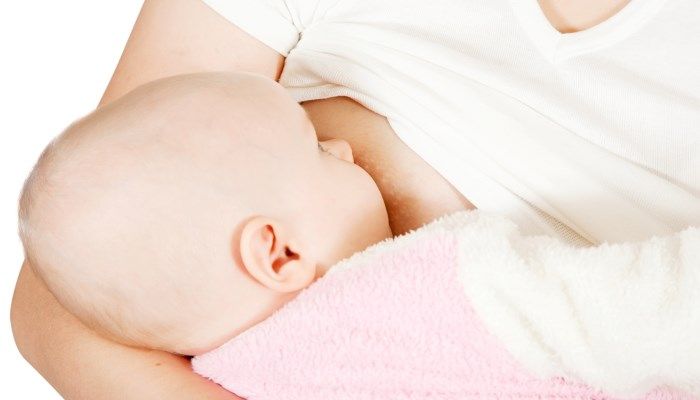
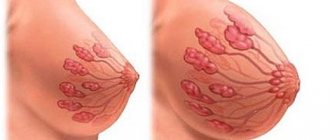
Breastfeeding is extremely important for a child's immunity. WHO recommends continuing natural feeding for at least six months. In the absence of mother's milk, the child's risk of developing infectious diseases increases and immunity decreases for the rest of his life. Therefore, it is important for a nursing mother to properly establish lactation. One possible problem is that there is no milk in one breast. This is a common occurrence, let’s look at the reasons and find out how to establish full lactation.
I'm not pregnant, why is there milk?
The discharge may be green or yellow; galactorrhea is more common in women who have given birth. Sometimes it is milk production caused by nipple compression, sexual stimulation, or clothing friction. Other reasons:
- Taking hormonal or psychotropic drugs
- Herbs that stimulate the mammary glands (anise, fennel)
- Drug use (marijuana)
- Tumors in the pituitary gland are often benign
- Hypothyroidism
Women who worry too much may touch their breasts frequently, exacerbating the problem. If you notice discharge from your breasts, try not to touch your breasts too often.
How to improve lactation
There are a few simple rules that will help increase milk production, regardless of the reason for the problems:
- The first rule is that it is necessary to equalize production; for this there must be stimulation of both glands.
- For a while, the deficient mammary gland should be made the main one for feeding. You can supplement from the other breast, but only if the baby is not getting enough. Excess milk from the second breast can be expressed.
- You need to find out when the baby takes the longest to breastfeed. And it is at these moments that we offer the problematic mammary gland.
- It is important to ensure that the problem is not due to poor posture or anatomy.
- You need to double-check your feeding position and adjust it. You need to teach your baby how to apply properly, and you yourself need to monitor the uniform emptying. It is often difficult to understand how to do it correctly, so it is better to consult a pediatrician. The consultant will tell you what exactly the child or his mother is doing wrong.
The following problem may arise: the baby will not like being offered breasts without milk. In this case, you need to keep trying. It is important to remember that the mother, not the child, sets the feeding rules.
If the baby does not take the breast under any circumstances, you need to express the milk with a breast pump. It is effective to use instead of natural stimulation. Over time, you may notice that there will be more milk. At this point, it is worth trying to give the same breast to the baby again.
So, the main rule is to adjust feeding so that the smaller mammary gland receives sufficient stimulation. Then lactation will improve, and the child will be able to eat well.

Galactorrhea - what is it, treatment, causes
Published: 02.22.2018
Galactorrhea is the release of milk substance from a woman’s mammary gland, which is not associated with breastfeeding after pregnancy. Galactorrhea occurs predominantly in women and much less frequently in men. The milky white substance may come from one or both breasts. ContentsCausesOther causes of galactorrhea:SymptomsDiagnosticsTreatment of pituitary tumors that stimulate milk productionPrevention Causes Galactorrhea has many causes, although sometimes the cause cannot be identified
no comments yet
Lactostasis
Symptoms of lactostasis.
One of the most common problems that a nursing mother faces is milk stagnation or lactostasis . Manifestations of lactostasis are quite unpleasant: chest pain , lumps in the breast , redness of the mammary gland above the lump, there may be an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees or more, general weakness.

