After childbirth, the mother’s body is depleted, as she gives all the useful substances to the child. And therefore, a nursing woman simply needs to compensate for the lack of vitamins and minerals. And proper nutrition and taking vitamin-mineral complexes will help her with this.
Magnesium B6 is a drug that compensates for the lack of magnesium in the body, and pyridoxine (B6) has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart and nervous system. The drug is prescribed to lactating women in case of neuromuscular, mental disorders, disorders of the heart and digestive tract. It is known that the active components enter the body of the newborn. How safe is it? This will be discussed further.
Why is magnesium so necessary for the human body?
A lack of magnesium can manifest itself in the human body for various reasons - lack of diet and healthy lifestyle, excessive physical activity or unbearable emotional stress. And magnesium during breastfeeding is really needed by a nursing woman, because a significant part of it is passed on to the baby along with breast milk. A useful microelement in the human body is valued for the following qualities:
- normalizes the supply of energy and vitality, replenishing the balance and preventing it from decreasing. Serves as a kind of “conductor” of energy to all tissues in the human body, that is, the more useful substances a person consumes, the more energetic he feels;
- normalizes the functioning of nerve impulses and reduces cell hyperactivity. At the same time, the person becomes less irritable, adequately perceives stress and conflict situations in life, and also remains in a calm and balanced state;
- regulates the functioning of the vascular system, maintains the elasticity of capillaries, which is why blood pressure in the veins and arteries remains normal;
- supports proper functioning of the heart muscle. That is, it reduces the load on the heart and prevents its wear and tear;
- Boosts immunity and protects the body from harmful bacteria, germs and possible allergic reactions.
Taking magnesium is recommended not only for women who are breastfeeding, but also during pregnancy for the proper formation and development of the fetus. For some expectant mothers, the drug is prescribed for preventive purposes, even in the absence of apparent reasons.
A distinctive feature of magnesium is its distribution throughout all vital systems in the human body. Most of it ends up in the teeth and bones; a fifth of the dose taken goes to muscle tissue, the heart and kidneys. And the circulatory system receives only one percent of the total share of the substance.
You can compensate for the lack of magnesium in the body by consuming appropriate foods.
Magnesium and its role in the human body
According to modern physiologists, magnesium is one of the main microelements in the human body. It is found in all tissues and is responsible for the proper functioning of muscle fibers and the transmission of nerve impulses; participates in metabolism, normalizes blood pressure and sugar levels .
Magnesium is distributed in the body as follows:
- In the cells of bones and tooth enamel - 4/5 of the total amount.
- In the muscles, heart, kidneys - approximately 1/5 of the microelement.
- In the blood - up to 1% of the total amount.
The body gets magnesium from food. Many types of cereals, nuts, herbs, animal products, fruits and dried fruits are rich in valuable microelements.
Photo gallery: foods high in magnesium
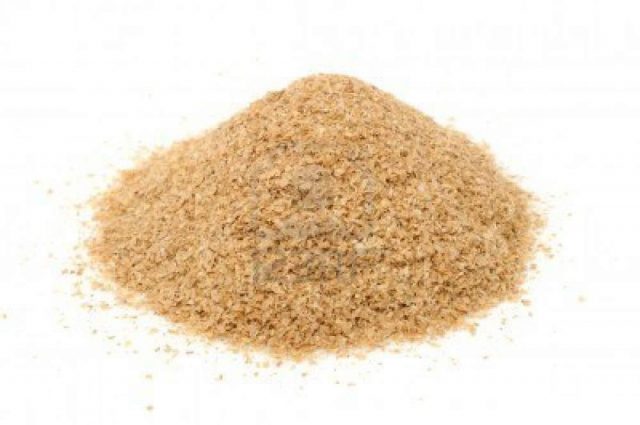

Wheat bran is in first place in terms of magnesium content (586 mg per 100 g)
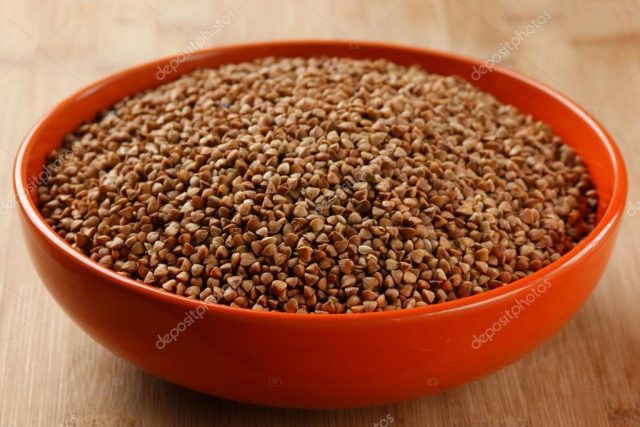

