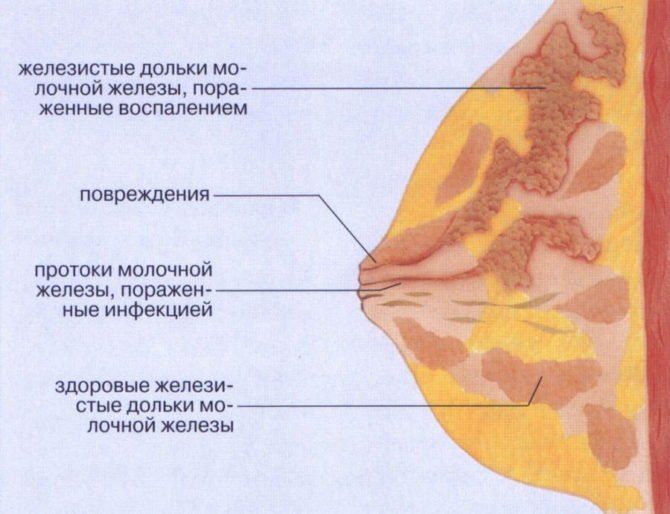
The problem of lactostasis does not bypass almost any nursing mother. It must be prevented and overcome immediately so that the breastfeeding process is not disrupted. There is certainly a lot of useful information out there. We want to share with you the most effective one. Lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct, which is caused by poor emptying of the breast or part of it. The chest consists of lobes. Their number ranges from 12 to 20, with each lobule having its own duct in the nipple. With lactostasis, you feel that some lobe of the breast is thickened and hurts, sometimes redness and swelling occur. When expressing the breast, you can see that milk flows from the nipple in fewer streams or from some part of the nipple flows a little, while from other parts it still flows in streams.
What is lactostasis?

Lactostasis is the stagnation of milk inside the mammary gland, in its ducts. Fluid production is regulated by the hormone prolactin. Under its influence, the breasts fill with milk in 3-4 hours. But to remove milk, another hormone is needed - oxytocin, which stimulates the cells of the end sections and dilates the ducts. The synthesis of this substance is accelerated by active sucking of the baby.
Without mechanical action on the areola of the breast, the ducts are not released, but milk continues to flow. Stagnant plugs form, which, as they grow, put pressure on the glandular lobules. Fermentation processes begin in milk, which leads to the development of first aseptic and then purulent inflammation - mastitis. Partial reabsorption of milk occurs, which contributes to a rise in temperature.
People's Councils
Limiting feeding or pumping leads to impaired milk flow, further blockage of the duct, and an increase in milk viscosity.
Fluid restriction aggravates lactostasis, and the viscosity of milk also increases.
It is better to prevent a child from sucking milk. Firstly, adults have a completely different sucking mechanism; they cannot suck out “stuck” milk. Secondly, the oral cavity of an adult is the most germ-contaminated place, and there is no need to transfer these microbes to the nipple of a nursing mother.
Causes and signs of lactostasis
The causes of lactostasis may be the following:
- incorrect position of putting the baby to the breast;
- violation of feeding technique (more often – clamping the nipple with a “scissors” grip to separate the baby’s nose from the breast);
- incorrect position of the glands during feeding - accumulation of milk in one part of the breast while others are completely emptied;
- irregular attachment of the baby to the breast;
- excessive milk production - hyperlactation (reasons - hormonal imbalance, too frequent pumping);
- weakening of the baby’s sucking reflex due to bottle feeding;
- lack of fluid in the mother’s diet;
- tight underwear;
- pathologies of the mammary glands – flat, inverted nipple;
- chest bruises;
- hypothermia;
- sleeping on your stomach at night.
The more often you put your baby to the breast, the lower the risk of lactostasis.
Signs of milk stagnation in a nursing mother:
- “petrification” of the breast;
- palpation of lumps in the mammary gland;
- pain and feeling of fullness in the chest, which decreases after feeding;
- inflammation, redness of the skin around the seal (rare);
- increase in body temperature up to 38°C (up to 39°C upon transition to mastitis).
Half of the cases of lactostasis occur during the first month after the birth of the baby. The skills of breastfeeding and pumping have not yet been developed, so during normal production, milk is not completely removed from the gland. Provoking factors act throughout the entire period of lactation, so the diagnosis is also found in experienced mothers.
Expert opinion
Sokolova L. S.
