≡ Home → Valerian → About valerian →
During the period of breastfeeding a child, young mothers sleep very little, often experience stress, worry a lot, and sometimes, in order to slightly reduce emotional stress, they decide to start taking valerian. In the instructions for use of many valerian preparations, breastfeeding is not considered a contraindication. However, almost everywhere there is insufficient data on the effect of valerian on an infant, who can receive a certain dose of the medicine through mother's milk. Valerian is strictly contraindicated for children under 3 years of age.
Practice shows that a nursing mother often needs not valerian, but normal rest.
How can a young mother take care of herself and not harm her child? Is it possible to take valerian, or is it better to give it up? To make the right decision, you need to understand how much of the drug passes into breast milk and what effect it can have on the baby. And after that, be sure to consult with your therapist and the pediatrician who is caring for the child.
Is it possible to take valerian while breastfeeding?
Valerian is included in many drugs, homeopathic remedies and dietary supplements. Some of them are approved for use during lactation, others are contraindicated. This is often due to the content of additional components in the drug. For example, valerian tincture is contraindicated for young mothers, since in addition to valerian extract, it contains about 70% ethyl alcohol. It can penetrate through mother's milk into the child's body, for whom alcohol is contraindicated even in the smallest dosages.
Like preparations containing only valerian, such complex remedies are contraindicated during breastfeeding.
The World Health Organization's monograph on medicinal plants states that the use of some valerian preparations is acceptable during breastfeeding as prescribed by a doctor. The same opinion is shared by specialists from the Committee for Herbal Medicines, subordinate to the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicines. At the same time, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA USA) does not recommend taking valerian during lactation.
Doctors and scientists have different opinions about the safety of using valerian during breastfeeding. To date, there is no scientific data that would allow us to make an unambiguous decision. Although scientific and clinical studies on the effects of valerian on the human body are carried out regularly, the issue of the effect on the course of pregnancy, the development of the fetus and the infant, who can receive a certain amount of the drug through mother's milk, still remains unclear. In view of this, doctors make decisions about the use of the drug by assessing the balance of benefit for the young mother and possible harm to the child. It is not recommended to drink valerian on your own without a doctor’s prescription.
On a note
In Spain, a pharmacological reference book E-lactancia was released for nursing mothers, in which the drugs were divided into 4 groups according to the degree of risk for the child. Valerian is classified in the second group, which includes drugs with probably low risk. The first group consists of drugs with an extremely low risk for the child, the third - with a high risk, and the fourth - with a very high risk. Accordingly, drugs of groups 3 and 4 are contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Can a nursing mother take Valerian drops?
Valerian drops act immediately after entering the oral cavity. But not all drip medications have the desired effect. Many of them are prepared with alcohol, which means that the use of these drugs by a nursing mother is impossible, since the alcohol will quickly get into the milk and can affect the baby’s health.
At the pharmacy you should choose a drug based on ordinary water. Take this drug strictly according to the instructions. The drops have a mild effect on the woman’s body and almost do not penetrate into the milk. You should not take valerian for more than two months, as long-term use of the drug will lead to overexcitement and irritability.
Do the active ingredients of drugs pass into breast milk?
The active ingredients of medications enter the blood and are distributed throughout the body through the circulatory system. Accordingly, they also pass into breast milk. The drugs have different permeability, but on average about 1% of the active substances enter the milk. At first glance, this may seem like quite a bit, but for an infant, even this dose can be dangerous.
Valerian tends to accumulate in the body, so its content in breast milk increases after each dose of medication. If a doctor prescribes this drug to a nursing mother, it is very important to adhere to the recommended dosage and not exceed its daily dose and the duration of the course of treatment. Increasing the single dose or using valerian for too long can cause an overdose, which is dangerous for both mother and child.
Thomas Hale, Doctor of Pharmacology and Professor of Pediatrics at Texas Tech University Medical School, published the reference book “Medicines and Mother's Milk.” In it, the professor writes that during breastfeeding, valerian should be used very carefully and in the smallest dosages, and in cases where the use of the drug can be abandoned, the doctor recommends doing so. Hale emphasizes that the permeability of valerian into breast milk has not been studied in any study, therefore, how much medicine the baby receives during feeding and how it affects him is not known. In the absence of confirmed data, it is impossible to talk about the safety of the drug.
On a note
In Australia, valerian extract is classified as a category A drug. They are considered the safest and are approved for use during pregnancy.