Buckwheat contains 2 times less magnesium than bran, but it is also sufficient
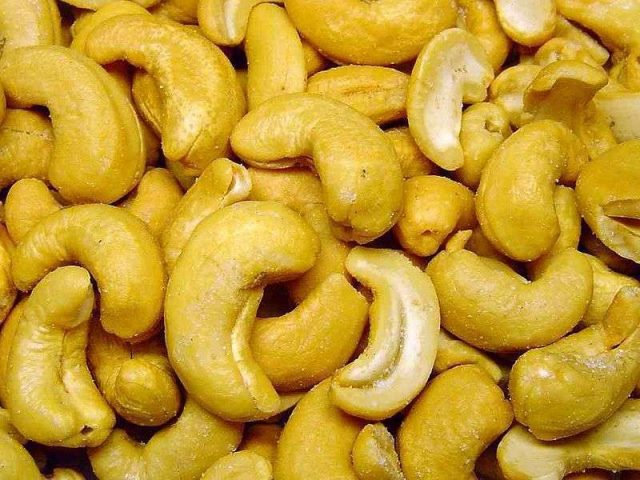

Cashew nuts contain magnesium 270 mg per 100g
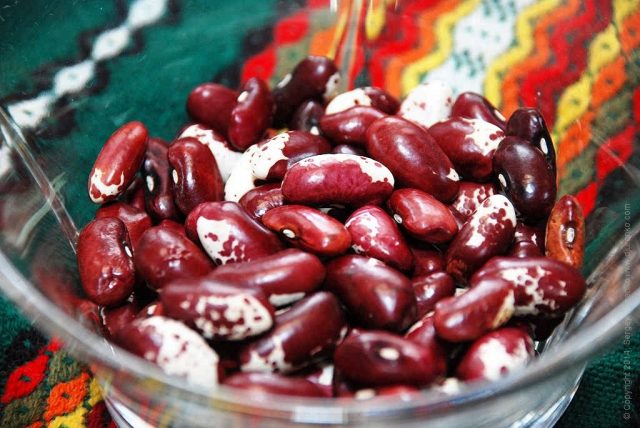

Beans are inferior to cashews - they contain magnesium 130 mg per 100g

Among greens, parsley is the leader in magnesium content

Hard cheese has no equal in the amount of magnesium among animal products

Persimmon is a fruit with a high magnesium content.
It is important to include foods with magnesium in your daily diet.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors, magnesium is washed out of organ tissues. Doctors warn: a long-term lack of a valuable microelement, which ensures the correct cycle of relaxation and contraction of the heart muscles, leads to a heart attack.
Among the consequences of magnesium deficiency are the following:
- disruptions in the digestive system - loss of appetite, constipation, vomiting;
- disruptions in the nervous system - irritability, drowsiness;
- disorders in the cardiovascular system - arrhythmia, hypertension, angina pectoris;
- complications in the immune system that increase the risk of cancer;
- formation of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder;
- development of diabetes mellitus.
A malignant tumor is one of the most severe possible consequences of a long-term lack of magnesium in the body.
According to statistics, approximately 4/5 of the population of megacities are deficient in magnesium.
When magnesium is not enough for a nursing mother
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the baby takes a significant part of the vital microelement from the mother. The situation can be complicated by the woman herself if:
- often experiences stress;
- does not eat properly;
- leads an unhealthy lifestyle;
- gets little rest.
As a result, a nursing mother develops alarming symptoms of magnesium deficiency:
- fatigue, insomnia;
- mental disorders - constant anxiety, irritability;
- convulsions, spasms, tremors;
- myocardial rhythm disturbance;
- stomach pain, diarrhea or, conversely, constipation;
- nausea, vomiting.
Together with the suffering mother, the child also experiences magnesium deficiency.
To prevent a health hazard, you need to seek help from a doctor. After studying the clinical picture, he will prescribe treatment. Perhaps the list your doctor gives you will include one of the medications containing magnesium.
Food categories rich in magnesium
Food is the only source of magnesium that can be obtained not from medications. Useful products include:
- cereals;
- nuts;
- greenery;
- fruits, fresh or dried;
- categories of products with animal origin.
The following ingredients contain the most magnesium (in descending order):
- Millet bran.
- Buckwheat.
- Nuts (cashews have the advantage).
- Beans.
- Fresh greens, mainly parsley.
- Hard cheese.
- Persimmon.
Women who are breastfeeding should make sure that these foods are included in their diet. With their daily consumption, a lack of magnesium does not threaten nursing mothers.

