take into account how health monitoring is done. If film devices were used, then the one-time load is from 0.2 to 0.25 mSv. The older the device, the higher the chances of getting unnecessary radiation, which could be avoided if you went to an office with a modern analogue.
According to the results of a scientific experiment, digital equipment has approximately 4 times less load. At the same time, traditional X-rays demonstrate a load one and a half times higher than even the oldest fluorograph.
It follows from this that the question: can radiography be used instead of radio photography can be answered in the affirmative. But for a preventive examination of the lungs, a fluorogram is suitable.
Errors in radiographic examination
As a rule, errors in research are rare and often depend on the human factor; well-programmed equipment does not fail. The likelihood of discrepancies between reality and the result of fluorography is possible when:
- confusion of patient images;
- inexperience of the specialist deciphering the result;
- if the person did not take off his jewelry during the study (pendants, chains, piercings, etc.) or did not pick up his hair.
When a pathology is detected, the results need to be clarified, and the person is re-sent for an x-ray of the lungs in two projections.
Classification of radio photography
Often people are sent to conduct research approximately once a year, which is sufficient for the main purpose of the examination - to identify tuberculosis of the lungs and bronchi.
People who are already registered at a tuberculosis dispensary are prescribed tests much more often. If the victim has just started a course of therapy, then the interval between procedures is about three to four months, depending on the intensity of treatment, the characteristics of the development of the disease, and the individual characteristics of the body.
If the treatment has produced positive changes in dynamics, then the regime changes. Initially, monitoring is carried out approximately every six months while maintenance therapy continues. But as soon as its time ends and the patient fully recovers, he is considered a full-fledged healthy member of society. This means that after deregistration, he needs to undergo examination on a general basis - just annually.
Today there are two main formats of radio photography, providing:
- traditional category;
- digital group.
What both visualizations show is no different, but the first option is considered an outdated approach. It is based on the ability of X-rays to pass through the body from back to front, and then be recorded on a cassette with a pre-installed photosensitive film.
After the waves collide with the film barrier, the process of releasing thermal molecules is started, which allows for detailed visualization of internal organs and bone structure.
The principle is based on the fact that the rays pass well through soft tissue, which cannot be said about the ribs, shoulder blades and collarbones. Then all that remains is to wait for the negative to be fully developed, then dry it and hand it over to the attending physician after receiving the conclusion.
The functioning of a digital camera is a little different, where the waiting time for a photo is literally a minute. The mechanism is based on the passage of a thin beam linearly in turn through the studied area. The image is then reconstructed using high-tech software. The result is displayed on a computer monitor. It can be:
- put on digital media;
- print on paper through a printer.
It is believed that the second variation is preferable today, since it eliminates the long hours of waiting for film development. Also, the resulting image can be stored for an unlimited amount of time. But, answering the question: is the old type of examination still performed, we get an affirmative answer.
Another positive aspect of digital technology is the ability to eliminate the need for a magnifying glass. To examine a supposedly problematic area, it is enough to simply adjust the scale using controls in a computer program.
Also, by storing all the collected data in the hospital database, the victim will not have to carry the old test with him to the doctor’s appointment in a year. When you enter your last name along with your residential address, the program will display all previously recorded survey results. All that remains is to compare the updated and past information to track the dynamics.
Main indications
The main task pursued by the method is to search for ailments related to deviations in the functioning of the lungs or bronchi. It is not for nothing that the technique is considered a preventive approach that prevents serious complications for diseases of the respiratory system.
Typically, a local physician or pulmonologist sends you to take the test at a clinic. The victim comes to them with three characteristic symptoms of possible pathologies in this part:
- prolonged persistent cough;
- dyspnea;
- pain syndrome in the chest area.
When the above signs are detected, the chance of detecting a pulmonary or bronchial deviation increases significantly. Often, a control cut allows you to establish:
- inflammatory process even at the initial stage of development;
- pneumothorax;
- neoplasms of malignant and benign nature;
- pleural damage;
- emphysema.
But more often than not, even a free test, which was a simple preventive measure, reveals tuberculosis. To catch such a terrible disease, which has a high fatality rate, doctors recommend not shirking the annual mandatory examination. You can create a schedule for checks yourself by simply setting a reminder in your phone.
In addition to standard indications, there are two more categories of reasons for sending to the diagnostic office. The first concerns the need to check family members living with pregnant women or newborns. This is necessary to minimize the risk of the baby contracting a dangerous disease. For the same reason, conscripts from military registration and enlistment offices also have to go and get tested.

The second case concerns unscheduled fluorography. This means that a person could have undergone an examination just a couple of months ago, but he will be sent to do everything again if they suspect:
- foreign body in the lungs;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- tumors of the mediastinal organs;
- diseases of the heart, large vessels.
Such precautions make it possible to recognize concomitant diseases such as fibrosis or sclerosis. Also, using a small image, it is possible to establish localization:
- cysts;
- cavern;
- abscesses;
- infiltrates;
- accumulations of gases.
Despite the productivity of the technique, fluorography can hardly be called the main argument for diagnosing pulmonary pathologies. Often it is necessary to use auxiliary tests such as sputum testing and MRI with contrast.
Pregnancy and other contraindications
Among the contraindications to manipulation, there are two categories of prohibitions. The first is absolute, providing for pregnancy and childhood. Many mothers are puzzled by the question of at what age can babies have radio photography. It is believed that the minimum threshold is 15 years, since before this time it will be difficult for children to tolerate increased radiation exposure.
Among the relative contraindications, which are sometimes ignored in case of excess of benefit over harm, are:
- claustrophobia;
- dyspnea;
- general serious condition.

But sometimes even pregnancy, which is a contraindication for almost all types of diagnostics, does not become an obstacle to the procedure. It should be done only after preliminary consultation with your doctor. Control must be carried out by a specialist throughout the entire manipulation.
An important factor in the success of diagnosis and safety for the baby is scheduling an appointment no earlier than the fetus is 25 weeks old. During this period, he will have time to form basic systems. You also need to take care to find in advance a special lead apron that will cover your stomach from increased background radiation.
The reasons for “photographing” the respiratory system of pregnant women and women during the breastfeeding period should be as compelling as possible. As an argument, conventional prevention will not work.
What documents determine the obligation to undergo a fluorographic examination?
The obligation of students and workers to undergo fluorographic examination is due to the need to ensure sanitary and epidemiological well-being, including on the territory of St. Petersburg Electrotechnical University "LETI", and is regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- Law of the Russian Federation dated November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ (as amended on May 29, 2019) “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation”,
- Federal Law No. 52-FZ of March 30, 1999 (as amended on July 26, 2019) “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population,”
- Federal Law No. 77-FZ dated June 18, 2001 (as amended on August 3, 2018) “On preventing the spread of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation”,
- By order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2017. No. 124n “On approval of the procedure and timing of preventive medical examinations of citizens in order to detect tuberculosis”,
- Appendix No. 12 to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 109 dated March 21, 2003 (as amended on June 5, 2017) “On improving anti-tuberculosis measures in the Russian Federation”,
- Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated October 22, 2013 No. 60 (as amended on 02/06/15) “On approval of sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 3.1.2.3114-13” “Prevention of tuberculosis”,
- By order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011. No. 302n “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) dangerous production factors and work, during the performance of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the procedure for conducting mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers engaged in heavy work and at work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions” (clause 18 of Appendix 2).
- Order No. OD/0220 dated April 26, 2019 “On the organization of fluorographic examination of students and workers at St. Petersburg Electrotechnical University “LETI””