The most common causes of lactostasis:
- improper latching of the breast by the child;
- ineffective sucking;
- insufficient emptying of the mammary gland;
- skipping feedings, rare and short feedings;
- use of breast substitutes: pacifiers, bottles;
- feeding with breast pads;
- chest bruise;
- tight underwear or incorrectly selected bra;
- blockage of the nipple or milk blister (callus);
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- sleeping in an uncomfortable position;
- feeding the baby mainly in one position;
- structural features of the mammary gland (cysts, mastopathy, previous injuries or operations, scars, adhesions, etc.);
- stress, general fatigue and lack of sleep in the mother.
What to do with lactostasis?
- Feed the baby as often as possible , placing him in such a position that his chin is directed towards the seal (at least once every 1.5-2 hours). If during lactostasis the milk is easily expressed on the first day, then you can express all the milk that easily comes out before feeding. This procedure can be repeated 2-3 times on the first day.
- At high temperatures, you can take antipyretic drugs that are compatible with breastfeeding. These are drugs based on ibuprofen (for example, Nurofen, ibufen, etc.) or based on paracetamol (Panadol, Tylenol, Efferalgan, Prodol).
- It is necessary to relieve the swelling that occurs when milk stagnates . To do this, we recommend applying cold (such as ice cubes in a bag or a cold towel) after each feeding for 7-10 minutes on the area of the lump. If you don’t have ice at home, you can also add a cold cabbage leaf.
- Before feeding the baby, you can do a lymphatic drainage massage for 10-15 minutes, this will also help relieve swelling and release flow.
- If the baby is separated or for some reason does not breastfeed, then it is necessary to express according to the scheme prescribed by the lactation consultant.
Is it necessary to warm the breasts during lactostasis?
Often, with lactostasis, you can hear advice to warm the area of the lump or go into a hot shower and try to express milk . Yes, this can be done, but only in the first day of lactostasis, and if the milk is easily expressed. However, in some cases, lactostasis quickly passes into the inflammatory stage, into an abscess or mastitis (lactostasis is especially dangerous in case of cracks and other damage to the nipples). Therefore, it is still undesirable to heat the sore spot, so as not to accelerate the inflammation process.
In any case, it is advisable to consult with a doctor experienced in breastfeeding or a certified lactation consultant.
Also, in order not to provoke additional flows of milk outside of feedings, during lactostasis it is advisable not to consume hot food or drink. At the same time, you should not limit your fluid intake; drink according to your thirst, but choose drinks at room temperature.

What not to do with lactostasis:
- stop feeding the child;
- forcefully knead the chest and in particular the area of the lump through pain, especially with the knuckles;
- warm if you are not going to feed the baby right away (consult a specialist!);
- offer to resolve lactostasis to someone other than the child (you can get an infection and also get swelling of the nipple);
- apply alcohol and vodka compresses , smear the seal area with Vishnevsky ointment or camphor;
- Lactostasis and mastitis cannot be treated with compresses, rubbing, devices and other dubious means.
If cope with lactostasis on your own in the first day, then you need to seek help from a lactation consultant and/or a mammologist or surgeon experienced in matters of lactostasis and mastitis.
If, in addition to lactostasis, you have cracked nipples, then there is no need to wait, call a lactation consultant immediately, because the presence of cracks is a clear sign of improper attachment, and in combination with lactostasis, your situation worsens sharply and can quickly lead to complications (mastitis or abscess).
The doctor will be able to perform an ultrasound of the mammary glands , and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics and ultrasound physiotherapy .
A lactation consultant will help identify the cause of lactostasis, check the correct latch on the breast , select a suitable position for feeding , teach how to attach the baby to the breast so that he can effectively cope with stagnation, give information about the fight against lactostasis that has already occurred and knowledge about the necessary prevention occurrence of lactostasis in the future. And most importantly, he will be able to send you to the right specialist in a timely manner before the need for surgical intervention arises.
Ksenia Orlova, lactation consultant, sling consultant (edited by Polina Novoselova, lactation consultant)
Call a consultant Do you have any questions? +7 (812) 956-3-954
What to do?
The first thing to do is stop any form of breast stimulation. Avoid touching the nipple area, squeezing, tight clothing, or sexually stimulating the breasts. If this does not help, you should consult a doctor, be sure to tell us about all the medications you took.
This is interesting: Lactation without pregnancy - reasons, can this happen?
