After the birth of a child, to improve growth and development, his body needs important vitamins and microelements, which it takes through mother’s milk. However, not all important and beneficial substances are found in breast milk in sufficient quantities. For example, vitamin D (calciferol), which is very important and necessary for a growing body, enters the body in insufficient quantities for the daily requirement. Therefore, it is important for a woman to replenish the child’s vitamin deficiency through medications in the form of drops. In order not to exceed the norm of consumption and to provide the body with a useful substance in the right quantity, you need to know how to properly give vitamin D to a baby when he is breastfed. We will consider these and other questions in this article.
The need for vitamins during breastfeeding
A woman who is breastfeeding needs more nutritional components. The further development of the child depends on proper nutrition and the amount of vitamins and mineral elements.
The baby receives all the components necessary for health through breast milk. If there are not enough of them in it, the woman’s body becomes the source of the necessary elements.
Active leaching of minerals will lead to exhaustion, suppression of the immune system and deterioration of the general condition.
After childbirth, when a woman begins to breastfeed, she should take vitamins only if she is not eating properly and there are signs of hypo- or vitamin deficiency.
If the diet is structured correctly and consists of natural products enriched with vitamins and minerals, the body will not need them additionally.
Vitamins necessary for breastfeeding.
Vitamin norm
It is important to know the consumption rate in order to best meet the needs of the child’s body. The daily dose for a newborn is 700 IU; if the child was born prematurely or with low weight, then the norm is doubled. For older children, 500 IU of calciferol per day is enough. However, an excess, like a lack of an element, can also provoke negative consequences for the child’s body. The fact is that calcium, which is absorbed excessively, settles in other organs (heart, kidneys, stomach, blood vessels), which can disrupt the functioning of the digestive system and provoke the appearance of atherosclerosis.
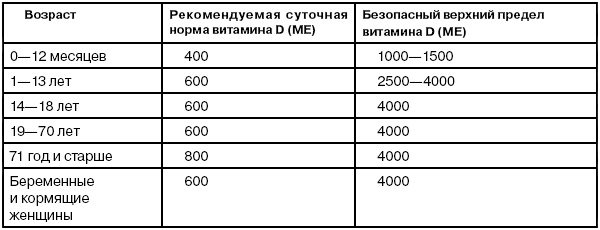
How many nutrients do you need for breastfeeding?
During lactation, a woman needs to receive vitamins in appropriate amounts in order to recover faster after childbirth and give the baby as many useful components as possible.
When breastfeeding women should consume:
- B vitamins regulate the functioning of the central nervous and digestive systems. Responsible for the good condition of hair, nails and skin.
- Vitamins A, C and E - are directly involved in the restoration of skin and hair after childbirth, have a strengthening effect on the immune system, and normalize altered hormonal levels.
- Vitamin D, phosphorus and calcium are essential for the full development of a child. These substances contribute to the proper formation of the musculoskeletal system and have a positive effect on vision.
- Zinc, iron and iodine restore the balance of hormones, prevent the development of anemia, and have a positive effect on the functioning of the child’s brain.
After childbirth, the female body needs all the vitamins and mineral components, but those listed above are the main ones, so emphasis should be placed on them.
Daily norm
Daily amount of nutrients:
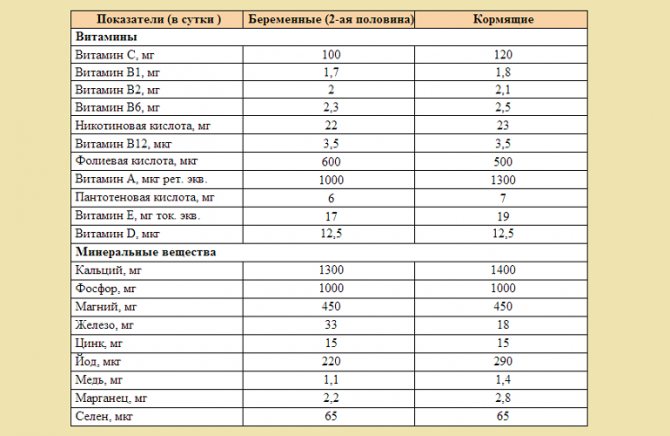
Table of daily vitamin intake for a nursing woman.
