Laboratory diagnosis of liver diseases. Tests for liver cirrhosis and fibrosis.
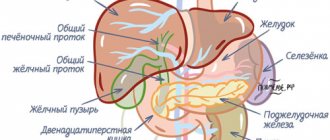
The liver is the largest gland and at the same time the “filter” of our body.
She is the first to react to poor nutrition, alcohol abuse and other unreasonable stress on our body. Diseases such as cirrhosis and liver fibrosis are among the most common diseases today, and liver cancer causes the death of more than a million people every year and is in the top ten tumors affecting humans. Diagnosis of liver diseases today is carried out using invasive and non-invasive methods.
Invasive methods for diagnosing liver diseases include puncture biopsy - a method in which liver cells or tissues are taken, followed by microscopic examination to determine the nature of the pathological process. The frequency of complications during liver biopsy, according to world literature, is 0.06-2%.
Due to the invasiveness, the rather large error of histological (microscopic) examination associated with “mistakes” of the needle during liver biopsy, the difference in the interpretation of results (subjectivity of assessment), for the early diagnosis of pathological processes, much attention is paid to non-invasive methods for diagnosing liver diseases.
Symptoms of liver disease
The main symptoms of liver disease are:
- weakness, malaise;
- muscle disease, especially in the right hypochondrium;
- skin rashes;
- dark urine, light stool;
- jaundice and intense itching;
- bitterness in the mouth.
But very often serious liver diseases are asymptomatic. One of them is liver cancer. In the early stages, liver cancer does not cause pain syndromes. The liver itself cannot hurt; it has no pain receptors. If a person begins to feel pain in the liver area, this indicates an advanced stage of cancer, when the liver enlarges and begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, causing pain.
FibroMetr® System
The FibroMetr® system is a non-invasive method for diagnosing liver diseases (using a blood test) and is characterized by high diagnostic efficiency. The method allows you to assess the severity of inflammation, the stage of fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver.
FibroMetr® can be successfully used for preventive examination, diagnosis of disease, dynamic observation and control of therapy. In some cases, diagnosing liver diseases using the FibroMetr® system may be an alternative to performing a needle biopsy of the liver.
You can undergo a comprehensive diagnosis of liver diseases using the unique FibroMetr® system (BioLiveScale, France) in the CMD laboratory.
Who treats and what tests need to be taken
Many people do not know which specialist to contact if they suspect a pathology of this organ. If you have complaints and symptoms, you should contact a therapist who will prescribe basic tests and instrumental studies.
This pathology is treated by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. If the disease has an infectious etiology, then the patient is treated by an infectious disease specialist. If cancer is diagnosed, the oncologist takes over the treatment. Depending on the nature of the disease, its course and complications, consultation with other specialists may be required.
The required minimum of tests and studies to assess the functioning of the gland are:
- Complete blood count - anemia can often be observed,
- General and biochemical urine analysis - albumin, bilirubin, urobilinogen,
- Biochemical screening: AST and ALT – an indicator of liver cell death. The more this indicator exceeds the norm, the more hepatocytes are destroyed,
- Bilirubin is a component of bile, which, in case of organ pathology, enters the bloodstream as a result of the destruction of hepatocytes, which gives the skin a yellow color,
- Prothrombin index is an indicator of blood clotting, which decreases with liver failure,
- Proteinogram – to assess blood protein levels,
If a more detailed diagnosis is necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional studies:
- Biopsy - allows you to identify abnormalities at the cellular level of the lesion. Rarely used due to the risk of complications.
- MRI is the safest and most painless procedure that allows you to study the structure of an organ in detail.
Liver fibrosis
Liver fibrosis is a disease characterized by the growth of connective (hard fibrous, scar) tissue in the liver without changing its structure. This is the main pathway for the progression of chronic liver diseases. The liver lobules themselves are not changed, but wide strands of fibrous connective tissue appear around them. Scar formation is a normal reaction of the body to injury, however, with liver fibrosis, the tissue healing process is disrupted and the liver begins to function less well. Unlike cirrhosis, liver fibrosis is not characterized by necrosis (death) of liver cells – hepatocytes.
The occurrence of liver fibrosis is promoted by: alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, exposure to toxins (arsenic, iron, copper), and taking certain medications. It is liver fibrosis that causes the formation of liver cirrhosis, so early diagnosis of liver fibrosis and the prescription of effective treatment are extremely important.
