Don't wait for a second wind. Breathe first!
My son, like many allergy sufferers, is at risk of developing bronchial asthma, so he was introduced to the unpronounceable peak flow meter at the age of 4.
Peak flowmetry, along with the measurement of exhaled nitric oxide, is considered the main method of asthma control, according to the scientific committee of GINA (Global Strategy for the Treatment and Prevention of Asthma).
The international GINA program has been operating since 1993, and involves leading asthma experts from around the world.
Why is the research being conducted?
Bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease require constant monitoring. With the help of peak flowmetry, you can monitor yourself without visiting a clinic. If respiratory function is impaired, the patient will be able to independently change the dose of medications.
Peak expiratory flow allows you to assess the functioning of the bronchi and timely notice the narrowing of their lumen. The larger it is, the easier it is for air to penetrate the bronchi. Goals for performing peak flow measurements:
- identification of a tendency to asthma, including occupational asthma,
- determining the reversibility of respiratory tract obstruction,
- identifying the degree of bronchial disorder,
- selection and adjustment of medication dosage,
- establishing the causes of bronchospasms: manipulation is carried out after the influence of provoking factors, for example, dust, pollen, chemicals.
Peak flowmetry tasks
The breadth of possibilities of the method has led to almost one hundred percent use of it by people suffering from various types of obstructions. The main objectives of the survey are:
- planning therapy for bronchial asthma - a plan for changes in PEF throughout the day created by a specialist will allow the patient to monitor his condition and adjust his medication intake;
- assessing the effectiveness of prescribed therapy with bronchodilators and inhalers using PEF testing before and after taking medications;
- control of bronchial hyperactivity - a decrease in morning PEF by more than 20%, which indicates the adequacy of the prescribed treatment.
In addition to the main tasks, the examination is recommended:
Bronchoscopy of the lungs
- to determine the degree of obstruction, which indicates the severity of asthma or COPD;
- identifying the causes leading to bronchospasm (domestic irritants or during professional activities);
- assessing the course of the disease in the patient’s usual environment (changes in obstruction throughout the day, after taking medications, at home and at work);
- making a forecast for the development of an exacerbation (a decrease in bronchial patency indicates an approaching deterioration of the asthmatic’s condition);
- determining the moment to change therapy to the most effective one (the appearance of a deterioration in the condition, the onset of an exacerbation);
- identifying addiction or disease progression during long-term therapy with the same drugs.
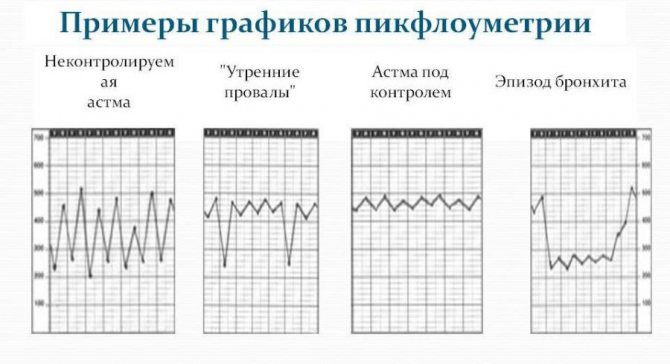
Examples of pathological conditions, to control the course of which diagnostics are carried out
The method is often used as a screening method to determine the presence of asthma when it is not possible to prescribe spirography (measurement of lung volume). It also allows you to determine the reversibility of obstruction and monitor the response to new medications prescribed for exacerbation.
What is the device and types of peak flow meters

A peak flow meter is a device for assessing the condition of the bronchi. It is a small tube that fits easily in your hand. The device has a scale divided into three zones: red, yellow and green. The simplicity of the tool allows the patient to determine his condition without a doctor.
The appearance, price and measurement accuracy of peak flow meters from different manufacturers may vary. And therefore you need to use one device. Fluctuations in the readings of different peak flow meters reach up to 15%, which can make it difficult to assess the patient’s condition.
Basic recommendations
To qualitatively assess the degree of bronchospasm in each patient, PEF should be measured after appropriate consultation with a physician. The doctor explains to the person all the nuances of the procedure and features that are worth paying attention to.
Basic recommendations:
- It is recommended that each patient purchase an individual peak flow meter for independent assessment of the condition of the bronchi at home;
- Perform the procedure three times at a time. The patient should exhale sharply into the tube three times. Between exhalations you need to take short pauses (up to 2 minutes);
- At least 2 measurements must be taken per day - in the morning and before bedtime;
- If there are significant changes in the function of the respiratory system, it is necessary to consult a doctor for possible correction of therapy.
Peak flowmetry for bronchial asthma, which allows you to correctly respond to changes in the patient’s condition. The key factor is the possibility of timely correction of drug treatment.
