What are ALT and AST
Aminotransferases (transaminases) are intracellular enzyme structures that accelerate transamination reactions.
The transamination reaction is the transfer of an amino group (NH2) from an amino acid to a fat metabolism product - a keto acid. As a result, a new amino acid is formed, synthesized directly in the human body, and a-keto acid. Vitamin B6 activates this process.
Transaminases are present in every cell of the human body; when the integrity of cellular structures is damaged, these enzymes enter the blood. Normally, aminotransferases are contained in the blood due to the presence of programmed cell death - apoptosis. This is the norm. However, with massive cell death and the release of a large number of enzymes, the indicators of biochemical research change; they can be exceeded tens of times, depending on the type of pathology and the size of the defect.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, AlAT) is an intracellular enzyme involved in the metabolism of the nonessential amino acid alanine. A substance such as alanine is found in high concentrations in hepatocytes - the structural cells of the liver; in lower concentrations they can be found in the cells of the myocardium and kidney tissue.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AST) is an enzyme localized in the Golgi complex and mitochondria, taking part in the breakdown of the non-essential amino acid - asparagine, by hydrolysis of the amide group, forming oxaloacetate, which participates in the Krebs cycle. This aminotransferase predominates in myocardial cells, liver - hepatocytes, and the central nervous system.
AST is an indicator of disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle. ALT is a hepatocellular enzyme that indicates a disruption in the functioning of hepatocytes and the hepato-biliary tract in general.
The presented types of analyzes are prescribed in the following situations:
- jaundice (jaundice staining of the sclera, mucous membranes, skin);
- dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, bowel dysfunction);
- stool discoloration;
- darkening of urine;
- the appearance of white foam in the urine;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- skin itching;
- the appearance of spider veins on the skin;
- hair loss, fragility, dullness of hair;
- “liver palms” – bright yellow, copper coloring of the skin of the palms and soles;
- the appearance of an unusual unpleasant smell of “baked apples”.
Deciphering the ALT analysis
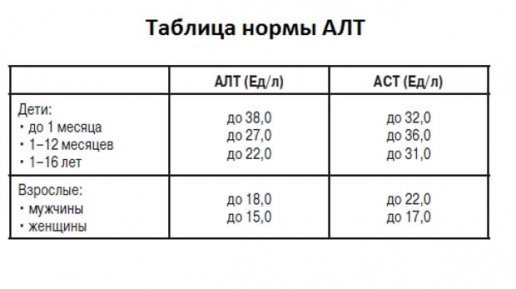
Alanine aminotransferase reference values for adults:
| Norm in U/l | Norm in mmol/l | |
| men | 45 | 252 |
| women | 34 | ≈ 190 |
WHY IS ALT LEVEL DETERMINED?
ALT is an enzyme of the transaminase group, present in a certain amount in the cells of the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system. Determining the concentration of this substance allows you to get an idea of the condition of the liver and heart, as well as the effectiveness and safety of the treatment. The basic indication for diagnosis is the suspicion of liver disease, cirrhosis, viral or toxic hepatitis (chronic and acute). Also, a blood test for ALT allows for the timely detection of malignant primary or secondary metastatic liver lesions.
An increase in the level of the above enzyme in various types of hepatitis manifests itself much earlier than the pathology progresses to the icteric stage. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to timely diagnose the disease at the initial stage of its development and begin treatment, which can significantly increase the survival rate of patients with this diagnosis.
The analysis is part of standard screening diagnostics, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s liver condition. The study is also carried out as part of preparation before planned hospitalization for surgical intervention. Often the analysis is prescribed in combination with an analysis of aspartate aminotransferase levels.
To assess the health status of a patient suffering from diseases of the pancreas (diabetes, pancreatitis, etc.) and gall bladder (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, etc.), determining the level of ALT is also necessary, as is identifying the amount of other enzymes. Diagnosis is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician, in the presence of objective indications - general weakness of unknown origin, fatigue, icteric coloration of the skin and sclera, vomiting, nausea, pain and heaviness in the abdomen and right hypochondrium.
