In healthy people, urine
, as a biological fluid, is sterile. But under the influence of various factors, it can easily become contaminated with pathogenic microflora. As a rule, such reasons are taking antibiotics, infection with microbes of the vagina, urethra and perineum, inflammatory processes in the urinary tract and various dysfunctions in the endocrine system.
Indications for examination
Microbiological examination of urine allows one to determine with high reliability the qualitative and quantitative composition of the flora. Therefore, this analysis is widely used in medical practice and is mandatory prescribed:
- pregnant women;
- patients with genitourinary system infections;
- patients with AIDS, diabetes mellitus and people with various disorders in hormonal metabolism.
Specific symptoms for urine culture for microflora include pain in the lower abdomen, painful or frequent urination. In children, urinary infections can manifest as irritability, an unreasonable decrease in appetite, and even an increase in body temperature.
The study is often prescribed as a control test to confirm the diagnosis in case of atypical symptoms and to monitor the effectiveness of prescribed therapy, as well as to determine the resistance of the flora to the main and extended range of antibiotics. The analysis is part of the general program for preparing patients before various surgical interventions (kidney transplant, resection of the prostate gland, etc.) and is prescribed to children to confirm the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux.
Detected pathologies
In relation to urogenitalia, only streptococci of the viridans group, Corynebacterium spp., Lactobacillus spp., Neisseria spp., Staphylococcus spp. are considered friendly. Therefore, their presence in the titer is considered normal, in contrast to the presence of bacteria such as:
- Candida spp;
- Escherichia coli;
- Klebsiella spp.;
- Proteus spp.;
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Pseudomonas spp;
- Enterobacteriaceae (Klebsiella, Salmonella, Citrobacter).
This is just a short list of likely pathogens. In fact, microflora culture provides more extensive information, which makes it possible to accurately determine the infection, and therefore select the most effective treatment for numerous diseases of the urinary system. These include:
- cystitis. Infectious inflammation of the bladder, accompanied by discomfort and frequent urination;
- pyelonephritis. An inflammatory process that affects the kidneys and has a bacterial etiology. If treated incorrectly, it can develop into acute renal failure or urosepsis;
- urethitis. Common diseases caused by microorganisms and occurring in acute and chronic forms. Often accompanied by purulent discharge and negatively affect pregnancy.

Bacterial infections contribute to the development of prostatitis. They also cause acute urethral syndrome and other urological diseases.
Preparing for the test correctly
When collecting biological material, it is extremely important to ensure its bacteriological purity. Therefore, urine is collected in a disposable sterile container with an adapter, which should be purchased from a pharmacy or laboratory in advance, and the patient must carefully perform personal hygiene procedures in the genital area. Transferring into another container is not permitted. Women and girls who have menstrual or other vaginal discharge at the time of the test must use a tampon. On the eve of the test, it is recommended not to drink alcoholic beverages or yeast breads. You should also stop taking medications.

Rules for collecting material
We will discuss below how to properly take a urine culture test during pregnancy, in adults and children. To ensure the accuracy of laboratory diagnosis of urological infection, it is important to comply with all stages of diagnosis, including its preanalytical part - the collection of urine samples and their delivery.
It is the need to determine the exact amount of bacterial agents in the test sample that places special demands on sample collection.
When conducting research in a hospital setting, the nursing staff of the hospital is responsible for preparing the patient, collecting material and transporting it to the laboratory. For such cases, laboratories have written instructions regulating all diagnostic steps.
When examined on an outpatient basis, the patient collects urine independently, without the supervision of a medical professional. In connection with the above, it is necessary to carefully instruct the patient on the technique of independently collecting the test material in order to avoid false analysis results.
- 1Urine collection must be done in a sterile disposable container specially designed for this purpose, which can be purchased at the pharmacy chain. It is not allowed to collect urine in non-sterile, previously used containers, jars or bottles;
- 2If possible, urine collection should be carried out before starting to take antibacterial drugs or in the intervals between drug courses, to avoid distortion of the information received;
- 3The most reliable study is the average morning urine sample - after a night's sleep and before breakfast;
- 4 In the evening, on the eve of urine collection, it is recommended, if possible, to refrain from taking diuretics, since when they are taken, the urine is diluted and the total number of bacteria in one milliliter is reduced;
- 5 To collect urine from infants, you should use special children's urinals with a hypoallergenic adhesive; the collected sample is subsequently poured into a urine collection container, labeled and transported to the laboratory.