- Retinol (A) - from 0.4 to 1.2.
- Thiamine (B1) - from 15 to 20 mg.
- Riboflavin (B2) - 2.2.
- Pyridoxine (B6) - 2.2.
- Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) - 0.04.
- Nicotinic acid (PP) - from 18 to 23 mg.
- Ascorbic acid (C) - 0.1.
- Tocopherol (E) - 15.
- Vitamin D - 0.01.
- Calcium - 1200 mg.
- Magnesium - 450.
- Ferum - 25.
- Phosphorus - from 1000 to 1200.
- Iodine - 0.2.
- Zinc - 25.
Due to the development of a possible overdose of vitamins, it is necessary to take multicomponent complexes especially carefully, strictly observing the dosages specified by the manufacturer.
In what form is it best to consume?
The choice of vitamin and mineral complexes intended for pregnant women is large. But even the most balanced formulations of drugs cannot replace natural food, which is the best source of vitamins.
Who especially needs vitamin D?
It is extremely important to provide the body of a newborn baby with the required amount of calciferol. Children have weak bones and an immature skeletal system; in order to strengthen it and ensure full growth and development for the baby, it is imperative to replenish the reserves of this useful substance. At the same time, it is important to remember that it makes no difference whether the baby eats his mother’s breast or an adapted milk formula during artificial feeding; additional vitamin D intake is required for any method of feeding. Breast milk contains a small amount of this beneficial substance. For those children who grow up on high-quality formulas, manufacturers sometimes include the required dose of vitamin in the milk. It is necessary to ensure that there is no excess of calcium if the daily requirement of calciferol is not met.
Calciferol drops should also be given to those children who do not have the opportunity to receive direct sunlight due to climate, illness or other reasons. Ultraviolet light, through contact with the skin, also promotes the production of this beneficial substance. Therefore, those who rarely walk in the sun need to additionally consume the vitamin in the form of drops.
What does a lack of vitamin D lead to in mothers and babies?
If a newborn’s body lacks vitamin D, then its bones, cartilage, and skeleton cannot strengthen, and their growth slows down. The skeletal system weakens and cannot cope with the load, muscles lose strength, and energy is lost. All this can lead to skeletal curvature, bone deformation, osteoporosis and the development of rickets in children. A catastrophic lack of this element can cause problems with the intestines (cracks, bleeding, abscesses), as well as problems with hair and skin.
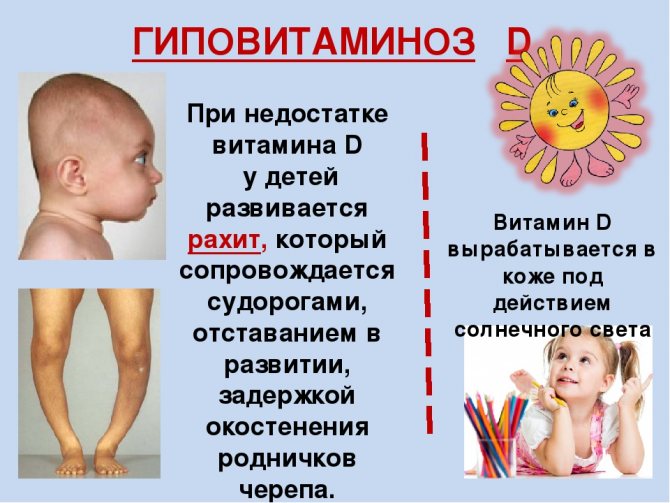
Symptoms of rickets
Rickets, a fairly common and dangerous disease for children, can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Baldness, especially on the back of the head;
- Frequent sweating, especially at night;
- Muscle weakness, lethargy;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Deformation of bones (skull, ribs, limbs).
Rickets has a detrimental effect on the skeletal, nervous and muscular systems, and slows down the development of the child's body. To avoid this disease, you need to follow the recommendations of doctors and ensure the absorption of calcium during the first 1.5 years of the baby’s life.
Vitamins in foods for nursing mothers
In order not to experience a lack of essential beneficial elements, breastfeeding mothers should correctly plan their diet, focusing on those foods that are enriched with all the necessary substances.