In addition, identifying the level of this enzyme is included in the standard diagnostic protocol for diseases of the cardiovascular system, especially when examining patients with suspected myocardial infarction or myocarditis. In case of organic lesions of the heart muscle, determining the level of ALT is not of paramount importance. Diagnosis is carried out if the patient is suspected of having myositis, muscular dystrophy and pain in the heart, which cannot be explained by excessive physical activity or any other objective reason.
All donors without exception undergo diagnostic testing of ALT levels. The concentration of this enzyme is necessarily assessed in the presence of certain types of chronic pathologies and before prescribing hepatotoxic drugs (antirheumatic, anticancer, antituberculosis and antimicrobial), as well as to monitor the liver condition during their use.
Preparing for analysis
In preparation for the analysis, perform the following manipulations:
- 3 days before the proposed study, you should stop drinking alcohol and cigarettes;
- 2 days before donating blood, refrain from eating fatty and fried foods;
- notify the attending physician about all medications taken in the last 10 days, if possible, stop taking medications 10 days before donating blood;
- reduce physical activity a week before the test;
- the last meal should be no later than 19:00 (light dinner);
- In the morning you are allowed to drink a glass of water and brush your teeth.
Decoding the results
When deciphering the results, you need to focus on the data presented in the table.
| Excess ALT up to 20 times AST up to 4 times | Acute hepatitis, cirrhosis in the decay stage, acute alcohol intoxication |
| ALT is 4 times higher than AST is 10 times higher | Acute myocardial infarction |
| AST exceeds the norm by 2 or more times | Myocarditis or myositis |
| ALT + free bilirubin | Other liver pathologies (fibrosis, cholangitis, cholecystitis), acute pancreatitis |
The degree of hepatitis activity is also determined.
| Minimum | increase in indicators to 3 norms |
| Mild | from 3 to 5 norms |
| Moderately expressed | from 5 to 10 norms |
| Sharply expressed | ≥ 10 norms |
If ALT and AST are performed for acute hepatitis, it is possible to determine which group it belongs to:
- acute viral hepatitis A (severe clinical form) – increase in indicators to 2000-3000 IU/l;
- acute viral hepatitis B (moderate degree of activity) – increase in indicators to 500 IU/l;
- acute hepatitis C (asymptomatic) – transaminase levels within 200 IU/l;
- alcoholic hepatitis (erased course) – up to 150-180 IU/l.
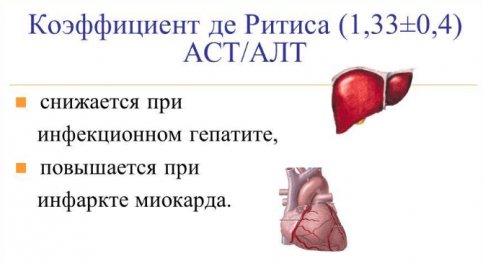
The ratio of AST to ALT is called the de Ritis coefficient and is AST/ALT = 1.33 ± 0.42.
The following indicators are distinguished:
- >2 – means damage to cardiomyocytes; the most common cause is acute myocardial infarction, necrosis of the heart wall;
- <1 – indicates acute liver damage.
| KDR < 1 | Acute hepatitis |
| KDR > 1 | Fatty hepatosis |
| KDR ≥2 | Myocardial infarction |
| KDR >1.8 | Myocarditis |
Differential diagnosis of chronic hepatitis
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis C | |||
| Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| Age | Up to 30 | Up to 30 | ||
| ALT U/l | 88,0 | 112,0 | 102,0 | 102,0 |
| Age | Up to 60 | Up to 60 | ||
| ALT U/l | 91,0 | 96,0 | 99,0 | 96,0 |
| Age | Over 60 | Over 60 | ||
| ALT U/l | 88,0 | 74,0 | 90,0 | 92,0 |
Suspicions of possible hepatitis C infection may be caused by elevated levels of liver enzymes - AST and ALT. Their increase indicates a disease of the organ, and measurement data indicates the degree of its damage. Patients diagnosed with hepatitis C need to monitor the level of these liver enzymes twice a year. At high levels, it is recommended to take medications. Otherwise, the enzymes will return to normal if the underlying pathology is excluded, after undergoing antiviral therapy.