For a long time, liver fibrosis was considered an irreversible pathological condition. However, advances in medicine have led to the understanding that liver fibrosis is reversible, and effective antifibrotic therapy can provide a favorable prognosis even in cases where cirrhosis has already developed. To assess liver function and prescribe the necessary treatment, it is necessary to promptly diagnose liver diseases.
Need for screening
“Screening” is the name given to a diagnostic program that is comprehensive and aimed at large-scale examination of people for the purpose of early diagnosis of various diseases, most of which develop without any symptoms.
A liver screening program is very important for individuals at risk. This group includes people:
- Overweight;
- Not eating rationally;
- Alcohol abusers;
- Taking medications that are toxic to the organ for a long period of time;
- Working in hazardous production conditions.
It would not be superfluous for pregnant women to undergo diagnostics, because their body is subject to increased stress during gestation.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic progressive liver disease characterized by the irreversible replacement of parenchymal liver tissue with fibrous connective tissue and the formation of a special nodular anatomical structure of the liver. The liver lobules are completely surrounded by strands of connective tissue, and their functional activity is significantly reduced. In response to this, enhanced pathological regeneration of hepatocytes begins. As a result, a special nodular structure of liver tissue is formed.
The process of formation of nodes is accompanied by a change in the vascular system of the liver with the creation of blood flow paths that bypass the liver cell complexes. The nodular type of liver tissue structure over time completely displaces its normal, homogeneous lobular structure. The nodules also compress blood vessels, bile ducts, and remaining normal liver tissue, causing inflammatory reactions and further progression of liver fibrosis. The result of these processes is the development of varying degrees of liver failure. The formation of liver cirrhosis occurs over many months or years.
The causes of liver cirrhosis are alcoholism (in different countries from 20 to 95%), viral hepatitis (10-40%), the presence of helminths and protozoa (Trichomonas) in the liver. Liver cirrhosis is more common in men than in women (3:1). In approximately 10-35% of patients the cause remains unclear. In the CIS countries, cirrhosis of the liver occurs in 1% of the population.
A special form of liver disease is primary biliary cirrhosis, in which the inflammatory process initially affects the smallest intrahepatic bile ducts, and only then spreads to liver cells, causing their damage and replacement with connective tissue. The causes of the disease are unknown. Genetic factors that cause immunoregulation disorders play a certain role. Mostly women aged 35-60 years suffer from biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
Liver cleansing foods
The liver also has helpers. Here are a few foods whose reasonable consumption will help make life easier for liver cells:
- Persimmons contain large amounts of sugar and fiber. The liver stores sugar in the form of glycogen - an energy material in reserve. And the coarse fibers of persimmon do not allow the absorption of up to 10-15% of fats and thereby reduce the toxic load on the liver.
- Daily consumption of garlic in small doses lowers cholesterol levels, which can interfere with the liver's ability to function. Garlic also stimulates the formation of certain enzymatic substances that help better cleanse the blood of toxic residues.
- Goji berries (barberry) help our body remove excess fat without accumulating it in the liver. In a situation of fatty liver disease, the substances contained in goji berries remove excess fat from the liver cells.
- Buckwheat contains a complex of plant substances that are also capable of removing fat from liver cells.
- Pumpkin contains carotene, which again helps to better absorb fatty foods, which means it makes life easier for the liver.
- Turmeric can act as a natural cleanser of liver cells, thereby stopping the process of scarring of liver tissue and stimulating the process of repair and new birth of healthy cells. It also does a good job as an antioxidant.
Why is liver elastometry necessary?
Examination of the liver using the Fibroscan device allows you to reliably determine the degree of liver damage, namely the degree of fibrosis and the degree of fatty hepatosis, without surgical intervention. The obtained data on the condition of the patient’s liver allows the hepatologist to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the correct treatment tactics, or, if necessary, adjust previously prescribed treatment. The sooner an accurate diagnosis is made and proper treatment is started, the higher the chance of maintaining a healthy liver.
What is elastometry or liver elastography?
Elastometry (elasthoraphy) or, as it is also called, liver fibroscanning
is a modern, non-invasive, non-surgical method for diagnosing the degree of fibrosis and the degree of fatty hepatosis, liver steatosis.
Unlike a biopsy, elastometry (elastography) of the liver allows you to study the entire organ, rather than a single fragment, which ensures high reliability of the results of the examination using the elastometry method. Liver elastometry - examination prices:
- Degree of fibrosis
3,500 rubles
- Degree of fatty hepatosis
2,500 rubles
- Consultation on results
for free!
on PROMOTION! (Moscow, Park Kultury metro station)
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back