>>Click here<
In what cases is magnesium insufficient during lactation?
The bulk of the valuable microelement passes to the baby through mother's milk. At the same time, the woman begins to feel its lack, and the longer the supply of magnesium in the mother’s body is not replenished, the more dangerous complications she can get. For example:
- failure in the gastrointestinal tract - constipation, attacks of nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite;
- imbalance in the functioning of the nervous system - increased excitability, irritability or, conversely, lack of taste for life, decadent mood and depression;
- heart disease and the development of pathologies - heart rhythm disturbances, arrhythmia, increased blood pressure, angina pectoris;
- reduced immunity - constant colds and viral diseases;
- disorders in the body in the field of endocrinology - the risk of developing diabetes increases.
The lack of sufficient immunity is a favorable environment for the development of a large number of diseases, including the most dangerous - cancer. And disrupted functioning of the digestive system can provoke the appearance of sand in the gallbladder or kidneys, and then the formation of stones. Therefore, a breastfeeding woman should not let the disease worsen, and even if she feels the first signs of illness, it is better to consult a doctor.
Vitamin D3
— it is necessary to take at least a preventive dosage of 1500-2000 IU (vitamin D). If analysis shows there is a deficit, then more. The child also needs to be given vitamin D, 1000 IU per day, as he gets very little through milk (6400 IU for the mother = 400 IU for the child). For the child it is the prevention of rickets, for the mother it is immunity, calcium absorption, prevention of various diseases, incl. breast cancer I have Jarrow Formulas capsules and liquid Thorne Research
Indications for taking Magnelis B6 for hepatitis B
Replenishing magnesium is an important part of caring for the health of a nursing woman, because its lack acutely affects the development of a newborn baby. If the magnesium contained in food products is not enough for the mother, then doctors recommend drinking magnesium while breastfeeding when vitamin deficiency occurs.
Magnelis B6 is considered one of the optimal medications. The Russian-made product effectively copes with the lack of a useful substance, replenishing its reserves. Some therapists refute this opinion, but if there is an acute shortage of a microelement in the body of a nursing woman, they still prescribe the drug for use. When breastfeeding, the drug is prescribed in the following cases:
- the appearance of signs of a nervous system disorder - trembling in the fingers, convulsions or spasms;
- unstable psycho-emotional state - fear, anxiety, increased excitability that arises for no reason, excessive irritability or lethargy, apathy to everything that happens;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- painful sensations in the epigastric region, problems with stool;
- attacks of nausea or vomiting.
Already when some of the described symptoms appear, we can talk about a lack of magnesium in the body of a nursing woman. Most often, these indications for the use of Magnelis B6 must be expressed clearly enough for the therapist to prescribe the drug for guards. After all, most doctors are afraid of harming the baby and prescribe medication only in exceptional cases.