Wait one menstrual cycle, and if the problem persists, be sure to visit your doctor, as breast discharge can be a symptom of breast cancer.
Especially pay attention to the fact that if there are blood clots in the discharge, then there can be no talk of galactorrhea; in this case, it is necessary to completely examine the mammary glands!
“Non-dairy moms are a myth.” Experts and mothers about breastfeeding
It's no secret that the key to a child's harmonious development is his nutrition from the first days of life. Breastfeeding is optimal for a child, which is due to the unique composition of mother's milk, its hypoallergenicity and ease of digestibility. In addition, it contributes to the emergence of a strong emotional bond between mother and child. As will become clear from our conversation, every mother can cope with difficulties and successfully feed her child.

Bobruisk maternity hospital. Photo by Alexander CHUGUEV is used as an illustration.
By the way, both of my sons are “Caesareans”; I nursed the older one for a year and a month; I plan to feed the younger one until he is about one and a half years old; I decided for myself that such a period is quite enough. We have free feeding and practice co-sleeping, which invariably causes outrage among the age group of our loved ones. We stoically overcome lactation crises, and at first – lactostasis with a temperature of “over 40” and cracks, despite efforts to make everything “like on the Internet.” To be honest, I do not feel wildly delighted during the feeding period, since for me this is a certain discomfort and restriction of freedom, but for the sake of the health of my children I am ready to endure minor inconveniences. There are also undoubted advantages of natural feeding: less fuss with feeding, better night's sleep for mother and baby, truly some kind of special, tender closeness with the child, and for many, an important point is also considerable budget savings.
Lactation consultant Alena Arsentyeva.
Alena Arsentyeva answered our questions about breastfeeding (Alena’s coordinates can be obtained from the editorial office or found on the Internet).
– Alena, how can a woman prepare and increase her chances of successful breastfeeding?
– I believe that no special preparation is required, we need to trust Mother Nature, who came up with everything for us. You just have to listen carefully to what your body tells you. Believing in yourself and in success is required - this forms a strong dominant attitude towards breastfeeding.
Tatyana N., mother of two children:
“I couldn’t feed my daughter because the nipples were “undeveloped,” she refused to suck, and my son developed dermatitis, and he also had to stop.
– In your opinion, are there “non-dairy mothers” and are there often objective contraindications for breastfeeding?
– This concept is a myth. Every woman is capable of feeding. According to statistics, only 3% of women in labor may experience a decrease in lactation for serious physiological reasons: due to a pituitary tumor, neoplasms in the mammary glands, for example. Neither the shape of the nipple, nor the size of the breast, nor the shape of the areola matters. A common contraindication is taking medications that are not compatible with breastfeeding. In such cases, the child is temporarily weaned.
Elena K., mother of a 3-year-old baby:
– I only fed for two months. There was jaundice. We were lying in the maternity hospital, warming ourselves under the dome, and I was pumping. Then I couldn’t go home for another two weeks either. And then there was no milk.
– How to learn how to attach to the breast correctly?
– Ideally, watching experienced mothers, the work of consultants: when they literally show where the baby’s arm, leg, and head should be. In Internet sources, mom may not notice some important points. Important: the breast must be placed in a wide open position, like a chick’s beak, the baby’s mouth, the nipple and areola should be almost completely in the mouth. If you move back slightly, you can see the tip of the child’s tongue on the lower gum, the lips are turned outward. Ears move when sucking. It is necessary to support the head and ensure that the baby does not slide off the nipple.
Julia, young mother:
– I stopped feeding after a couple of months, because the milk was not enough and “empty”, the child did not get enough.
– How can a mother know that everything is okay - the child is eating correctly?
– An important indicator is monthly weight gain. At home, counting “pees”: the daily norm for boys is 14, for girls 12. But for this, the baby needs to be kept in clean diapers for a day. If the baby exceeds the norm, the mother has enough milk. The concept of “empty milk” is a prejudice. Human milk does not contain as much fat as cow's milk; you cannot see it with the naked eye, and the bluish color, which is usually taken as a sign of low fat content, is given to it by immunoglobulins.
Nastya, mother of children the same age:
– I’m after a caesarean section. There wasn't really any milk there either. While still in the maternity hospital, we switched to formula.
– Should I feed both breasts at one feeding?
