| Discharge after childbirth may be normal, or it may indicate pathology. All young mothers and inexperienced gynecologists are concerned with the question of how long after childbirth discharge from the genital tract should continue, how much it should be, what smell and shade it normally has. |
- Briefly about the postpartum period
- Subinvolution of the uterus
- Lochiometra
- Postpartum endometritis
- Symptoms of acute and subacute endometritis
- Discharge from the mother when the child grows up
- Postpartum hygiene
Briefly about the postpartum period
The postpartum period is considered from the moment the placenta appears, and not the baby. After childbirth there are two stages:
- the first two hours are early
- 6-8 weeks after birth - late
During childbirth, the placenta is separated from the uterine wall and comes out. Where he was, there is a wound on the mucous membrane: the vessels are exposed, blood flows from them. Urgent contractions of the uterus begin, the walls tense, as a result of which the torn vessels are compressed. In the early postpartum period, the discharge is bright red, like blood. The amount should be moderate: no more than 0.4 liters or 0.5% of the young mother’s body weight.
If there is more discharge than described above, doctors think about hypotonic bleeding, rupture of the perineum, cervix or vaginal walls. After the placenta emerges from the mother, the weight of the uterus is approximately one kilogram. When the postpartum period ends, the uterus becomes the same size and weight as before. It weighs only 60 to 70 grams. To return to previous parameters, uterine contractions continue. But they do not cause as much pain and have a smaller amplitude than in those hours when the child is born.
A woman may feel the contractions described above as minor cramps in the lower abdomen. They become stronger when the newborn begins breastfeeding. This is explained by the fact that during nipple stimulation the hormone oxytocin is released, which activates contractions of the organ. The postpartum involutional process includes the return of the uterus to its previous weight and size, as well as the healing of the wound surface on the mucosa.
Within 24 hours after the placenta is delivered, the edge of the uterus can be felt approximately at the level where the navel is located. Therefore, there is a decrease in the organ by about 1 cm every 24 hours. Discharge after childbirth is called “lochia.” Their components:
- red and white blood cells
- decidua
- plasma
- lymph
- slime
A month after giving birth, it is normal for the discharge to stop. By the third hour after birth, the discharge begins to have a dark red or brownish tint. Remember that their amount should be moderate, it should not be massive bleeding. Discharge of this nature continues for at least 5 days, maximum one week. In the first 72 hours, approximately 300 ml of discharge will be released from a woman in labor. Therefore, the diaper needs to be changed every two hours.
Blood clots may be present in the discharge of a woman who has given birth. This is the norm. A week after the birth of the baby and the placenta, the discharge becomes a different color. Don't be surprised if you notice whitish or yellow-tinged discharge. The reason is that there are more leukocytes in the secretions. They are needed for the mucosal wound to heal fully.
From the ninth (sometimes from the 10th) day, the discharge becomes light and watery. They contain a lot of mucus. Their number is becoming less and less. By the third or fourth week, the discharge from a woman who has given birth should disappear.
After childbirth
After the birth of a child, a woman begins to change in her body: prolactin and oxytocin are produced - hormones necessary for lactation. In the first hours after birth and during the first few days, the discharge is bloody, which is a consequence of the healing process of the internal reproductive organs.
For another 5-6 weeks, while the uterus acquires its usual size, the production of postpartum secretion, called lochia, continues.
At first, they are quite abundant and similar to discharge during menstruation, which indicates the natural process of cleansing the uterine cavity. White or yellow, odorless discharge in women after a natural birth lasts about two months, and after a cesarean section it lasts a little longer, since the rate of uterine recovery is slowed down.
Subinvolution of the uterus
Involution is the reverse development of the uterus with the restoration of the woman’s normal physiology. This process leads to the restoration of the cycle of critical days. The ability to conceive and bear a child is restored. If the contractility of the uterus is not strong enough, purulent-septic complications may occur.
To assess the involution process, a woman who has given birth should come for an appointment with her obstetrician-gynecologist 10 days after discharge from the maternity hospital. The doctor conducts an examination. If, by palpation, he discovers that the uterus has a loose and soft structure, and is also large in size, this means subinvolution.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs is performed. The method makes it possible to establish the reasons why there are no healthy uterine contractions. A certain amount or part of the placenta may remain in the woman in labor. Subinvolution of an organ is possible in the presence of the following factors:
- birth of two, three or more children at once
- gestosis
- uterine fibroids
- labor too fast
- protracted labor process
- polyhydramnios
Some women with this diagnosis are admitted to hospital, while others do not need such measures. This must be decided by the doctor. In the absence of complaints, normal general condition, and absence of a baby's place in the uterus, the woman who gave birth should be prescribed uterotonic medications . Often this is:
- methylergometrine
- oxytocin
- water pepper tincture (natural remedy)
If parts of the fetal membranes remain in the uterus, they need to be removed using a vacuum suction. For some patients, diffuse uterine lavage with antibiotics or antiseptics is used. For prevention, a woman needs to take antibacterial drugs for 2-3 days.