The menu should give preference to the following products:
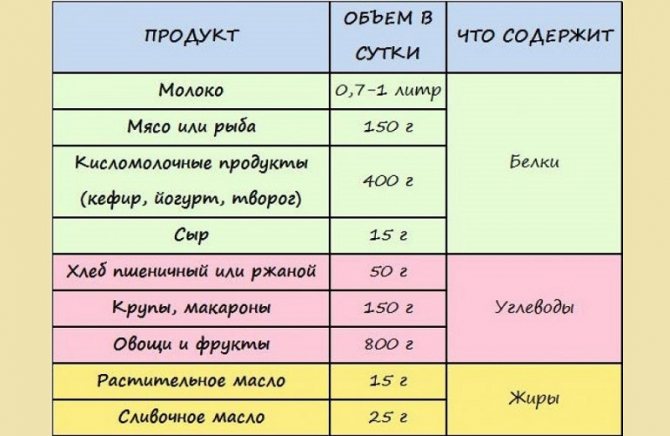
Recommended average daily food intake for a nursing woman.
- Meat is a source of protein. Red varieties contain iron, which saturates the blood with hemoglobin and prevents the development of anemia.
- Eggs are a source of B vitamins, which regulate the functioning of the liver and take part in the process of hematopoiesis.
- Nuts - enriched with phosphorus and vitamin B6.
- Dairy and fermented milk products contain a high concentration of calcium, which is involved in the formation of the musculoskeletal system.
- Beef liver is rich not only in group B, but it also contains vitamin A, which has a positive effect on vision, skin, hair and nails.
- Fish is a source of phosphorus, iodine, magnesium and potassium. These substances have a positive effect on the functioning of the heart muscle and central nervous system. Iodine is essential for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Cereals contain B1, which takes part in metabolic processes and the formation of NS.
- Green vegetables are sources of ascorbic acid, B vitamins and phosphorus.
- Fruits contain large quantities of vitamin C, which supports and strengthens the immune system.
- Vegetable oils are sources of vitamin E, without which the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for the process of producing breast milk, will not be produced.
To avoid vitamin deficiency, these products must be present in the diet every day.
Products containing vitamin D
To increase the amount of vitamin in breast milk, a nursing mother needs to monitor her diet and eat right. For better absorption of calcium and phosphorus, a nursing mother should eat herring, salmon, cod liver, fish oil, milk, and butter during breastfeeding. It is important to be careful about new foods in the diet so as not to cause negative reactions in the child.

Symptoms of vitamin deficiency during lactation
You can understand that a woman lacks vitamins by the presence of the following signs:
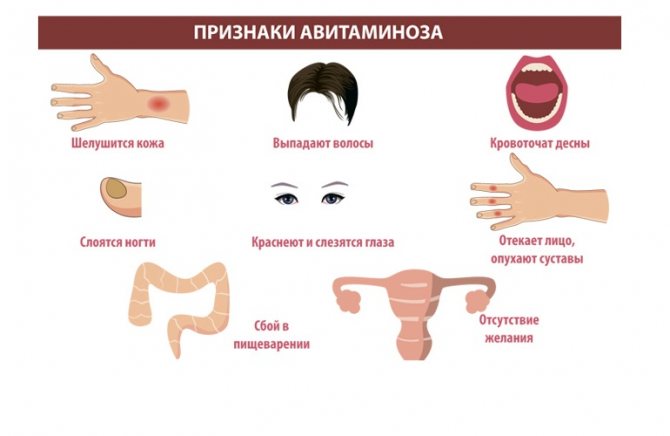
Signs of vitamin deficiency.
- Deterioration in appearance: hair loss, brittle nails, pale and flaky skin.
- A constant feeling of weakness, rapid fatigue even after minor exertion, frequent attacks of dizziness.
- Suppression of the immune system—susceptibility to frequent viral and infectious diseases.
- Severe dryness of the mucous membranes.
- Feeling of numbness in the muscles.
- Frequent disorders of the digestive system.
- Excessive irritability, lack of appetite, insomnia.
- Headaches, depression.