Alternative Methods
There are other medications that help fight stress and nervousness. Medicines should be taken after consultation with a doctor. Persen has proven itself well, as well as Glycine and motherwort extract. It is worth noting that Persen has a fairly strong effect, so it can only be used as prescribed by a specialist. The use of other drugs when feeding a baby with breast milk is undesirable, as they can cause harm to the baby.

Although valerian is not a dangerous drug for mother and baby, you should not use the medication without consulting a doctor.
How valerian preparations can affect a child’s well-being
How exactly valerian affects infants is not known, since relevant studies have not been conducted. Experts say that in a child the drug can cause:
- Allergic reaction;
- Overexcitement and sleep disturbances;
- Lethargy;
- Intestinal colic;
- Constipation and other disorders of the digestive system. A child may develop an allergy even after taking the drug once by the mother. Moreover, the younger the child, the higher the likelihood of such consequences. The baby may develop a skin rash, itching, redness, as well as a runny nose and cough. In this case, it is better to avoid using valerian and replace it with another remedy.
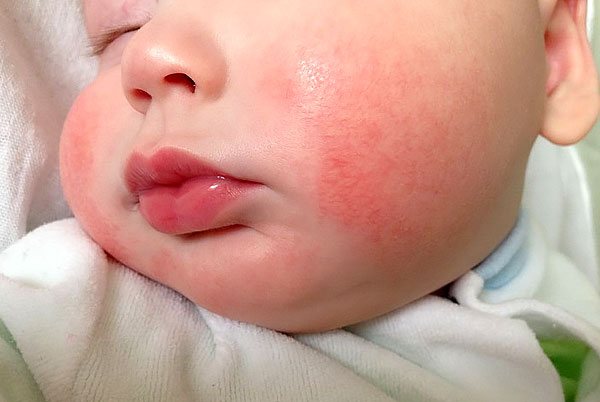
Typical signs that substances taken by the mother have affected the child’s condition.
The second most common side effect is overstimulation. Despite the fact that valerian has a sedative and hypnotic effect, sometimes its effect is exactly the opposite. The child's sleep and usual behavior may be disrupted. The baby may not fall asleep at the usual time, often wake up, cry and be capricious. Valerian can also have a strong sedative effect on the baby. The baby may become lethargic, sleep more, refuse to breastfeed during feedings, and show no interest in favorite toys.
The effect of the drug on the gastrointestinal tract is also not uncommon. There is a risk of colic, constipation and other functional disorders.
The effect of using valerian is not observed immediately, but only after a course of treatment. This is due to the properties of valerian to accumulate in the body. Accordingly, side effects of the drug may also appear after some time. It is very important to monitor changes in the baby’s well-being and behavior, since if any changes occur even 2 weeks after starting to use the medicine, they can also be caused by it.
On a note
Neonatologists recommend that nursing mothers refrain from using valerian and other sedatives and hypnotics for at least the first 4-5 weeks after birth. The possible sedative effect that the drug can have on the child is extremely undesirable during the neonatal period. Also, experts do not recommend taking valerian in case of premature birth or the birth of a child with insufficient body weight.
Action of the product
Valerian is quickly absorbed into the blood, after which the active substances enter the nerve cells and inhibit the transmission of nerve impulses, simultaneously cleansing the blood vessels.
The product has the following effects:
- vasodilator (primarily for coronary vessels);
- lowering pressure;
- antispasmodic (for headaches and stomach pain);
- sedative (relieves stress and anxiety);
- mild hypnotic effect.
The effect of the drug is felt 20-40 minutes after administration, but to achieve a sustainable effect for chronic disorders, a course of treatment with valerian is necessary.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of valerian by a nursing mother are:
- insomnia;
- depression;
- migraine;
- nervousness;
- tachycardia, arrhythmia.
Thus, valerian not only allows you to restore emotional balance, sleep and get rid of headaches, but can also act as a natural remedy for pathologies of the cardiovascular system and manifestations of hypertension. In addition, the plant is effective for disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (improves intestinal motility and regulates stomach acidity).
The most common use of the product is in the form of tincture or tablets, while valerian in tablets is considered a more effective and safe option for use during lactation.
Precautionary measures
Valerian has a fairly extensive list of contraindications and side effects. Only a doctor can decide whether to prescribe the drug to a nursing woman. In this case, you need to consult with a pediatrician who can assess the likely risk for the child.
Valerian is included in many medicines, and therefore before using them you should carefully read the instructions. Some valerian-based drugs are contraindicated during breastfeeding.