How to determine the condition by the color of the discharge
Depending on the color of the discharge, the general condition of the reproductive system can be determined. A yellowish secretion with an unpleasant odor indicates suppuration or the onset of endometritis. The condition is accompanied by a rapid increase in body temperature and severe pain in the lower abdominal cavity.

The cycle does not recover immediately after childbirth
A curdled secretion is the result of taking any medications. The condition returns to normal immediately after stopping medication. The drugs provoke a deficiency of lactobacilli in the vagina.
After 2-4 months, spotting may occur. This may be the result of a gynecological examination, sexual intercourse or excessive exercise.
At 4 months, brownish discharge may occur. This indicates that the menstrual cycle is gradually beginning to recover. The condition can subside for several months in a row before the onset of full menstruation.
Bright red discharge is short-lived - first menstruation. After a couple of such periods, the condition will normalize and the cycle will be restored. The early arrival of critical days is a reason to seek advice from a doctor.
Lochiometra
This is the name of one of the complications after childbirth. With it, lochia lingers in the uterus of the woman who has given birth. This condition is diagnosed in most cases on the 7-9th day after birth. The reasons may vary. Among them, insufficient contractile activity of the uterus and mechanical blockage of the cervical canal are common. The reason may be that the uterus is strongly bent forward.
If there are obstructions in the cervical canal, these may be:
- parts of the membranes
- decidua (not completely)
- blood clots
The uterus contracts less if the fetal sac is overstretched during childbirth or while carrying a child. If the lochiometer is not detected in time, the postpartum woman will feel normal, there will be no changes in pulse, as well as changes in body temperature. The manifestation may be a tiny amount or complete absence of lochia.
When a doctor palpates the uterus of a patient with this diagnosis, he finds that the organ is enlarged (more than the previous day), and pain also appears. If this condition is not detected, endometritis develops. If the disease is detected, the doctor creates an outflow of lochia from the uterus for medicinal purposes. Treatment begins with conservative methods. The woman is prescribed parenteral administration of papaverine or no-shpu. Then you need to take oxytocin or other uterotonics prescribed by your doctor. Something cold is applied to the lower abdomen.
If lochiometra appears due to a strong uterine bend, bimanual palpation is performed, thereby returning the uterus to its previous, physiologically normal place. If the cervical canal is blocked, the doctor should gently widen it with a finger. If the case is severe, then Hegar dilators are used.
There are cases when the above treatment is carried out, but the condition still remains. Then the scraping method is used. This is an instrumental release of the uterine cavity. Vacuum aspiration can be used in some cases. For prophylaxis after this, the woman should take antibiotics in the indicated course.
What is the duration of lochia
The duration of lochia may vary. The table describes the average timing and what affects the duration of uterine cleansing after delivery.
| What affects the duration | The duration of lochia directly depends on: • blood clotting in the woman’s body; • features of bearing a child and method of delivery; • size and weight of the born child; • method of feeding. |
| Average terms | The faster the uterus contracts, the faster the cleansing process will end. On average, lochia ends by the 6th week after delivery. If there was a cesarean section, then the lochia will end in about 9 weeks. Already three months after the birth of the baby, the uterus should be completely clean. |
It is worth noting that the complete absence of discharge after childbirth is a deviation. In this case, lochia accumulates in the body and does not have the opportunity to leave.