How to use the device correctly
Before the first manipulation, the doctor must explain to the patient how to take measurements correctly. Peak flowmetry does not require any preparation; you just need to relax and breathe as freely as possible.
After purchasing the device, there is no need to configure it - the device is immediately ready for use. Once every 2-3 weeks the device should be washed in warm boiled water. Each patient should become familiar with the following basic principles:
- When used for the first time, the peak flow meter is disinfected; in the future, if it is used by one person, the surface must be wiped,
- the device must be parallel to the floor, and the position of the slider must always be at the beginning of the scale,
- Diagnostics can be carried out standing or sitting,
- Each result is recorded in a measurement diary.
The main thing is to perform the manipulation correctly. The patient should tightly clasp the tube with his lips and exhale sharply. During the examination, there is no need to cover the hole with your tongue.
Algorithm for performing peak flowmetry
The algorithm for performing peak flowmetry is very simple:
- In the morning after waking up, take the first measurement of PEF, according to the method of using the device described above;
- Spend a normal day;
- In the evening before going to bed, repeat the procedures and note the results in a special diary.
No special preparation is required for peak flowmetry. Before the procedure, it is recommended to relax and rest for 5-10 minutes to stabilize breathing.
How to correctly evaluate the results obtained
To determine your condition, you need to know the decoding of the indicators:
- PEF (peak expiratory flow) more than 90% - the condition is satisfactory, does not require adjustment of therapy or contact a doctor;
- PEF at the level of 80 - 89% - additional therapy is not prescribed, but the patient should monitor his health more often;
- PEF 50 - 79% - intensification of treatment is required;
- PEF is less than 50% - there is a severe deterioration in the condition, a doctor’s consultation with further hospitalization is necessary.
These are standard norms; the doctor will tell each patient how to evaluate the results at the appointment.
What is peak flowmetry?
Peak flowmetry is one of the popular and accessible methods for diagnosing the functional characteristics of the human bronchopulmonary system. The procedure allows you to set the value of peak expiratory flow (PEF), an indicator that reflects the presence or absence of airway spasm.
Carrying out the corresponding measurement involves the use of a specialized device - a peak flow meter. The purpose of such a diagnosis is to determine the severity of bronchospasm at home or in a hospital setting. At the same time, the effectiveness of therapeutic measures is assessed.

Fact! Peak flowmetry for patients with asthma and COPD is as important as measuring blood pressure for hypertensive patients or determining the amount of blood sugar for diabetics. Using this procedure, it is possible to timely adjust the dosage of appropriate medications and prevent the worsening of the patient’s condition.
PSV norm indicators
The normal peak flow rate in adults is determined individually: it depends on weight, height, age and the presence of additional diseases. Certain standards have been described above, which are advisory in nature and can be adjusted.
To identify the norms of PEF in a patient, he must be examined for 3 weeks. To determine optimal indicators, measurements are taken during the period of remission, when respiratory function is not impaired. Every day you need to make a schedule with minimum and maximum indicators.
Green Zone
These values indicate a satisfactory condition. To determine the optimal indicator, you need to multiply the maximum value of NSV for 21 days by 0.8. For example, the highest indicator was 430 l/min, the result will be 344 l/min. All human values above this mark will be in the green zone and indicate the norm.
Yellow zone
When the reading enters the yellow zone, it indicates deterioration of the condition and the need for enhanced therapy and close monitoring. To determine an individual parameter, you need to multiply the maximum value by 0.5. If we take the previous indicator as a basis, the result will be 215 l/min. That is, all values in the interval 215‒344 will be in the yellow zone.
Red zone
The red zone is the most dangerous for the patient; it means a deterioration in a person’s respiratory function when a doctor’s help is required. This zone includes all values below the yellow mark. According to the parameters described above, patients with a value of 215 and below will be at risk.
Peak flowmetry norms
According to GINA 2018
Peak flow meter zones are marked with colored markers, similar to a traffic light: green, yellow, red.
Green zone (80-100% of the norm) – everything is fine. Everything's under control. Normal lung condition.
Yellow zone (50 – 80% of normal) – attention. Warning of deterioration of condition. Analyze the diary indicators and be sure to consult a doctor - you need to find the reason for the deterioration of the condition.
Red zone (less than 50% of the norm) – danger! You must immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Interestingly, bronchial patency changes throughout the day. Fluctuations in patency in healthy children should not change by more than 15% of normal. 20% of the norm – in children with bronchial asthma in remission.
Peak flow measurements in children
Norms for children under 15 years of age depend on their height. The manipulation is indicated for patients over 4 years of age; infants cannot exhale correctly, which will not allow them to control their condition.
For the study, mini peak flow meters are used, which record values in the range of 30 – 370 l/min.