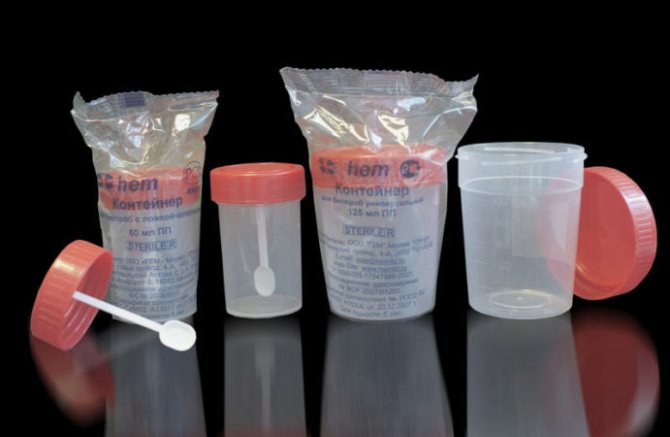
Figure 1 - Sterile containers for collecting urine for analysis (without a spatula)
How is urine collected for analysis?
The biomaterial is collected immediately after sleep. It is important to note that at least 4 hours must pass from the last meal and urination.
Only average morning urine is used for analysis, that is, the first portion of biological fluid that comes out in the first two seconds is not collected. Subsequent urine in an amount of about 50 ml is collected for testing.
In children, the procedure is carried out with the help of parents. In some cases, it is possible to collect urine at other times of the day, as well as using a catheter or performing a puncture from the bladder.
The collected material is provided to the laboratory within 1 ÷ 2 hours. If this is not possible, the container can be left for short-term storage in the refrigerator, but no more than 6 hours later it should be delivered for examination.
How to collect and donate urine?
Compliance with the recommendations for preparing for the study and proper collection of material will ensure that the results of the analysis are obtained. To do everything correctly, it is important to follow the recommendations:
- purchase a sterile plastic container from the pharmacy;
- before collecting urine, exclude exotic foods and foods that affect the color of urine (beets, carrots) from your diet, and do not use diuretic medications;
- the day before the analysis, eliminate physical activity;
- collect urine in the morning after hygiene procedures without using foam for intimate hygiene;
- After wiping the genitals, you then need to urinate into the prepared container. The labia should not touch the edges of the container;
- pregnancy is accompanied by a large volume of discharge, you need to close the entrance to the vagina with a tampon. This will help prevent foreign bacteria from entering the container;
- After filling the container, close it tightly with a lid and no later than 2 hours later, transfer it to the laboratory.
Do not touch the inside surface of the sterile jar under any circumstances. For analysis, it is better to provide an average portion of urine. After you start urinating, you need to hold the urine, then continue urinating into the container.
Decoding the results: norm and deviation
An analytical assessment of bacterial culture is given after 48 hours of incubation. It is important that the laboratory test data be interpreted by the attending physician.
Interpretation of results
- The microbial concentration threshold of less than 1000 CFU/ml is “negative” (no microbial growth is observed);
- The number of bacteria more than 100,000 CFU/ml is “positive” (microbiological forms are present in the urine and can be pathogens).
- The concentration of microorganisms ranges from 103 to 105, indicating various clinical symptoms and is interpreted depending on the patient’s condition and general history.
Some people have multiple types of bacteria. If their number is more than 3, and the concentration in the crop is the same, then this indicates a mixed flora and no further identification is carried out.
In what cases is a false answer possible?
It is not recommended to take the test earlier than 2 weeks after completing the course of hormonal and antibacterial therapy. In such cases, there is a high probability of a false research result.
Also, an incorrect result can be obtained if the purity of the biological material is compromised. Or if it was provided to the laboratory later than 6 hours after collection and was stored at a temperature above +15 ˚С.
Urine collection rules
Collect urine for analysis using the following algorithm:
- A sterile plastic container is purchased, where the urine will be collected. The container can be purchased at the pharmacy.
- The genitals are thoroughly cleaned. It is recommended to use warm water for washing; the use of shower gels and soap is prohibited.
- To obtain a true test result, it is necessary to provide an average dose of urine. It is recommended to urinate into the toilet for a couple of seconds, then into a sterile jar, and finish the process of urinating again into the toilet.
- After collecting the required volume of liquid, the container is tightly closed. Do not touch the inside of the container because this will distort the final result.
- The collected material must be sent to the laboratory as quickly as possible. The shelf life of the biomaterial is 6 hours, and this is provided that the urine is stored in a dark and cool place.
To detect the presence of pathogens, you need to use only morning urine (it should be collected immediately after the person wakes up). In some situations, the doctor insists on collecting urine throughout the day. In this situation, one rule must be observed: only urine isolated no earlier than 2-3 hours after the previous collection of biological material is suitable for research.
The portion of urine submitted for studying microflora should be 5-10 ml. Otherwise, you will not be able to get a reliable result.
If the patient has a catheter, urine collection is carried out strictly under the supervision of a healthcare professional. The nurse, using tweezers, clamps the catheter, after which he sterilizes with alcohol and, using a needle, takes out the required amount of liquid. After which the urine is poured into a special container and taken for examination. When submitting urine for analysis, it is recommended to indicate not only the patient’s data, but also the time of collection, the method used and the possible diagnosis.
The procedure also has a significant drawback - the duration of the study. Quite often, the doctor is forced to prescribe treatment even before receiving the test results.