– Doing this is detrimental to lactation and is not beneficial for the child. Milk is divided into fore and hind milk. Foremilk is liquid, easily separated, quenches thirst, and hind milk is thicker, responsible for weight gain and stool. In addition, the anterior one contains the milk sugar lactose, and the posterior one contains the enzyme that breaks it down, lactase, and fats. Therefore, the child must drink both of these fractions of milk together. Up to 1.5-2 months, one breast is offered to the child for 1-1.5 hours, regardless of the number and duration of feedings during this period: this can be three times for 20 minutes, or one for 40 minutes, or several times for five minutes. As the baby grows, the time for alternating left and right breasts will be approximately 2-3 hours. If a woman experiences hyperlactation that causes discomfort, you need to understand the reasons. You can only slightly pump the breasts when the areola becomes engorged. The chest needs to be “taught” to work correctly. Hyperlactation is quite common, since many women are induced with oxytocin during labor. Over time, everything returns to normal. Over 10 years of practice, I met only one woman with natural hyperlactation.
– Tell mothers what improves milk production?
– I would like to draw the attention of mothers to the fact that lactogenic agents should not be used thoughtlessly. Serious drugs can cause lactostasis. But pharmaceutical products such as “Mlekoin” are rather a psychological move, and besides, they can cause allergies in a child. You can drink teas, such as “Leros for nursing mothers”, it strengthens the immune system. Milk production is directly affected by the psycho-emotional state of the mother, the productivity of rest and sleep.
Tatyana G., mother of many children:
– I still use the advice of the neonatologist at our maternity hospital, which I received when I was still pregnant for the first time: in order to breastfeed, you need to feed without any additional feeding, and if the milk does not come, you need to sleep with the baby (meaning keeping the baby near the breast), and nature will definitely do its job.
– Does co-sleeping affect the situation?
– I have a positive attitude towards co-sleeping, as it improves the quality of rest of mother and child and enhances their tactile contact. Between three and eight in the morning, 2-3 full feedings are optimal, which allows you to form a “bank” of milk for the next day. Excellent writing about the benefits of co-sleeping by the Sears (meaning W. and M. Sears, authors of books on pregnancy and child development - author's note).
– Should I use bottles, nipples, and pacifiers?
– Since the technique of sucking the breast and the pacifier is different, “nipple confusion” occurs, and the child refuses the breast. The absence of nipples is one of the WHO requirements for breastfeeding.
– Alena, tell us how to prevent and eliminate nipple problems?
– In the early stages, cracks occur very often. The Purelan cream has proven itself well, softening and healing microcracks. But it only works in combination with proper application. It is important to carefully study all the nuances using the Internet or a specialist. The pictures most often show babies 2-3 months old, and mothers often make a mistake: trying to look at the baby’s sponge turned out in the right way, displacing the breast, they themselves pull back the skin on the nipple, violating the correct attachment. There is no need to do this; you should focus on the absence of prolonged pain. Please note that in the first two weeks, application is accompanied by severe burning pain, which goes away within a few seconds after suction. This happens because the skin of the areola is very thin, with many nerve endings. The child presses it with his tongue, like a spatula, and, as it were, grinds the skin - as a result, a so-called “milk callus” is formed. The skin gradually becomes rougher and the pain syndrome disappears. If it hurts all the time when feeding, the baby is not attached correctly; most likely, he is injuring the areola with his gums. It is very important to pick up the breast correctly - under no circumstances pull on the nipple, as a result of which the baby’s gums will damage the top layer of skin, which will turn microcracks into wounds with the next incorrect application. You need to insert a clean index finger or little finger into the corner of your mouth between the gums, and the breast will easily release.
– What should be done with lactostasis?
– The most common mistake is pumping. It is effective only in the first 12 hours. Usually mothers understand that the duct is clogged when the temperature rises, thickening and redness of the skin appear. Since the duct is clogged with a milk plug, the arriving milk puts pressure on the walls of the blood vessels, almost forming an internal hematoma, and by expressing, we also create an external one. The best way is drainage, and no one except the child will provide the ideal effect. Therefore, we “hang” the baby on the sore breast, but do not forget to look after the second one. In place of the redness, make a cottage cheese or honey cake.
– What is the best way to feed – on demand or on a schedule?