Few people pay attention to these signs, believing that the deterioration in general condition and appearance is caused by the young mother’s lack of sleep. But these symptoms of vitamin deficiency are initial.
If you do not pay proper attention to them, the situation will worsen and complications will arise in the functioning of the internal organs.
Signs of overdose
Not only vitamin deficiency is dangerous, but also hypervitaminosis.
The following manifestations indicate that the concentration of vitamins in the body is exceeded:

Symptoms of vitamin hypervitaminosis.
- extensive swelling;
- skin rash;
- disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
In a child, an overdose has its own clinical signs:
- Increased incidence of colic.
- Anxiety and nervousness.
- Rash on the skin.
- Changes in stool, manifested by frequent diarrhea or prolonged constipation.
If such symptoms appear, you must immediately stop taking the medications.
List of the best vitamin and mineral complexes
To choose effective complexes, you need to consult a doctor. Depending on the symptoms, the specialist will determine what substances are missing in the body and what is the best way to replenish them.
Femibion 2
The complex is recommended from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and during breastfeeding. Main substances: vitamin E, folic acid, iodine. This vitamin series has a positive effect on the immune system, increases the level of hemoglobin in the blood, preventing the occurrence of anemia. Available in the form of tablets and capsules. You need to take them 1 piece at a time. per day, preferably in the morning (before 12 o'clock).
The drug acts quickly. Within a week, women note that they began to feel much better. They experience fatigue and drowsiness, and the appearance and condition of hair, skin and nails improve. The recommended duration of therapy is until breastfeeding is completed.
Elevit Pronatal
Among complex drugs, this remedy is considered one of the best. The composition contains vitamins (12 pcs.) and mineral elements (7 pcs.). The disadvantage of the complex is the lack of iodine in it. If a woman has a deficiency of this element, it should be consumed separately. Dosage: 1 tablet per day, preferably at the same time.
Mom is complimentary
These are inexpensive vitamins with a concentration of nutrients lower than in other drugs. It is recommended to take the complex only for the purpose of preventing vitamin deficiency, for example, in the winter, when it is not possible to enrich the diet with a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits.
The drug is not suitable for use with severe symptoms of vitamin deficiency. In this case, you will need to choose a more potent remedy.
Vitrum Prenatal Forte
Contains 3 microelements and 10 types of vitamins. Despite the fact that there are drugs with a more enriched composition, the price for this complex is quite high. The emphasis is on iron, which increases hemoglobin in the blood. Recommended for women who are at high risk of developing anemia.

Vitrum Prenatal Forte is recommended for women to prevent the development of anemia.
Take 1 tablet per day. The dosage should not be exceeded, since excess ferum can have a negative impact on health.
Alphabet mom's health
The drug contains all the substances necessary for the body. The advantage of the product is its affordable price. Disadvantage - the components in the composition have a low concentration, so if there are severe signs of vitamin deficiency, the product may not help.
Another drawback is the inconvenience of use. The drug is available in tablet form.
To make it easier to take each type of tablet, which is designed for its own time, the manufacturer produces them in different colors.
Multi Tabs Renatal
This drug for nursing mothers is also considered one of the best. It contains 9 microelements and 11 vitamins. The product not only saturates the body with necessary substances, but also fights anemia and stimulates the process of producing breast milk. The disadvantage is that the tablets are large in diameter, making them difficult to swallow.
Taking a vitamin complex helps improve the condition of nails, skin and hair. The drug has a strengthening effect on the immune system.
Finnish vitamins Minisan mom
This product appeared on the CIS markets recently, but is already gaining a leading position. It is considered the most effective complex for women with breastfeeding, as it promotes active milk production.

The vitamin preparation Minisan Mama is recommended for use by nursing women.
The composition includes the most necessary components for the body of a woman and baby. The taste of the tablets is neutral, the diameter is small, the shape is flat - everything is provided for maximum ease of use. Dosage - 1 tablet per day.