Pediatrician of the highest category
Lactostasis is often cured on its own, without drug therapy. But if the pathology has progressed to the stage of inflammation, with severe pain, a temperature of 38°C or more, you need to see a doctor. A preliminary diagnosis will be made by a gynecologist. If mastitis is suspected, consultation and treatment with a surgeon is recommended. To exclude oncology, the patient is sent for a consultation with a mammologist.
It is necessary to cure lactostasis within 3-5 days after the first symptoms appear. If there is no positive dynamics during this time, the risk of developing inflammation increases. Without medical intervention, milk stagnation leads to mastitis.
Video in which Nina Zaichenko talks about the causes of lactostasis and first aid for it.
Pumping
A breast pump may not help remove milk due to lactostasis and mastitis. If you can’t latch on to your baby often, we use minimally painful hand expression. The pumping regimen is usually individual. Expressing “to the last drop” is not necessary (and difficult to do) - it is important to eliminate unpleasant sensations in the chest (bloating, pressure, tingling, etc.). The first option (if breastfeeding) is to remove the available milk and then introduce the baby. The second option (if the mother is feeding with expressed milk) is to express after removing the milk that easily flows out with gentle pressure on the compacted area.
How to treat lactostasis: compresses, ointments and tablets
It is important to begin treating chest congestion at the first sign of trouble. If a woman feels tightness or heaviness in her breasts, she needs to start daily massage of the mammary glands. It is better to carry out the procedure in the shower - under the influence of heat, the ducts expand, the effect is enhanced.
Be sure to massage the lumps before feeding and pumping. The hardened areas are kneaded with your fingers, the hand moves from the middle of the gland to the nipple. The pressure should be gentle and soft.
Compresses
In the treatment of lactostasis, in combination with massage and regular feeding, folk remedies are used, in particular, compresses on sore breasts.
Honey cake
Mix honey with rye flour in equal proportions, knead the dough. Apply to your chest, under plastic wrap, put on underwear, hold for 40 minutes. Course 5 days.
Cabbage leaf
Crush a fresh cabbage leaf, apply tightly to your chest, under your bra for 1.5-2 hours. The compress can be kept without intervals for a day, changing the “gasket” every 2 hours. Cabbage leaf is the No. 1 remedy in the prevention and treatment of lactostasis.
Camphor oil
Mix 1:1 with water, moisten gauze. Apply to the glands under polyethylene, wrap with a warming cloth. Holding time – 30 minutes. Course 3-5 days.
Magnesia compress
Moisten a cotton swab with the contents of an ampoule of magnesium solution (1-2 ml), apply to the seal, under the polyethylene. Wrap a scarf around your chest. Leave for 1 hour, changing the cotton wool every 15 minutes.
Semi-alcohol compress
Heat the vodka until warm, moisten the gauze, and apply it to the inflamed gland. Keep warm for 30 minutes. Alcohol is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio.
Dimexide
The question of using Dimexide in the treatment of lactostasis remains open. Since the drug passes into breast milk within 20-30 minutes, there is a risk that the baby will refuse to feed due to the specific taste. An argument is also made about the dangers of the breakdown products of the drug in breast milk. Although reviews from nursing mothers about the use of this product are mostly positive.
After compresses, be sure to put the baby to the breast and monitor the circumference of the nipple - the baby’s chin should be directed towards the seal. Baby sucking is the main tool in freeing the ducts from stagnation.
Ointments for lactostasis
Antispasmodic and decongestant ointments effectively treat lactostasis. They promote the resorption of compactions, expansion of the ducts, and stimulation of the passage of the milk plug. Apply between feedings to the breasts warmed up with a warm shower. The ointment is gently rubbed into problem areas or applied under a bandage for 2-3 hours.
The following ointments are used in the treatment of lactostasis:
- Malavit;
- Troxevasin;
- Arnica;
- Traumeel;
- Heparin ointment;
- Levomekol;
- Vishnevsky ointment.
The instructions for the drugs indicate that the effect of the constituent components on breast milk has not been studied. But ointments are prescribed by doctors for lactostasis; no reviews of side effects have been recorded. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Drug treatment
Oxytocin
Lactostasis is one of the indications for prescribing hormonal drugs, because in every third case the cause is a lack of oxytocin after childbirth. When the endocrine system malfunctions, the synthesis of the necessary hormone is weakened. Then the woman is prescribed a synthetic drug. Oxytocin during lactostasis stimulates muscle contraction and soft removal of milk from the ducts. Administered intravenously and/or intramuscularly.