– I am definitely in favor of feeding on demand. And applications should be very frequent in the first months. The hormone prolactin, responsible for milk production, disintegrates in the blood within 1.5 hours. Accordingly, it is necessary to constantly replenish its reserves by feeding the baby and stimulating the work of the pituitary gland.
– Do babies need to drink extra food?
– One of the conditions for successful feeding is the exclusion of additional water, teas, etc. Breast milk contains 87-90% water, which can fully satisfy the need for fluid. In addition, supplementation creates a false feeling of fullness, since the centers of hunger and thirst in the brain are located nearby.
Ekaterina Sh., young mother: – No one really explained to me how to take care of my breasts! They just signed the papers that the conversation was held! And then it turned out that if you are breastfeeding, you can’t eat everything... even in the maternity hospital there are foods that nursing mothers can’t eat!
– Share your experience on nutrition while breastfeeding.
– My opinion is this: the baby still gets acquainted with the mother’s diet through the placenta. I fed all the children until self-weaning and only excluded foods with all kinds of glutamates and harmful additives. I monitored expiration dates and took products with shorter ones. She didn’t exclude coffee and sausages, and that’s probably why she was always happy and happy (laughs).
treat, for example, a cold while breastfeeding
– If you feel unwell, consult a doctor immediately. Select medications that are compatible with breastfeeding; there are many of them now.
Tatyana D., mother of many children: – She fed her daughters until she was three, and her son until he was almost four, at night. I didn’t particularly bother with complementary foods. At one time, we somehow lost interest in breasts.
– Until what age is it best to feed?
– Every mother chooses for herself. Let me just say that a week is better than a day, and a month is better than a week, and so on. WHO recommends feeding for up to two years or more. The Bible also indicates a period of two years - by the way, have you paid attention to the age of the children depicted on the icons at the mother’s breast? And Muslims, for example, feed until five years. So it all depends on the situation. Feeding in the first year and in two or three years are completely different things. The baby gradually learns to do without the breast, a certain behavior is brought up: do not ask for the breast at the table, in front of people. After a year, this is already a sacred process, controlled by the mother, and not the child. The psychological factor is also important for us. We perceive as the correct model what is in front of our eyes: a baby doll with a bottle, a doll with a pacifier. You won’t find women openly breastfeeding their children here. And mothers who breastfeed for a long time begin to doubt themselves. To increase self-confidence, you should use everyday techniques: paintings depicting breastfeeding women, communicating with similar mothers. Feeding should be a thrill for mom.
– How to finish breastfeeding painlessly?
– To avoid any discomfort, it is optimal to feed until the baby is self-weaned. However, if for some reason you decide to complete the process earlier, there are medicinal methods. But this must be done under the supervision of a doctor (author’s note).
– How does breastfeeding affect the health of the mother?
– Despite my long experience, I have my own teeth, hair, nails and skin (laughs). But seriously, breastfeeding has the most beneficial effect on a woman. This is rejuvenation of the body due to changes in hormonal levels, prevention and even treatment of mastopathy and other breast problems. Long-term feeding is a way to prevent the appearance of neoplasms of the female reproductive system, since a sudden cessation of feeding has long-term consequences, which many do not think about.
– Where can Bobruisk women go for advice on breastfeeding issues?
– We have few experienced and competent specialists in our city. I have been consulting for the past 11 years. She studied at the Minsk City Institute for Educational Development. Telephone consultations are free, almost all problems can be solved remotely, since they are a consequence of the mother’s incomplete information. In rare cases - underweight, organizing the feeding of twins, natural hypolactation - I go to your home; in such cases, transportation costs are negotiated individually. In general, it’s easy to find a consultant on the Internet by entering your locality. But you need to be careful: more than once we had to solve problems caused by the illiterate approach of some consultants who took newfangled paid courses.
Nutrition specialist during pregnancy Maria Litvinova.
Maria Litvinova , a specialist in nutrition during pregnancy, obstetrician-gynecologist, nutritionist, told us about the nutrition of a nursing mother to prevent colic and allergies
– You may be surprised by the fact that in order to protect the baby from allergies, a woman should eat a varied diet while breastfeeding. Food allergies occur in newborns and children in approximately 2-10% of cases, and its cause is not a violation of the diet, but the peculiarities of the functioning of the immune system. This can be either a genetically determined mechanism or insufficient maturity of the gastrointestinal tract and immune system of the newborn.
How to start eating varied while breastfeeding?
