Purpose of determining prothrombin time
The process is controlled by the protein prothrombin circulating in the plasma. Normal synthesis of this substance is possible only in the absence of vitamin K deficiency in the body.
In healthy men and women, prothrombin in the bloodstream is stable; an active surge in the concentration of the substance occurs only after contact with deformed tissues. The indicator is determined during a blood test. In practice it matters:
- PTI – prothrombin index: the ratio of normal prothrombin time to the test blood sample;
- INR (international normalized ratio) is a decoding of test results from any laboratory in the world based on any diagnostic methods.
Prothrombin time is determined to:
- determination of blood viscosity while taking antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants (Aspirin, Warfarin, Clopidogrel);
- research into the effectiveness and adequacy of treatment;
- assessing a woman’s health status when planning pregnancy;
- identifying the causes of liver dysfunction;
- diagnosis of vascular pathologies to prevent stroke, heart attack, early diagnosis of aneurysm;
- determination of vitamin K levels;
- prevention of thrombosis;
- hemophilia control;
- control of disseminated vascular coagulation syndrome;
- detection of anemia in chronic form;
- monitoring dysfunction of homeostasis.
The analysis is carried out by taking blood from a vein or finger and examining the material on an automatic analyzer. Despite its simplicity, this is an informative technique. It is suitable for accurate diagnosis.
Interpretation of the results obtained
As is known, prothrombin time is the period of time from the addition of the third tissue factor to the blood until the formation of a clot. At the same time, the effectiveness of the external and general blood coagulation pathways is assessed.
Prothrombin time, the norm of which was indicated, may be one of the first factors that can indicate the state of hemostasis.
The time of clot formation along the external pathway is directly proportional to the concentration of clotting factor 7. Vitamin K affects its synthesis and content in the blood plasma. Therefore, if this vitamin is insufficient in the body, the concentration of factor 7 decreases, which leads to an increase in prothrombin time. If vitamin K is contained in excess, PV decreases. In addition, liver diseases accompanied by impaired anabolic function can also influence an increase in PT.
An increase in the INR level above 5 indicates a high risk of bleeding; a decrease below 0.5 indicates a high risk of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombosis. During warfarin therapy, normal INR levels are 2-3.
Valid values
In domestic medicine, the prothrombin time method in seconds is used:
- children - from 14 to 18 seconds;
- adult men and women – from 10 to 15.
In practice, different laboratories use different reagents and therefore obtain different ranges of standards. To standardize the process, the result is assessed within the framework of the INR. In healthy men and women, the normal prothrombin time is the same:
- for a newborn, an interval of 14 to 18 seconds is considered normal;
- for children under six years of age – from 13 to 18;
- for adults – from 15 to 20.
If the analysis is carried out in a technical laboratory, then the optimal value for children is from 70 to 100%, for adults - from 95 to 105%.
The normal prothrombin time in pregnant women depends on the trimester:
- in the first and third trimester – from 0.8 to 1.3;
- in the second – from 0.8 to 1.1.
When using blood thinners, levels can increase to 3.5 units in the INR.
Reduced clotting time
Prothrombin time may be below normal (clotting faster than normal) in the presence of the following diseases:
- Genetic diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Taking certain groups of medications.
- Pregnancy in the last months.
If your prothrombin time is normal, you don’t have to worry about the development of pathologies such as thrombosis or hemorrhage. However, today only half of the people in the world are so lucky. The second half has chronic and periodic deviations in the prothrombin index.
Increasing the indicator
If the prothrombin time exceeds the norm, this indicates that blood clotting is too slow. It is liquid due to many reasons:
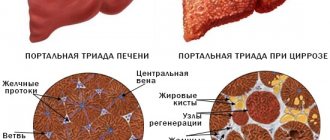
- liver dysfunction as a result of hepatitis, cirrhosis, when hepatocytes are gradually replaced by connective tissue, the synthesis of coagulation factors fades;
- taking medications: anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Warfarin);
- lack of vitamin K - impaired prothrombin synthesis;
- disturbances in the synthesis of fibrinogen and other clotting factors;
- hereditary pathologies;
- blood transfusions;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diabetes mellitus;
- tumor growth.