Antibiotics
For lactostasis they are not prescribed as harmful and useless drugs. Stagnation in the ducts is a mechanical disorder not caused by bacterial pathogens, so the use of antibiotics is unjustified. These drugs are used when there is a risk of infection in the gland or suspected purulent mastitis.
Physiotherapeutic methods
In the complex treatment of lactostasis, hardware methods are also used. Physiotherapy increases local immunity, reduces pain, reduces swelling and inflammation. After the course of treatment, the well-being of the nursing mother, the quality and flow of milk improves.
- Vitafon is a vibroacoustic device that enhances capillary blood flow and stimulates the movement of lymph at the point of impact. Course – 10 sessions.
- Ultrasound – massage + thermal effect stimulates blood flow in the glands. After 5-10 sessions, the milk plug comes off.
- Darsonval - impact on compaction with pulsed alternating current. The course of treatment is 7 days.
After physiotherapy, it is recommended to express the milk as it is unsuitable for consumption by the child.
Physiotherapy is contraindicated for tumors, cysts, and mastitis. Before the appointment, an ultrasound examination of the glands is carried out.
What to do at elevated temperatures
Antipyretics for lactostasis are prescribed only at levels above 38°C. If the temperature is below 38°C, it means that the body copes with the disturbances on its own, and there is no need to reduce the fever. For lactostasis, a value of 37.8-38.2 °C is allowed. In this case, drugs in pediatric doses without side effects are recommended - based on paracetamol and ibuprofen. It is allowed to take Panadol, Efferalgan, Brufen, Nurofen, Solpaflex, etc.
Rectal antipyretic suppositories are often prescribed - Nurofen, Cefekon. The concentration of the active substance in these suppositories is minimal and does not pass into breast milk, so the drugs are approved during pregnancy and lactation.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Ultrasound therapy and other interventions can alleviate the condition, but are only auxiliary means of treatment. Physiotherapeutic procedures are not recommended, in particular, when the temperature rises above 38 ° C and the formation of an acute purulent process. Therefore, before physiotherapeutic treatment, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound scan from a competent specialist who has experience working with breastfeeding women.
The most common treatment is with ultrasound (UT), which acts using thermal, mechanical and physico-chemical factors - it increases the temperature in the tissues affected, activates metabolic processes, and promotes the release of biologically active substances. With lactostasis, such consequences are not always useful.
Some services offering care for lactostasis and mastitis advertise home physiotherapy treatment at the first appointment, when this service is actually needed by a small number of women. In addition, if adequate recommendations are followed correctly and consistently, no additional treatment is required.
Medications
Antispasmodics, for example, no-spa. Antispasmodics work in the presence of smooth muscle spasm. With stagnation and mastitis, there is no spasm, but there is swelling that interferes with the release of milk. The viscosity of the milk may also be increased. In addition, no-spa (drotaverine hydrochloride) is generally used abroad extremely rarely, especially in nursing women.
Vishnevsky ointment has a pungent odor and bothers the baby. Leads to encapsulation of the inflamed area and promotes the formation of an abscess.
Arnica ointment causes tissue heating, has a local irritant effect, and activates blood circulation.
Dostinex and bromocriptine are serious drugs with severe side effects, which occur to one degree or another in every woman who takes them. Make sure that the prescription is made by a doctor who supports lactation (that is, it is really necessary). Suppression of lactation is not a way to treat lactostasis!
Dimexide is a drug with a pungent odor that can cause skin irritation and is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age and during lactation.
Progestogel is a hormonal ointment that reduces lactation. Purpose incompatible with breastfeeding.
Antipyretic drugs. It is worth starting to bring down the temperature with physical methods - remove clothes, wipe the skin with cool water, etc. It is permissible to take only ibuprofen (preferably) or paracetamol in case of poor general condition (headache, weakness, dizziness, etc.) at a temperature above 38-38.5 ° C.
Antibiotics incompatible with breastfeeding. To treat mastitis, modern drugs are used that do not have a harmful effect on the child. You can check whether the prescribed drug is compatible with breastfeeding on the website of the Spanish hospital Marina Alta.
In extremely rare situations, with a persistent course of the disease and a serious condition of the patient, it is possible to prescribe treatment that is incompatible with feeding. In such cases, it is necessary to ensure that the doctor prescribing the drug supports breastfeeding and the prescription of a specific drug is necessary. In addition, you should receive advice on how to maintain lactation during treatment and how to continue breastfeeding after treatment ends. Systemic antifungal therapy is usually not required after antibiotic treatment.