– We use the “rule of nutrition for the first month.” From my own experience, I can say that the most cautious period regarding food is the first month after childbirth. The baby’s gastrointestinal tract has just become acquainted with food that is new to him, it is populated with beneficial microflora, enzyme systems begin to function - during this period you need to be extremely careful in choosing foods. Do not forget about the importance of colostrum in the first days of a child’s life - a nutritious and antibody-rich product that will launch immune defense processes in the newborn’s body. I advise you to start with easily digestible foods: dairy-free porridge, boiled chicken breast, turkey, rabbit, chicken broth, pasta, cheese, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, zucchini, cauliflower, carrots, broccoli, cucumbers, potatoes, cereal soups. For the first two to three weeks, it is better to eat the vegetables listed in processed form: steamed, stewed. It is better to introduce raw vegetables and fruits after a month, when the child’s digestive system is ready for “stress.” If you really want fruits and vegetables, I would recommend baby fruit purees. They are thermally processed, easily digestible and do not put any strain on the intestines. During this period, monitor the nature of the baby’s stool - if it is liquid, frequent, greenish - limit vegetables and fruits; if you are prone to constipation, on the contrary, focus on pear puree, prunes, and boiled beets.
Do not overuse legumes; it is better to exclude them from your diet in the first month. Monitor your child's reactions: it could be urticaria, dermatitis. If you notice a connection with a certain product, limit it for a while. After 1-2 weeks, administer again in small portions - this way you will help “train” the immune system and reduce the risk of developing food allergies in the child in the future. If there is no reaction to food, then you should not remove the product from your diet. Some children take longer than others to develop immune tolerance, up to three years of age.
Currently, the most potent allergens are cow's milk protein, eggs, peanuts, shellfish, fish and sesame. If you have not noticed any allergies in your child, there is no need to give up these products.
The cause of colic in a newborn can be both intestinal immaturity and allergies. To prevent them, use the “first month nutrition rule.” From the second month, diversify your diet, it is advisable to introduce one new product per day. It is advisable to include a lot of fatty fish in your diet, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, or take omega-3 nutritional supplements, they accelerate the development of the immune system. If you have tuna or salmon on your menu less than 2-3 times a week, then you can additionally take fish oil.
Ekaterina Novitskaya is the host of the “Mom on Maternity Day” column, a very suspicious mother of wonderful boys, 12 years and 7 months old. You can send any questions about the development, upbringing, problems of your children to: [email protected]
By the way, recent studies have found that milk from mothers who use hot spices or garlic may taste better to breastfed babies? So you shouldn’t limit spices, onions and garlic. Within reasonable limits, of course.
Instead of a resume
Moms, don't be shy to ask for advice and believe in the success of breastfeeding. And next time we’ll talk about artificial things.
When to worry about milk without pregnancy
Only your doctor can tell you for sure whether what is happening to you is normal or not. Below are several factors that are atypical for galactorrhea and require careful examination:
- One cause for concern is the presence of blood in milk.
- When discharge comes from only one breast
- Milk appears from the breast unexpectedly, without pressure or stimulation
Milky discharge from the breasts in non-pregnant women ranges from minor to serious health problems, below are detailed explanations:
Do I need to wean?
If there is less milk, this is not a reason to wean the baby off from feeding. Even if there is little milk, it is necessary to continue natural feeding. Over time, the breasts will get used to producing enough milk, and the ducts will become wider. If you refuse to feed, lactation will not be restored.
During the period of treatment of lactostasis (and it can also be the cause of reduced function of one breast), you should also not stop feeding. It is important to support natural processes. This is important not only for the child, who needs to receive a full range of nutrients. Also for the mother, who will establish lactation faster if she receives stimulation of the mammary glands during feeding.

Minor reasons for the appearance of milk
- Hormonal change . Hormonal changes during puberty, after pregnancy, and during menopause can cause milk production. Cushing's disease can also be caused by breast discharge.
- Use of contraceptives . Oral contraceptives may cause breast discharge, which usually goes away after a while.
- Recent breastfeeding . If you have been breastfeeding your baby for the previous two years, then in this case, discharge from the breast is completely normal.
- Antidepressants . These medications increase prolactin in the body. Prolactin – stimulates the body to produce milk.