Excessive clotting time
Blood clotting time may be higher than normal (longer) with the following pathologies:
- Liver diseases. It is in the liver cells that prothrombin is formed, and if the liver does not function properly, there is a lack of it in the blood.
- Low vitamin K content. This microelement is necessary for the synthesis of prothrombin and with its deficiency, protein cannot be synthesized in the required volume.
- DIC syndrome.
- Increased antithrombin content (factor III). The third factor is responsible for blocking thrombin. This is necessary to prevent blood clots from forming in the vessels. The increased content of this substance blocks the formation of a blood clot when a vessel is damaged.
- Increased reaction of thrombin dissolution in the blood. This mechanism is responsible for the resorption of the blood clot after it has completed its function.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blood pathologies.
- Increased red blood cell count.
- Hemophilia.
- Pregnancy. The norm in women may decrease during pregnancy. This occurs in the first and second trimester due to a lack of vitamins in the blood of women. If these abnormalities are observed in the third trimester, this condition must be corrected to avoid severe blood loss during childbirth.
Preparing and conducting analysis
No special preparation is required for the test. To increase the reliability and accuracy of the testing, a couple of days before the upcoming manipulation you need to give up green tea, soy, liver, cabbage of any kind, leafy vegetables, beans, and alcohol.
Blood sampling for analysis is carried out in a laboratory in compliance with all rules of asepsis and antisepsis, on an empty stomach. The sequence is as follows:
- during intravenous sampling, a tourniquet is applied to the forearm to reduce the speed of blood flow and provide convenient access to the vein;
- the injection site is treated with an antiseptic;
- After drawing blood, the tourniquet is removed and the injection site is disinfected.
A blood sample taken from a finger or vein is submitted for testing: the required amount of blood is added to a test tube with sodium citrate so that the blood does not clot. To completely neutralize the effect of the clotting factor, the test sample is centrifuged by adding thromboplastin and calcium chloride. The time of clot formation is recorded - prothrombin time.
Today you can carry out such testing at home using a special analyzer. This is necessary for patients who are being treated with Warfarin against the background of thromboembolism, pre-infarction, when certain fluctuations in PTI or prothrombin time save a person’s life. The analyzer has a simple device and does not require special skills to operate.
Indications and contraindications
This indicator is not determined in all patients. For this there must be certain indications. These include:
- Determination of the state of the coagulation system before and after surgery.
- Presence of symptoms of internal bleeding.
- Monitoring the activity of coagulation systems during treatment with direct and indirect anticoagulants.
- Diagnosis of diseases of the blood and digestive system.
- History of thrombosis and thromboembolism of the load-bearing branches of various organs.
- Diagnosis of cancer and chronic anemia.
- Monitoring the normal course of pregnancy.
- Diagnostic operations.
- Preventive examinations after liver diseases.
This analysis should not be performed in the following situations:
- Persons in a state of significant dehydration.
- Suffering from neuroses and characterized by violent behavior.
- Persons with defects or decompensation of the cardiovascular system.
- Having massive burn lesions over the entire surface of the body.
What affects the accuracy of the result?
In some cases, the analysis result is inaccurate. The following can increase blood clotting time: alcohol, overeating, fatty foods, legumes, vegetables. Medicines reduce PTI: antibiotics, anticoagulants, anabolics, heparin, diuretics, laxatives.
The time period can be shortened by: eating foods rich in vitamin K (cabbage in all varieties, primarily spinach, beef liver), dehydration of various origins, antihistamines, contraceptives, caffeine-containing substances.
Unity and struggle of opposites
Disturbances in the hemostasis system lead to the development of coagulopathies, where pathology with a tendency to thrombosis is usually designated by the term “thrombophilia,” and diseases that are accompanied by increased bleeding are called “hemorrhagic diathesis.” Violations of blood coagulation abilities can be hereditary in nature or result from conditions formed during life (diseases of the liver parenchyma, vitamin K deficiency, the use of anticoagulants for medicinal purposes, activation of the fibrinolytic system).