Excerpt from instructions for Valerian Extra
Most often, women are prescribed valerian extract in tablets or a decoction that can be prepared at home from dried rhizomes. The tablets can be anything, including the well-known yellow (Valerian Forte), brown (Valerian Belmed) and others. The drops cannot be taken as they contain alcohol.
For adults and children, valerian extract is prescribed 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day, while the maximum dose per day is 6 tablets. During lactation, women are recommended to take the medicine in a minimum dosage, often 1-2 tablets 2 times a day. However, the dosage and course of treatment are determined by the doctor individually and may differ significantly from the general recommendations.
It is very important to adhere to your doctor's orders. You should not exceed a single dose of valerian, as this increases the risk of overdose. However, this will not increase the effectiveness of the medicine. Valerian does not have a quick, but stable effect, which manifests itself gradually, in accordance with the accumulation of the active substances of the drug in the body. The risk of overdose also appears with long-term use of valerian. During breastfeeding, the course of treatment with the drug rarely exceeds 7-10 days.
An overdose can be dangerous for both the woman and the child. Its symptoms may be:
- Drowsiness and apathy;
- Frequent dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- Nervous overexcitation, sleep disturbance;
- Increased blood pressure, increased heart rate for no reason;
- Headache;
- Disorders of the digestive tract (nausea, constipation or diarrhea). If you drink valerian, one or more symptoms may appear in the mother or baby. In this case, it is recommended to immediately stop taking the drug and be sure to consult a doctor.
Adverse reactions
In case of prolonged use of the drug or when using an excessively high dosage, undesirable reactions may occur:
- Irritability, nervousness.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Allergic reaction.

Negative aspects of using the plant can also be observed in the baby:
- Allergic rashes.
- Constipation and colic.
- Overexcitement of the child, sleep disturbance.
- In some situations, the consequences are just the opposite: lethargy, prolonged sleep.
- Long-term consequences may include increased intracranial pressure and deterioration of cognitive function.
Of course, if any of the listed symptoms appear, you should stop taking the drug and seek advice from a medical facility.
Interesting fact! There is a popular myth that valerian can suppress lactation. There is no scientific evidence for this.
How can I replace valerian?
Valerian extract is not always used as a sedative during breastfeeding. In some cases, doctors recommend taking motherwort infusion, Glycine, Novo-Passit or Persen.

Motherwort tincture is also allowed to a limited extent for nursing mothers, and the decision to take it should only be made by a doctor.
Motherwort is often prescribed when a woman is allergic to valerian or is contraindicated for other reasons. Motherwort also has a mild sedative and hypnotic effect, but also has other effects. The question of its use during breastfeeding should also be decided by the doctor.
Novo-Passit contains valerian extract, St. John's wort herb and guaifenesin. The syrup also contains alcohol, so it is not recommended for nursing women. As for the use of tablets, breastfeeding is not a direct contraindication, but the instructions say that the effect of the drug on the child through mother's milk has not been studied.
Persen also contains valerian extract, as well as lemon balm and peppermint. The drug is contraindicated in case of allergies to its components, arterial hypotension, bronchial asthma and some other conditions.
Glycine is prescribed for decreased mental performance and emotional stress. It has a mild sedative effect and, after a course of treatment, helps normalize sleep and improve mood. How much of the drug passes into mother's milk and how it can affect the baby is unknown. At the same time, the active ingredient of the product - the amino acid glycine - is a natural and necessary component for humans, and therefore it is unlikely that its entry into the child’s digestive tract will have any undesirable effects.
The effect of using glycine is similar to that of valerian, but glycine is completely safe, since it is one of the 20 amino acids necessary for the human body.
Easier and safer remedies that a young mother can use are baby soothing teas, which are approved for use in children aged 1 or 4 months. Such products of different brands - Hipp, Humana, Bebivita - can be found in baby food departments. They are intended for infants, but adults can also drink them if they are made more concentrated. When a nursing woman uses such products, the risk to the child is much less than when taking medications, but do not forget that herbal remedies can cause allergic reactions and other undesirable effects.
Homeopathic remedies taken by the mother will not cause harm to the child. The amount of active ingredient in them is so small that there is practically no risk of it passing into breast milk and affecting the baby. However, it is worth considering that you should not expect significant results from the use of such means. During clinical studies, it was found that there is practically no difference in the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies and placebo.
There are a lot of drugs with a mild sedative effect. They are often positioned as safe, but any drug has a number of contraindications and side effects. During breastfeeding, the use of sedatives should be coordinated not only with the therapist, but also with the pediatrician.