Vitamins during breastfeeding
Let's consider the deficiency of which vitamins and microelements is typical for a woman during lactation:
- The complex of vitamins for nursing mothers must include calcium, as it helps strengthen the hair, nails and teeth of a nursing mother - sufficient intake of calcium into the baby’s body through breast milk contributes to the proper formation of the baby’s skeletal system;
- Vitamin D during breastfeeding promotes good absorption of calcium and, when reaching the baby through breast milk, serves as a good prevention of rickets;
- Almost all women who have undergone pregnancy and childbirth note a deficiency of selenium, which is simply indispensable for the full functioning of the immune system and the prevention of inflammatory diseases;
- Vitamin E deficiency during lactation contributes to the development of postpartum depression and muscle weakness in young mothers.
Complex vitamins for nursing mothers
Special multivitamins have been developed for a nursing mother, which contain the necessary vitamins and microelements needed during an important period for her.
Vitamins for pregnant and lactating mothers Elevit are one of the most commonly recommended vitamins during lactation. It contains 12 vitamins and 7 microelements that help the mother’s body recover after pregnancy and childbirth, restore beauty and energy, and also feed your baby with full-fledged breast milk.
Vitrum vitamins for nursing mothers are optimal in their composition and contain 10 vitamins and 3 microelements. They are an excellent prevention of calcium deficiency and are easy to use. The daily dose is 1 capsule, which contains the necessary doses of vitamins and minerals.
Vitamins for nursing mothers Alphabet contains three types of tablets that must be taken separately from each other. One tablet contains iron and vitamins that promote better absorption. The other contains vitamins with antioxidant properties (C, A, E, selenium, beta-carotene), and the third contains calcium and vitamin D.
Every day, a nursing mother produces from 500 to 900 ml of breast milk, which receives a large amount of vitamins and minerals from the mother’s body, so taking vitamins during lactation is simply necessary to preserve the beauty and health of the young mother.
Let's look at what factors influence the production of vitamin D, and how the level of vitamin D in a mother's blood affects her child.
First, let's determine what is considered a normal vitamin D level.
Vitamin D levels can be checked in a laboratory by measuring 25(OH)D in the blood. Many sources and studies provide different data, but most of them agree that a vitamin D blood level below 20 ng/ml is considered a deficiency state.
The Endocrine Society considers a result of 30-100 ng/ml sufficient, and The Vitamin D Council (an independent organization that studies vitamin D) says that a level above 40 ng/ml maintains health at the desired level.
Vitamin D requirements can be fully met with sufficient ultraviolet light. However, the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin is influenced by many factors:
- skin pigmentation: the darker the skin, the less vitamin D is produced
-age: with age, the skin’s ability to synthesize vitamin D decreases
-wavelength of light
-environmental conditions: latitude and longitude of human habitation, time of year, and atmospheric conditions significantly affect the intensity of ultraviolet rays and their ability to reach the surface of the earth.
- use of sunscreens: a product with SPF 2 blocks up to 50% of ultraviolet rays, and
SPF10 – up to 90%, SPF30 – up to 97%.
-skin covered by clothing. There is one interesting study conducted among Eastern women who regularly wear the hijab. It turned out that 96% of women out of 2032 studied had a vitamin D deficiency in the blood (less than 20ng/mL).
- chronic kidney disease: in this case, the synthesis of vit D decreases and its excretion in urine increases.
-Breastfeeding: Breastfed babies, especially those with dark skin who do not receive enough UV rays or vitamin D supplementation, are at risk for vitamin D deficiency.
-efficiency of vitamin D synthesis: depends on the level of D-binding protein circulating in the blood, which is influenced by genetic polymorphisms.
-magnesium deficiency: magnesium regulates the functioning of enzymes that are necessary for the metabolism of vitamin D
- overweight (a body mass index of more than 30 increases the risk of vitamin D deficiency)
-gastrointestinal diseases, such as Crohn's disease
Breast milk contains little vitamin D - on average 10-80 IU of vitamin D per 1 liter. If we consider that the average volume of milk drunk per day is 0.75 liters, then the child receives 8-60 IU per day.
This table reflects data from various studies to determine the level of vitamin D in the blood of mothers with and without vitamin D supplementation.
However, all this does not mean that breast milk is not suitable as a source of vitamin D. In fact, the reason for vitamin D deficiency in a child is that the mother herself receives little vitamin D, and as a result, her milk contains less of it.