Normal peak flow readings for children:
| Height, cm | 91 | 99 | 107 | 114 | 122 | 130 | 137 | 145 | 152 | 160 | 168 | 175 |
| Indicator, l/min. | 100 | 120 | 140 | 170 | 210 | 250 | 285 | 325 | 360 | 400 | 440 | 480 |
How to evaluate results
Test results will depend on age, gender, weight and height. You cannot expect the same results from a young athlete and an elderly couch potato.
The generally accepted table for assessing peak flowmetry data compares indicators only by height, which is not entirely correct. Therefore, do not chase the results according to the table; remember that the results depend on many factors.
For example, some children can inflate a balloon at 2 years old, while others find it difficult to cope with this task even at 7 years old. It is important to understand which numbers are optimal for your baby.
Table of approximate norms of peak flowmetry in children depending on height
| height (m) | result (L/min) | height (m) | result (L/min) |
| 0.85 | 87 | 1.30 | 212 |
| 0.90 | 95 | 1.35 | 233 |
| 0.95 | 104 | 1.40 | 254 |
| 1.00 | 115 | 1.45 | 276 |
| 1.05 | 127 | 1.50 | 299 |
| 1.10 | 141 | 1.55 | 323 |
| 1.15 | 157 | 1.60 | 346 |
| 1.20 | 174 | 1.65 | 370 |
| 1.25 | 192 | 1.70 | 393 |
Explanations for the table
First, you need to find out what exhalation parameters will be normal for your child. The norm is determined when the child is healthy and there are no exacerbations of the disease.
Let's say your child's expiratory rate (EF) is 200 l/min. This means that indicators of at least 160 l/min will be a green zone for him (up to 80% of his norm).
If the exhalation rate is in the range from 100 to 160 l/min. – this is the yellow zone (below 80% of normal).
Indicators are less than 100 l/min. (less than 50% of the norm) is the red zone. You need to see a doctor urgently.
Diary and peak flow graph
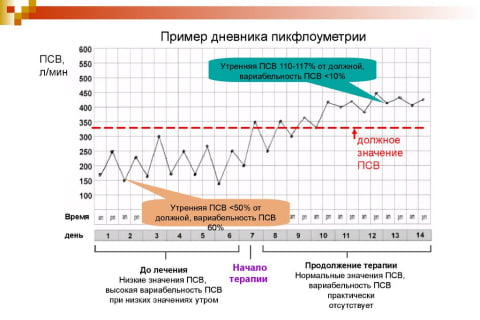
The peak flow meter comes with a special diary for recording measurements. It is designed for 1 month, where the patient must enter two indicators: morning and evening. The table already has digital data - the patient places dots or other symbols next to the required parameters, and after a month draws a graph where changes in the indicators can be observed. Normally, the line should be close to flat, small peaks are acceptable.
Important! If a person starts or stops taking any medications, all data is entered into the diary in the open fields. This information will allow the doctor to adequately assess the result and choose the right treatment.
Peak flowmetry for children
Due to the fact that in children the PEF norm is determined based on their height, the created table of values differs significantly from the adult one, in which more parameters are indicated. To find out the norm of peak flowmetry for a child, you should find his height in the table and, therefore, PSV will be indicated opposite this mark. You should not expect that the indicators entered in the table will exactly correspond to the results obtained.
It is necessary to focus on the concept of an individual norm established when measuring PEF over several days when the child’s condition is satisfactory. If the individual norm differs to a lesser extent from the table values, you should definitely consult with a specialist.
PSV schedule
Parents with a child suffering from asthma should keep a special diary in which they can regularly record peak flow readings, fully monitoring the course of the disease. It will be most convenient to do this in a squared notebook. In the morning and evening, points are entered into the diary indicating the best result of three attempts. Afterwards the points are connected. The diary should have space for daily notes.
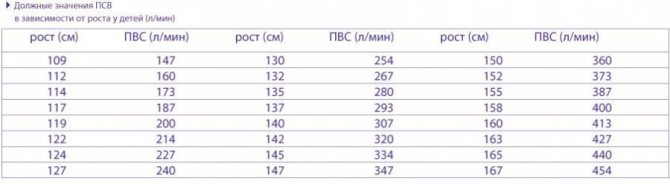
The table of proper values is correlated with the child’s individual indicators
They must indicate all the medications taken by the baby during the day, and all the reasons that could have influenced his condition: emotional stress, weather, viral diseases.
A thorough analysis of all causes and circumstances will help in the future to avoid relapses of the disease and determine the most effective drugs to maintain the normal condition of the child.
Peak flowmetry – thorough health care! It would seem that such a simple and quick way to control respiratory function can eliminate many problems with the occurrence of asthma attacks and help select the appropriate therapy. The main thing for patients and their relatives is not to be lazy and do regular health checks, and such an insidious enemy as asthma will not be able to prevent them from living a full life.