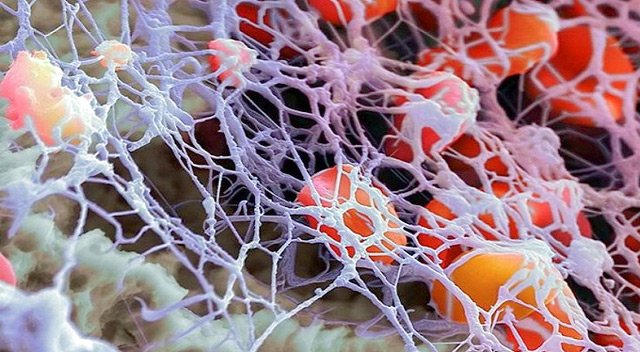
The development of hemocoagulation disorder syndrome is caused by the loss (or decrease) of the ability of liver cells to biosynthesize coagulation factors. Moreover, it should be noted that the factors of the coagulation, anticoagulation and fibrinolysis systems do not exist in isolation; disruption of the activity of any one link leads to pathological conditions of other components. For example:
- A disorder in the biosynthesis of the protein we are considering, prothrombin, will certainly entail a disruption in the production of other factors (VII, IX, X) and a deficiency of all components of the prothrombin complex, which will subsequently result in a decrease in the activity of FV, an increase in the concentration of fibrin monomers, a decrease in the activity of FXIII and an increase in the ability of fibrin to lysis.
- Disruption of fibrinogen metabolism will cause a change in the structural structure of the profibrin layer of blood vessels, opening the way for the movement of red blood cells through the vascular walls.
The combination of seemingly completely opposite properties of the above systems (provided they are functioning normally) ensures the liquid state of blood, freely moving through all the blood vessels of the body, and its coagulation if there is a need to patch a gap formed as a result of tissue damage.
Therapeutic measures
If the study reveals a decrease in prothrombin time compared to the norm, the patient is prescribed direct (Heparin) or indirect (Warfarin) anticoagulants, a special diet is recommended: fatty fish (halibut, herring, mackerel), oatmeal with olive or flaxseed oil, cranberries, figs , blueberry, plum, ginger. Drinks include green tea and cocoa.
When the PTI indicator is higher than normal, you need to take coagulants or synthetic blood clotting accelerators (Vikasol). Dietary nutrition involves excluding from the diet fatty foods, buckwheat, greens, legumes, red currants, chokeberries, blackberries, wheat baked goods, and smoked meats.
Reduces blood viscosity by drinking clean drinking water in accordance with the age and weight drinking ration (40 ml per 1 kg of weight).
Prothrombin time is an indicator of coagulation, which literally saves a person’s life if determined in a timely manner.
Who is the test assigned to?
Prothrombin time analysis is prescribed in the following cases:
- As part of a comprehensive study of blood clotting.
- With increased bleeding gums.
- For nosebleeds.
- In the process of coagulation correction.
- With thrombosis.
- During a heart attack.
- For varicose veins.
- When diagnosing a deficiency of clotting factors.
- For chronic liver diseases.
- With DIC syndrome.
Blood clotting process

In order to understand what prothrombin time (PTT) is, it is necessary to consider the process of blood clotting.
Blood clotting is a complex process that starts when wounds appear. A blood clot forms on their surface, which prevents the infection from penetrating into the body and at the same time prevents large blood loss. Fibrinogen, a special blood protein, is responsible for this function. When injured, it is modified into dense fibrin threads, similar to a network. They prevent blood from leaving the wound. Thanks to fibrin, a blood clot is formed, which becomes denser over time, leading to wound healing.
The coagulation process consists of three stages and is a complex chain of molecular interactions:
Activation. At this stage, prothrombin, a complex protein, turns into thrombin.
Coagulation. At this stage, fibrin is formed from fibrinogen.
Retraction. At the final stage, a dense fibrin clot, a thrombus, is formed.
However, this scenario does not always work. If a person has serious illnesses, the clotting process is disrupted - this leads to an increase in the amount of time. As a result, the patient may experience severe bleeding.
There are other clotting disorders where a blood clot forms too quickly. This is possible because the blood becomes thicker and more viscous. This happens as a result of certain diseases. Early formation of blood clots is deadly for the body, because can lead to sudden death from heart attacks, strokes, gangrene of the limbs and other serious diseases.
To prevent such dangerous pathologies and for their early diagnosis, a blood test for prothrombin time is performed.