There are many indications for taking magnesium supplements, from cramps and spasms, for example, in the legs at night, to disorders of the psycho-emotional state.
What is included in the drug and its release form
Magnelis B6 is produced in the form of coated tablets. One tablet contains magnesium lactate (470 mg) and pyridoxine hydrochloride (5 mg).
The composition of the drug is supplemented by other active substances: sucrose, talc, magnesium stearate, etc. The vitamin complex is produced in two variations:
- Small jars - they contain 60 tablets or 90.
- Cardboard packages - contain 3 or 5 strips of 10 tablets.
The main active ingredient - magnesium lactate - is considered an antispasmodic, has an antiplatelet effect, due to which neuromuscular tissue is restored. Recommended for replenishing magnesium in professional athletes, with increased mental stress, and also during pregnancy.
The second active component - pyridoxine hydrochloride - is considered a toxic substance, but the drug contains it within the permissible dosage and does not have a negative effect on the body. With it, magnesium is better absorbed and distributed throughout the cells.
The daily dose of Magnelis B6 is individual in each case, but not more than 6 tablets per day.
Analogues of the drug
The following structural analogues of the drug Magne B6 exist:
Magnelis B6
Available in the form of white biconvex tablets. It has the same indications and contraindications as Magne B6. It should not be used in conjunction with tetracycline antibiotics, as well as with drugs containing iron, phosphates and calcium. Do not use in patients with diabetes mellitus due to the sucrose contained in the drug. The drug is compatible with lactation in the same way as Magne B6, i.e. Only a doctor can prescribe it, taking into account the benefits for the mother and possible harm to the child.
Recommended dose
As a rule, for each individual patient, the doctor recommends a different dosage, depending on how severe the symptoms are. Thus, a nursing mother can be prescribed a different number of tablets per day, but in any case no more than 6 per day.
Take the tablets either at once or in several approaches. It is better to drink Magnelis B6 with food, and it is recommended to take the product with plenty of water.
Use the drug in courses, more than once! As soon as the indicators return to normal, the medication is stopped.
Overdose
An excess of the drug in a woman’s body can lead to negative consequences if the nursing mother has kidney problems. Then Magnelis B6 can cause poisoning, which is expressed as follows:
- pressure surge;
- attack of nausea with vomiting;
- delayed manifestation of body reactions and reflexes;
- labored breathing;
- failure of the heart, sometimes to the point of falling into a coma.
Compliance with dosage limits is extremely important for women's health. Exceeding the recommended amount may be fatal. Therefore, only a doctor can prescribe medication after a thorough examination. In case of overdose, hemodialysis, rehydration therapy or diuresis are prescribed.
Dosage
The drug in the form of a solution is taken orally during meals. The solution must be diluted in 100 ml of purified water.
Daily dose of solution:
- patients from 12 months, whose weight is above 10 kg - from 1 to 4 ampoules, frequency of administration from 1 to 3 times;
- adults – 3 ampoules three times.
The therapeutic course lasts no longer than a month and is regulated by a doctor.

Tablets are taken in the following dosage:
- patients over 6 years old, weighing more than 20 kg - from 4 to 6 tablets every day;
- adults – from 6 to 8 tablets, 1 piece per dose.
Take the tablet with purified water without gas (200 ml).
The effect of Magnelis B6 on the body of a breastfeeding woman
The use of the drug during breastfeeding is permitted only with the prescription of a physician and under his close supervision. After all, the use of the drug and the consequences after taking it during lactation have not been fully studied. But there is a practice of taking the drug during pregnancy and no negative effects on the woman’s body and the development of the child have been found. Therefore, Magnelis B6 cannot be classified as a medication that is strictly contraindicated during lactation. In addition, the medicine is well tolerated by a nursing woman and does not cause drowsiness.

How Magnelis B6 behaves towards infants is unknown, since not enough research has been done so far.
In general, most therapists recognize that the benefits of using medication for a lack of magnesium in a nursing mother’s body are much higher than the possible harm from taking pills. And to reduce the aggressiveness of the drug during breastfeeding, magnesium can be taken in the form of a solution.
Adverse reactions
If a woman has hypersensitivity or individual intolerance to any components of the drug, allergic reactions in the form of rash, itching or redness are possible. Therefore, when breastfeeding while taking any medications, you should carefully monitor your well-being and the condition of the baby. A side effect when taking magnesium in young mothers can occur in the digestive system. Magnelis B6 can cause an attack of nausea, stool upset, increased gas formation and pain.
special instructions
Magnesium B6 is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Hypersensitivity to active or additional components.
- Phenylketonuria.
- Taking Levodopa.
- Children under 1 year (solution), patients under 6 years (tablets).
- Fructosemia (when taking tablets).
- Glucose-galactose malabsorption.
- Atrioventricular block.
- Arterial hypotension.
- Hypermagnesemia or hypervitaminosis B6.
- Functional kidney failure.
Under the supervision of a doctor, the drug is taken during lactation.
In rare cases, side effects occur in the form of a rash on the skin. Some patients complain of nausea and vomiting. The drug can cause diarrhea, excessive gas accumulation, and abdominal pain.
When taking the drug in a patient with functional renal failure, there is a risk of the following symptoms:
- dyspepsia: heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- arterial hypotension;
- inhibition of reflexes due to suppression of the nervous system;
- changes in the myocardium on the cardiogram;
- anuria (lack of urine);
- cessation of heart activity;
- coma;
- labored breathing.