Milk production rate and breast capacity
Breasts produce milk 24 hours a day. This was proven back in the middle of the last century [3]. Previously, as lactation consultant Linda Smith writes [5], it was thought that milk was produced during feeding, with hot flashes, but studies have shown that during feeding it simply flows out faster, and is not produced faster at all. Even during the so-called “tidal lactation” (a term popular in the Runet).
In the first days, lactation is determined and triggered by the mother’s hormones. This phase is called endocrine. Next, the milk production regulation system comes into play, which is controlled by breast emptying, the frequency and quality of the baby’s sucking. This is autocrine regulation.
Researchers from the University of Western Australia, led by Peter Hartmann [1], found that the rate of milk production varies throughout the day. It is inversely proportional to breast fullness. The more empty the breast is, the faster milk is produced in it. The rate of milk production varied from approximately 40 ml/hour in a well-emptied breast to 10 ml/hour in a full one. The rate of milk production in the breast did not depend on the level of prolactin in the blood or on the rate of synthesis in the opposite breast. If a child emptied one breast during feeding, then after feeding milk production in it was in full swing, and in the second, unused one, it was very slow, although the level of prolactin in the blood was, of course, the same for both one and the second breast. The fact is that milk accumulating in the breast itself stops the work of the cells that produce it - due to the fact that it contains an “inhibitor” protein, and because lactocytes, stretched due to overcrowding of the alveoli, react worse to prolactin . Perhaps there are some other mechanisms that are still unknown.
The produced milk gradually accumulates in the alveoli and ducts, but not indefinitely. Each woman has a different breast capacity, the maximum volume of milk that can collect there. This volume can be very different. The same Australian scientists, using a sophisticated computerized system for scanning breast volume [1], found that some women who participated in their studies had this volume as low as 80, and in others even 600 ml. The capacity of the left and right breasts of one woman also differed. Interestingly, all these mothers, regardless of breast capacity, were able to fully provide their babies with milk. The daily amount of milk was almost the same; for these mothers it was 859 and 890 ml. On average, the daily volume of milk drunk by a fully breastfed child from one month to six months, according to various studies (conducted by different methods), was approximately constant and equal to 750 (plus or minus 150) ml [4]. After 6 months, both breast capacity, its external size, and the daily volume of milk produced decrease [2]. Interestingly, at the same time, the efficiency of the breast - the amount of milk produced per unit volume of glandular tissue - on the contrary, increases. Therefore, after a year, mothers could produce enough milk for their children, despite the fact that the breasts returned to their “pre-pregnancy” size.
How is it that breast capacity does not affect daily milk production?
We remember that the less milk in the breast, the faster it is produced, and vice versa. In mothers with large breast capacity, the child often cannot empty the breast “in one sitting” - it simply won’t fit into it that much. Therefore, in the morning, while these mothers’ breasts were full after the night, the rate of synthesis was the lowest - the child suckled, ate as much as he wanted, but there was still a lot left. At the next feeding, the total volume of milk was slightly lower than at the previous one. Only towards the evening the child still ate most of what was in the breast, at which time milk was produced quickly.
And in women with a small capacity, the child very quickly ate all the reserves, emptying the breast almost every time. Their rate of milk formation was consistently high. Frequent feedings were necessary for these mother-baby pairs.
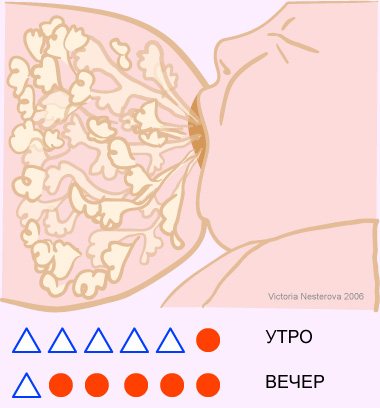
It turns out that those mothers who have a large breast capacity can theoretically feed the child (if he agrees to it) and according to the regime, without experiencing any problems - at least in the first two to three months (there are also hormonal regulation mechanisms ). Perhaps this is where the stories come from: “I fed as my mother/doctor/nurse advised me, according to the regimen, I didn’t do the newfangled feeding on demand - and there was a lot of milk! And that’s how you feed, don’t listen to these fanatics/consultants.” And women with small breast capacity need frequent emptying, and recommendations to “take breaks of 3 to 3.5 hours” are detrimental to their lactation. If they decide to follow the experience described above, or listen to the advice of others to introduce a strict regime for the child, they may find that the baby stops eating. These moms may conclude that they are non-dairy, but they are not!