A 2015 study published in the journal Pediatrics included 334 breastfeeding women. They were divided into three groups, each of which received 400, 2400 or 6400 IU of vitamin D3 per day for 6 months. Infants of mothers in the first group receiving 400 IU per day also received 400 IU per day.
Infants in other groups received a placebo. According to the results of the study, the lowest level of vitamin D in the blood was in children whose mothers took 2400 IU. Vitamin D levels in children whose mothers took 6400 IU did not differ from those in children who took 400 IU directly.
Conclusion: If a nursing mother receives enough vitamin D (6400 IU in this study), then there is no need to give an additional dose to the baby.
Another study conducted much earlier, in 2004, showed that in the breast milk of mothers who received 2000 IU of vitamin D daily, the vitamin D content increased by 34 IU/L (from 35.5 to 69.7 IU/L), and in those who received 4000 IU – by 94 IU/L (from 40.4 to 134.6 IU/L). At the same time, the level of vitamin D in the blood of babies was directly dependent on the level of vitamin D in the mother.
Unfortunately, very few studies have been conducted that examine the effect of recommended dosages of vitamin D on the health of breastfeeding women and their children. According to one study, a standard dosage of 400 IU can increase blood levels of vitamin D by only 2.8 ng/mL when taken daily for 5 months. From this we can conclude that a dosage of 400 IU may not be sufficient for a nursing mother and her baby, especially during periods of low insolation.
In 2003, 90 mothers and their breastfed children living in the United Arab Emirates and South Asia were examined. It turned out that the average concentration of vitamin D in the blood of mothers was 8.6 ng/mL, in children - 4.6 ng/mL. 61% of mothers and 82% of children had a vitamin D deficiency of less than 10 ng/mL. As this study shows, even in countries with sufficient sunny days, vitamin D deficiency is possible.
A similar study was conducted in 2010 in Korea. Blood samples were taken from 78 children. The greatest vitamin D deficiency was found in breastfed children without supplemental vitamin D. A 2006 study conducted in Greece says almost the same thing.
The table below shows data from studies of maternal blood samples to determine vitamin D levels conducted in different countries. From the table it becomes clear what the real situation is with vitamin D deficiency in women of childbearing age.
To make the picture clearer, I will present data from one interesting study. It affected newborns born at latitude 32 (southeastern US). It turned out that most children were deficient in vitamin D immediately after birth. This suggests that little attention is paid to preventing vitamin D deficiency before and during pregnancy.
WHY IS SO MUCH ATTENTION PAID TO VITAMIN D?
At its core, vitamin D is more of a prohormone, since its influence on many processes in the human body is very great. It is responsible for the formation of bone tissue, regulates immune responses, controls the secretion of hormones, etc. Surprisingly, almost all organs and tissues have calcitriol receptors. Vitamin D in the form of 1,25(OH)2D activates these receptors, which in turn can trigger gene activation.
Official medicine strongly recommends protecting children from the sun's rays: hiding them in the shade, wearing covered clothes, and applying sunscreen. For example, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends against exposing your baby to sunlight before 6 months of age. However, a modern person who lives in a city and spends most of the day indoors has very little chance of getting the required dose of Vit D. And by following the above recommendations, we negatively affect the important process of Vit D formation in the skin, which has been built up over millions of years. The lack of sun rays is especially severe in dark-skinned people, as it takes them longer to generate Vit D3.
Another reason for vitamin D deficiency in breastfed children is inadequate levels of this vitamin in the blood of nursing mothers.
In fact, getting vitamin D is quite simple: when exposed to direct sunlight for 10-15 minutes in the summer, with as much exposed areas of the body as possible, up to 8,000-10,000 IU of vitamin D3 is produced in the skin.
The peak concentration of vit D in blood plasma is recorded 24 hours after solar irradiation.
Why, in the end, is the breast milk of a modern woman not a reliable source of vitamin D? In order to understand this, you need to delve a little deeper into physiology. Vitamin D in the form D3 is formed in the skin under the influence of sunlight. Even after a short exposure to the sun, a large concentration of vitamin D appears in the blood - thousands of IU. The peak concentration of D3 in the blood is reached 24 hours after sun exposure. Next, vitamin D3 binds to a special protein and is transformed in the liver to 25(OH)D. And in this form it can exist in the blood for up to 3 weeks.