Postpartum endometritis
This is a dangerous complication that can occur after childbirth. The term means an inflammatory process in the uterus. A pregnant woman's body's defenses are weakened so that the body does not mistake the fertilized egg for a hostile foreign object. Then the immunity returns to its previous state 5-6 days after birth. If there was a caesarean section, then the restoration of immunity should only be expected on the tenth day. Decreased immunity threatens inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system. There are also risk factors for developing postpartum endometritis :
- abortions
- history of fibroids or inflammation of the uterus
- age under 18 and over thirty years
- poor nutrition
- alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking
- endocrine diseases
- Caesarean section performed before the baby is conceived
- unfavorable living conditions
- chronic extragenital pathologies
Factors for the development of the diagnosis in question during childbirth:
- more than 3 vaginal examinations to diagnose the obstetric picture
- a period without water of more than 12 hours
- protracted labor
- manual control of the uterine cavity
- obstetric aids during childbirth
- performing a caesarean section
- anomalies of ancestral forces
- premature (too early) birth
- clinically narrow pelvis
Factors in the development of postpartum endometritis during pregnancy (before childbirth):
- threat of miscarriage
- infection of the vagina before childbirth with various STDs
- abnormal development of the placenta
- infections in pregnant women
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases during pregnancy
- vaginal inflammation
- inflammatory process in the cervix
- treatment of isthmic-cervical insufficiency with surgical methods
- bearing several fruits at once
- polyhydramnios
- large size/weight of the unborn baby
- incorrect position of the child
- anemia
- toxicosis that began after the 20th week
Video: odorless yellow discharge in women
What discharge is considered pathological, watch in the video:
Vaginal discharge, inflammatory processes:

While breastfeeding, mothers may experience unusual vaginal discharge. Although menstruation is absent for almost the entire lactation period, there is discharge during breastfeeding, which is considered normal. Which color and consistency of vaginal secretions are standard and which should cause concern. What can cause deviations, and what to do for prevention to avoid health problems in the intimate area.
What is considered normal
In the first 4-7 weeks after childbirth, all women experience so-called lochia. This is heavy bleeding.
Their appearance is associated with the departure of the placenta from the uterus and the movement of the child along the birth canal.
In this case, bleeding occurs, which ends in due time. The presence of blood clots in them is considered normal.
This is not a cause for concern, but rather evidence of correct natural processes. This means that the uterus is cleansed of the remaining parts of the placenta.
During this period, a woman may experience pain in the abdomen similar to contractions. These are spasms or contractions of the uterus.
They help speed up the cleansing process.
During traditional childbirth, already 2-3 weeks after delivery, spotting becomes less abundant and turns pale. If the mother had a caesarean section, this period may last longer.
This is explained by the fact that during the operation the uterus is severely injured - it is cut open and it takes more time to recover.
When the peak of the discharge is left behind, it turns brown.
The cessation of discharge and the appearance of a whitish or transparent secretion of mucous consistency indicates the correct passage and completion of the restoration of the uterus.
This light discharge may continue throughout the entire feeding period.
They may take on a light yellow tint. Their characteristic features are the absence of odor, pain and discomfort in the genital area.
Symptoms of acute and subacute endometritis
This complication has an acute onset. In almost all cases it begins to appear on the third day. A woman who has given birth notices that her discharge has become the color of meat slop or has turned brown. Then the lochia becomes purulent and green in color. Postpartum discharge due to endometritis smells unpleasant, reminiscent of rotten meat.
The woman's general condition also worsens. Body temperature becomes 38 – 39˚С. Heartbeat too fast. There is a feeling of malaise and general weakness. The doctor orders a peripheral blood test. Results for endometritis show signs of inflammation.
If the complication occurs in a subacute form, it may be noticed when the woman has already been discharged home. The discharge is bloody in nature for up to tenths or even 12th days. There may be a slight increase, but in some women who give birth, the temperature reaches febrile levels. Postpartum discharge becomes purulent in nature. Their smell is unpleasant if you ignore the disturbing symptoms for the first three days after birth.
If endometritis occurs after childbirth, the woman is hospitalized (taken to the hospital). There they do a hysteroscopy to understand whether parts of the fetal membranes remain in the uterus, etc. Then the treatment regimen is as indicated above.
What should be normal postpartum discharge?
Immediately after childbirth, active changes begin in the female body. The uterus becomes smaller in size. The remains of the placenta come out, as well as the fetal sac. At first, the condition is always accompanied by lochia.
The first two days after birth, the discharge has a rich color. The color is brown or bright scarlet. The consistency is relatively dense. Sometimes blood clots may be present.
Gradually, postpartum lochia becomes less saturated and intense. This is a natural process of cleansing the uterus. Normally this stops after a few months.
By the end of the process of cleansing the uterus, the discharge acquires a light yellow-brown color. This color is considered normal. The first menstrual flow after childbirth appears around the 10th month, provided breastfeeding. With artificial feeding, the critical days come much earlier, usually by 4-6 months.