What is the normal range of AST and ALT in a healthy person?
ALT and AST are aspartate aminotransferase and aminotransferase found in the liver, heart and kidneys. If these enzymes increase, gastroenetrologists recommend undergoing a comprehensive liver examination. Although high rates may also indicate diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Normal enzyme levels in a healthy person are as follows:
- men – up to 41 U/L ALT and 37 U/L AST;
- women – up to 31 U/L ALT and 30 U/L AST.
If laboratory blood tests show exceeding the specified limits, they must be retaken and undergo further examination.
Diseases affecting the growth of ALT and AST:
- cirrhosis;
- necrosis;
- hepatitis C and others;
- pancreatitis;
- myocarditis;
- mononucleosis;
- benign tumors.
An increase in transminase activity is also observed with alcohol abuse, lead poisoning, psychological stress, drug use, and chemotherapy given to patients.
Hepatitis C and transminases - the relationship
Transminases in hepatitis C remain within normal limits for a long time. Enzyme activity usually appears 5-10 years after infection. Hepatitis C can be suspected based on transminases based on the de Ritis coefficient - the ratio of ALT and AST. If ALT is increased by more than 1.33 times, then we are talking about hepatitis, but if AST is increased, then most likely the reason lies in the cardiovascular system.
The activity of transminases during HCV infection occurs in waves, two weeks after infection, after 1.5 months, after which the indicators return to normal and appear years later. If, however, the patient is diagnosed with hepatitis C and laboratory tests show an excess of AST relative to ALT, it is necessary to additionally test tumor markers, since the situation signals a possible tumor.
What is worth knowing about transminases is that with hepatitis C they are elevated in 100% of cases.
How to prepare for the test and in what cases is it necessary to take it?
A biochemical blood test with data on ALT and AST must be taken if the following symptoms occur:
- yellowness of the skin of the sclera;
- diarrhea;
- discomfort in the liver area;
- frequent belching.
Blood for this test is given in the morning on an empty stomach. The sampling is carried out from a vein, since it is venous blood that shows reliable data. Before taking the test, you must abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages for at least a week.

The laboratory must provide a list of medications that were taken the day before.
What to do if ALT and AST are increased?
Of course, patients with elevated transminases are interested in the question of how to achieve a decrease in activity. In fact, normal indicators are possible if the underlying pathology is excluded - hepatitis C. The disease can be cured based on treatment protocols with innovative antiviral drugs - Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir, Ledipasvir, Velpatasvir, you can buy them on our website.
If therapy is postponed indefinitely for a number of reasons, then diet therapy will help reduce enzyme activity. Fatty and protein foods are contraindicated; it is not recommended to consume onions, garlic, sparkling water, chocolate, marinades and baked goods, and coffee. The diet should consist of fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals, lean fish and varieties of meat.
In addition to diet therapy, healthy sleep, walks in the fresh air, and a positive psychological attitude will help correct ALT and AST. It will not be superfluous to take immunomodulators.
Normal indicators
The following indicators of test norms are distinguished depending on age.
| ALT(U/l) | ALS(U/l) | |
| up to 1 month | 38,0 | 32,0 |
| 1-12 months | 27,0 | 36,0 |
| 1-14 years | 20,0 | 34,0 |
| 15-18 years old | 22,0 | 31,0 |
| Men | 18,0 | 22,0 |
| Women | 15,0 | 17,0 |
Reasons for deviations
A decrease in indicators can be caused by the following pathologies:
- Hepatitis. Acute viral (herpesvirus, cytomegalovirus, A, B, C, E). Chronic viral (B, C, co- and superinfection of hepatitis D). Toxic, alcoholic, medicinal, iatrogenic. Autoimmune. Steatohepatitis.