Admission rules and restrictions
You need to take vitamin and mineral complexes correctly during lactation, following a number of recommendations and restrictions.
Basic requirements for taking these medications:
- It is strictly forbidden to exceed the dosage specified by the manufacturer. Many women mistakenly think that the more vitamins they take, the better. But that's not true. An overdose will negatively affect not only the condition of the mother, but also the child. For example, if a woman consumes too much calcium, there is a high probability of premature overgrowth of the fontanel. The dose must strictly correspond to that indicated in the instructions.
- The duration of the course must not be exceeded. Most drugs are designed to be taken for up to 1 month, after which a break must follow. If the manufacturer does not indicate the duration of therapy, you should consult your doctor.
- The health of both mother and child should be closely monitored. There is always a possibility of an allergic reaction. If a woman or baby develops an allergic rash on the skin after starting therapy, or if the child has increased colic, the drug must be discontinued immediately.
- Taking several vitamin-mineral complexes at the same time is strictly prohibited, because in this case the likelihood of an overdose will be maximum.
It is best to consult a doctor when choosing medications. If a woman does not have enough vitamin D, only this will be prescribed to prevent an overabundance of other substances in the case of taking multicomponent products. By the same principle, vitamin E in capsules, calcium, iron, etc. can be prescribed.
Types of vitamin D preparations
To strengthen the skeletal system and prevent rickets, doctors prescribe vitamins D2 and D3. The solution in which these elements are dissolved can be oily or aqueous. A water base is the safest for babies, but the vitamin is more difficult to absorb. Oily, on the contrary, often causes adverse reactions in a newborn, but is absorbed faster. Often, such drugs may contain additional substances, such as flavorings and sucrose, which can also cause allergic reactions. After the first dose of the medicine, you need to monitor the baby's reaction. If you feel unwell, have poor sleep, or have problems with your stool, you need to reconsider how you get the vitamin and consult your doctor.
Dosage
The dosage depends on several factors and is selected by the pediatrician individually. The daily dose of calciferol is influenced by the child’s age, place of residence, seasonality, and method of feeding. Using these parameters, the doctor determines how much vitamin is needed to prevent rickets. On average, this is 400-500 IU per day; with artificial feeding, a little less is prescribed.
How to give?
Calciferol is given to infants in drops, dissolved in a small amount of water. There is a method of one-time administration of the vitamin in the amount of 10 mg of oil solution at one month of age. The long-term method involves taking the medicine daily by the baby. In late spring, summer and early autumn, the vitamin is not prescribed to prevent rickets, since it is produced under the influence of direct sunlight. It is enough to give your baby daily sunbathing.
Common myths about vitamins
There are many myths about vitamins for women while breastfeeding.
You need to figure out which of the above is true and which is false:
- The more the better - wrong. Nutrients should be supplied exactly as much as the body can absorb. Despite the fact that a nursing mother needs an increased amount of vitamins, an excess of them should not be allowed. This will cause a negative reaction from the body.
- A child receives nutrients from food consumed by a woman - this is incorrect. Vitamins and mineral components enter milk through the blood. To ensure that the baby does not experience a deficiency of vitamins, they must always be in the body in the appropriate concentration.
- Vitamin complexes are safe - this is an extremely dangerous misconception that leads to hypervitaminosis in many women. If you take such drugs thoughtlessly, they can greatly harm not only the mother, but also the child. If the concentration of one of the substances is greatly exceeded, the resulting overdose can lead to liver or kidney dysfunction and the occurrence of osteoporosis.
- It is necessary to take medications throughout the entire lactation period - it is wrong. On average, the course of therapy lasts from 3 to 4 weeks. If you need to take it again, you must take a break for several weeks.
- Vitamins can be taken as a prophylaxis to prevent hypovitaminosis - a wrong opinion. Do not think that multicomponent complexes are safe. These are medications that have their own indications, so you cannot prescribe them yourself.