How to visualize this:
There are several people. In front of everyone there is a plate of porridge, the same for everyone (this is our daily milk volume). Imagine that one of the eaters was given a tablespoon, another a teaspoon, and the third a ladle (this is our breast capacity). After all, it is unreasonable to demand from the owner of a teaspoon that he empty his plate, scooping the same number of times as the owner of the ladle? He'll still be able to handle his plate, he'll just have to scoop more often. Lactation consultant Christina Smillie believes that breast capacity is not a fixed value for each mother, strictly determined genetically. How often and for how long the baby suckles also affects breast capacity in each lactation, even for the same mother with different children [6]. There are still many unknowns in this area.
Conclusions:
- Milk synthesis is regulated by the degree of emptying of the breast.
- Empty breasts = rapid milk synthesis. Full breasts = slow milk synthesis
- This regulation system is very flexible
- Frequent latching by the baby maintains a high rate of milk production in the breast and the daily volume of milk the baby drinks increases.
- There is no point in hoarding milk - it will only lead to a decrease in lactation
- Occasional pumping does not immediately trigger hyperlactation in the mother
Victoria Nesterova, for AKEV magazine
Literature
- Cox, D. B., Owens, R. A., and Hartmann, P. E. Studies on human lactation: the development of the computerized breast measurement system (1998). https://mammary.nih.gov/reviews/lactation/Hartmann001/index.html
- Jacqueline C. Kent, Leon Mitoulas, David B. Cox, Robyn A. Owens and Peter E. Hartmann. — Breast volume and milk production during extended lactation in women Experimental Physiology. - (1999), 84:435-447
- Peterson, W. E. Lactation. Physiol Rev 1944; 24: 340-71.
- Riordan J, Auerbach KG: Breastfeeding and human lactation(ed 2). Sudbury (Mass): Jones and Bartlett Publishers, pp. 98-104, 1998
- Smith Linda J How Mother's Milk Is Made. —LEAVEN, Vol. 37 No. 3, June-July 2001, p. 54-55
- Smillie C, Campbell H, Iwinski S. Hyperlactation: How Left-brained “Rules” for Breastfeeding Can Wreak Havoc With a Natural Process. — Newborn and Infant Nursing Reviews, Vol 5, No 1 (March), 2005: pp 49-58
- Jacqueline C. Kent, Leon R. Mitoulas, Mark D. Cregan, Donna T. Ramsay, Dorota A. Doherty, and Peter E. Hartmann. — Volume and Frequency of Breastfeedings and Fat Content of Breast Milk Throughout the Day. Pediatrics Vol. 117 No. 3 March 2006, pp. e387-e395
Tweet Pin It
Diseases and other causes
In rare cases, reduced production in one mammary gland may be the result of a disease:
- Lactostasis is stagnation in one gland. Characterized by severe swelling, engorgement, and pain. The symptoms are clear, the disease can be diagnosed independently. Treatment is decantation. In difficult situations, you can consult a doctor who will give individual recommendations.
- Mastitis. Often develops against the background of untreated lactostasis. Symptoms are fever, redness, pain, swelling. Non-infectious mastitis is not a contraindication to feeding. If the disease is caused by an infection, you will have to stop feeding and take a course of antibiotics.
- Tumors. Benign and malignant neoplasms can cause narrowing of the milk ducts. Tumors may not manifest themselves for a long time, and the first symptom will be difficulties with lactation.
- Congenital anomalies. Narrow milk ducts and pathologies of glandular tissue can be congenital. In such a situation, no treatment will help. It is worth sensibly assessing the situation - will there be enough food from just one mammary gland? If not, you should use mixtures in addition to natural nutrition. By the way, WHO does not recommend giving up breastfeeding even in conditions of insufficient milk supply.
- Consequences of operations. Some plastic surgeries involve crossing the milk ducts. The ducts become damaged, which can lead to undesirable consequences. There is also no treatment; the recommendations are the same as for girls with congenital anomalies. Very often, plastic surgeons recommend cosmetic surgery only after children are born.
If there is a suspicion of any disease, then self-medication is unacceptable. It's worth seeing a doctor.