- Oncological liver diseases (primary, secondary nodular cancer, leiomyosarcoma, liver fibrosarcoma).
- Cirrhosis and fibrosis of the liver.
- Cholangitis, cholestasis, choledocholithiasis, cholecystitis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Wilson-Konovalov disease.
- Alcohol or drug intoxication.
- Taking anabolic steroids.
An increase in ALT and AST levels can be caused by the presence of the following diseases:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- cardiogenic shock;
- myocarditis;
- crash syndrome;
- myositis;
- acute pancreatitis.
For further choice of tactics and differential diagnosis, biochemical indicators such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), total cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), total protein, alpha globulins, gamma globulins, conjugated bilirubin, free bilirubin, protein-sedimentary tests - thymol and sublimate.
In addition to biochemistry, it is necessary to take a clinical blood test (BAT), a coprogram.
Thymol test (MacLagan test) is a reaction between the thymol reagent and substances synthesized by the liver (alpha and gamma globulins, total protein, lipoproteins). An increase in values above normal (0-4 UDS-H) indicates a violation of the synthetic function of the liver.
Sublimate test (Takata-Ara reaction) - mercuric chloride and sodium carbonate are added to blood serum, causing a flocculation reaction. Normally, a colloidal solution is formed; in pathology, coarse particles are deposited.

The most important indicator of the presence of hepatitis is the exchange of bilirubin. In “biochemistry” it is reflected in the form of indicators of unconjugated, conjugated and total bilirubin.
| Normal values | Pathology | |
| Total bilirubin | 1,7-17,1 | 18,0-35,5 |
| Direct bilirubin | up to 3.5 | 3,6-15,2 |
| Indirect bilirubin | 1,7-12,7 | 12,8-86,7 |
| Urine bilirubin and urobilin | – | ++ |
| Stercobilin | + | – |
In children, bilirubin levels are slightly different from those in adults.
| General | Connected | Free | |
| Newborn | 23,09 | 8,72 | 14,37 |
| 2 days | 54,22 | 8,72 | 45,5 |
| 4 days | 90,1 | 7,87 | 82,2 |
| 6 days | 69,0 | 7,72 | 63,2 |
| 9 days | 53,0 | 8,72 | 44,3 |
Laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis C
Blood tests can be specific and nonspecific. The first group of analyzes includes ELISA and PCR. They make it possible to assess the level of antibodies, detect virus antigens, and also identify the genetic material of the pathogen.
As for the second group of studies, it includes biochemistry, which includes the following indicators:
- transaminases. An increase in ALT and AST in hepatitis C is observed due to the destruction of liver cells, after which the enzymes are released into the blood. These indicators allow one to suspect the disease at a preclinical stage;
- gemma-glutamyltransferase – is involved in the transfer of amino acids. The enzyme is localized in the pancreas, liver and renal tissues. Due to physiological cell death, it is present in the blood in a small volume. Its high level indicates massive tissue death;
- bilirubin (total, fractions) is a product of hemoglobin conversion. It circulates in the blood in an indirect form, which, after entering the liver, becomes bound;
- alkaline phosphatase – participates in hydrolysis. The enzyme is found in the liver, bone structures and intestines. Its moderately elevated level is considered normal for children, due to their rapid growth.
What can distort the results of the study?
Polypharmacy and uncontrolled use of antibiotics, antimycotics, antivirals, drugs that lower plasma glucose levels (sulfonylurea), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorol, Spazmalgon, Nimesulide, Paracetamol), Heparin.
The results are also affected by taking echinacea as a dietary supplement, recent heart surgery, and the onset of allergies.
It is not recommended to combine such studies as:
- fluorography;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- plain radiography of the chest and abdominal cavities;
- introduction of radiopaque substances and radioisotopes;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis).
Low levels of aminotransferases in a biochemical study of the patient’s blood plasma may indicate a deficiency of vitamin B-B6 (pyridoxine). This vitamin is involved in the metabolism of microelements, neurotransmitters, and the synthesis of the oxygen carrier protein - hemoglobin.