It is important to understand that valerian is often prescribed when a young mother, due to fatigue and emotional stress, complains of poor sleep, mood swings or despondency. Sometimes you can improve your well-being in simpler ways that definitely won’t harm your baby. For example, you can agree with one of your relatives to look after your child for a few hours, and go for a massage, to a spa, just take a walk down the street or get some sleep. After the birth of a child, a woman’s lifestyle changes greatly, and she urgently needs the opportunity to relax and pay attention to herself. After a well-planned and well-executed day with breaks for rest, it may turn out that there is no need to use valerian at all, since the mother’s emotional state is normalized due to the normal rhythm.
Permissible doses
In the pharmacy the drug can be found in several forms:
- dried herbs in paper bags;
- roots - they are used to prepare tincture;
- dragee;
- alcohol tincture.
So, in what quantities should a nursing mother drink valerian? Is it possible to use tinctures?
The instructions are extremely simple - take the drug 2-3 times a day, 1 tablet. Most often, the average course lasts about 10 days, but in particularly advanced cases it can be extended. Valerian should not be taken constantly; each drug has its own course of treatment, so take the drug exactly as long as prescribed by the doctor. Do not abuse the drug - it is especially dangerous during feeding.
So, after all, is it possible for a nursing mother to use valerian during breastfeeding? Only your therapist and yourself will give you the final answer to this question. The list of side effects of the drug is extremely small and most often the listed problems arise when the drug is abused. Take valerian strictly according to your doctor’s prescription, without exceeding the dose, and this medicinal herb will not harm either you or the child.
The instructions for use of valerian say that this remedy can be taken by a nursing mother, but only after approval of its use by the attending physician.
The use of valerian extract is indicated if the following symptoms are present:
- problems falling asleep and insomnia;
- headache caused by migraine;
- excessive nervous excitement;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- spasms of the gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with the cardiovascular system.
The main active ingredient of the drug is valeric acid, which has an antispasmodic effect, helps relax smooth muscles and reduce the excitability of the nervous system.
Release forms and dosage of the drug
For ease of administration, the drug is available in several forms. You can choose the one that suits you best:
- medicine in tablets;
- herbal tea for brewing tea;
- dragee;
- collected roots for preparing infusion;
- ready-made tincture with extracts.
During lactation, the drug is most often prescribed in tablets. Their effect is much milder in contrast to tinctures. Taking products containing alcohol can harm your baby. It is enough for the patient to give a couple of tablets a day to achieve optimal results.
READ ALSO: what sedatives can be taken during lactation?
The positive effect does not occur immediately after administration, but after some time. Before you calm down, you should not increase the dose, you will only harm yourself. Soon you will notice a sedative effect, the result will be stable and long-lasting. The course of treatment must be continued for several days - usually 10 days is enough. In rare cases it is necessary to extend the period.
Benefit or harm?
In medicine, there are no descriptions of cases in which it is indicated that valerian extract negatively affected the health of an infant. But this does not mean that you can drink this drug without paying attention to the baby’s well-being. Every nursing mother needs to remember that everyone’s body is different, which means the reaction to valerian may be different. Especially when a child is prone to allergies, you should not take any medications on your own. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment and dosage during the appointment.
When can you drink?
Valerian is an excellent remedy for those who are constantly under stress. This medicine is taken for:
- migraine;
- insomnia;
- depressed state;
- nervous excitement;
- spasms that occur in the stomach or genitourinary tract.
Most often, valerian is taken in tablets; tincture also copes well with the problems listed above. Valerian Forte in tablet form provides a stronger calming effect. In any case, a nursing mother should not take the medicine on her own. You should definitely consult your doctor, since the dosage and form of the medicine may vary depending on the disease.
Sources
- https://floragaz.ru/mamam/mozhno-pit-valeryanku-grudnom-vskarmlivanii
- https://my-grudnichok.ru/valeryanka-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii-komarovskij.html
- https://prokrohu.ru/kormlenie/valeryanka-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://1child.ru/kormlenie-grudyu/valeryanka-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii-dozirovka.html
- https://its-kids.ru/valeryanka-pri-gv.html
- https://VseProRebenka.ru/laktaciya/samochuvstvie-mamy/valeryanka-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://KormiGrudyu.ru/valeryanka-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii
- https://heart-info.ru/lekarstva/mozhno-li-pit-valerjanku-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii/
- https://amymama.ru/lekarstva/mozhno-li-valeryanku-kormyashchej-mame.html