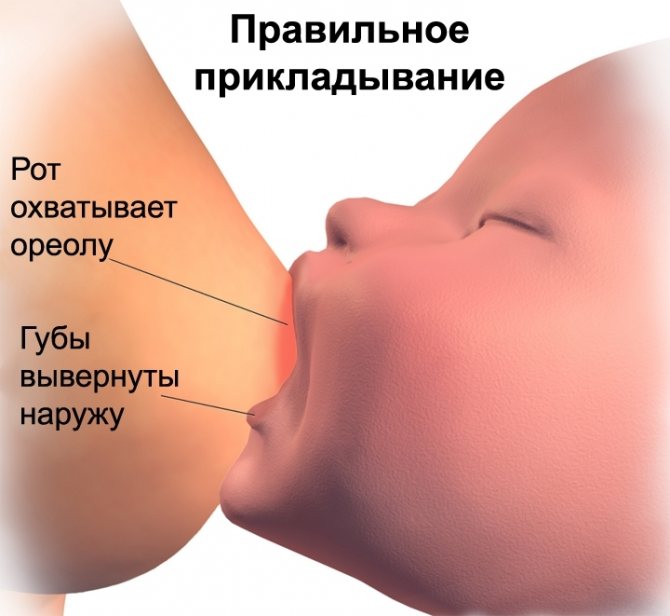
You should also use contraceptives when breastfeeding
Despite many misconceptions, contraception should also be used when breastfeeding. It is also possible to become pregnant again in the first year of a child's life.
The first menstruation after the birth of a child differs from the usual critical days. The discharge is more scanty and lighter. As a rule, a woman no longer has the unpleasant symptoms that accompanied her period before pregnancy.
Discharge from the mother when the child grows up
Questions about birth control after childbirth should be addressed in advance with your doctor. When breastfeeding and the baby is 1 month old, the discharge becomes moderately mucous in nature and there should be no unpleasant odor. And the nature of the discharge does not change while the mother is breastfeeding the baby (during lactation).
An alarming symptom is the appearance of yellow discharge after the release of lochia. Leucorrhoea may have a bad odor. Discomfort and itching of the external genitalia and vagina are also likely. These symptoms should prompt you to see a doctor. The cause of such discharge can only be determined by a qualified specialist, and not by advisers on the Internet!
The doctor will take a smear to see if the patient’s vaginal microflora is normal. Then treatment will be prescribed according to the indications. Yellow discharge may be a symptom of colpitis. If there is not only pathological discharge, but also abdominal pain, fever, etc., there may be inflammation in the appendages or in the uterus itself.
Signs of normal discharge after childbirth
White lochia begins in a woman in labor after 1-1.5 weeks. The mucus can be either white or transparent, stretchy; normally there should be no odor. Many women claim that after childbirth, the discharge looks like snot (see photo).

An increase in body temperature and yellow discharge after childbirth, even if odorless, requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
The main reason for mucous accumulation in the uterus is the appearance of fluid that passes through the lymph nodes and blood vessels. It is worth noting that most mucus appears in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. This is explained by hormonal changes in the body. Thus, the vagina is better lubricated, which makes it less aggressive for sperm. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, mucus becomes clogged in the cervix and cervical canal, and it is this that comes out from the beginning of the second half of the cycle. The abundance of mucus increases during sexual intercourse. These processes contribute to fertilization.
The mucus that appears may disappear at the end of the postpartum period, but it may remain. Everything is purely individual.
ATTENTION! Sometimes mucous secretion appears even 4 months after birth. This occurs due to an allergic reaction to food or medications. With the appearance of leucorrhoea, a woman’s body also reacts to a change in climate or emotional background.
Normally, mucus in the discharge should disappear after the menstrual cycle normalizes. In a nursing mother, mucous discharge stops faster. Usually, mucous discharge stops after childbirth after 2 months.
If menstruation has resumed, but in the first days of the cycle it is not blood that comes out, but mucus, in the absence of pain, there is no need to worry. In this uneven manner, particles of dead tissue come out.
Black mucous discharge is also considered normal. If there is no pain, no unpleasant odor, and the temperature does not rise, there is no need to see a doctor. This is explained by hormonal changes in a woman’s body.
The presence of light pink inclusions in the mucus indicates a slight placental abruption. Blood cells accumulate in the uterus and come out through the vagina. In such cases, aching pain in the lumbar region sometimes occurs.
Postpartum hygiene
In order for the process of uterine involution in a woman who has given birth to be successful, you need to follow some hygiene rules:
- sleep on your stomach to stimulate contraction of the uterus and place it and the cervix on the same side in order to enhance the outflow of lochia
- Uterine contractions worsen when you want to go to the toilet “big” or “small”, so go there as soon as you want
- change pads every 2 hours maximum, otherwise pathological bacteria may appear in the released lochia
- A woman who has given birth should not use tampons
- 2-3 times a day you need to wash yourself with boiled water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- feeding should be free: the child asks for the breast, and the mother gives him something to eat, and does not wait for some appointed time
Take care of yourself and be healthy!