Transamination rates in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the need for many nutrients increases significantly, including B vitamins. For the physiological formation of the biliary tract of the fetus, pyridoxine is required 3 times more. Therefore, in pregnant women, especially in the second trimester, these indicators are reduced.

An increase in these indicators often indicates the development of a severe complication of pregnancy - gestosis. This requires urgent contact with your doctor.
Prevention of pathological changes
The following points will help prevent deviations from the norm in the described tests:
- Healthy lifestyle. No bad habits (alcohol, smoking), emotional stress.
- Culture of sexual behavior (minimum number of sexual partners, protection with barrier contraceptives).
- Since viral hepatitis B, C, D can be infected through blood contact, use the services of only trusted tattoo, manicure, and piercing artists.
- Annual visits to such specialists as a gastroenterologist, therapist, hepatologist, taking a biochemical blood test during a preventive examination.
Diet for increased ALT and AST
It is necessary to refrain from eating excessively sweet, salty foods, fried, fatty and smoked foods.

Priority is given to boiled chicken, rabbit, turkey meat, lean beef, and beef liver. Buckwheat, lentils, and beans are recommended as a side dish. You can use walnuts as snacks.
Medicines that improve liver function
The mechanism of action of such drugs is based on strengthening the cell membrane - the hepatocyte. They also improve the functional abilities of transaminases.
Common medications include the following:
- Essential phospholipids (Essentiale, Phosphogliv).
- Plant flavonoids (Legalon, Karsil).
- Amino acid derivatives (Heptor, Hepasol).
- Preparations of ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodex, Urso-100).
- Corn silk.
- Vitamins of group B, E.
Thus, changes in alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels in a biochemical study of human blood may indicate many different pathologies. Only a highly qualified doctor can cope with their differential diagnosis. You should not self-medicate; if elevated levels of ALT and AST are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why does ALT increase with hepatitis C?
ALT are protein compounds that participate in the metabolism of amino acids and are synthesized in the cells of the liver and other organs. They are also present in the blood, but in minimal quantities. This is considered the norm. They get there when cells die due to natural aging. The average for men should not exceed 37 units per liter, for women - 31 units/l.
Hepatitis C massively destroys liver cells, which promotes the release of proteins and, consequently, an increase in their levels in the blood. Biochemical analysis is based on determining such changes. The biomaterial is taken from a vein, and this procedure takes no more than two minutes. The injection site should be sealed to prevent infection. The results will be ready the next day.
Together with ALT, biochemistry determines the AST index, which also increases when liver cells are damaged. But most of these proteins are synthesized in myocardial cells, so if their level is twice as high as ALT, then there are heart problems.
During the development of hepatitis C, ALT and AST levels may rise and fall several times. Elevated protein levels are first observed at the end of the incubation period, which lasts on average 6-12 weeks. The second rise begins simultaneously with the appearance of the first symptoms of hepatitis C (nausea, fatigue, weakness, pain under the right rib, etc.). Depending on the state of the immune system, this can happen in two months, or maybe in six months. After this, ups and downs will be observed more than once.
During peak periods, ALT levels are 5-10 times higher than normal values. However, timely treatment of hepatitis C with the use of direct-acting antiviral drugs - Sofosbuvir, Ledipasvir, Daclatasvir - can bring these indicators back to normal in 3-4 months.
To reduce the level of ALT and AST in hepatitis C, you will have to adjust your diet. Limit intake of sour, spicy, fried, smoked, salty, fatty and sweet foods. Add boiled chicken, turkey, rabbit meat, lean beef or beef liver to the menu. We recommend porridge cooked in low-fat milk or water, as well as fresh fruits and vegetables.
Some patients will have to reconsider their usual lifestyle:
- Rest more and sleep at least 8 hours a day so that the body recovers faster.
- Be less irritated, nervous, and conflict.
- Walk more.
Sometimes, to reduce the concentration of liver enzymes in the blood, vitamin therapy is carried out or drugs are prescribed that improve the functioning of the immune system.