To eliminate the symptoms described above, it is recommended to carry out forced diuresis (increasing the excretory function of the kidneys) while simultaneously introducing a large volume of fluid into the body. If kidney function is impaired, peritoneal dialysis (cleansing the blood of toxic substances) is prescribed.
Contraindications
You cannot prescribe the drug yourself also because the attending physician must familiarize yourself with the patient’s medical record before recommending use. After all, if a nursing mother has diabetes, the medicine will be replaced with another, since Magnelis contains sucrose.
One of the contraindications for taking the drug is considered to be a hereditary disease - phenylketonuria, which disrupts the metabolism of amino acids.
Still, the main items on the dangerous list are kidney diseases and allergies. In the second case, situations are known when the body of an allergic person can show a negative reaction even to completely safe vitamin supplements. If a rash or swelling appears, stop taking the medication and consult a doctor about prescribing a similar but safe remedy.
When should Magnelis B6 not be taken?
The drug has few contraindications:
- severe renal failure;
- hereditary disease phenylketonuria (disorder of amino acid metabolism, damage to the central nervous system);
- individual sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- age up to 6 years;
- diabetes mellitus (use with caution).
Relative contraindications, along with diabetes, are moderate kidney problems; the drug is excreted precisely through them, and if the kidneys cannot cope with the task, magnesium will be retained in the body. As a result, an excess is formed and hypermagnesemia, which is dangerous to health, occurs. Taking Magnelis B6 in case of moderate renal failure is not prohibited; the main thing is to carefully monitor the condition of the body and not miss the first symptoms of hypermagnesemia .
To exclude any unwanted reactions to Magnelis B6, before going to the pharmacy to buy it, it is recommended to take urine and blood tests.
What medications are it not recommended to take Magnelis B6 with?
To compensate for the lack of magnesium during lactation, the components of the drug must be dissolved in the body and absorbed in a certain way. But there are a number of medications that interfere with the absorption of magnesium when taken in parallel with Magnelis B6. This:
- calcium-containing products and medications that contain phosphates. They interfere with the penetration of magnesium into cell membranes;
- drugs from the tetracycline category. Their effect is simply absent if magnesium is taken at the same time. They can be combined, but then you need to take a break of at least three hours between taking each tablet;
- complex products based on iron. Magnesium interferes with the absorption of beneficial microelements intended to treat anemia;
- levodopa - since one of the components of Magnelis, pyridoxine, interferes with the full effect of this medicine.
To avoid the negative consequences of medication incompatibility, you should tell your doctor all your symptoms and a complete medical history. And also analyze hemoglobin indicators: if its value is low, magnesium will only aggravate the problem.
Analogues of Magnelis B6 during lactation
Magnesia is considered the main analogue. This is an intravenous drug that is prohibited during breastfeeding and is prescribed only for medical reasons. The medicine quickly penetrates into the blood, then into mother's milk. Therefore, breastfeeding should be avoided while using Magnesia.
Similar medications approved for hepatitis B are also considered:
- Magne B6.
- Magnesium Plus B6.
- Magnistad.
- Magnicum.
When breastfeeding a child, a woman should be as responsible as possible about her health. After all, milk production, and therefore the baby’s adequate nutrition, depends on her well-being. You should not listen to the advice of friends or trust advertising - you need to consult a doctor and follow all his recommendations, in particular if you need to take magnesium-containing medications.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency

A nursing mother is obliged to closely monitor her health, because the health of her child depends on it. With a lack of magnesium, the body signals the following symptoms:
- neuromuscular disorders in the form of muscle pain, spasms, numbness, tremor;
- mental disorders - a woman is constantly in a state of stress for no apparent reason, sleep is disturbed, irritation and emotional instability begin to dominate her character;
- disturbances in the rhythm and sequence of myocardial contractions;
- digestive system disorder - flatulence, diarrhea or frequent constipation, stomach pain.
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe Magne B6, he will write a prescription.










